|
Anisotropy
Anisotropy () is the structural property of non-uniformity in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. An anisotropic object or pattern has properties that differ according to direction of measurement. For example, many materials exhibit very different physical or mechanical properties when measured along different axes, e.g. absorbance, refractive index, conductivity, and tensile strength. An example of anisotropy is light coming through a polarizer. Another is wood, which is easier to split along its grain than across it because of the directional non-uniformity of the grain (the grain is the same in one direction, not all directions). Fields of interest Computer graphics In the field of computer graphics, an anisotropic surface changes in appearance as it rotates about its geometric normal, as is the case with velvet. Anisotropic filtering (AF) is a method of enhancing the image quality of textures on surfaces that are far away and viewed at a shallow angle. Older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope detects a faint background glow that is almost isotropic, uniform and is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other astronomical object, object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The accidental Discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation, discovery of the CMB in 1965 by American radio astronomers Arno Allan Penzias and Robert Woodrow Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s. The CMB is landmark evidence of the Big Bang scientific theory, theory for the origin of the universe. In the Big Bang cosmological models, during the earliest periods, the universe was filled with an Opacity (optics), opaque fog of dense, hot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
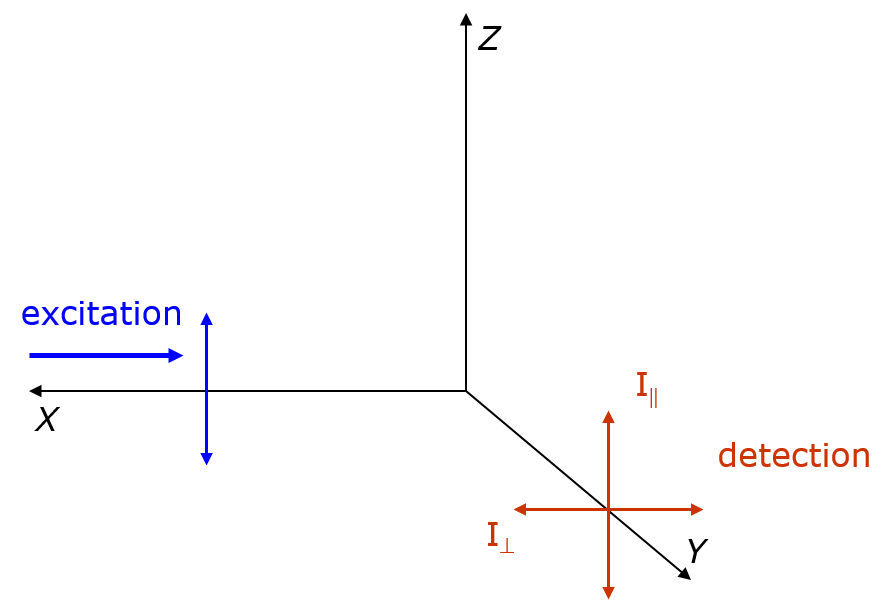
Fluorescence Anisotropy
Fluorescence anisotropy or fluorescence polarization is the phenomenon where the light emitted by a fluorophore has unequal intensities along different axes of polarization. Early pioneers in the field include Aleksander Jablonski, Gregorio Weber, and Andreas Albrecht. The principles of fluorescence polarization and some applications of the method are presented in Lakowicz's book.Lakowicz, J.R., 2006. ''Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy'' (3rd ed., Springer. Chapter 10-12 deal with fluorescence polarization spectroscopy.) Definition of fluorescence anisotropy The anisotropy (r) of a light source is defined as the ratio of the polarized component to the total intensity (I_T): :r=\frac When the excitation is polarized along the z-axis, emission from the fluorophore is symmetric around the z-axis(Figure). Hence statistically we have I_x=I_y. As I_y=I_, and I_z=I_, we have :r=\frac=\frac. Principle – Brownian motion and photoselection In fluorescence, a molecule absorbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisotropic Filtering
In 3D computer graphics, anisotropic filtering (AF) is a technique that improves the appearance of Texture filtering, textures, especially on surfaces viewed at sharp Viewing angle, angles. It helps make textures look sharper and more detailed by reducing blur and aliasing that can occur when surfaces are angled away from the viewer. Anisotropy, Anisotropic filtering works by applying different amounts of filtering in different directions, unlike simpler methods like Bilinear filtering, bilinear and trilinear filtering which filter equally in all directions. While it requires more processing power than these simpler methods, anisotropic filtering became a standard feature in most graphics cards in the late 1990s and is now commonly used in games and other 3D applications, often with user-adjustable settings. Comparison to isotropic algorithms Anisotropic filtering enhances texture sharpness, counteracting the blur introduced by mipmapping, a common Anti-aliasing filter, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birefringence
Birefringence, also called double refraction, is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are described as birefringent or birefractive. The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress. Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in Iceland spar (calcite) crystals which have one of the strongest birefringences. In the 19th century Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotropy
In physics and geometry, isotropy () is uniformity in all orientations. Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix ' or ', hence ''anisotropy''. ''Anisotropy'' is also used to describe situations where properties vary systematically, dependent on direction. Isotropic radiation has the same intensity regardless of the direction of measurement, and an isotropic field exerts the same action regardless of how the test particle is oriented. Mathematics Within mathematics, ''isotropy'' has a few different meanings: ; Isotropic manifolds: A manifold is isotropic if the geometry on the manifold is the same regardless of direction. A similar concept is homogeneity. ; Isotropic quadratic form: A quadratic form ''q'' is said to be isotropic if there is a non-zero vector ''v'' such that ; such a ''v'' is an isotropic vector or null vector. In complex geometry, a line through the origin in the direction of an is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (physics)
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string, for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WMAP 2010
The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), originally known as the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP and Explorer 80), was a NASA spacecraft operating from 2001 to 2010 which measured temperature differences across the sky in the cosmic microwave background (CMB) – the radiant heat remaining from the Big Bang. Headed by Professor Charles L. Bennett of Johns Hopkins University, the mission was developed in a joint partnership between the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and Princeton University. The WMAP spacecraft was launched on 30 June 2001 from Florida. The WMAP mission succeeded the COBE space mission and was the second medium-class (MIDEX) spacecraft in the NASA Explorer program. In 2003, MAP was renamed WMAP in honor of cosmologist David Todd Wilkinson (1935–2002), who had been a member of the mission's science team. After nine years of operations, WMAP was switched off in 2010, following the launch of the more advanced Planck spacecraft by European Space Agenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Materials Properties
A material property is an intensive property of a material, i.e., a physical property or chemical property that does not depend on the amount of the material. These quantitative properties may be used as a metric by which the benefits of one material versus another can be compared, thereby aiding in materials selection. A property having a fixed value for a given material or substance is called material constant or constant of matter. (Material constants should not be confused with physical constants, that have a universal character.) A material property may also be a function of one or more independent variables, such as temperature. Materials properties often vary to some degree according to the direction in the material in which they are measured, a condition referred to as anisotropy. Materials properties that relate to different physical phenomena often behave linearly (or approximately so) in a given operating range . Modeling them as linear functions can significan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere, such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree, it performs a mechanical-support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients among the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, woodchips, or fibers. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Property
A physical property is any property of a physical system that is measurable. The changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its changes between momentary states. A quantifiable physical property is called ''physical quantity''. Measurable physical quantities are often referred to as '' observables''. Some physical properties are qualitative, such as shininess, brittleness, etc.; some general qualitative properties admit more specific related quantitative properties, such as in opacity, hardness, ductility, viscosity, etc. Physical properties are often characterized as intensive and extensive properties. An intensive property does not depend on the size or extent of the system, nor on the amount of matter in the object, while an extensive property shows an additive relationship. These classifications are in general only valid in cases when smaller subdivisions of the sample do not interact in some physical or chemical process when combined. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Resistivity And Conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called volume resistivity or specific electrical resistance) is a fundamental specific property of a material that measures its electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows electric current. Resistivity is commonly represented by the Greek alphabet, Greek letter (Rho (letter), rho). The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm-metre (Ω⋅m). For example, if a solid cube of material has sheet contacts on two opposite faces, and the Electrical resistance, resistance between these contacts is , then the resistivity of the material is . Electrical conductivity (or specific conductance) is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. It represents a material's ability to conduct electric current. It is commonly signified by the Greek letter (Sigma (letter), sigma), but (kappa) (especially in electrical engineering) and (gamma) are sometimes used. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refraction, refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflectivity, reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |