|
Aphanizomenon Gracile
''Aphanizomenon'' is a genus of cyanobacteria that inhabits freshwater lakes and can cause dense blooms. They are unicellular organisms that consolidate into linear (non-branching) chains called trichomes. Parallel trichomes can then further unite into aggregates called rafts. Since Aphanizomenon is a genus in the cyanobacteria phylum. Bacteria in the Cyanobacteria phylum are known for using photosynthesis to create energy and therefore use sunlight as their energy source. Aphanizomenon bacteria also play a big role in the Nitrogen cycle since they can perform nitrogen fixation. Studies on the species ''Aphanizomenon flos-aquae'' have shown that it can regulate buoyancy through light-induced changes in turgor pressure. It is also able to move by means of gliding, though the specific mechanism by which this is possible is not yet known. Ecology Overcoming phosphate limitation ''Aphanizomenon'' may become dominant in a water body partially due to their ability to induce phosphate-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphanizomenon Flos-aquae
''Aphanizomenon flos-aquae'' is a brackish and freshwater species of cyanobacteria found around the world, including the Baltic Sea and the Great Lakes. Ecology ''Aphanizomenon flos-aquae'' can form dense surface aggregations in freshwater (known as "cyanobacterial blooms"). These blooms occur in areas of high nutrient loading, historical or current. Toxicity ''Aphanizomenon flos-aquae'' has both toxic and nontoxic forms. Most sources worldwide are toxic, containing both hepatic and neuro endotoxins. Most cyanobacteria (including ''Aphanizomenon'') produce BMAA, a neurotoxin amino acid implicated in ALS/ Parkinsonism. Toxicity of ''A. flos-aquae'' has been reported in Canada, Germany and China. ''Aphanizomenon flos-aquae'' is known to produce endotoxins, the toxic chemicals released when cells die. Once released ( lysed), and ingested, these toxins can damage liver and nerve tissues in mammals. In areas where water quality is not closely monitored, the World Health Org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
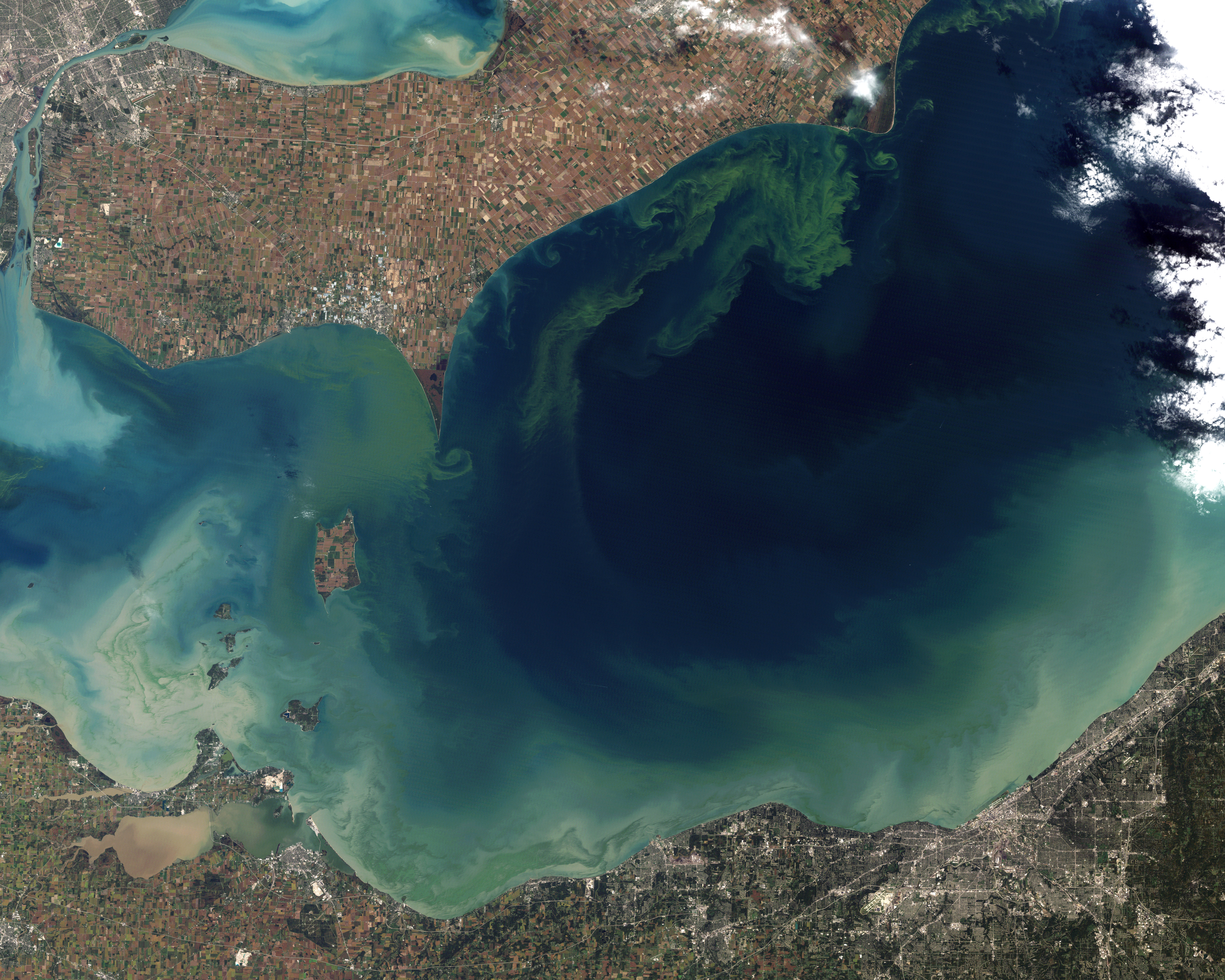
Algal Bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompasses many types of aquatic photosynthetic organisms, both macroscopic multicellular organisms like seaweed and microscopic unicellular organisms like cyanobacteria. ''Algal bloom'' commonly refers to the rapid growth of microscopic unicellular algae, not macroscopic algae. An example of a macroscopic algal bloom is a kelp forest. Algal blooms are the result of a nutrient, like nitrogen or phosphorus from various sources (for example fertilizer runoff or other forms of nutrient pollution), entering the aquatic system and causing excessive growth of algae. An algal bloom affects the whole ecosystem. Consequences range from the benign feeding of higher trophic levels to more harmful effects like blocking sunlight from reaching other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanotoxin
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they reproduce exponentially to form blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning. Some of the most powerful natural poisons known are cyanotoxins. They include potent neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and endotoxins. Despite the similarity in name, they are unrelated to cyanides. Exposure to cyanobacteria can result in gastro-intestinal and hayfever symptoms or pruritic skin rashes. Exposure to the cyanobacteria neurotoxin BMAA may be an environmental cause of neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxitoxin
Saxitoxin (STX) is a potent neurotoxin and the best-known paralytic shellfish toxin (PST). Ingestion of saxitoxin by humans, usually by consumption of shellfish contaminated by toxic algal blooms, is responsible for the illness known as paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP). The term saxitoxin originates from the genus name of the butter clam ('' Saxidomus'') from which it was first isolated. But the term saxitoxin can also refer to the entire suite of more than 50 structurally related neurotoxins (known collectively as "saxitoxins") produced by protists, algae and cyanobacteria which includes saxitoxin itself (STX), neosaxitoxin (NSTX), gonyautoxins (GTX) and decarbamoylsaxitoxin (dcSTX). Saxitoxin has a large environmental and economic impact, as its presence in bivalve shellfish such as mussels, clams, oysters and scallops frequently leads to bans on commercial and recreational shellfish harvesting in many temperate coastal waters around the world including the Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatoxin (other) , a neurotoxin produced by cyanobacteria
{{disambig ...
Anatoxin may refer to: * Toxoid, a bacterial toxin (usually an exotoxin) whose toxicity has been weakened or suppressed * Anatoxin-a, a neurotoxin produced by cyanobacteria * Anatoxin-a(S) Guanitoxin (GNT), formerly known as anatoxin-a(S) "Salivary", is a naturally occurring cyanotoxin commonly isolated from cyanobacteria (specifically of the genus ''Anabaena'') and causes excess salivation in mammals via inhibition of acetylcholin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
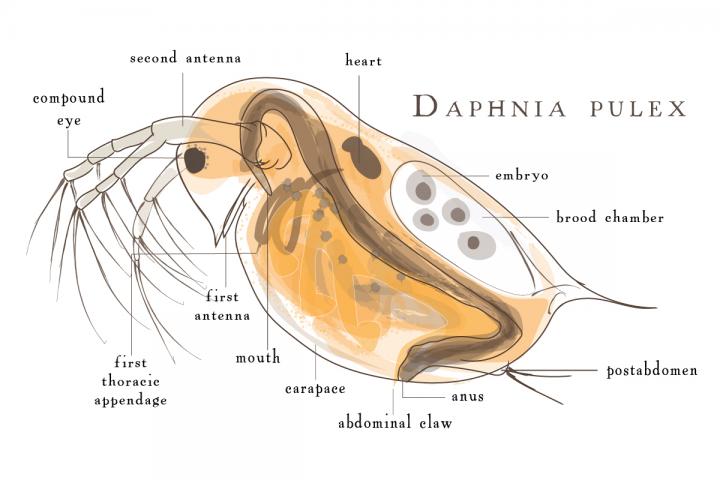
Daphnia
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are '' D. pulex'' (small and most common) and '' D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: '' Moina'', which is in the Moinidae family instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into segments, although this division is not visible. The head is fused, and is generally bent down towards the body with a visible notch separating the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphanizomenon Bloom Upper Klamath Lake USGS
''Aphanizomenon'' is a genus of cyanobacteria that inhabits freshwater lakes and can cause dense blooms. They are unicellular organisms that consolidate into linear (non-branching) chains called trichomes. Parallel trichomes can then further unite into aggregates called rafts. Since Aphanizomenon is a genus in the cyanobacteria phylum. Bacteria in the Cyanobacteria phylum are known for using photosynthesis to create energy and therefore use sunlight as their energy source. Aphanizomenon bacteria also play a big role in the Nitrogen cycle since they can perform nitrogen fixation. Studies on the species ''Aphanizomenon flos-aquae'' have shown that it can regulate buoyancy through light-induced changes in turgor pressure. It is also able to move by means of gliding, though the specific mechanism by which this is possible is not yet known. Ecology Overcoming phosphate limitation ''Aphanizomenon'' may become dominant in a water body partially due to their ability to induce phosphate-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US EPA
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an Independent agencies of the United States government, independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on December 2, 1970, after Nixon signed an executive order. The Reorganization Plan No. 3, order establishing the EPA was ratified by committee hearings in the House and Senate. The agency is led by its Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency, administrator, who is appointed by the President of the United States, president and approved by the United States Senate, Senate. The current administrator is Michael S. Regan. The EPA is not a Cabinet of the United States, Cabinet department, but the administrator is normally given Cabinet of the United States#Cabinet-level officials, cabinet rank. The EPA has its headquarters in Washington, D.C., regional offices for ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMAA
β-Methylamino--alanine, or BMAA, is a non-proteinogenic amino acid produced by cyanobacteria. BMAA is a neurotoxin and its potential role in various neurodegenerative disorders is the subject of scientific research. Structure and properties BMAA is a derivative of the amino acid alanine with a methylamino group on the side chain. This non-proteinogenic amino acid is classified as a polar base. Sources and detection BMAA is produced by cyanobacteria in marine, freshwater, and terrestrial environments. In cultured non-nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria, BMAA production increases in a nitrogen-depleted medium. The biosynthetic pathway in cyanobacteria is unknown, but involvement of BMAA and its structural analog 2,4-diaminobutanoic acid (2,4-DAB) in envioronmental iron scavenging has been hypothesized. BMAA has been found in aquatic organisms and in plants with cyanobacterial symbionts such as certain lichens, the floating fern '' Azolla'', the leaf petioles of the tropica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxitoxin
Saxitoxin (STX) is a potent neurotoxin and the best-known paralytic shellfish toxin (PST). Ingestion of saxitoxin by humans, usually by consumption of shellfish contaminated by toxic algal blooms, is responsible for the illness known as paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP). The term saxitoxin originates from the genus name of the butter clam ('' Saxidomus'') from which it was first isolated. But the term saxitoxin can also refer to the entire suite of more than 50 structurally related neurotoxins (known collectively as "saxitoxins") produced by protists, algae and cyanobacteria which includes saxitoxin itself (STX), neosaxitoxin (NSTX), gonyautoxins (GTX) and decarbamoylsaxitoxin (dcSTX). Saxitoxin has a large environmental and economic impact, as its presence in bivalve shellfish such as mussels, clams, oysters and scallops frequently leads to bans on commercial and recreational shellfish harvesting in many temperate coastal waters around the world including the Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatoxin-a
Anatoxin-a, also known as Very Fast Death Factor (VFDF), is a secondary, bicyclic amine alkaloid and cyanotoxin with acute neurotoxicity. It was first discovered in the early 1960s in Canada, and was isolated in 1972. The toxin is produced by multiple genera of cyanobacteria and has been reported in North America, South America, Central America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. Symptoms of anatoxin-a toxicity include loss of coordination, muscular fasciculations, convulsions and death by respiratory paralysis. Its mode of action is through the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAchR) where it mimics the binding of the receptor's natural ligand, acetylcholine. As such, anatoxin-a has been used for medicinal purposes to investigate diseases characterized by low acetylcholine levels. Due to its high toxicity and potential presence in drinking water, anatoxin-a poses a threat to animals, including humans. While methods for detection and water treatment exist, scientists have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O-antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Today, the term ''endotoxin'' is often used synonymously with LPS, although there are a few endotoxins (in the original sense of toxins that are inside the bacterial cell that are released when the cell disintegrates) that are not related to LPS, such as the so-called delta endotoxin proteins produced by '' Bacillus thuringiensis''. Lipopolysaccharides can have substantial impacts on human health, primarily through interactions with the immune system. LPS is a potent activator of the immune system and pyrogen (agent that causes fever). In severe cases, LPS can play a role in causing septic shock. In lower levels and over a longer time period, there is evidence LPS may play an important and harmful ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |