|
Aryne
In organic chemistry, arynes and benzynes are a class of highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemical Chemical species, species derived from an aromatic ring by removal of two substituents. Arynes are examples of didehydroarenes (1,2-didehydroarenes in this case), although 1,3- and 1,4-didehydroarenes are also known. Arynes are examples of alkynes under high Ring strain, strain. Bonding in arynes The alkyne representation of benzyne is the most widely encountered. Arynes are usually described as having a strained triple bond (left), but resonance contributors include a cumulene form (middle) and biradical form (right): Geometric constraints on the triple bond in benzyne result in diminished overlap of in-plane p-orbitals, and thus weaker triple bond. The vibrational frequency of the triple bond in benzyne was assigned by Radziszewski to be 1846 cm−1, indicating a weaker triple bond than in unstrained alkyne with vibrational frequency of approximately 2150 cm−1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reactive Intermediate
In chemistry, a reactive intermediate or an intermediate is a short-lived, high-energy, highly reactive molecule. When generated in a chemical reaction, it will quickly convert into a more stable molecule. Only in exceptional cases can these compounds be isolated and stored, e.g. low temperatures, matrix isolation. When their existence is indicated, reactive intermediates can help explain how a chemical reaction takes place. Most chemical reactions take more than one elementary step to complete, and a reactive intermediate is a high-energy, hence unstable, product that exists only in one of the intermediate steps. The series of steps together make a reaction mechanism. A reactive intermediate differs from a reactant or product or a simple reaction intermediate only in that it cannot usually be isolated but is sometimes observable only through fast spectroscopic methods. It is stable in the sense that an elementary reaction forms the reactive intermediate and the elementary rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
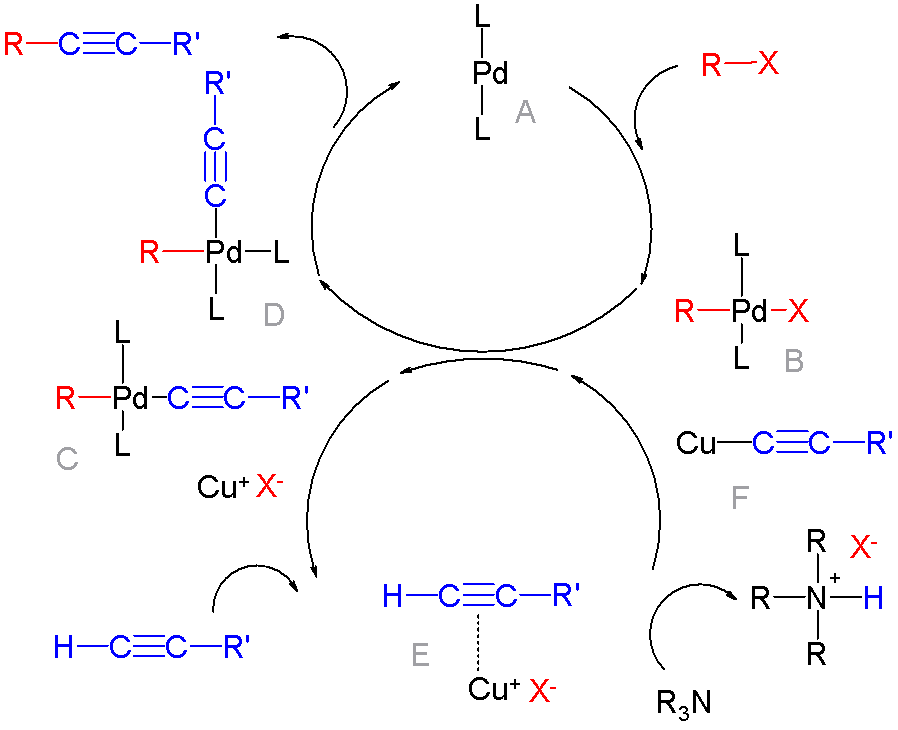
Cross-coupling Of Arynes
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two different fragments are joined. Cross-couplings are a subset of the more general coupling reactions. Often cross-coupling reactions require metal catalysts. One important reaction type is this: : (R, R' = organic fragments, usually aryl; M = main group center such as Li or MgX; X = halide) These reactions are used to form carbon–carbon bonds but also carbon-heteroatom bonds. Cross-coupling reaction are a subset of coupling reactions. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions. Mechanism Many mechanisms exist reflecting the myriad types of cross-couplings, including those that do not require metal catalysts. Often, however, cross-coupling refers to a metal-catalyzed reaction of a nucleophilic partner with an electrophilic partner. In such cases, the mechanism generally involves reductive eliminat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuc Addn To Benzyne
{{More citations needed, date=April 2008 A nuc, or nucleus colony, is a small honey bee colony created from larger colonies, packages, or captured swarms. A nuc hive is centered on a queen bee, the nucleus of the honey bee colony. Layout A nuc hive has all the features of a standard 10 frame Langstroth hive, except for a reduced width. A typical nuc has 5 Langstroth frames arranged side-by-side. Nucs can also be created using other hive dimensions, with the British modified national hive being the most common in the United Kingdom. According to FERA's (Food and Environment Research Agency) National Bee Unit guidelines, the nucleus should be between 3–6 frames of bees, including a queen, workers, brood in all stages, and honey stores. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead(IV) Acetate
Lead(IV) acetate or lead tetraacetate is an metalorganic compound with chemical formula , often abbreviated as , where Ac is acyl. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in nonpolar, organic solvents, indicating that it is not a salt. It is degraded by moisture and is typically stored with additional acetic acid. The compound is used in organic synthesis. Structure In the solid state the lead(IV) centers are coordinated by four acetate ions, which are bidentate, each coordinating via two oxygen atoms. The lead atom is 8 coordinate and the O atoms form a flattened trigonal dodecahedron. Preparation It is typically prepared by treating of red lead with acetic acid and acetic anhydride (), which absorbs water. The net reaction is shown: : The remaining lead(II) acetate can be partially oxidized to the tetraacetate by Cl2, with a by-product: : Reagent in organic chemistry Lead tetraacetate is a strong oxidizing agent, a source of acetyloxy groups, and a general reagent for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic Acid
Hydroxylamine-''O''-sulfonic acid (HOSA) or aminosulfuric acid is the inorganic compound with molecular formula H3NO4S that is formed by the sulfonation of hydroxylamine with oleum. It is a white, water-soluble and hygroscopic, solid, commonly represented by the condensed structural formula H2NOSO3H, though it actually exists as a zwitterion and thus is more accurately represented as +H3NOSO3−. It is used as a reagent for the introduction of amine groups (–NH2), for the conversion of aldehydes into nitriles and alicyclic compound, alicyclic ketones into lactams (cyclic amides), and for the synthesis of variety of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. Preparation According to a laboratory procedure hydroxylamine-''O''-sulfonic acid can be prepared by treating hydroxylamine sulfate with fuming sulfuric acid (oleum). The industrial process is similar. :(NH3OH)2SO4 + 2SO3 → 2H2NOSO3H + H2SO4 The sulfonation of hydroxylamine can also be effected with chlorosulfonic acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzotriazole
Benzotriazole (BTA) is a heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula . It can be viewed as the fusion of a benzene and triazole rings. It is a white solid, although impure samples can appear tan. It is used as a corrosion inhibitor for copper. Structure and synthesis : Benzotriazole features two fused rings. It can in principle exist as tautomers, but X-ray crystallography establishes the depicted structure. The N=N and HN-N distances are 1.306 and 1.340 Å. Benzotriazole can be prepared by the monodiazotization of o-Phenylenediamine, ''o''-phenylenediamine using sodium nitrite and acetic acid.Robert A. Smiley "Phenylene- and Toluenediamines" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Reactions Acid-base behavior BTA is a weak Bronsted acid with a pKa = 8.2. It is a weak Brønsted base, as indicated by the low pKa 0.1 μg/L. One source of this pollution is their use as anti-icing/deicing agents in airports. Benzotriazo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |