|
Arboreal Locomotion
Arboreal locomotion is the animal locomotion, locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolution, evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally (scansorial), but others are exclusively arboreal. The habitats pose numerous mechanical challenges to animals moving through them and lead to a variety of anatomical, behavioral and ecological consequences as well as variations throughout different species.Matt Cartmill, Cartmill, M. (1985). "Climbing". pp. 73–88 ''In'': Hildebrand, Milton; Bramble, Dennis M.; species:Karel Frederik Liem, Liem, Karel F.; David B. Wake, Wake, David B. (editors) (1985). ''Functional Vertebrate Morphology''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, Belknap Press. 544 pp. . Furthermore, many of these same principles may be applied to climbing without trees, such as on rock piles or mountains. Some animals are exclusively arboreal in habitat, such as tree snails. Biomechanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
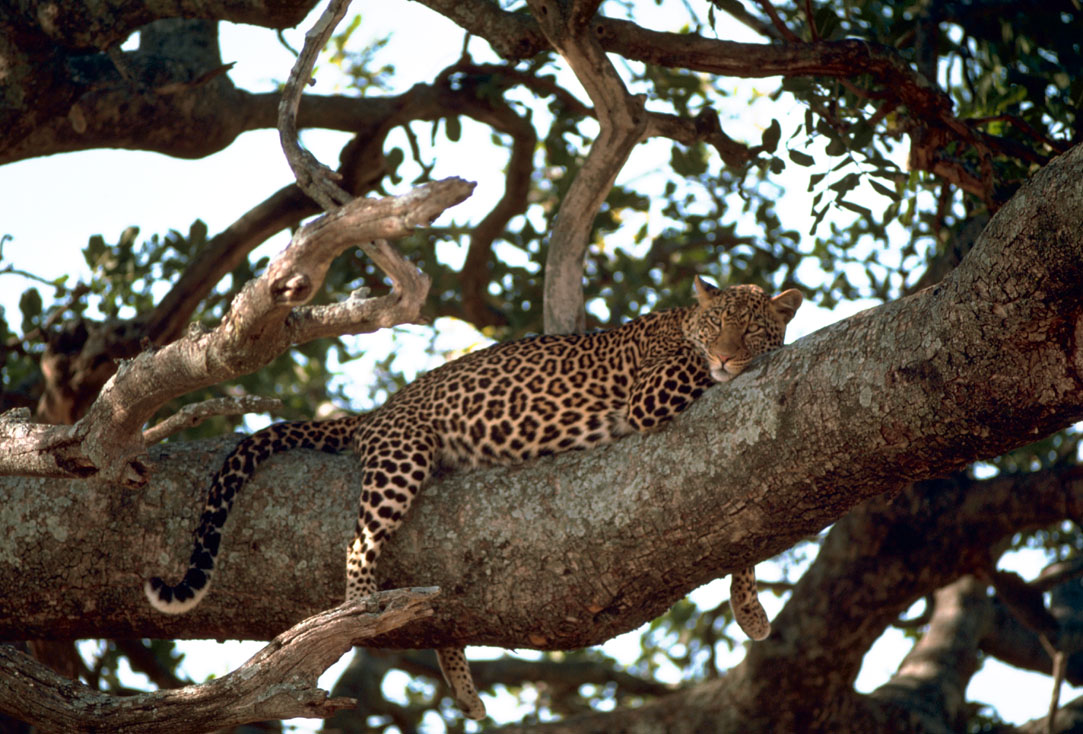
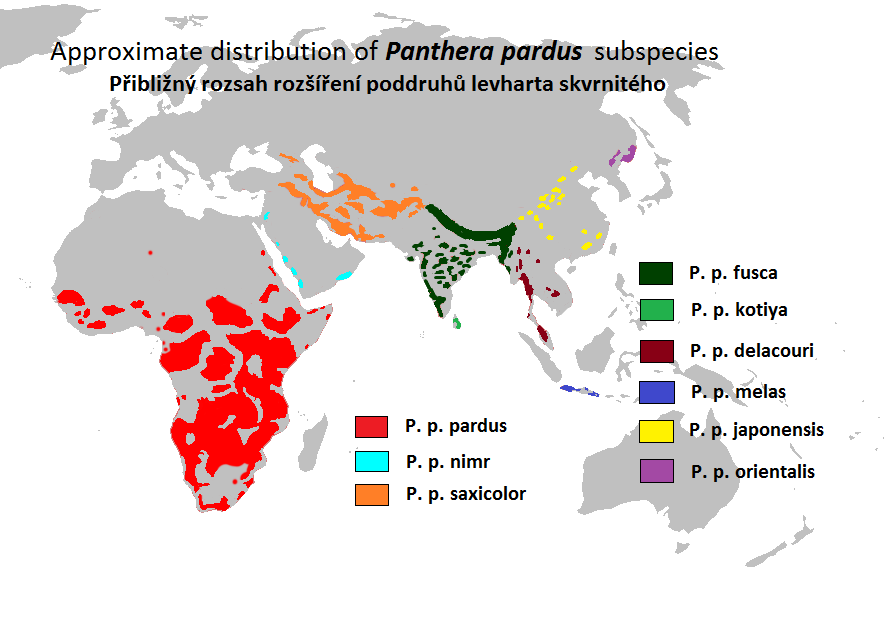
Leopard On The Tree
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the Genus (biology), genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in Rosette (zoology), rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a long tail and a shoulder height of . Males typically weigh , and females . The leopard was first Species description, described in 1758, and several subspecies were proposed in the 19th and 20th centuries. Today, eight subspecies are recognised in its wide range in Africa and Asia. It initially evolved in Africa during the Early Pleistocene, before migrating into Eurasia around the Early–Middle Pleistocene transition. European leopard, Leopards were formerly present across Europe, but became extinct in the region at around the end of the Late Pleistocene-early Holocene. The leopard is adapted to a variety of habitats ranging from rainforest to steppe, including Aridity, arid and montane areas. It is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Tree Python
The green tree python (''Morelia viridis''), is a species of snake in the family Pythonidae. The species is native to New Guinea, some islands in Indonesia, and the Cape York Peninsula in Australia. First described by Hermann Schlegel in 1872, it was known for many years as ''Chondropython viridis''. As its common name suggests, it is a bright green snake that can reach a total length (including tail) of and a weight of , with females slightly larger and heavier than males. Living generally in trees, the green tree python mainly hunts and eats small reptiles and mammals. It is a popular pet, and numbers in the wild have suffered with large-scale smuggling of wild-caught green tree pythons in Indonesia. Despite this, the green tree python is rated as least concern on the IUCN Red List of endangered species. Taxonomy German naturalist Hermann Schlegel described the green tree python in 1872 as ''Python viridis'', from two specimens collected in the Aru Islands of Indonesia. His co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Der Waals Force
In molecular physics and chemistry, the van der Waals force (sometimes van der Waals' force) is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and therefore more susceptible to disturbance. The van der Waals force quickly vanishes at longer distances between interacting molecules. Named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, the van der Waals force plays a fundamental role in fields as diverse as supramolecular chemistry, structural biology, polymer science, nanotechnology, surface science, and condensed matter physics. It also underlies many properties of organic compounds and molecular solids, including their solubility in polar and non-polar media. If no other force is present, the distance between atoms at which the force becomes repulsive rather than attractive as the atoms approach one another is called the van der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gecko
Geckos are small, mostly carnivorous lizards that have a wide distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. Belonging to the infraorder Gekkota, geckos are found in warm climates. They range from . Geckos are unique among lizards for their vocalisations, which differ from species to species. Most geckos in the family Gekkonidae use chirping or clicking sounds in their social interactions. Tokay geckos (''Gekko gecko'') are known for their loud mating calls, and some other species are capable of making hissing noises when alarmed or threatened. They are the most species-rich group of lizards, with about 1,500 different species worldwide. All geckos, except species in the family Eublepharidae lack eyelids; instead, the outer surface of the eyeball has a transparent membrane, the brille. They have a fixed lens within each iris that enlarges in darkness to let in more light. Since they cannot blink, species without eyelids generally lick their own brilles whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arboreal Salamander
The arboreal salamander (''Aneides lugubris'') is a species of climbing salamander. An insectivore, it is native to California and Baja California, where it is primarily associated with oak and sycamore woodlands, and thick chaparral. Description ''Aneides lugubris'' is SVL (snout-vent length), with plain purplish-brown coloring, usually spotted dorsally with gold or yellow, although it may also be unspotted. This salamander has longer and sharper teeth than many others within the order, Urodela. ''Aneides lugubris'' are insectivorous and have been found to eat beetles, caterpillars, sow bugs, ants, and centipedes. The tail is prehensile. The juvenile is dark overall, clouded with greyish color and fine yellow speckling on the back. The male of this species can be distinguished by its broad triangular head, with the front teeth of the jaw extending beyond the bottom lip. A large adult can inflict a painful bite. This species is an excellent climber and difficult to capture. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
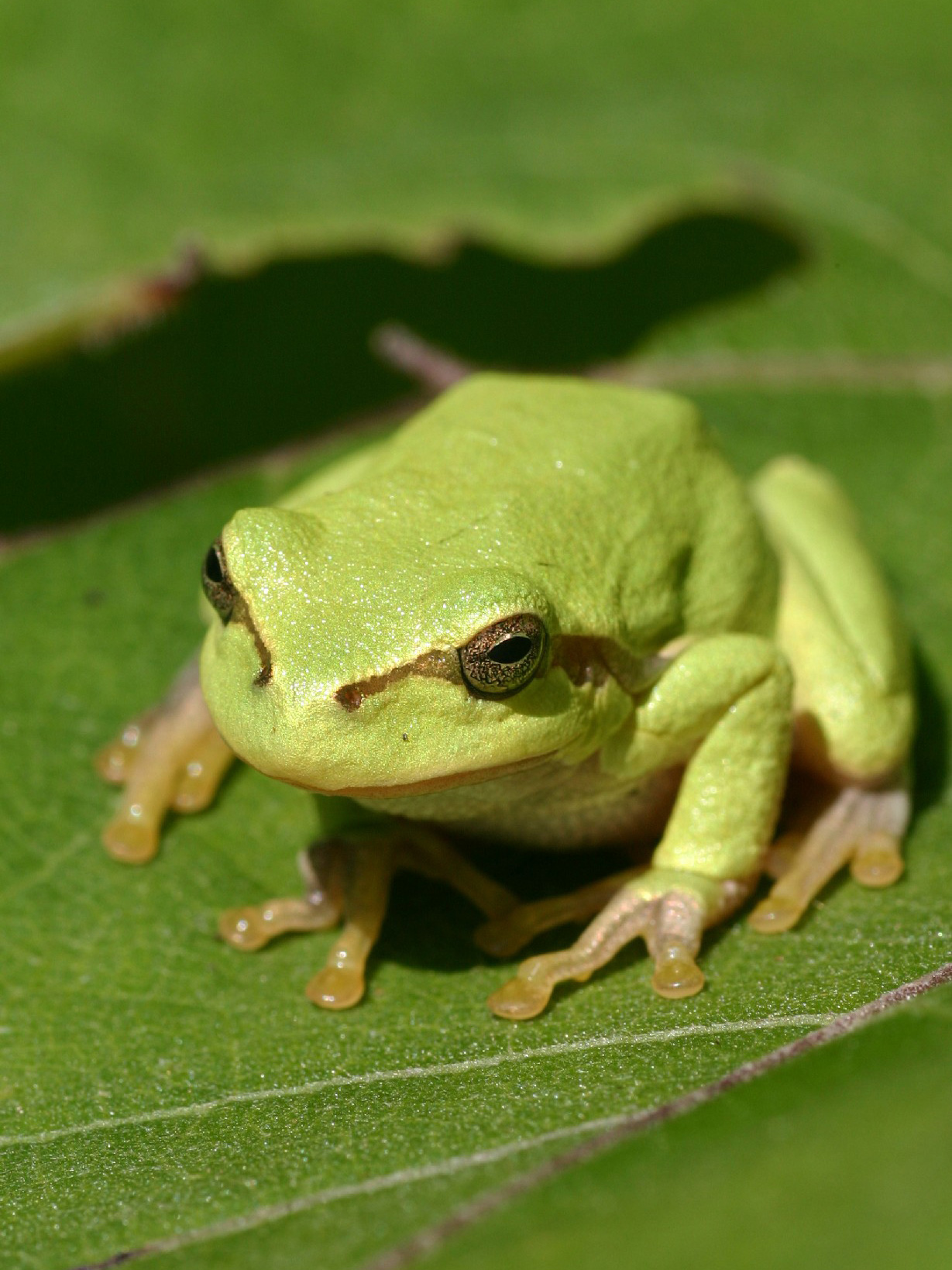
Tree Frog
A tree frog (or treefrog) is any species of frog that spends a major portion of its lifespan in trees, known as an arboreal state. Several lineages of frogs among the Neobatrachia suborder have given rise to treefrogs, although they are not closely related to each other. Millions of years of convergent evolution have resulted in very similar morphology even in species that are not very closely related. Furthermore, tree frogs in seasonally arid environments have adapted an extra-epidermal layer of lipid and mucus as an evolutionary convergent response to accommodate the periodic dehydration stress. Description As the name implies, these frogs are typically found in trees or other high-growing vegetation. They do not normally descend to the ground, except to mate and spawn, though some build foam nests on leaves and rarely leave the trees at all as adults, and '' Eleutherodactylus'' has evolved direct development and therefore does not need water for a tadpole stage. Tree fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae (), a family that includes small or medium-sized rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrels. Squirrels are indigenous to the Americas, Eurasia, and Africa, and were introduced by humans to Australia. The earliest known fossilized squirrels date from the Eocene epoch, and among other living rodent families, the squirrels are most closely related to the mountain beaver and dormice. Etymology The word ''squirrel'', first attested in 1327, comes from the Anglo-Norman which is from the Old French , the reflex of a Latin language">Latin word , which was taken from the Ancient Greek word (; from ) 'shadow-tailed', referring to the long bushy tail which many of its members have. ''Sciurus'' is also the name of one of its genuses. The native Old English language, Old English word for the squirrel, , only survived into Middle Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
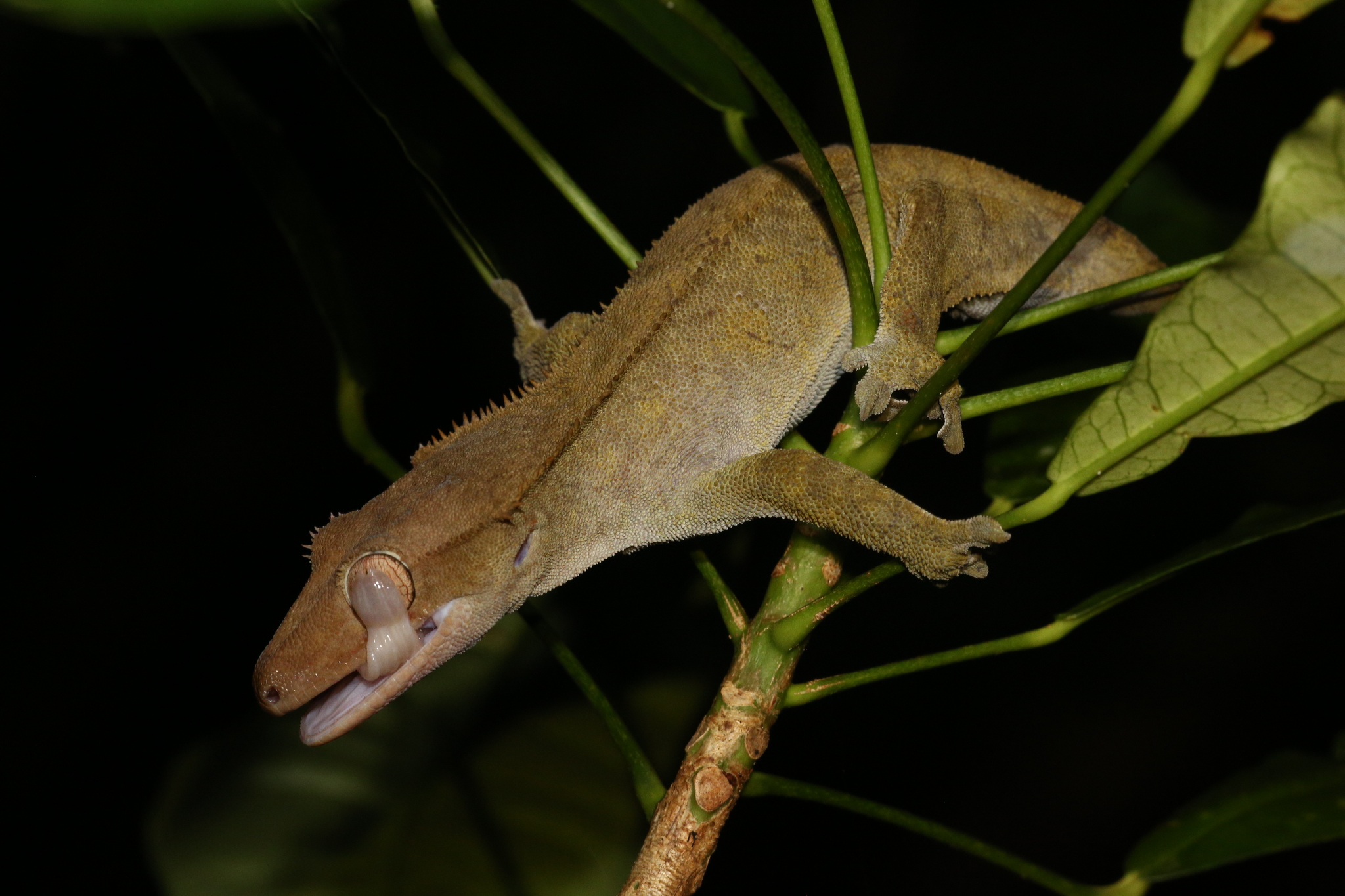
Crested Gecko
The crested gecko (''Correlophus ciliatus''), also known Common name, commonly as the eyelash gecko, is a species of lizard in the Family (biology), family Diplodactylidae. The species is native to southern New Caledonia. Originally species description, described in 1866 by French zoologist Alphonse Guichenot, the species was thought to be extinction, extinct until it was rediscovered in 1994 during an expedition led by German herpetologist species:Robert Seipp, Robert Seipp. (in German). Along with several other New Caledonian gecko species, it is being considered for protected status by the CITES, Convention on the International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Flora and Fauna. Taxonomy The species was first described in 1866 as ''Correlophus ciliatus'' by the Guichenot in an article entitled "''Notice sur un nouveau genre de sauriens de la famille des geckotiens du Muséum de Paris'' [Notice of a new genus of saurians of the gecko family from the Paris Museum]" in the ''Mém ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehensile Tail
A prehensile tail is the tail of an animal that has Adaptation (biology), adapted to grasp or hold objects. Fully Prehensility, prehensile tails can be used to hold and manipulate objects, and in particular to aid arboreal creatures in finding and eating food in the trees. If the tail cannot be used for this it is considered only partially prehensile; such tails are often used to anchor an animal's body to dangle from a branch, or as an aid for climbing. The term ''prehensile'' means "able to grasp" (from the Latin ''prehendere'', to take hold of, to grasp). Evolution One point of interest is the distribution of animals with prehensile tails. The prehensile tail is predominantly a New World adaptation, especially among mammals. Many more animals in South America have prehensile tails than in Africa and Southeast Asia. It has been argued that animals with prehensile tails are more common in South America because the forest there is denser than in Africa or Southeast Asia. In contra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
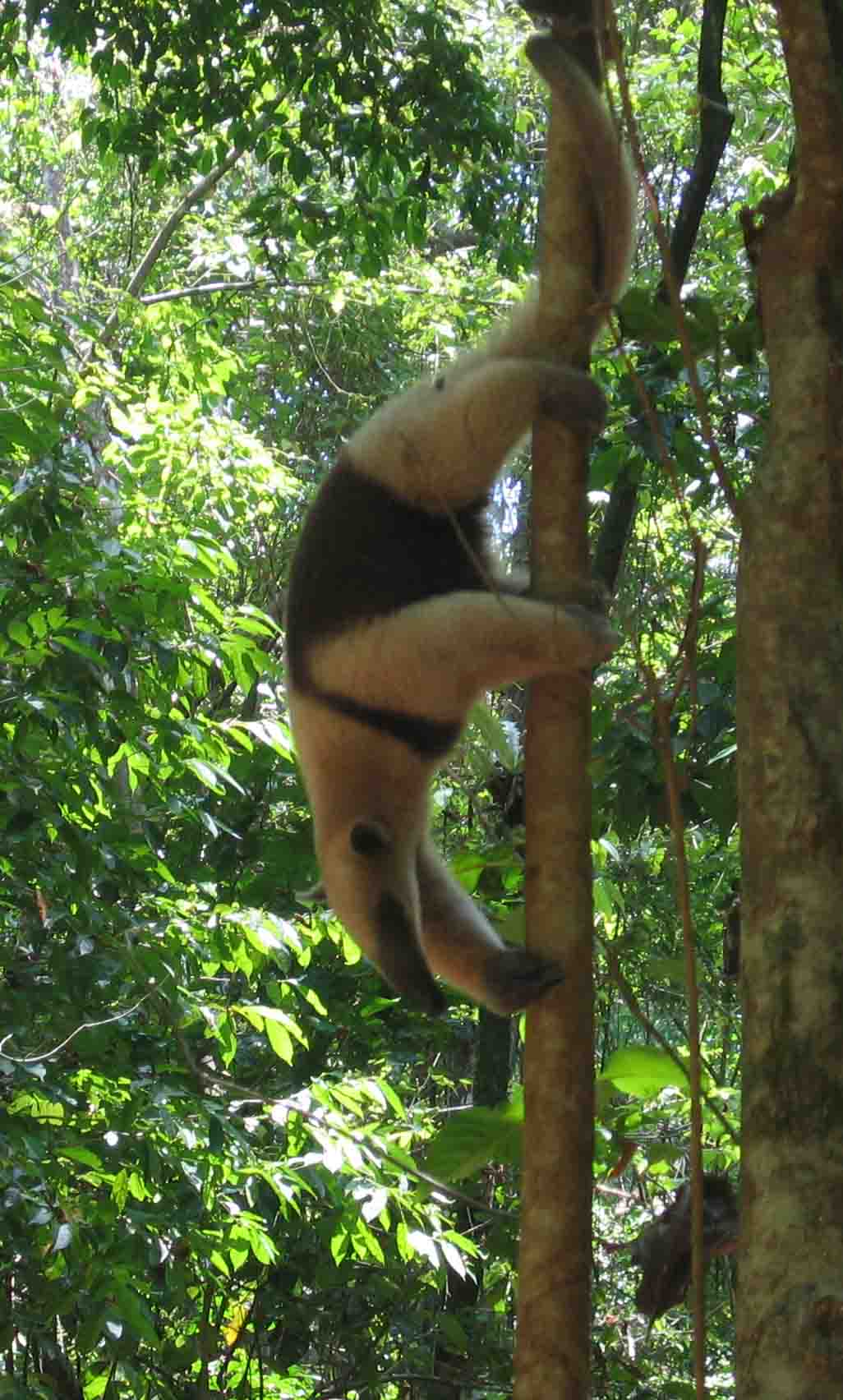
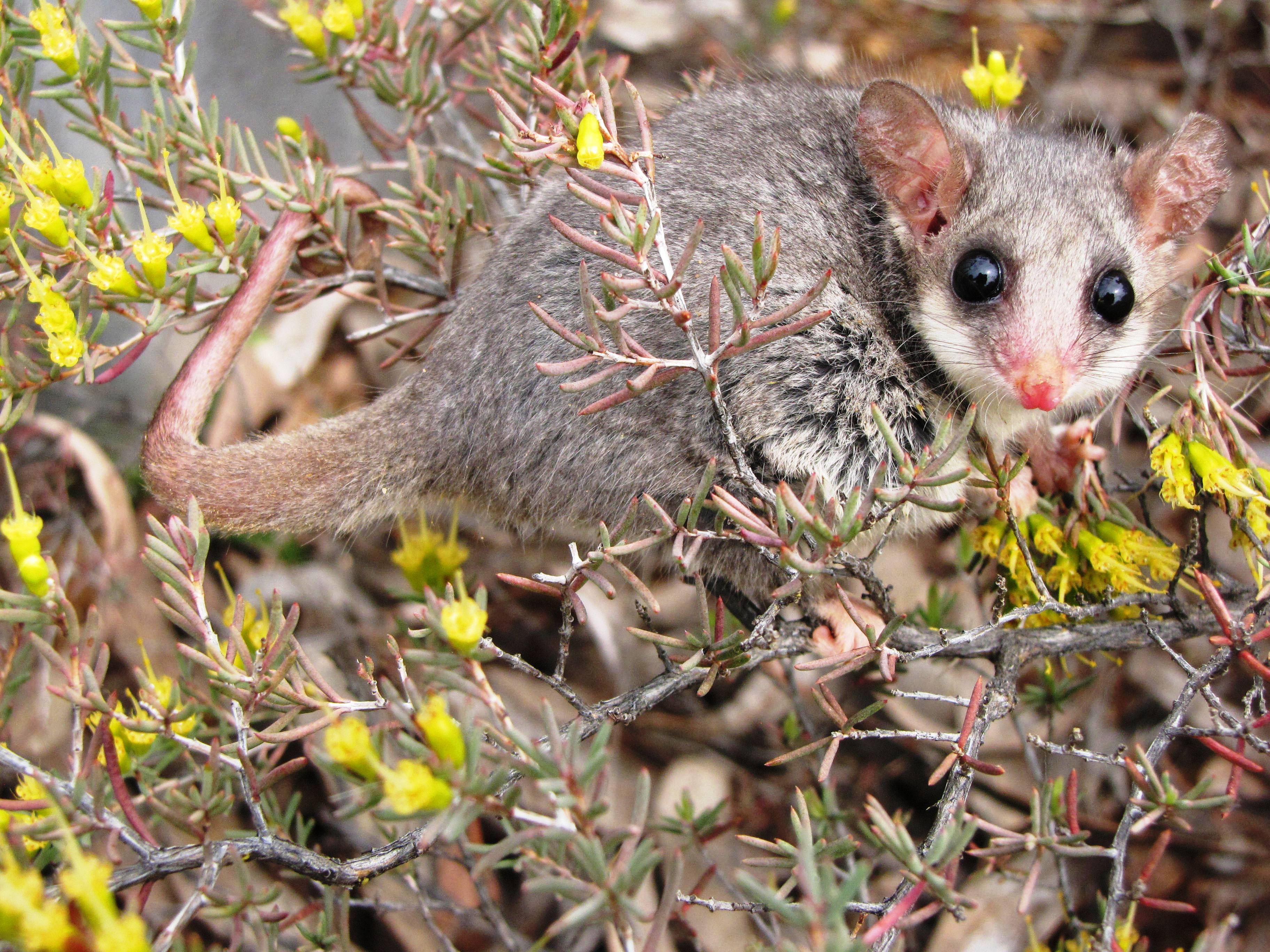
Phalangeriformes
Phalangeriformes is a paraphyletic suborder of about 70 species of small to medium-sized arboreal locomotion, arboreal marsupials native to Australia, New Guinea, and Sulawesi. The species are commonly known as possums, opossums, gliders, and cuscus. The common name "(o)possum" for various Phalangeriformes species derives from the creatures' resemblance to the opossums of the Americas (the term comes from Powhatan language ''aposoum'' "white animal", from proto-Algonquian language, Proto-Algonquian *''wa·p-aʔɬemwa'' "white dog"). However, although opossums are also marsupials, Australasian possums are more closely related to other Australidelphia, Australasian marsupials such as kangaroos. Phalangeriformes are quadrupedalism, quadrupedal Diprotodontia, diprotodont marsupials with long tails. The smallest species, indeed the smallest diprotodont marsupial, is the Tasmanian pygmy possum, with an adult head-body length of and a weight of . The largest are the two species of be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
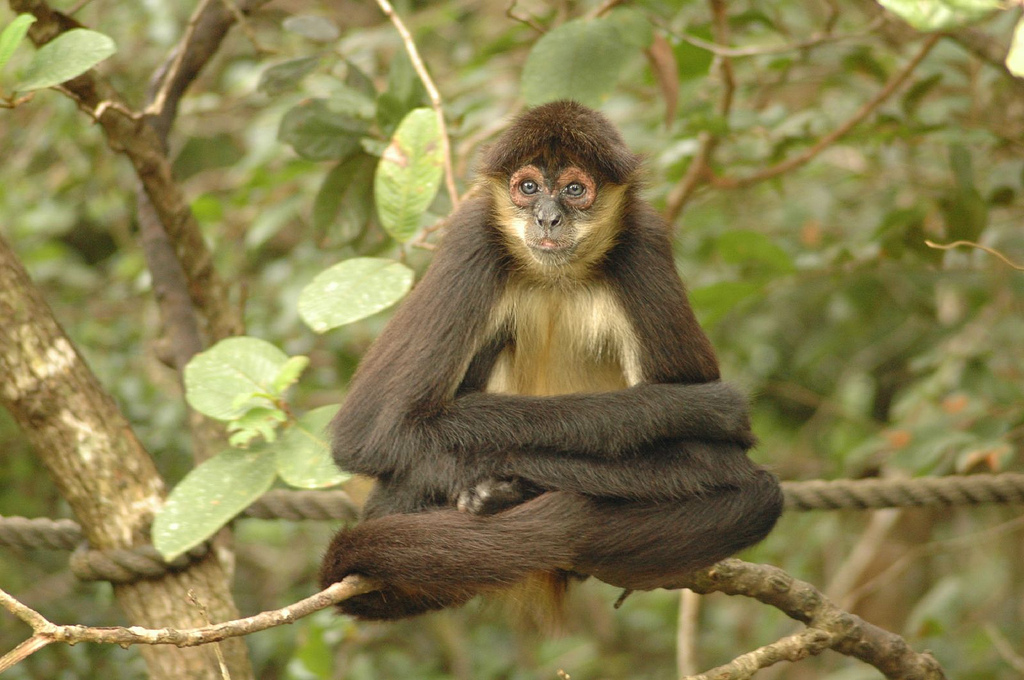
Spider Monkey
Spider monkeys are New World monkeys belonging to the genus ''Ateles'', part of the subfamily Atelinae, family Atelidae. Like other atelines, they are found in tropical forests of Central and South America, from southern Mexico to Brazil. The genus consists of seven species, all of which are under threat; the brown spider monkey is critically endangered. They are also notable for their ability to be easily Monkey breeding, bred in captivity. Disproportionately long limbs and long prehensile tails make them one of the largest New World monkeys and give rise to their common name. Spider monkeys live in the upper layers of the rainforest and forage in the high canopy, from . They primarily eat fruits, but will also occasionally consume leaves, flowers, and insects. Due to their large size, spider monkeys require large tracts of moist evergreen forests, and prefer undisturbed primary rainforest. They are social animals and live in bands of up to 35 individuals, but will split up to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |