|
Antigua Guatemala
Antigua Guatemala (), commonly known as Antigua or La Antigua, is a city in the Guatemalan Highlands, central highlands of Guatemala. The city was the capital of the Captaincy General of Guatemala from 1543 through 1773, with much of its Baroque-influenced architecture and layout dating from that period. These characteristics had it designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979. Antigua Guatemala serves as the capital of the homonymous municipality and the Sacatepéquez Department. Population The city had a peak population of some 65,000 in the 1770s; the bulk of the population moved away in the late 18th century after the 1773 Guatemala earthquake. Despite significant population growth in the late 20th century, the city had only reached half that number by the 1990s. At the time of the 2007 census, the city had 34,685 inhabitants. History ''Antigua Guatemala'' means "Old Guatemala" and was the third capital of Guatemala, formerly called "Santiago de los Caballeros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arco De Santa Catalina
The Santa Catalina Arch is one of the distinguishable landmarks in Antigua Guatemala, Guatemala, located on 5th Avenue North. Built in the 17th century, it originally connected the Santa Catalina convent to a school, allowing the cloistered nuns to pass from one building to the other without going out on the street. A clock on top was added in the era of the Central American Federation, in the 1830s. The Guatemala Post Office Building in Guatemala City is based upon the arch. References arches and vaults buildings and structures in Antigua Guatemala {{Guatemala-struct-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Belize
Belize is a country on the north-eastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a maritime boundary with Honduras to the southeast. Part of the Caribbean region, Belize is a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Commonwealth Caribbean, the historical British West Indies. The Maya civilization spread into the area of Belize between 1500 BCE and 300 CE and flourished until about 1200. European contact began in 1502–04 when Christopher Columbus sailed along the Gulf of Honduras. European exploration was begun by English settlers in 1638. Spanish Empire, Spain and Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain both laid claim to the land until Britain defeated the Spanish in the Battle of St. George's Caye (1798). It became British Honduras, a British colony in 1840, and a Crown colony in 1862. Belize achieved its independence from the United Kingdom on 21 September ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and largest city is Tuxtla Gutiérrez. Other important population centers in Chiapas include Ocosingo, Tapachula, San Cristóbal de las Casas, Comitán, and Arriaga, Chiapas, Arriaga. Chiapas is the southernmost state in Mexico, and it borders the states of Oaxaca to the west, Veracruz to the northwest, and Tabasco to the north, and the Petén Department, Petén, Quiché Department, Quiché, Huehuetenango Department, Huehuetenango, and San Marcos Department, San Marcos departments of Guatemala to the east and southeast. Chiapas has a significant coastline on the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. In general, Chiapas has a humid, tropical climate. In the northern area bordering Tabasco, near Teapa Municipality, Teapa, rainfall can average more than pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Central America
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually defined as consisting of seven countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. Within Central America is the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot, which extends from southern Mexico to southeastern Panama. Due to the presence of several active geologic faults and the Central America Volcanic Arc, there is a high amount of seismic activity in the region, such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes, which has resulted in death, injury, and property damage. Most of Central America falls under the Isthmo-Colombian cultural area. Before the Spanish expedition of Christopher Columbus' voyages to the Americas, hundreds of indigenous peoples made their homes in the area. From the year 1502 onwards, Spain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Volcán De Agua
Volcán de Agua (also known as Junajpú by Maya) is an extinct stratovolcano located in the departments of Sacatepéquez and Escuintla in Guatemala. At , Agua Volcano towers more than above the Pacific coastal plain to the south and above the Guatemalan Highlands to the north. It dominates the local landscape except when hidden by cloud cover. The volcano is within of the city of Antigua Guatemala and several other large towns situated on its northern apron. These towns have a combined population of nearly 100,000. It is within about of Escuintla (population, ) to the south. Coffee is grown on the volcano's lower slopes. Brief description and history The local Kaqchikel people have always called the volcano Hunapú "place of flowers" or Jun Ajpu' "one hunter" (The calendar date for the sacred site; a typical method for naming sacred sites in Mayan cosmovision) in current Kaqchikel orthography. The Spanish conquistadors also called it Hunapú until a lahar from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lahar
A lahar (, from ) is a violent type of mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of Pyroclastic rock, pyroclastic material, rocky debris and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along a valley, river valley. Lahars are often extremely destructive and deadly; they can flow tens of metres per second, they have been known to be up to deep, and large flows tend to destroy any structures in their path. Notable lahars include those at Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines and Nevado del Ruiz in Colombia, the latter of which killed more than 20,000 people in the Armero tragedy. Etymology The word ''lahar'' is of Javanese language, Javanese origin. Berend George Escher introduced it as a geological term in 1922. Description The word ''lahar'' is a general term for a flowing mixture of water and pyroclastic debris. It does not refer to a particular rheology or sediment concentration. Lahars can occur as normal stream flows (sediment concentration of less than 30%), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ciudad Vieja
Ciudad Vieja () is a town and municipality in the Guatemalan Departments of Guatemala, department of Sacatepéquez. According to the 2018 census, the town has a population of 32,802 Population of cities & towns in Guatemala and the municipality a population of 33,405. Ciudad Vieja was the second site of Santiago de los Caballeros de Guatemala, the colonial capital of the country. San Miguel Escobar is the modern name for the district that contains the ruins of the second colonial capital of the Guatemala region. The Spaniards founded their capital here in 1527, after their previous capital at Tecpán Guatemala became untenable. The city was destroyed by a catastrophic lahar from Volcan de Agua in 1541, and the survivors had no choice but to abandon the site. Among the casualties was the governor Beatriz de la Cueva. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
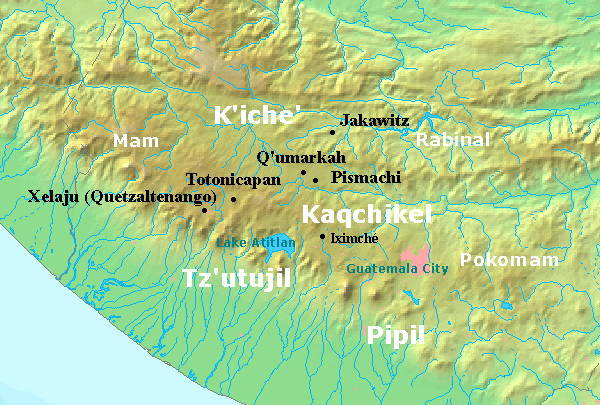
Kaqchikel People
The Kaqchikel (also called Kachiquel) are one of the Indigenous Maya peoples of the midwestern highlands of Guatemala and of southern Mexico. They constitute Guatemala's third largest Maya group. The name was formerly spelled in various other ways, including Cakchiquel, Kakchiquel, Caqchikel, and Cachiquel. Language The Kaqchikel language, one of the Mayan languages from the Quichean branch, is spoken today by 400,000 people. It is closely related to the Tzutujil language. Location In Guatemala they live in the departments of Sololá, Chimaltenango, Sacatepéquez, Guatemala, Baja Verapaz Department, and Escuintla. In Mexico, the Kaqchikel communities are located in the state of Chiapas, in the municipalities of Amatenango de la Frontera, Mazapa de Madero, Motozintla, Frontera Comalapa, El Porvenir and Villa Comatitlan, due to recent migrations, there are small Kaqchikel communities in the state of Campeche located in the municipalities of Campeche and Champotón ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
James, Son Of Zebedee
James the Great ( Koinē Greek: Ἰάκωβος, romanized: ''Iákōbos''; Aramaic: ܝܥܩܘܒ, romanized: ''Yaʿqōḇ''; died AD 44) was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus. According to the New Testament, he was the second of the apostles to die after Judas Iscariot and the first to be martyred. Saint James is the patron saint of Spain and, according to tradition, what are believed to be his remains are held in Santiago de Compostela in Galicia. He is also known as James, son of Zebedee, Saint James the Great, Saint James the Greater, St. James Son of Thunder, St. James the Major, Saint James the Elder, or Saint Jacob, James the Apostle or Santiago. In the New Testament James was born into a family of Jewish fishermen on the Sea of Galilee. His parents were Zebedee and Salome. Salome was a sister of Mary (mother of Jesus) which made James the Great a cousin of Jesus. James is styled "the Greater" to distinguish him from the Apostle James "the Less," with "greater" me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Santiago De Los Caballeros De Guatemala
Santiago de los Caballeros de Guatemala ("St. James of the Knights of Guatemala") was the name given to the capital city of the Spanish colonial Captaincy General of Guatemala in Central America. It is located in present-day Antigua Guatemala. History ;Quauhtemallan — Guatemala :The name was first associated with the Kaqchikel Maya capital Iximche, adopted as the Spanish capital soon after the Spanish conquest of Guatemala began in July 1524. The Kaqchikel capital was called Guatemala by the Spanish, with its origin in the Nahuatl word ''Quauhtemallan'', which means "forested land". The Spanish took the name of the city used by their Nahuatl-speaking Mexican allies and applied it to the new Spanish city and, by extension, to the Captaincy General of Guatemala. From this comes the contemporary name of the country, Guatemala. The day of the city's foundation was 25 July, which is the feast day of St. James, hence the full name of the city.Turismo Cultural. ;Almolonga — Ciuda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iximche
Iximcheʼ () (or Iximché using Spanish orthography) is a Pre-Columbian Mesoamerican archaeological site in the western highlands of Guatemala. Iximche was the capital of the Late Postclassic Kaqchikel Maya kingdom from 1470 until its abandonment in 1524. The architecture of the site included a number of pyramid-temples, palaces and two Mesoamerican ballcourts. Excavators uncovered the poorly preserved remains of painted murals on some of the buildings and ample evidence of human sacrifice. The ruins of Iximche were declared a Guatemalan National Monument in the 1960s.Centro de Acción Legal - Ambiental y Social de Guatemala (CALAS). The site has a small museum displaying a number of pieces found there, including sculptures and ceramics. It is open daily. For many years the Kaqchikel served as loyal allies of the Kʼicheʼ Maya.Schele & Mathews 1999, p.295. The growing power of the Kaqchikel within the alliance eventually caused such friction that the Kaqchikel were forced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |