|
Australian Cornish Mining Sites
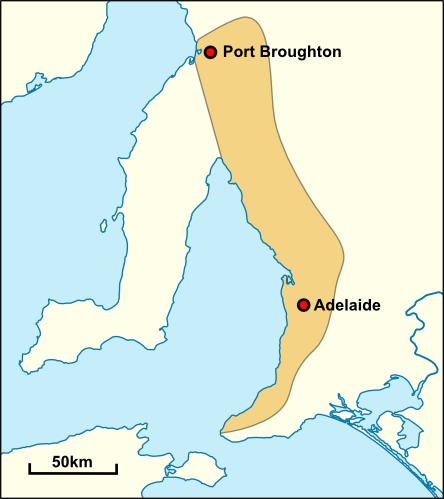
The Australian Cornish Mining Sites are historic sites in South Australia listed jointly on the Australian National Heritage List. There are two distinct sites – Burra in the mid-north of the state and Moonta Mines in the northern Yorke Peninsula region. The heritage value of both sites relates to their history as mines worked by migrant miners from Cornwall. The sites were inscribed on the Australian National Heritage List on 9 May 2017. Background In 1841, copper deposits were discovered in Kapunda and Burra, though mining only began in 1844 and 1845 respectively. By 1850 the region would become the third largest copper producer in the world. Settlers were drawn to Southern Australia to take part in the great copper boom, including Cornish miners and their families. In 1859, traces of copper were discovered in South Australia's Yorke peninsula and mines were quickly established in Moonta, Kadina, and Wallaroo. The area bordered by these towns became known as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Site
A historic site or heritage site is an official location where pieces of political, military, cultural, or social history have been preserved due to their cultural heritage value. Historic sites are usually protected by law, and many have been recognized with the official national historic site status. A historic site may be any building, landscape, site or structure that is of local, regional, or national significance. Usually this also means the site must be at least 50 years or older. The U.S. National Park Service defines a historic site as the "location of a significant event, a prehistoric or historic occupation or activity, or a building or structure, whether standing, ruined, or vanished, where the location itself possesses historic, cultural, or archeological value regardless of the value of any existing structure". Historic sites can also mark public crimes, such as Tuol Sleng Genocide Museum in Phnom Penh, Cambodia or Robben Island, South Africa. Similar to museums ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic Ocean, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, with the River Tamar forming the border between them. Cornwall forms the westernmost part of the South West Peninsula of the island of Great Britain. The southwesternmost point is Land's End and the southernmost Lizard Point. Cornwall has a population of and an area of . The county has been administered since 2009 by the unitary authority, Cornwall Council. The ceremonial county of Cornwall also includes the Isles of Scilly, which are administered separately. The administrative centre of Cornwall is Truro, its only city. Cornwall was formerly a Brythonic kingdom and subsequently a royal duchy. It is the cultural and ethnic origin of the Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burra Mine Site
Burra may refer to: Places *Burra, South Australia, a pastoral centre and historic tourist town in the mid-north of South Australia **District Council of Burra (1872–1935) **District Council of Burra Burra (1935–1997) **Corporate Town of Burra (1876–1969) **Electoral district of The Burra (1857–1875) **Electoral district of Burra (1875–1902), (1938–1970) **Electoral district of Burra Burra * Burra, Shetland, the collective name for two of the Shetland Islands ** West Burra ** East Burra * Burra, New South Wales, a locality located near Canberra, Australia * Burra Parish (Murray County), a land administrative division, essentially identical with the above locality * Burra Parish (Kennedy County), a land administrative division in central western New South Wales * Burra Burra Mine (Tennessee), named after the South Australian mine People * Djambu "Sambo" Burra Burra (born 1946), noted Aboriginal Australian artist living at Ngukurr, NT * Edward Burra (1905-1976), an Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as " the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulley
A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft that is designed to support movement and change of direction of a taut cable or belt, or transfer of power between the shaft and cable or belt. In the case of a pulley supported by a frame or shell that does not transfer power to a shaft, but is used to guide the cable or exert a force, the supporting shell is called a block, and the pulley may be called a sheave. A pulley may have a groove or grooves between flanges around its circumference to locate the cable or belt. The drive element of a pulley system can be a rope, cable, belt, or chain. The earliest evidence of pulleys dates back to Ancient Egypt in the Twelfth Dynasty (1991-1802 BCE) and Mesopotamia in the early 2nd millennium BCE. In Roman Egypt, Hero of Alexandria (c. 10-70 CE) identified the pulley as one of six simple machines used to lift weights. Pulleys are assembled to form a block and tackle in order to provide mechanical advantage to apply large forces. Pulle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to either a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea are: short duration watery diarrhea, short duration bloody diarrhea, and persistent diarrhea (lasting more than two wee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications may include dehydration. The cause of dysentery is usually the bacteria from genus '' Shigella'', in which case it is known as shigellosis, or the amoeba '' Entamoeba histolytica''; then it is called amoebiasis. Other causes may include certain chemicals, other bacteria, other protozoa, or parasitic worms. It may spread between people. Risk factors include contamination of food and water with feces due to poor sanitation. The underlying mechanism involves inflammation of the intestine, especially of the colon. Efforts to prevent dysentery include hand washing and food safety measures while traveling in areas of high risk. While the condition generally resolves on its own within a week, drinking sufficient fluids such as oral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time. Epidemics of infectious diseases are generally caused by several factors including a significant change in the ecology of the areal population (e.g., increased stress maybe additional reason or increase in the density of a vector species), the introduction of an emerging pathogen to an areal population (by movement of pathogen or host) or an unexpected genetic change that is in the pathogen reservoir. Generally, epidemics concerns with the patterns of infectious disease spread. An epidemic may occur when host immunity to either an established pathogen or newly emerging novel pathogen is suddenly reduced below that found in the endemic equilibrium and the transmission threshold is exceeded. For example, in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in excess of 15 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Water
Mineral water is water from a mineral spring that contains various minerals, such as salts and sulfur compounds. Mineral water may usually be still or sparkling (carbonated/effervescent) according to the presence or absence of added gases. Traditionally, mineral waters were used or consumed at their spring sources, often referred to as "taking the waters" or "taking the cure", at places such as spas, baths, or wells. The term ''spa'' was used for a place where the water was consumed and bathed in; ''bath'' where the water was used primarily for bathing, therapeutics, or recreation; and ''well'' where the water was to be consumed. Today, it is far more common for mineral water to be bottled at the source for distributed consumption. Travelling to the mineral water site for direct access to the water is now uncommon, and in many cases not possible because of exclusive commercial ownership rights. There are more than 4,000 brands of mineral water commercially available worldwide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelaide
Adelaide ( ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre. The demonym ''Adelaidean'' is used to denote the city and the residents of Adelaide. The Native title in Australia#Traditional owner, Traditional Owners of the Adelaide region are the Kaurna people. The area of the city centre and surrounding parklands is called ' in the Kaurna language. Adelaide is situated on the Adelaide Plains north of the Fleurieu Peninsula, between the Gulf St Vincent in the west and the Mount Lofty Ranges in the east. Its metropolitan area extends from the coast to the Adelaide Hills, foothills of the Mount Lofty Ranges, and stretches from Gawler in the north to Sellicks Beach in the south. Named in honour of Queen Adelaide, the city was founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moonta Mines Hughes' Enginehouse 4 (22049325459)
Moonta may refer to: Places * Moonta, South Australia, a locality in the Copper Coast Council including: ** East Moonta ** Moonta Bay **Moonta Cemetery **Moonta Mines ** North Moonta *Corporate Town of Moonta, a former local government area *New Moonta, a suburb in Bundaberg, Queensland Ships *MV Moonta MV ''Moonta'' is a 1931 built Australian coastal passenger ship. Later in life she became the landlocked casino ship and tourist attraction ''Casino Le Lydia'' in Le Barcarès, France. Service years ''Moonta'' was launched in June 1931 Burmei ..., a cruise ship now used as a casino *SS Moonta (refer ''Moonta Herald and Northern Territory'' ''Gazette'') {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kernewek Lowender
The Kernewek Lowender (officially the Kernewek Lowender Copper Coast Cornish Festival) is a Cornish-themed biennial festival held in the Copper Coast towns of Kadina, Moonta and Wallaroo on Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. 'Kernewek Lowender' means 'Cornish happiness' in the Cornish language. It is held in the late autumn starting on the second Monday of May, in odd-numbered years. The Kernewek Lowender claims to be the world’s largest Cornish Festival outside Cornwall. Activities The festival is held over seven days with the highlight being 'The Big Weekend', featuring three large fairs: the Village Green Fair, Fer Kernewek, and a Classic Cavalcade of Cars (with over 500 vintage cars and motorcycles). Traditional Cornish food, such as Cornish pasties and Swanky beer is served during the Festival. maypole performances, furry dancing, and the selection of a May Queen are also included. Other events include a street parade, a bake-off, the Gathering of the Bards and the Dres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_2016.jpg)