|
Aysheaia2
''Aysheaia'' is an extinct genus of soft-bodied lobopod, known from the middle Cambrian of North America, with an average body length of 1–6 cm. Anatomy ''Aysheaia'' has ten body segments, each of which has a pair of spiked, annulate legs. The animal is segmented, and looks somewhat like a bloated caterpillar with a few spines added on — including six finger-like projections around the mouth and two grasping legs on the "head". Each leg has a subterminal row of about six curved claws. No jaw apparatus is evident. A pair of legs marks the posterior end of the body, unlike in onychophorans where the anus projects posteriad; this may be an adaptation to the terrestrial habit. Ecology Based on its association with sponge remains, it is believed that ''Aysheaia'' was a sponge grazer and may have protected itself from predators by seeking refuge within sponge colonies. ''Aysheaia'' probably used its claws to cling to sponges. A terminal mouth is also seen in tardigrades t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgess Shale Fossils
The fossils of the Burgess Shale, like the Burgess Shale itself, formed around 505 million years ago in the Mid Cambrian period. They were discovered in Canada in 1886, and Charles Doolittle Walcott collected over 65,000 specimens in a series of field trips up to the alpine site from 1909 to 1924. After a period of neglect from the 1930s to the early 1960s, new excavations and re-examinations of Walcott's collection continue to reveal new species, and statistical analysis suggests that additional discoveries will continue for the foreseeable future. Stephen Jay Gould's book '' Wonderful Life'' describes the history of discovery up to the early 1980s, although his analysis of the implications for evolution has been contested. The fossil beds are in a series of shale layers, averaging and totalling about in thickness. These layers were deposited against the face of a high undersea limestone cliff. All these features were later raised up above current sea level during the cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
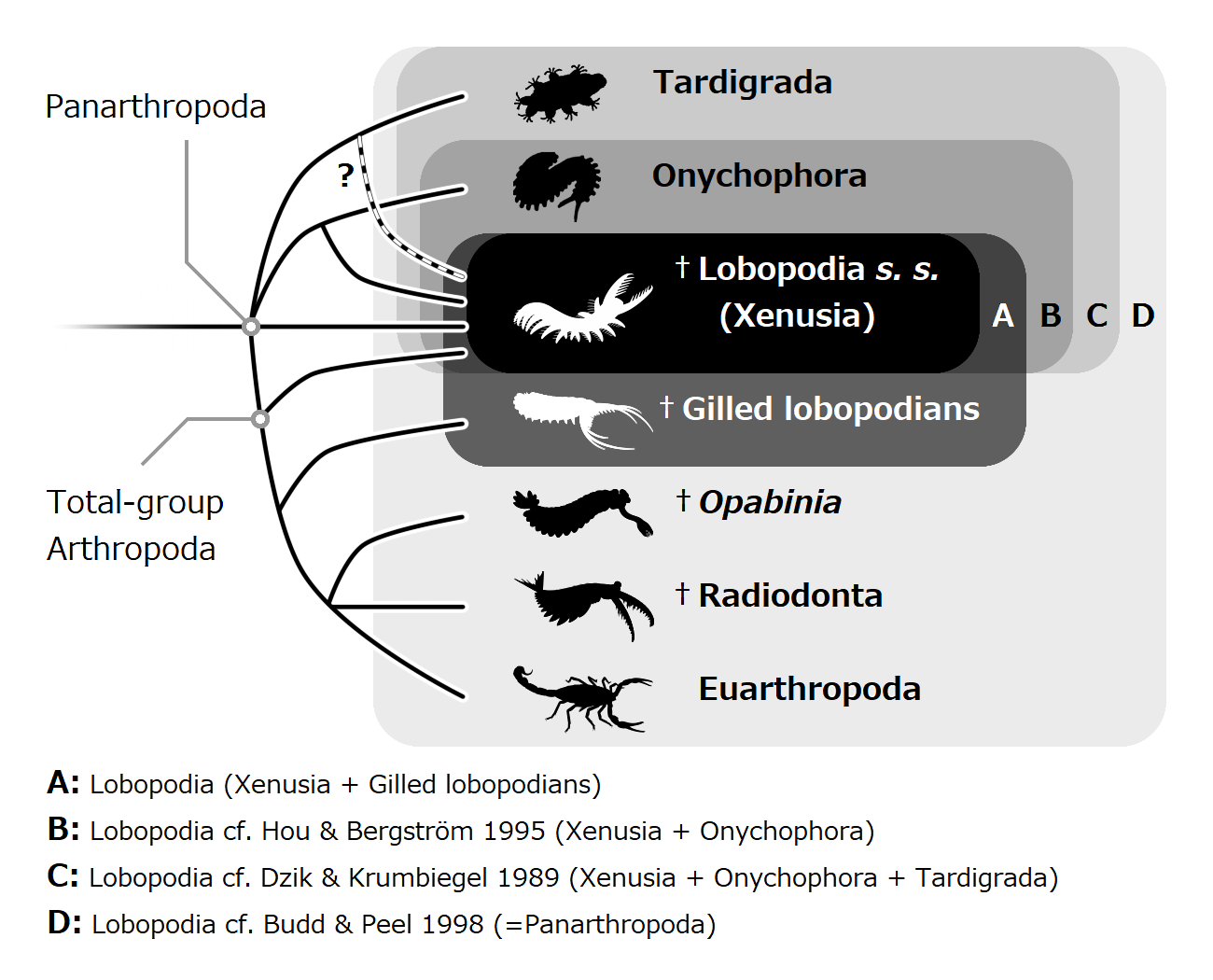
Lobopodia
The lobopodians, members of the informal group Lobopodia (from the Greek, meaning "blunt feet"), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998), are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, worm-like fossil panarthropods such as ''Aysheaia'' and ''Hallucigenia''. The oldest near-complete fossil lobopodians date to the Lower Cambrian; some are also known from Ordovician, Silurian and Carboniferous Lagerstätten. Some bear toughened claws, plates or spines, which are commonly preserved as carbonaceous or mineralized microfossils in Cambrian strata. The grouping is considered to be paraphyletic, as the three living panarthropod groups (Arthropoda, Tardigrada and Onychophora) are thought to have evolved from lobopodian ancestors. Definitions The Lobopodian concept varies from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aysheaia2
''Aysheaia'' is an extinct genus of soft-bodied lobopod, known from the middle Cambrian of North America, with an average body length of 1–6 cm. Anatomy ''Aysheaia'' has ten body segments, each of which has a pair of spiked, annulate legs. The animal is segmented, and looks somewhat like a bloated caterpillar with a few spines added on — including six finger-like projections around the mouth and two grasping legs on the "head". Each leg has a subterminal row of about six curved claws. No jaw apparatus is evident. A pair of legs marks the posterior end of the body, unlike in onychophorans where the anus projects posteriad; this may be an adaptation to the terrestrial habit. Ecology Based on its association with sponge remains, it is believed that ''Aysheaia'' was a sponge grazer and may have protected itself from predators by seeking refuge within sponge colonies. ''Aysheaia'' probably used its claws to cling to sponges. A terminal mouth is also seen in tardigrades t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aysheaia Pedunculata
''Aysheaia'' is an extinct genus of Soft-bodied organisms, soft-bodied Lobopodia, lobopod, known from the middle Cambrian of North America, with an average body length of 1–6 cm. Anatomy ''Aysheaia'' has ten body segments, each of which has a pair of spiked, annulate legs. The animal is segmented, and looks somewhat like a bloated caterpillar with a few spines added on — including six finger-like projections around the mouth and two grasping legs on the "head". Each leg has a subterminal row of about six curved claws. No jaw apparatus is evident. A pair of legs marks the posterior end of the body, unlike in onychophorans where the anus projects posteriad; this may be an adaptation to the terrestrial habit. Ecology Based on its association with sea sponge, sponge remains, it is believed that ''Aysheaia'' was a sea sponge, sponge grazer and may have protected itself from predators by seeking refuge within sponge colonies. ''Aysheaia'' probably used its claws to cling to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllopod Bed
The Phyllopod bed, designated by USNM locality number 35k, is the most famous fossil-bearing member of the Burgess Shale fossil '' Lagerstätte''. It was quarried by Charles Walcott from 1911–1917 (and later named Walcott Quarry), and was the source of 95% of the fossils he collected during this time; tens of thousands of soft-bodied fossils representing over 150 genera have been recovered from the Phyllopod bed alone. Stratigraphy and location The phyllopod bed is a 2.31 m thick layer of the 7 m thick Greater Phyllopod Bed, found in the Walcott Quarry on Fossil Ridge, between Wapta Mountain and Mount Field, at an elevation of around , around north of the railway town of Field, British Columbia, in the Canadian Rocky Mountains. It is adjacent to Mount Burgess, where Walcott first discovered the Burgess Shale formation. Walcott divided the bed into twelve units based on the rock type and fossil content. Certain fossil beds provide reference levels and ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|