|
Armstrong Phase Modulator
In 1933, Edwin H. Armstrong patented a method for generating frequency modulation of radio signals. The Armstrong method generates a double sideband suppressed carrier signal, phase shifts this signal, and then reinserts the carrier to produce a frequency modulated signal. Frequency modulation generates high quality audio and greatly reduces the amount of noise on the channel when compared with amplitude modulation. Early broadcasters used amplitude modulation because it was easier to generate than frequency modulation and because the receivers were simpler to make. The electronics theory indicated that a frequency modulated signal would have infinite bandwidth; for an amplitude modulated signal, the bandwidth is approximately twice the highest modulating frequency. Armstrong realized that while a frequency modulated signal would have an infinite bandwidth, only the first few sets of sidebands would be significant; the rest could be ignored. An amplitude modulated voice ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwin H
The name Edwin means "wealth-friend". It comes from (wealth, good fortune) and (friend). Thus the Old English form is Ēadwine, a name widely attested in early medieval England. Edwina The name Edwina is a feminine form of the male name Edwin, which derives from Old English and means "rich friend." Edwin was a popular name until the time of the Norman Conquest, then fell out of favour until Victorian era, Victorian times. People ... is the feminine form of the name. Notable people and characters with the name include: Historical figures * Edwin of Northumbria (died 632 or 633), King of Northumbria and Christian saint * Edwin (son of Edward the Elder) (died 933) * Eadwine of Sussex (died 982), Ealdorman of Sussex * Eadwine of Abingdon (died 990), Abbot of Abingdon * Edwin, Earl of Mercia (died 1071), brother-in-law of Harold Godwinson (Harold II) * Edwin Sandys (bishop) (1519–1588), Archbishop of York Modern era * E. W. Abeygunasekera, Sri Lankan Sinhala politi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
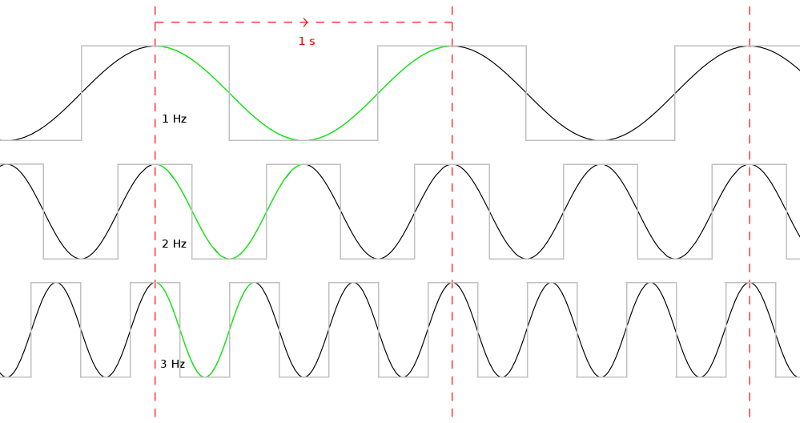
Megahertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base units is 1/s or s−1, meaning that one hertz is one per second or the reciprocal of one second. It is used only in the case of periodic events. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. For high frequencies, the unit is commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. The units are sometimes also used as a representation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating Frequency
Clock rate or clock speed in computing typically refers to the frequency at which the clock generator of a processor can generate pulses used to synchronize the operations of its components. It is used as an indicator of the processor's speed. Clock rate is measured in the SI unit of frequency hertz (Hz). The clock rate of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), the first personal computers from the 1970s through the 1980s had clock rates measured in megahertz (MHz). In the 21st century the speed of modern CPUs is commonly advertised in gigahertz (GHz). This metric is most useful when comparing processors within the same family, holding constant other features that may affect performance. Determining factors Binning Manufacturers of modern processors typically charge higher prices for processors that operate at higher clock rates, a practice called binning. For a given CPU, the clock rates are determined at the end of the manufacturin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal representing sound or a video signal representing images, in an electronic device or communication channel. Distortion is usually unwanted, and so engineers strive to eliminate or minimize it. In some situations, however, distortion may be desirable. For example, in noise reduction systems like the Dolby noise-reduction system, Dolby system, an audio signal is deliberately distorted in ways that emphasize aspects of the signal that are subject to electrical noise, then it is symmetrically "undistorted" after passing through a noisy communication channel, reducing the noise in the received signal. Distortion is also used as a Distortion (music), musical effect, particularly with electric guitars. The addition of Electronic noise, noise o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Deviation
Frequency deviation (f_) is used in FM radio to describe the difference between the minimum or maximum extent of a frequency modulated signal, and the nominal center or carrier frequency. The term is sometimes mistakenly used as synonymous with frequency drift, which is an unintended offset of an oscillator from its nominal frequency. The frequency deviation of a radio is of particular importance in relation to bandwidth, because less deviation means that more channels can fit into the same amount of frequency spectrum. The FM broadcasting range between 87.5 and 108 MHz uses a typical channel spacing of 100 or 200 kHz, with a maximum frequency deviation of +/-75 kHz, in some cases leaving a buffer above the highest and below the lowest frequency to reduce interaction with other channels. The most common FM transmitting applications use peak deviations of +/-75 kHz (100 or 200 kHz spacing), +/-5 kHz (15–25 kHz spacing), +/-2.5 kHz (3.75-12. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
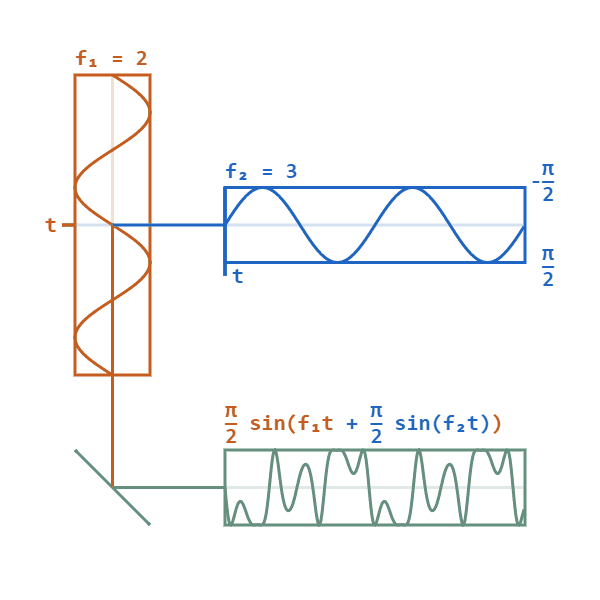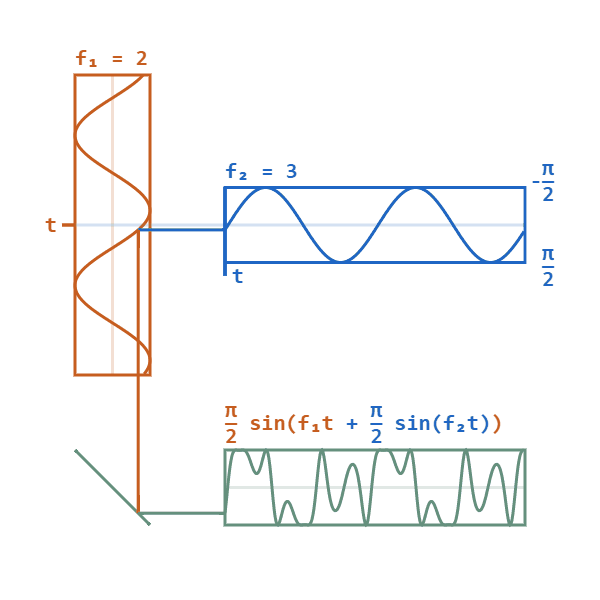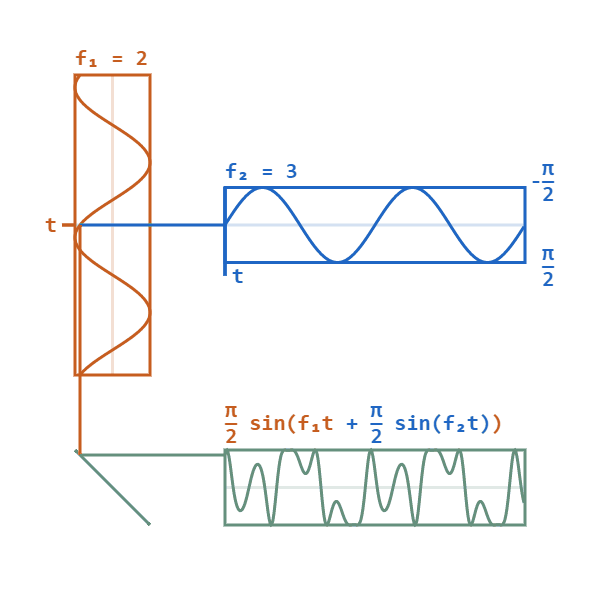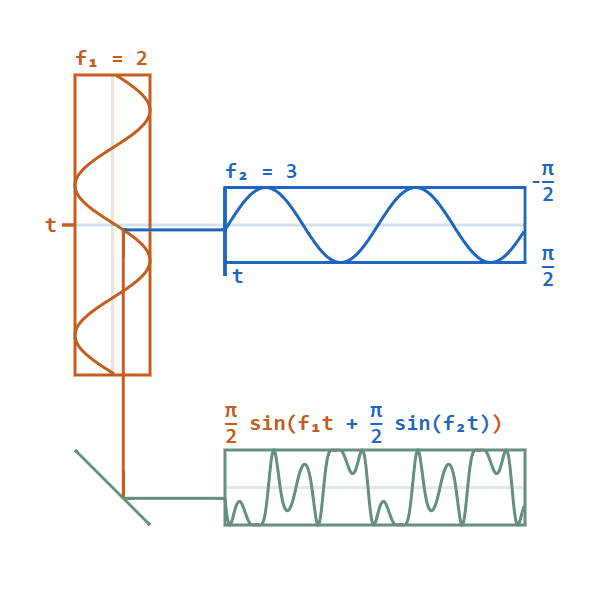
Phase Modulation
Phase modulation (PM) is a signal modulation method for conditioning communication signals for transmission. It encodes a message signal as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. Phase modulation is one of the two principal forms of angle modulation, together with frequency modulation. In phase modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the baseband signal modifies the phase of the carrier signal keeping its amplitude and frequency constant. The phase of a carrier signal is modulated to follow the changing signal level (amplitude) of the message signal. The peak amplitude and the frequency of the carrier signal are maintained constant, but as the amplitude of the message signal changes, the phase of the carrier changes correspondingly. Phase modulation is an integral part of many digital transmission coding schemes that underlie a wide range of technologies like Wi-Fi, GSM and satellite television. However it is not widely used for transmitting analog audio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio Signal
An audio signal is a representation of sound, typically using either a changing level of electrical voltage for analog signals or a series of binary numbers for Digital signal (signal processing), digital signals. Audio signals have frequencies in the audio frequency range of roughly 20 to 20,000 Hz, which corresponds to the lower and upper Human hearing range, limits of human hearing. Audio signals may be Synthesizer, synthesized directly, or may originate at a transducer such as a microphone, Pickup (music technology), musical instrument pickup, phonograph cartridge, or tape head. Loudspeakers or headphones convert an electrical audio signal back into sound. Digital audio systems represent audio signals in a variety of digital formats.Hodgson, Jay (2010). ''Understanding Records'', p.1. . An audio channel or audio track is an audio signal communications channel in a data storage device, storage device or mixing console. It is used in operations such as multi-track recordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter (often abbreviated as XMTR or TX in technical documents) is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna with the purpose of signal transmission to a radio receiver. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the Antenna (radio), antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna Electromagnetic radiation, radiates radio waves. Transmitters are necessary component parts of all electronic devices that communicate by radio communication, radio, such as radio broadcasting, radio (audio) and television broadcasting stations, cell phones, walkie-talkies, Wireless LAN, wireless computer networks, Bluetooth enabled devices, garage door openers, two-way radios in aircraft, ships, spacecraft, radar sets and navigational beacons. The term ''transmitter'' is usually limited to equipment that generates radio waves fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FM Bandwidth
FM or Fm may refer to: Technology and computing * Adobe FrameMaker, document processing software * .fm, country-code top-level domain of the Federated States of Micronesia * FM Towns, Fujitsu personal computers * Foundation model, a large machine learning model trained on vast datasets * Frequency modulation, a radio broadcasting technology ** FM broadcasting ** FM broadcast band * Nissan FM platform, a car layout * Volvo FM, heavy truck range Science and medicine * Femtometre (fm), a unit of length * Femtomolar (fM), a unit of molar concentration * Fermium, (Fm) a chemical element * FM (chemotherapy) regimen * Family medicine Sports and games * FIDE Master, a chess title * Formula Mazda, in car racing * ''Football Manager'', a video game series Film and television * ''FM'' (film), 1978 * ''FM Fun Aur Masti'' or ''FM'', 2007 film * FM (TV channel), US * ''FM'' (American TV series), 1989–1990 * ''FM'' (British TV series), 2009 Literature * ''F.M.'' (novel), by Bori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Modulator
Frequency modulation (FM) is a signal modulation technique used in electronic communication, originally for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In frequency modulation a carrier wave is varied in its instantaneous frequency in proportion to a property, primarily the instantaneous amplitude, of a message signal, such as an audio signal. The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and computing. In analog frequency modulation, such as radio broadcasting of voice and music, the instantaneous frequency deviation, i.e. the difference between the frequency of the carrier and its center frequency, has a functional relation to the modulating signal amplitude. Digital data can be encoded and transmitted with a type of frequency modulation known as frequency-shift keying (FSK), in which the instantaneous frequency of the carrier is shifted among a set of frequencies. The frequencies may represent digits, such as ''0'' and ''1''. FSK is wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |