|
Altrincham Interchange
Altrincham Interchange is a transport hub in Altrincham, Greater Manchester, England, owned and managed by the Bee Network. It consists of a bus station on Stamford New Road, a Northern Trains-operated heavy rail station on the Mid-Cheshire Line, and a light rail stop which forms the terminus of Manchester Metrolink's Altrincham line. The original heavy rail element of the station was opened by the Manchester, South Junction and Altrincham Railway as Altrincham and Bowdon railway station in April 1881, changing to Altrincham railway station in May 1974. The Metrolink element opened in June 1992. The Interchange underwent a complete redevelopment, at a cost of £19 million, starting in mid-July 2013. The new, redeveloped interchanged opened on 7 December 2014. The interchange joined the Bee Network on 5 January 2025, who operate the local buses and the Manchester Metrolink, Metrolink trams from the interchange. The trains running through Altrincham will join the Bee Network by 2030 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altrincham
Altrincham ( , locally ) is a market town in Trafford, Greater Manchester, England, south of the River Mersey. It is southwest of Manchester, southwest of Sale, Greater Manchester, Sale and east of Warrington. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the built up area had a population of 49,680. It lies within the Historic counties of England, historic county boundaries of Cheshire, and became part of Greater Manchester in 1974. Altrincham developed as a market town following the right to hold a market being granted in 1290; the market continues today. Further socioeconomic development came with the extension of the Bridgewater Canal to Altrincham in 1765 and the arrival of the railway in 1849, stimulating industrial activity in the town. Outlying villages were absorbed by Altrincham's subsequent growth, along with the grounds of Dunham Massey Hall, formerly the home of the Earl of Stamford, and now a tourist attraction with three Grade I Listed Buildings and a deer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altrincham Line
The Altrincham Line is a tram line of the Manchester Metrolink running from Manchester to Altrincham in Greater Manchester. Originally a railway line, it was, along with the Bury Line, converted into a tramway during 1991–92, as part of the first phase of the Metrolink system. Route The line runs south-west from Manchester city centre, rising from a ramp which takes the tracks onto the streets of central Manchester, just east of stop, and then runs along a former railway viaduct, parallel to the heavy rail Manchester to Warrington and Liverpool line as far as ; just west of which the Eccles Line diverges to the north-west, and the Altrincham line runs south-west under the railway through an underpass. Cornbook stop was opened in 1999 as an interchange stop between the Altrincham and Eccles lines. The line then runs south-west along the former MSJ&AR line, and connects the towns of Stretford and Sale before running to Altrincham. The line uses old railway lines converted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 ( 11 & 12 Geo. 5. c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an act of Parliament enacted by the British government, and was intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four large companies, dubbed the " Big Four". The system of the "Big Four" lasted until the nationalization of the railways in 1947. During World War I, the British government took control, although not ownership, of British railways. The intention was to reduce inefficient internal competition between railway companies, and retain some of the benefits which the country had derived from a government-controlled railway system during the war. The provisions of the act took effect from the start of 1923. History The British railway system had been built up by more than a hundred railway companies, large and small, and often, particularly locally, in competition with each other. The parallel railways of the East Midlands, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
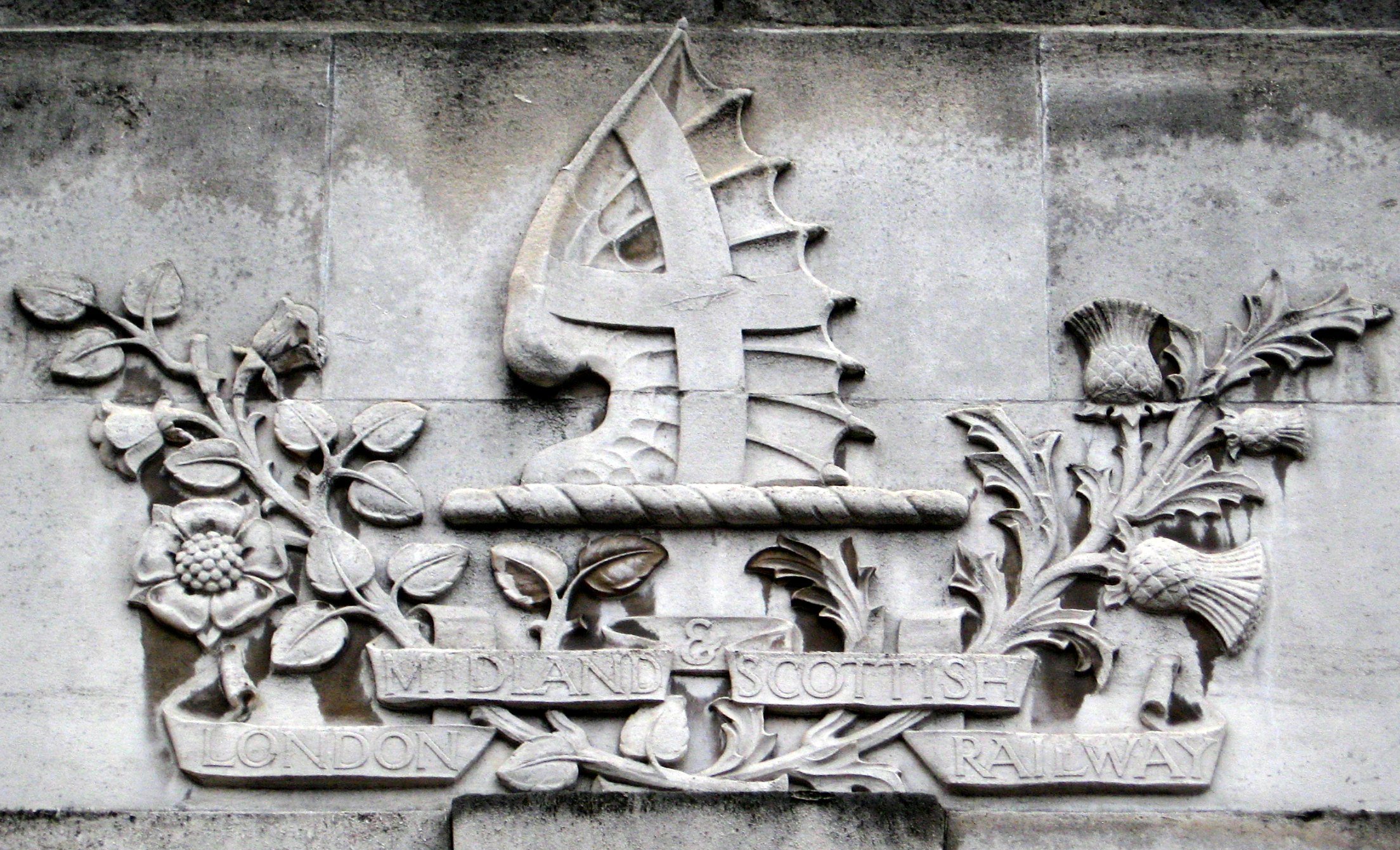
London, Midland And Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with London and North Eastern Railway, LNER, Great Western Railway, GWR and Southern Railway (UK), SR. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway's corporate image used LMS, and this is what is generally used in historical circles. The LMS occasionally also used the initials LM&SR. For consistency, this article uses the initials LMS.) was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railways into four. The companies merged into the LMS included the London and North Western Railway, the Midland Railway, the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (which had previously merged with the London and North Western Railway on 1 January 1922), several Scottish railway companies (including the Caledonian Railway), and numerous other, smaller ventures. Besides being the world's largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
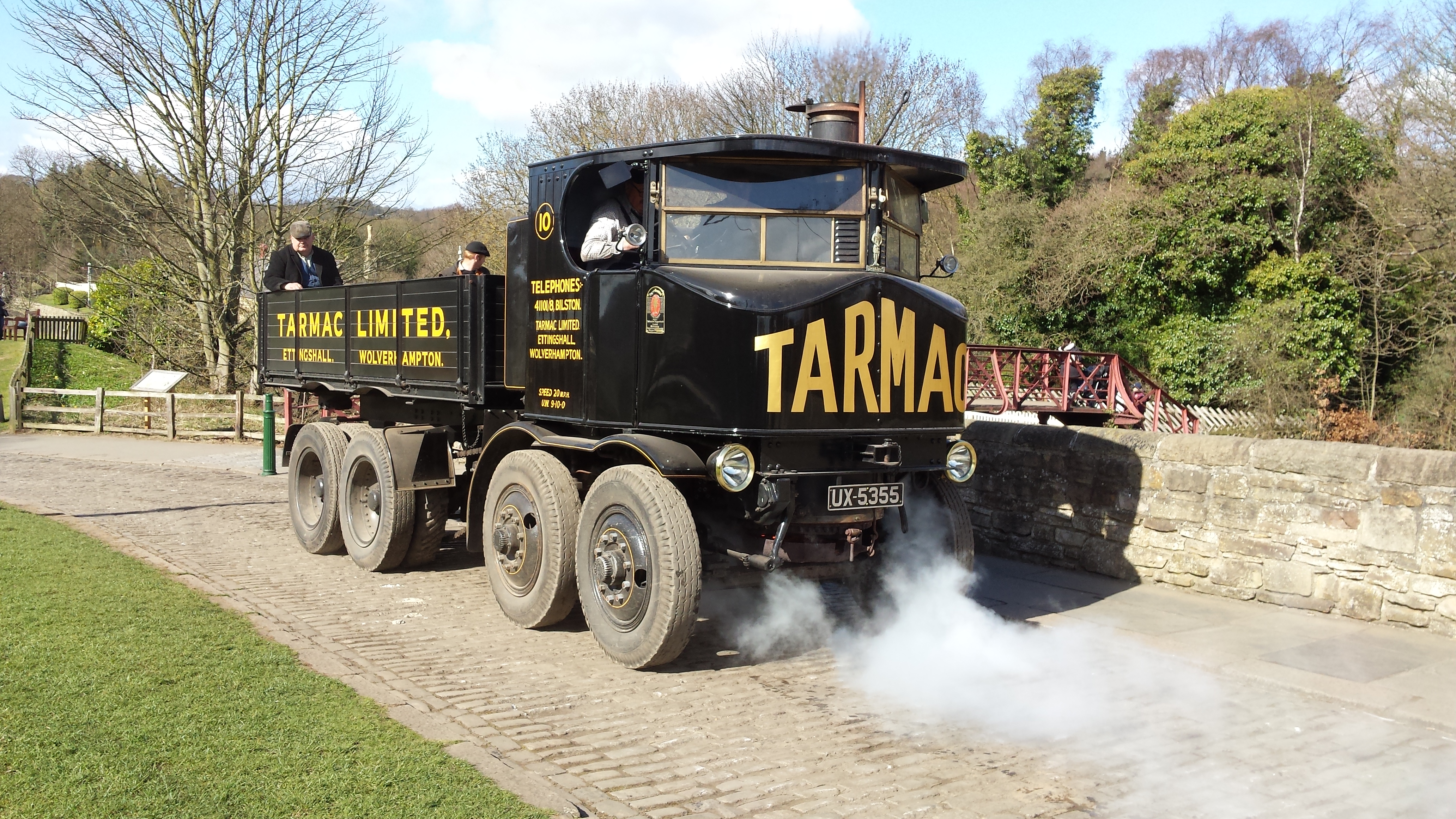
Sentinel Waggon Works
Sentinel Waggon Works Ltd was a British company based in Shrewsbury, Shropshire that made steam-powered lorry, lorries (steam wagons), railway locomotives, and later, diesel engined lorries, buses and locomotives. History Alley & MacLellan, Sentinel Works, Jessie Street Glasgow Alley & MacLellan was founded in 1875 and was based in Polmadie, Glasgow. This company continued in operation until the 1950s. Initially manufacturing valves and compressors for steam engines, and later whole steamships, Alley & MacLellan acquired Simpson and Bibby of Horsehay, Shropshire, manufacturer of steam-powered road vehicles, in 1903. They began producing steam road vehicles in 1905 and in 1906 introduced a five-ton vertical-boiler steam wagon, which featured a two-cylinder undertype engine and chain drive. Around 1915, Alley & McLellan moved the steam wagon production to a new factory in Shrewsbury and it continued under a separate company (see below), and in 1918 the company also opened A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chester Northgate Railway Station
Chester Northgate is a former railway station in Chester, Cheshire, England; it was a terminus for the Cheshire Lines Committee and Great Central Railway. It was the city centre's second station, after Chester General, with regular services to , and . History The station, which was located on Victoria Road in the Newtown area of the city, was originally planned by the West Cheshire Railway in 1865. A year later, the company was acquired by the Cheshire Lines Committee (CLC) which opened the station on 1 May 1875 for services to Manchester Central on the Mid-Cheshire Line via . The CLC track crossed the London, Midland and Scottish Railway and Great Western Railway line over a flying junction at Mickle Trafford. Chester Northgate had a station building and a covered roof for each platform; it had four tracks with two side platforms, the central tracks being used to store carriages. One of the roofs had been removed by 1966. There were also lower level sidings that conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwich Railway Station
Northwich railway station serves the town of Northwich in Cheshire, England. The station has two platforms in use (and a third platform now disused and fenced off). It is located on the Mid-Cheshire line southwest of Manchester Piccadilly railway station, Manchester Piccadilly. History The first railway to reach the town was the Cheshire Midland Railway (CMR) route from , which opened to traffic on 1 January 1863. The CMR was one of the constituent routes of the Cheshire Lines Committee (CLC) from its formation. The original CMR terminus station in Northwich was likely the building that became the goods station but was replaced early, in 1869, as the continuing line towards Hartford was being constructed as part of the West Cheshire Railway (WCR). Further lines to via Middlewich (opened in November 1867 by the London and North Western Railway), Helsby (the West Cheshire Railway, opened in 1869) and a short goods branch to Winnington (also opened in 1869) would complete the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester Central Railway Station
Manchester Central was a railway station in Manchester city centre, England. One of Manchester's main railway terminals between 1880 and 1969, the building was converted into an exhibition and conference centre which was opened in 1986; originally known as ''G-MEX'', it is now named Manchester Central Convention Complex, ''Manchester Central''. The structure is a Grade II* listed building. On 27 March 2020, the UK government announced that the building would be converted into an emergency hospital, intended to deal with the COVID-19 pandemic and with 1,000 beds. It was opened in April 2020 and closed in March 2021. History The station was built between 1875 and 1880 by the Cheshire Lines Committee (CLC), and was opened officially on 1 July 1880. The architect was Sir John Fowler, 1st Baronet, Sir John Fowler and the engineers were Richard Johnson, Andrew Johnston and Charles Sacré for the three companies which formed the CLC. While it was being built, a temporary facility, Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheshire Lines Committee
The Cheshire Lines Committee (CLC) was formed in the 1860s and became the second-largest joint railway in Great Britain. The committee, which was often styled the Cheshire Lines Railway, operated of track in the then counties of Lancashire and Cheshire. The railway did not become part of the ''Big Four'' during the implementation of the 1923 grouping, surviving independently with its own management until the railways were nationalised at the beginning of 1948. The railway served Liverpool, Manchester, Stockport, Warrington, Widnes, Northwich, Winsford, Knutsford, Chester and Southport with connections to many other railways. Formation The Cheshire Lines Committee evolved in the late 1850s from the close working together of two railways, the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR) and the Great Northern Railway (GNR); this was in their desire to break the near monopoly on rail traffic held by the London and North Western Railway (LNWR) in the Southern Lancashi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowdon Railway Station
Bowdon railway station served the district of Bowdon, Cheshire (now Greater Manchester), between 1849 and 1881. The station was built by the Manchester, South Junction and Altrincham Railway The Manchester South Junction and Altrincham Railway (MSJ&AR) was a suburban railway which operated an route between Altrincham in Cheshire and Manchester London Road railway station (now Manchester Piccadilly station, Piccadilly) in Manches ... (MSJ&AR), and opened on 22 September 1849, the same day that a short southerly extension to the MSJ&AR line to reach Bowdon was completed from the original Altrincham station of 20 July 1849.Butt p 41 Bowdon station was located on Lloyd Street/Railway Street in Altrincham, near to the boundary with Bowdon. A service of steam-hauled trains ran via Sale station to Manchester Oxford Road. The station served the locality until 3 April 1881, when both it and the first Altrincham station were closed, replaced by the new large facility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altrincham (1st) Railway Station
Altrincham railway station served the town of Altrincham (historically in Cheshire), now Greater Manchester, England between 1849 and 1881. The station was built by the Manchester, South Junction and Altrincham Railway (MSJ&AR) and opened on 20 July 1849. This first Altrincham station was located just south of Stockport Road level crossing and its junction with Stamford Street. The station consisted of two platforms and a station building. It served the locality until 3 April 1881 when both it and Bowdon railway station Bowdon railway station served the district of Bowdon, Cheshire (now Greater Manchester), between 1849 and 1881. The station was built by the Manchester, South Junction and Altrincham Railway The Manchester South Junction and Altrincham R ... were closed, being replaced by the new large facility named Altrincham and Bowdon (now Altrincham railway station), situated between the two former stations. There are no remains of this station today. Referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altrincham Station Clock Tower
Altrincham ( , locally ) is a market town in Trafford, Greater Manchester, England, south of the River Mersey. It is southwest of Manchester, southwest of Sale and east of Warrington. At the 2021 census, the built up area had a population of 49,680. It lies within the historic county boundaries of Cheshire, and became part of Greater Manchester in 1974. Altrincham developed as a market town following the right to hold a market being granted in 1290; the market continues today. Further socioeconomic development came with the extension of the Bridgewater Canal to Altrincham in 1765 and the arrival of the railway in 1849, stimulating industrial activity in the town. Outlying villages were absorbed by Altrincham's subsequent growth, along with the grounds of Dunham Massey Hall, formerly the home of the Earl of Stamford, and now a tourist attraction with three Grade I Listed Buildings and a deer park. Altrincham has good transport links to Manchester, Sale, Stretford and Sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |