|
Artemis VIII
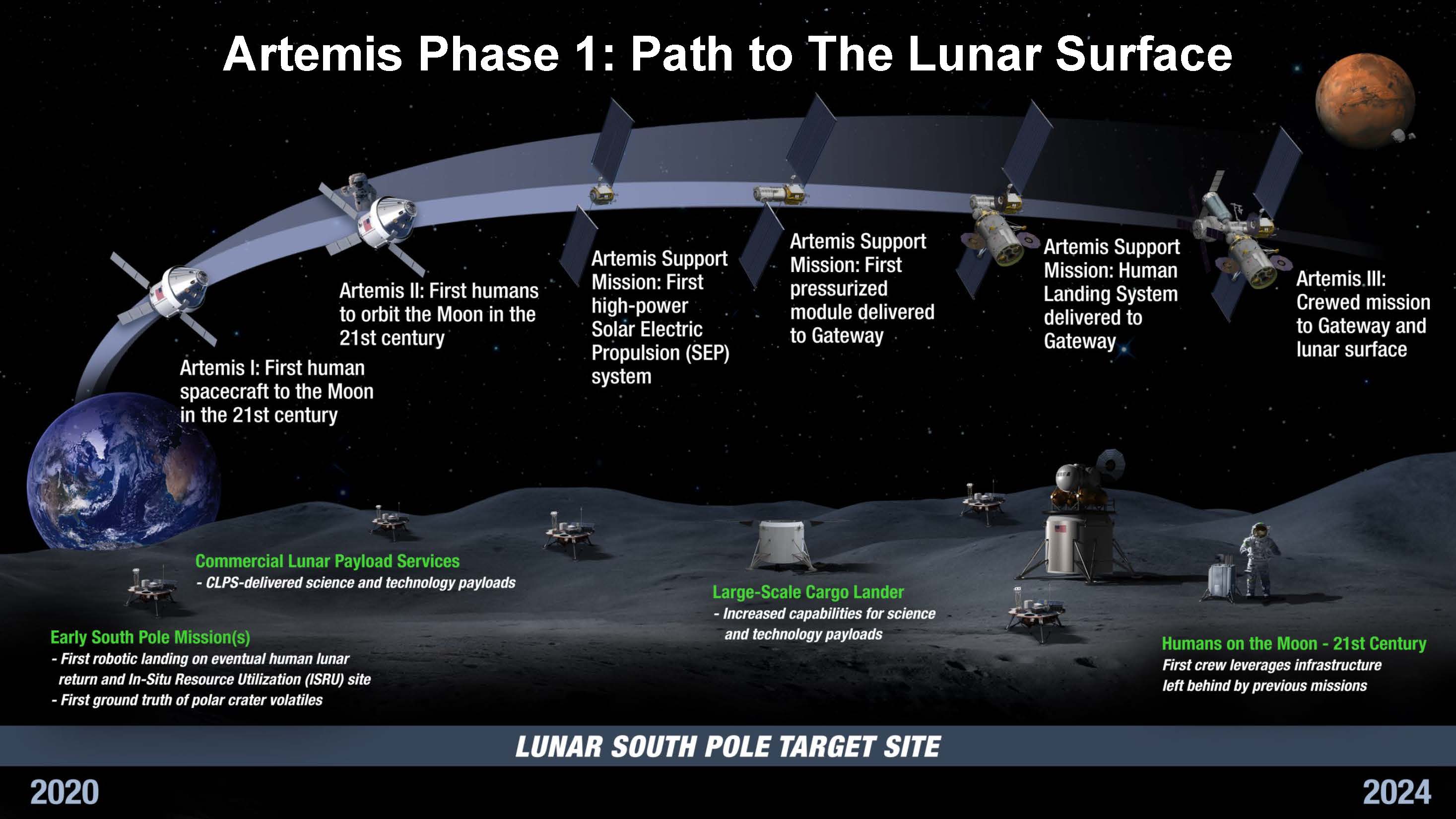
The Artemis program is a Moon exploration program led by the United States' National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), formally established in 2017 via Space Policy Directive 1. The program's stated long-term goal is to establish a permanent base on the Moon to facilitate human missions to Mars. It is intended to reestablish a human presence on the Moon for the first time since the Apollo 17 mission in 1972 and continue the direct exploration of Mars begun with data from the Mariner 9 probe in the same year. Two principal elements of the Artemis program are derived from the now-cancelled Constellation program: the Orion spacecraft (with the ESM instead of a US-built service module) and the Space Launch System's solid rocket boosters (originally developed for the Ares V). Other elements of the program, such as the Lunar Gateway space station and the Human Landing System, are in development by government space agencies and private spaceflight companies, collabora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Gateway
The Lunar Gateway, or simply Gateway, is a planned space station which is to be assembled in orbit around the Moon. The Gateway is intended to serve as a communication hub, science laboratory, and habitation module for astronauts as part of the Artemis program. It is a multinational collaborative project: participants include NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), and the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC). The Gateway is planned to be the first space station beyond low Earth orbit. However, the Second presidency of Donald Trump, Trump administration has called for ending the Gateway program in its 2026 budget proposal. The science disciplines to be studied on the Gateway are expected to include planetary science, astrophysics, Earth observation, heliophysics, Astrobiology, fundamental space biology, and Health, human health and performance. As of April 2024, construction is underway o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Service Module
The European Service Module (ESM) is the service module component of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft, serving as its primary power and propulsion component until it is discarded at the end of each mission. In January 2013, NASA announced that the European Space Agency (ESA) will contribute the service module for Artemis I, based on the ESA's Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV). It was delivered by Airbus Defence and Space in Bremen, in northern Germany to NASA at the end of 2018. After approval of the first module, the ESA will provide the ESMs from Artemis II to Artemis VI. However, the Second presidency of Donald Trump, Trump administration has called for the termination of Orion spacecraft program after Artemis III. The module's first flight was Artemis I, the first major milestone in NASA's Artemis program to return humans to the Moon, on November 16, 2022. The Space Launch System launched Orion toward the Moon, where the ESM placed the spacecraft into distant retrograd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation Program
The Constellation program (abbreviated CxP) was a crewed spaceflight program developed by NASA, the space agency of the United States, from 2005 to 2009. The major goals of the program were "completion of the International Space Station" and a "return to the Moon no later than 2020" with a crewed flight to the planet Mars as the ultimate goal. The program's logo reflected the three stages of the program: the Earth (ISS), the Moon, and finally Mars—while the Mars goal also found expression in the name given to the program's booster rockets: Ares V, Ares (the Greek equivalent of the Roman god Mars (mythology), Mars). The technological aims of the program included the regaining of significant astronaut experience beyond low Earth orbit and the development of technologies necessary to enable sustained human presence on other planetary bodies. Constellation began in response to the goals laid out in the Vision for Space Exploration under NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe and President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner Mars '71 / Mariner-I) was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971, from Spaceport Florida Launch Complex 36, LC-36B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, and reached the planet on November 14 of the same year, becoming the first spacecraft to orbit another planet – only narrowly beating the Soviet Union, Soviet probes ''Mars 2'' (launched May 19) and ''Mars 3'' (launched May 28), which both arrived at Mars only weeks later. After the occurrence of Climate of Mars#Dust storms, dust storms on the planet for several months following its arrival, the orbiter managed to send back clear pictures of the surface. Mariner 9 successfully returned 7,329 images, covering 85% of Mars' surface, over the course of its mission, which concluded in October 1972. Objectives Mariner 9 was designed to continue the atmospheric studies begun by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo 17
Apollo 17 (December 7–19, 1972) was the eleventh and final mission of NASA's Apollo program, the sixth and most recent time humans have set foot on the Moon. Commander Gene Cernan and Lunar Module Pilot Harrison Schmitt walked on the Moon, while Command Module Pilot Ronald Evans (astronaut), Ronald Evans orbited above. Schmitt was the only professional geologist to land on the Moon; he was selected in place of Joe Engle, as NASA had been under pressure to send a scientist to the Moon. The mission's heavy emphasis on science meant the inclusion of a number of new experiments, including a Fe, Fi, Fo, Fum, and Phooey, biological experiment containing five mice that was carried in the command module. Mission planners had two primary goals in deciding on the landing site: to sample Lunar highlands, lunar highland material older than that at Mare Imbrium and to investigate the possibility of relatively recent Volcano, volcanic activity. They therefore selected Taurus–Littrow, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Mission To Mars
The idea of sending humans to Mars has been the subject of aerospace engineering and scientific studies since the late 1940s as part of the broader exploration of Mars. Long-term proposals have included sending settlers and terraforming the planet. Currently, only robotic landers, rovers and a helicopter have been on Mars. The farthest humans have been beyond Earth is the Moon, under the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Apollo program which ended in 1972. Conceptual proposals for missions that would involve human explorers started in the early 1950s, with planned missions typically being stated as taking place between 10 and 30 years from the time they are drafted. The list of crewed Mars mission plans shows the various mission proposals that have been put forth by multiple organizations and space agencies in this field of space exploration. The plans for these crews have varied—from scientific expeditions, in which a small group (between two an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moonbase
A moonbase (or lunar base) is a human outpost on or below the surface of the Moon. More than a mere site of activity or temporary camp, moonbases are extraterrestrial bases, supporting uncrewed spaceflight, robotic or crewed spaceflight, human activity, by providing surface infrastructure. List of missions to the Moon, Missions to the Moon have realized single-mission bases, (Tranquility Base being the first), as well as Moon#Human presence, some small permanent infrastructure like Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment, lunar laser ranging installations. Plans for establishing moonbases, with surface or sub-surface research stations, have been proposed and are actively pursued nationally and increasingly internationally. As of 2024, the two most advanced projects to set up moonbases have been pursued Multilateralism, multilaterally as part of the United States, US-led Artemis program, with its planned Artemis program#Shelter building construction, Artemis Base Camp and as the China-led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Policy Directive 1
The space policy of the first Donald Trump administration, as of December 2020, comprises six Space Policy Directives and an announced "National Space Strategy" (issued March 28, 2018), representing a directional shift from the policy priorities and goals of his predecessor, Barack Obama. A National Space Policy was issued on December 9, 2020. History 2017: Space Policy Directive-1 On December 11, 2017, President Donald Trump issued a presidential memorandum also known as "Space Policy Directive-1". This directive amended Barack Obama's "Presidential Policy Directive 4," by replacing the paragraph beginning “Set far-reaching exploration milestones...” with the paragraph “Lead an innovative and sustainable program of exploration with commercial and international partners to enable human expansion across the Solar System and to bring back to Earth new knowledge and opportunities. Beginning with missions beyond low-Earth orbit, the United States will lead the return of human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Aeronautics And Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the United States's civil space program, aeronautics research and space research. Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the lunar Artemis program. NASA's science division is focused on better understanding Earth through the Earth Observing System; advancing heliophysics through the effor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Of The Moon
The physical exploration of the Moon began when ''Luna 2'', a space probe launched by the Soviet Union, made a deliberate impact on the surface of the Moon on 14 September, 1959. Prior to that the only available means of lunar exploration had been observations from Earth. The invention of the optical telescope brought about the first leap in the quality of lunar observations. Galileo Galilei is generally credited as the first person to use a telescope for astronomical purposes, having made his own telescope in 1609, the mountains and craters on the lunar surface were among his first observations using it. Human exploration of the Moon since Luna 2 has consisted of both crewed and uncrewed missions. NASA's Apollo program has been the only program to successfully land humans on the Moon, which it did six times on the near side in the 20th century. The first human landing took place in 1969, when the Apollo 11 astronauts Buzz Aldrin and Neil Armstrong touched down on the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Glenn
New Glenn is a heavy-lift launch vehicle developed and operated by the American company Blue Origin. The rocket is designed to have a Reusable launch vehicle, partially reusable, two-stage design with a diameter of . The first stage is powered by seven BE-4 engines, while the second stage relies on two BE-3, BE-3U engines, all designed and built in-house by Blue Origin. It launches from Cape Canaveral Launch Complex 36, with future missions planned from Vandenberg Space Launch Complex 9. Development of New Glenn began prior to 2013 and was officially announced in 2016. The rocket is named in honor of NASA astronaut John Glenn, the first American to orbit Earth. The inaugural vehicle was unveiled on the launch pad in February 2024. Its maiden flight took place on 16 January 2025, carrying a prototype Blue Ring spacecraft, marking the first launch from LC-36 since NROL-23 in 2005. This mission served as the first of several demonstration launches required to be certified for use b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |