|
Accompong Town
Accompong (from the Akan name ''Acheampong'') is a historical Maroon village located in the hills of St. Elizabeth Parish on the island of Jamaica. It is located in Cockpit Country, where Jamaican Maroons and indigenous Taíno established a fortified stronghold in the hilly terrain in the 17th century. They defended it and maintained independence from the Spanish and then later the British, after the colony changed hands. Accompong is reportedly named after the son of Miguel Reid, the first African Maroon leader in western Jamaica, and allegedly the first leader of Cudjoe's Town (Trelawny Town). This would make Accompong brother to Kojo or Cudjoe, and possibly Cuffee, Quaco and Nanny of the Maroons. Accompong Town was reportedly built by Kojo who assigned his Brother Accompong to watch over it. After years of raiding and warfare, they established their autonomy, self-government and recognition as an indigenous people by a peace treaty with the British in 1739. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
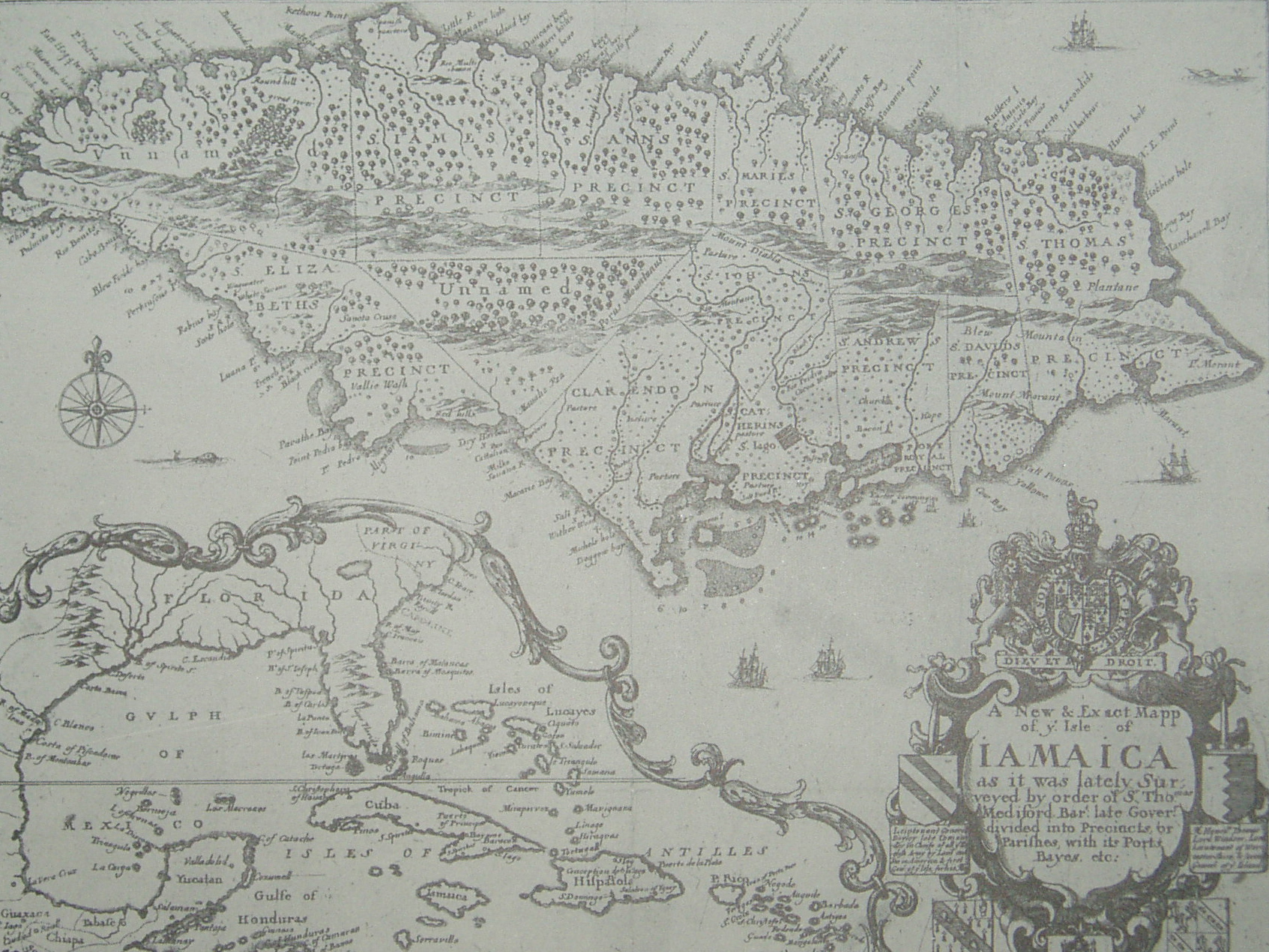
Parishes Of Jamaica
The parishes of Jamaica are the main units of local government in Jamaica. They were created following the English Invasion of Jamaica in 1655. This administrative structure for the Colony of Jamaica developed slowly. However, since 1 May 1867 Jamaica has been divided into the current fourteen parishes. These were retained after independence in 1962. They are grouped into three historic counties, which no longer have any administrative relevance. Every parish has a coast; none are landlocked. List (1) The parishes of Kingston and Saint Andrew together form the '' Kingston and St. Andrew Corporation''. (2) The parish of Kingston does not encompass all of the city of Kingston. Most of the city is in the parish of St. Andrew. History Early history Following the English conquest of Jamaica the first phase of colonisation was carried out by the Army, with a system of Regimental plantations. These were drawn up on the southern flat lands, with the Regimental commanders charge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Thistlewood
Thomas Thistlewood (16 March 1721 ‒ 30 November 1786) was an English planter in colonial Jamaica. Thistlewood migrated to the western end of the Colony of Jamaica where he became a plantation overseer, plantation owner and slaver. His lengthy and detailed diary is an important historical document chronicling the history of Jamaica and slavery there during the 18th century. The diary includes a detailed account of the brutal treatments of his slaves, including his torture and rape of enslaved women. Thistlewood routinely punished his slaves with fierce floggings and other cruel and gruesome punishments. Known as 'The Diary of Thomas Thistlewood', the 14,000-page diary provides a detailed record of his behaviour and deep insight into plantation life and owner-slave relations. In 1751, he became overseer of a sugar plantation called Egypt; within days he began raping the enslaved women. His diary chronicles 3,852 acts of rape with 138 black women. He systematically raped enslaved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferron Williams
Ferron Williams is a Maroon politician and from 2009 - 2021 he was Colonel-in-Chief of Accompong, Jamaica, a self-governing community of Jamaican Maroons established in 1739 by treaty with Great Britain. Biography Ferron Williams was born on June 14, 1955, to parents Advira Elizabeth Anderson-Williams and Robert Williams, members of the Maroon community of Accompong. He attended local schools and joined the police service. After 37 years Williams resigned from the force at the rank of Inspector of Police. He was elected as Colonel-in-Chief of Accompong in 2009. This position leads the Maroon Council, with whom the Colonel shares executive responsibilities. On April 16, 2015, Colonel Williams was elected to his second term in office. After 11 years as Colonel of Accompong, he was succeeded by Richard Currie following his defeat in an election held in February 2021. He has become notable for his climate change program, which seeks to protect the ecology of the Island's Cockpit re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UN Declaration On The Rights Of Indigenous Peoples
The Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (UNDRIP or DOTROIP) is a legally non-binding resolution passed by the United Nations in 2007. It delineates and defines the individual and collective rights of Indigenous peoples, including their ownership rights to cultural and ceremonial expression, identity, language, employment, health, education, and other issues. Their ownership also extends to the protection of their intellectual and cultural property. The Declaration "emphasizes the rights of Indigenous peoples to maintain and strengthen their own institutions, cultures and traditions, and to pursue their development in keeping with their own needs and aspirations."Frequently Asked Questions: Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maroon Council
On the Island of Jamaica, the Maroon Council is the executive body with administrative powers and obligations for the Maroon communities. Maroon Council members are appointed by the Colonel-in-Chief (Colonel), while the Colonel is officially elected by the community as the Head of Government. Each Maroon Community (Accompong, Nanny Town Old Nanny Town was a village in the Blue Mountains of Portland Parish, north-eastern Jamaica, used as a stronghold of Jamaican Maroons (escaped slaves). They were led in the early 18th century by an Ashanti escaped slave known as Granny Nanny, ..., Charles Town, Trelawny Town, and Scotts Hall) has its own independent Maroon Council with legislative authority.http://moj.gov.jm/sites/default/files/minister-speeches/6th%20Annual%20International%20Maroon%20Conference.pdf References Organisations based in Jamaica Maroons (people) Jamaican Maroons {{Jamaica-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asante People
The Asante, also known as Ashanti () are part of the Akan ethnic group and are native to the Ashanti Region of modern-day Ghana. Asantes are the last group to emerge out of the various Akan civilisations. Twi is spoken by over nine million Asante people as a first or second language. The wealthy, gold-rich Asante people developed the large and influential Ashanti Empire, along the Lake Volta and Gulf of Guinea. The empire was founded in 1670, and the capital Kumase was founded in 1680 by Asantehene (emperor) Osei Kofi Tutu I on the advice of Okomfo Anokye, his premier. Sited at the crossroads of the Trans-Saharan trade, the Kumase megacity's strategic location contributed significantly to its growing wealth. Over the duration of the Kumase metropolis' existence, a number of peculiar factors have combined to transform the Kumase metropolis into a financial centre and political capital. The main causal factors included the unquestioning loyalty to the Asante rulers and the Kumas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Sharpe
Samuel Sharpe, or Sharp (1801 – 23 May 1832), also known as Sam Sharpe, was an enslaved Jamaican who was the leader of the widespread 1831–32 Baptist War slave rebellion (also known as the Christmas Rebellion) in Jamaica. He was proclaimed a National Hero of Jamaica in 1975 and his image is on the $50 Jamaican banknote. Biography Samuel Sharpe was born into slavery in the parish of St James, Jamaica, on a plantation owned by Samuel and Jane Sharpe. The Slave Return of 1832 announcing his death gave his name as Archer aka Samuel Sharpe, the son of Eve, and he was only 28 years old when he died. The Slave Return of Samuel and Jane Sharpe in 1817 showed a young 12-year-old Archer on the plantation with his mother Juda Bligom and siblings Joe (2 years old) and Eliza (20 years old). He was allowed to become educated, for which he was well respected by his enslaved peers. Sharpe became a well-known preacher,leader and missionary in the Baptist Church, which had long welco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baptist War
The Baptist War, also known as the Sam Sharp Rebellion, the Christmas Rebellion, the Christmas Uprising and the Great Jamaican Slave Revolt of 1831–32, was an eleven-day rebellion that started on 25 December 1831 and involved up to 60,000 of the 300,000 slaves in the Colony of Jamaica. The uprising was led by a black Baptist deacon, Samuel Sharpe, and waged largely by his followers. The revolt, though militarily unsuccessful, played a major part in the abolition of slavery throughout the British Empire. Ideology The missionary-educated rebels had been following progress of the abolitionist movement in London; their intention was to call a peaceful general strike.Craton, Michael. ''Testing the Chains: Resistance to Slavery in the British West Indies'' (Cornell University Press, 1983), pp. 297–98 Compared with their Presbyterian, Wesleyan, and Moravian counterparts, Baptist slaves seemed more ready to take action. This may have reflected a higher level of absenteeism among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willoughby Cotton
Lieutenant General Sir Willoughby Cotton (1783 – 4 May 1860) was a British soldier. Family Willoughby Cotton was born in 1783, to Vice-Admiral Rowland Cotton and Elizabeth Aston. They also had a daughter, Sydney Arabella Cotton. Rowland Cotton was from a well-established Chester family, was the second son of Sir Lynch Cotton, 4th Baronet, while Elizabeth was the eldest daughter of Sir Willoughby Aston, 5th Baronet Aston, of Aston, Chester. Cotton married Lady Augusta Maria Coventry on 16 May 1806 in Marylebone, London. They had three children together, Augusta Mary Cotton, Willoughby Cotton and Maj.-Gen. Corbet Cotton. School years Willoughby Cotton entered Rugby School at the age of 12 in 1795. Cotton, aged 14, was a ringleader in the " Great Rebellion" of November 1797. Aggrieved by the attitude of the Head Master, Dr. Henry Ingles (1794–1806), following the breaking of a window, students blew his classroom door off with gunpowder and followed this by burning desks and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Me-no-Sen-You-no-Come
Me-no-Sen-You-no-Come is a village in the Cockpit Country of western Jamaica. It is now a part of a district called Aberdeen, Jamaica, in the north-east section of Saint Elizabeth Parish, and is not extinct, as was originally believed. From the Jamaican dialect, the village name translates in English as, 'If I don't send for you, don't come.' Located at 430 metres above sea level, it was founded by runaway slaves escaping from estates in Trelawny Parish at the start of the nineteenth century. Origins In 1812, a community of runaways started when a dozen men and some women escaped from the sugar plantations of Trelawny into the Cockpit Country, and they created a village named Me-no-Sen-You-no-Come. It is located near some cliffs and boasted fertile soils in its valleys. The unofficial maroon community of Free black people in Jamaica grew from its start of less than 20 runaway slaves to a large village that supported 14 buildings with shingle roofs and wood floors, raised poultry, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuffee (Jamaica)
Cuffee was an escaped slave in Jamaica who led other runaway slaves to form a community of Free black people in Jamaica in the island's forested interior, and they raided white plantation owners at the end of the eighteenth century. The name Cuffee is a variation of the Twi Akan name Kofi, which is the name given to a boy born on a Friday. Origins In 1798, Cuffee escaped from a Jamaican plantation run by James McGhie, and he found refuge in the forested interior of the Cockpit Country. Many of the escaped slaves who joined his community had secured their freedom by fighting in the Second Maroon War. Cuffee's community of runaway slaves It was previously believed that Cuffee only led a small band of just 43 runaway slaves. However, recent research has shown that Cuffee's community counted more than twice that number of runaway slaves. The community was so large that they occupied several makeshift villages in the Cockpit Country, with their headquarters at a place called High Windw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland". Most of the population are native English-speakers, and the province's population is 969,383 according to the 2021 Census. It is the most populous of Canada's Atlantic provinces. It is the country's second-most densely populated province and second-smallest province by area, both after Prince Edward Island. Its area of includes Cape Breton Island and 3,800 other coastal islands. The Nova Scotia peninsula is connected to the rest of North America by the Isthmus of Chignecto, on which the province's land border with New Brunswick is located. The province borders the Bay of Fundy and Gulf of Maine to the west and the Atlantic Ocean to the south and east, and is separated from Prince Edward Island and the island of Newfoundland by the Northumberland and Cabot straits, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |