|
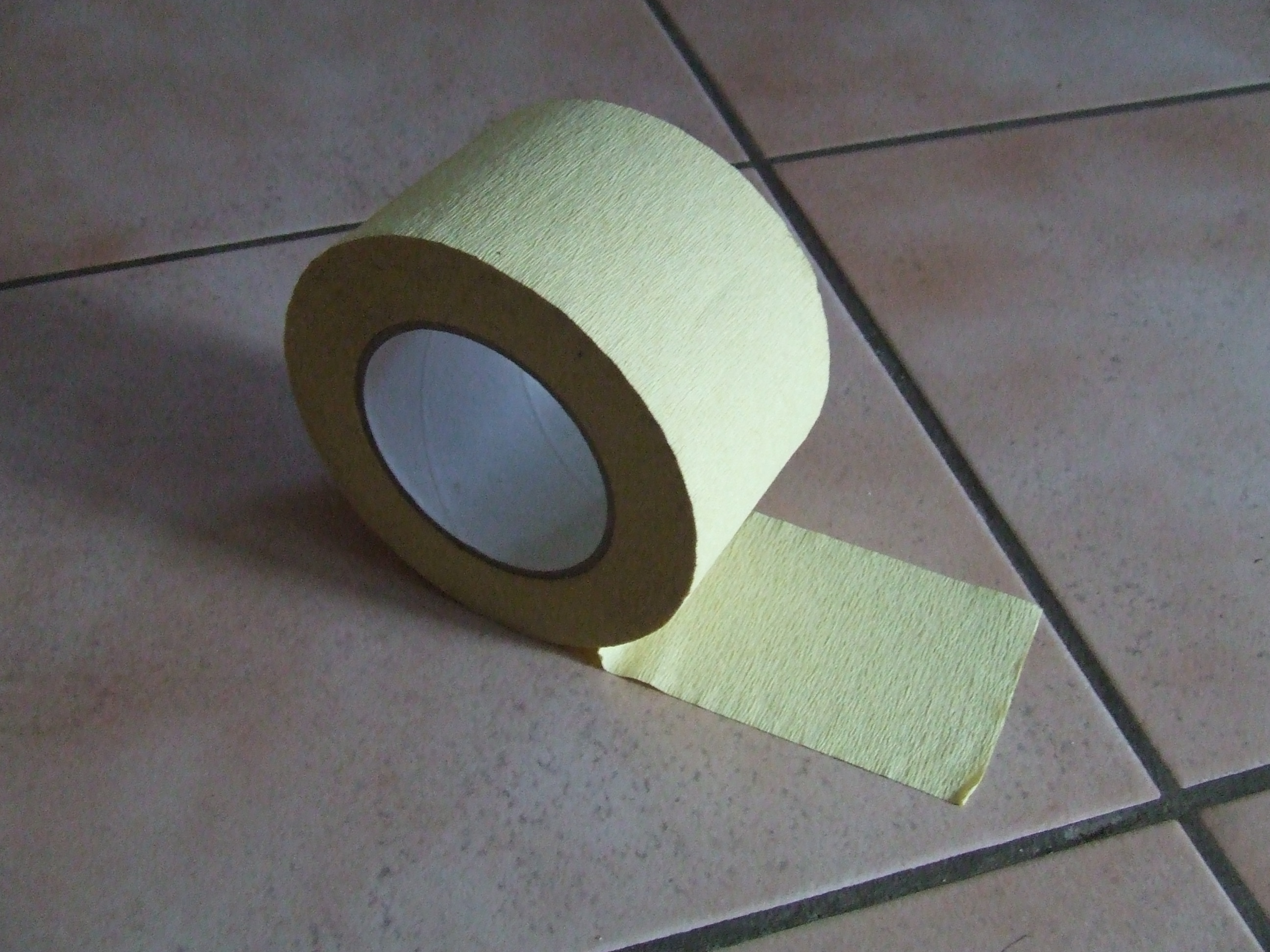
Autoclave Tape
Autoclave tape is an adhesive tape used in autoclaving (heating under high pressure with steam to sterilise) to indicate whether a specific temperature has been reached. Autoclave tape works by changing color after exposure to temperatures commonly used in sterilization processes, typically 121°C in a steam autoclave. Small strips of the tape are applied to the items before they are placed into the autoclave. The tape is similar to masking tape but slightly more adhesive, to allow it to adhere under the hot, moist conditions of the autoclave. One such tape has diagonal markings containing an ink which changes colour (usually beige or blue to black) upon heating. The presence of autoclave tape that has changed color on an item does not ensure that the product is sterile, as the tape will change color upon exposure only. For steam sterilization to occur, the entire item must completely reach and maintain 121°C for 15–20 minutes with proper steam exposure to ensure sterilizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhesive Tape
Adhesive tape is one of many varieties of backing materials coated with an adhesive. Several types of adhesives can be used. Types Pressure-sensitive tape Pressure-sensitive tape, PSA tape, self-stick tape or sticky tape consists of a pressure sensitive adhesive coated onto a backing material such as paper, plastic film, cloth, or metal foil. It is sticky (tacky) without any heat or solvent for activation and adheres to surfaces with light pressure. Typical adhesives are polymers such as acrylates, natural rubber, natural, and synthetic rubber. These tapes usually require a release agent on their backing or a release liner to cover the adhesive. Sometimes, the term "adhesive tape" is used for these tapes. Water-activated tape Water-activated tape, gummed paper tape or gummed tape is starch- or sometimes animal glue-based adhesive on a paper backing which becomes sticky when moistened. A specific type of gummed tape is called reinforced gummed tape (RGT). The backing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
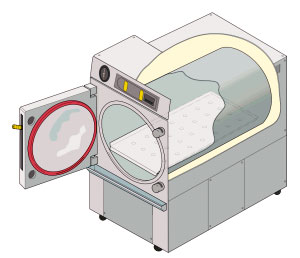
Autoclave
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites. Many autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to pressurized saturated steam at for 30–60 minutes at a gauge pressure of 103 kPa depending on the size of the load and the contents. The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the steam digester was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek ''auto-'', ultimately meaning self, and Latin ''clavis'' meaning key, thus a self-locking device. Uses Sterilization autoclaves are widely us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masking Tape
Masking tape, also known as painter's tape, is a type of pressure-sensitive tape made of a thin and easy-to-tear paper, and an easily released pressure-sensitive adhesive. It is available in a variety of widths. It is used mainly in painting, to Masking (in art), mask off areas that should not be painted. Some inexpensive masking tapes are suited for general use in homes and offices. Others are designed for professional house painters. Masking tapes for automotive or aircraft use have special characteristics for these demanding applications. History Masking tape was created in 1925 by 3M employee Richard Gurley Drew. Drew observed automobile, autobody workers growing frustrated when they removed butcher paper they had taped to cars they were painting. The strong adhesive on the tape peeled off some of the paint they had just applied. Touching up the damaged areas increased their costs. Drew realized the need for tape with a gentler adhesive. Constructions Several const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beige
Beige ( ) is variously described as a pale sandy fawn color, a grayish tan, a light-grayish yellowish brown, or a pale to grayish yellow. It takes its name from French, where the word originally meant natural wool that has been neither bleached nor dyed, hence also the color of natural wool. The word "beige" has come to be used to describe a variety of light tints chosen for their neutral or pale warm appearance. ''Beige'' began to commonly be used as a term for a color in France beginning approximately 1855–1860; the writer Edmond de Goncourt used it in the novel ' in 1877. The first recorded use of ''beige'' as a color name in English was in 1887. Beige is notoriously difficult to produce in traditional offset CMYK printing because of the low levels of inks used on each plate; often it will print in purple or green and vary within a print run. Beige is also a popular color in clothing, such as for men's trousers, as well as for interior design. Various beige colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB color model, RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB color model, RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between Violet (color), violet and cyan on the optical spectrum, spectrum of visible light. The term ''blue'' generally describes colours perceived by humans observing light with a dominant wavelength that's between approximately 450 and 495 nanometres. Most blues contain a slight mixture of other colours; Azure (color), azure contains some green, while ultramarine contains some violet. The clear daytime sky and the deep sea appear blue because of an optical effect known as Rayleigh scattering#Cause of the blue colour of the sky, Rayleigh scattering. An optical effect called the Tyndall effect explains Eye color#Blue, blue eyes. Distant objects appear more blue because of another optical effect called aerial perspective. Blue has been an important colour in art and decoration since ancient t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''Psychologie de la couleur – effets et symboliques'', pp. 105–26. Black and white have often been used to describe opposites such as good and evil, the Dark Ages versus the Age of Enlightenment, and night versus day. Since the Middle Ages, black has been the symbolic color of solemnity and authority, and for this reason it is still commonly worn by judges and magistrates. Black was one of the first colors used by artists in Neolithic cave paintings. It was used in ancient Egypt and Greece as the color of the underworld. In the Roman Empire, it became the color of mourning, and over the centuries it was frequently associated with death, evil, witches, and magic. In the 14th century, it was worn by royalty, clergy, judges, and governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Carbonate
Lead(II) carbonate is the chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a white, toxic solid. It occurs naturally as the mineral cerussite. Structure Like all metal carbonates, lead(II) carbonate adopts a dense, highly crosslinked structure consisting of intact and metal cation sites. As verified by X-ray crystallography, the Pb(II) centers are seven-coordinate, being surrounded by multiple carbonate ligands. The carbonate centers are bonded bidentate to a single Pb and bridge to five other Pb sites. Production and use Lead carbonate is manufactured by passing carbon dioxide into a cold dilute solution of lead(II) acetate, or by shaking a suspension of a lead salt more soluble than the carbonate with ammonium carbonate at a low temperature to avoid formation of basic lead carbonate. : Lead carbonate is used as a catalyst to polymerize formaldehyde to poly(oxymethylene). It improves the bonding of chloroprene to wire. Regulations The supply and use of this compound is re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead(II) Oxide
Lead(II) oxide, also called lead monoxide, is the inorganic compound with the molecular formula Pb O. It occurs in two polymorphs: litharge having a tetragonal crystal structure, and massicot having an orthorhombic crystal structure. Modern applications for PbO are mostly in lead-based industrial glass and industrial ceramics, including computer components. Types Lead oxide exists in two polymorphs: * Red tetragonal (α-PbO), obtained at temperatures below * Yellow orthorhombic (β-PbO), obtained at temperatures above Synthesis PbO may be prepared by heating lead metal in air at approximately . At this temperature it is also the end product of decomposition of other oxides of lead in air: :PbO2->[] Pb12O19 ->[] Pb12O17 ->[] Pb3O4 ->[] PbO Thermal decomposition of lead(II) nitrate or lead carbonate, lead(II) carbonate also results in the formation of PbO: :2 → 2 PbO + 4 + : → PbO + PbO is produced on a large scale as an intermediate product in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laboratory Equipment
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratories are found in a variety of settings such as schools, universities, privately owned research institutions, corporate research and testing facilities, government regulatory and forensic investigation centers, physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, regional and national referral centers, and even occasionally personal residences. Overview The organisation and contents of laboratories are determined by the differing requirements of the specialists working within. A physics laboratory might contain a particle accelerator or vacuum chamber, while a metallurgy laboratory could have apparatus for casting or refining metals or for testing their strength. A chemist or biologist might use a wet laboratory, while a psychologist's laboratory might be a room with one-way mirrors and hidden cameras in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Equipment
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assurance before regulating governments allow marketing of the device in their country. As a general rule, as the associated risk of the device increases the amount of testing required to establish safety and efficacy also increases. Further, as associated risk increases the potential benefit to the patient must also increase. Discovery of what would be considered a medical device by modern standards dates as far back as in Baluchistan where Neolithic dentists used flint-tipped drills and bowstrings. Study of Archaeology, archeology and Roman medical literature also indicate that many types of medical devices were in widespread use during the time of ancient Rome. In the United States it was not until the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Hygiene
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for patients, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of creativity and skill), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |