|
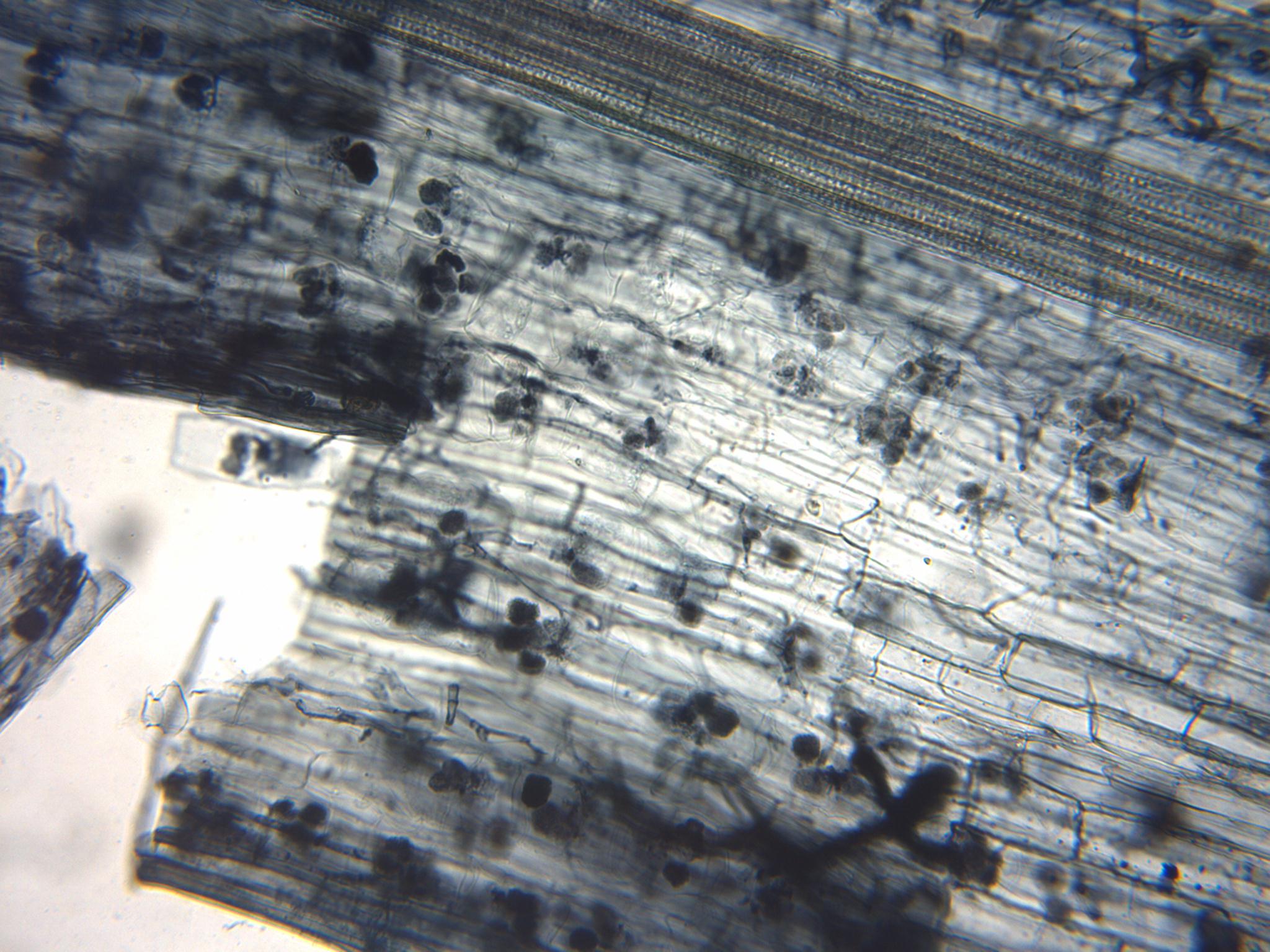
Arbuscule
An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (''Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. Arbuscular mycorrhiza is a type of endomycorrhiza along with ericoid mycorrhiza and orchid mycorrhiza (not to be confused with ectomycorrhiza). They are characterized by the formation of unique tree-like structures, the arbuscules. In addition, globular storage structures called vesicles are often encountered. Arbuscular mycorrhizae are formed by fungi in the subphylum Glomeromycotina. This subphylum, along with the Mortierellomycotina, and Mucoromycotina, form the phylum Mucoromycota, a sister clade of the more well-known and diverse dikaryan fungi. AM fungi help plants to capture nutrients such as phosphorus, sulfur, nitrogen and micronutrients from the soil. It is believed that the development of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis played a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleobiological
Paleobiology (or palaeobiology) is an interdisciplinary field that combines the methods and findings found in both the earth sciences and the life sciences. An investigator in this field is known as a paleobiologist. Paleobiology is closely related to the field of paleontology, although the latter focuses primarily on the study and taxonomic classification of fossil records, while paleobiology incorporates a broader ecological, evolutionary and geological perspectives of the history of life on Earth. It is also not to be confused with geobiology, which focuses more on the contemporary interactions between the modern biosphere and the physical Earth. Paleobiological research uses biological field research of current biota and of fossil evidence millions of years old to draw parallel and answer questions about the molecular evolution and the evolutionary history of life. In this scientific quest, macrofossils, microfossils and trace fossils are typically analyzed. However, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Effects Of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal (AM) Colonization
Positive is a property of positivity and may refer to: Mathematics and science * Positive formula, a logical formula not containing negation * Positive number, a number that is greater than 0 * Plus sign, the sign "+" used to indicate a positive number * Positive operator, a type of linear operator in mathematics * Positive result, a result that has been found significant in statistical hypothesis testing * Positive test, a diagnostic test result that indicates some parameter being evaluated was present * Positive charge, one of the two types of electrical charge * Positive (electrical polarity), in electrical circuits * Positive lens, in optics * Positive (photography), a positive image, in which the color and luminance correlates directly with that in the depicted scene * Positive sense, said of an RNA sequence that codes for a protein Philosophy and humanities * Affirmative (policy debate), the team which affirms the resolution * Negative and positive rights, concernin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in the cities. While humans started gathering grains at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers only began planting them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs, and cattle were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. In the 20th century, industrial agriculture based on large-scale monocultures came to dominate agricultural output. , small farms produce about one-third of the world's food, but large farms are prevalent. The largest 1% of farms in the world are greater than and operate more than 70% of the world's farmland. Nearly 40% of agricultural land is found on farms larger than . However, five of every six farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
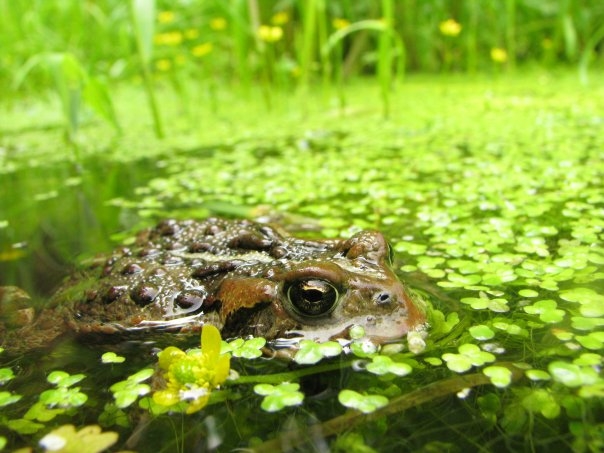
Ecosystem Restoration
Ecological restoration, or ecosystem restoration, is the process of assisting the recovery of an ecosystem that has been degraded, damaged, destroyed or transformed. It is distinct from conservation in that it attempts to retroactively repair already damaged ecosystems rather than take preventative measures. Ecological restoration can help to reverse biodiversity loss, combat climate change, support the provision of ecosystem services and support local economies. The United Nations has named 2021–2030 the Decade on Ecosystem Restoration. Habitat restoration involves the deliberate rehabilitation of a specific area to reestablish a functional ecosystem. This may differ from historical baselines (the ecosystem's original condition at a particular point in time). To achieve successful habitat restoration, it is essential to understand the life cycles and interactions of species, as well as the essential elements such as food, water, nutrients, space, and shelter needed to suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem Management
Ecosystem management is an approach to natural resource management that aims to ensure the long-term sustainability and persistence of an ecosystem's function and services while meeting socioeconomic, political, and cultural needs. Although indigenous communities have employed sustainable ecosystem management approaches implicitly for millennia, ecosystem management emerged explicitly as a formal concept in the 1990s from a growing appreciation of the complexity of ecosystems and of humans' reliance and influence on natural systems (e.g., disturbance and ecological resilience). Building upon traditional natural resource management, ecosystem management integrates ecological, socioeconomic, and institutional knowledge and priorities through diverse stakeholder participation. In contrast to command and control approaches to natural resource management, which often lead to declines in ecological resilience, ecosystem management is a holistic, adaptive method for evaluating and achi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomalin
Glomalin is a hypothetical glycoprotein produced abundantly on hyphae and spores of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi in soil and in roots. Glomalin was proposed in 1996 by Sara F. Wright, a scientist at the USDA Agricultural Research Service, but it was not isolated and described yet. The name comes from Glomerales, an order of fungi. Most AM fungi are of the division Glomeromycota. An elusive substance, it is mostly assumed to have a glue-like effect on soil, but it has not been isolated yet. Definition and controversy The specific protein glomalin has not yet been isolated and described. What has been described is an extraction process involving heat and citrate, producing a mixture containing a substance that is reactive to a monoclonal antibody Mab32B11 raised against crushed AM fungi spores. The substance is then provisionally named "glomalin". As many laboratories do not have the equipment to perform an antibody-based isolation (ELISA), a crude mixture called glomalin-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance (ecology), abundance, biomass (ecology), biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; ecological succession, successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiology
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organ (biology), organs, cell (biology), cells, and biomolecules carry out chemistry, chemical and physics, physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into clinical physiology, medical physiology, Zoology#Physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysics, biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostasis, homeostatic control mechanisms, and cell signaling, communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathology, pathological state'' refers to abnormality (behavior), abnormal conditions, including human diseases. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigasporaceae
The Gigasporaceae are a family of fungi in the order Diversisporales. Species in this family are widespread in distribution, and form arbuscular mycorrhiza An arbuscular mycorrhiza (AM) (plural ''mycorrhizae'') is a type of mycorrhiza in which the symbiont fungus (''Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi'', or AMF) penetrates the cortical cells of the roots of a vascular plant forming arbuscules. Arbuscul ... in roots. A species under Gigasporaceae is ''Gigaspora gigantea''. The spores of ''G. gigantea'', found in specific sand dunes, commence in a healthy state of newly formed spores to dead and blackened in seven months through four identifiable steps: they begin as healthy greenish-yellow spores, turn into yellow with brown spots, then reddish-orange-brown, and ultimately dead. A cause of the symptoms of death in spores are soil organisms such as bacteria, protists, and microfauna. References Diversisporales Fungus families {{Glomeromycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |