|
Alioune Sarr
Alioune Sarr (September 1, 1908 – July 12, 2001 ) was a Senegalese historian, author and politician whose family gained prominence in the Serer precolonial Kingdom of Sine and Saloum around the 14th century. They also made up the ''"sulbalƃe"'' class of Futa Toro (all in present-day Senegal). Sarr was born at Foundiougne. His father (Koly Samba Sarr) was a former Chief of Foundiougne, Gandoune, former head of the constituency of Ndiaye-Ndiaye and former prime minister of Diognick in Senegal. Although Sarr was a prominent politician like his father during the colonial era, he is best known as a historian and author especially after his famous work ''Histoire du Sine-Saloum'' which was officially published in 1949 and peer reviewed by historians.Klein, 277 Politics In 1963, Sarr was President of the Regional Assembly of Sine-Saloum, ( Kaolack, Senegal) (French: Président de l’Assemblée Régionale du Sine-Saloum), a position he occupied when the historian Martin A. Klei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambia
The Gambia, officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. Geographically, The Gambia is the List of African countries by area, smallest country in continental Africa; it is surrounded by Senegal on all sides except for the western part, which is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean.Hoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A–Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publications. p. 11. . Its territory is on both sides of the lower reaches of the Gambia River, which flows through the centre of the country and empties into the Atlantic. The national namesake river demarcates the elongated shape of the country, which has an area of and a population of 2,769,075 people in 2024 which is a 47% population increase from 2013. The capital city is Banjul, which has the most extensive metropolitan area in the country. The second and third-largest cities are Serekunda and Brikama. Arab Muslims, Arab Muslim merchants traded with indigenous West Africans in The Gambia throughout the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
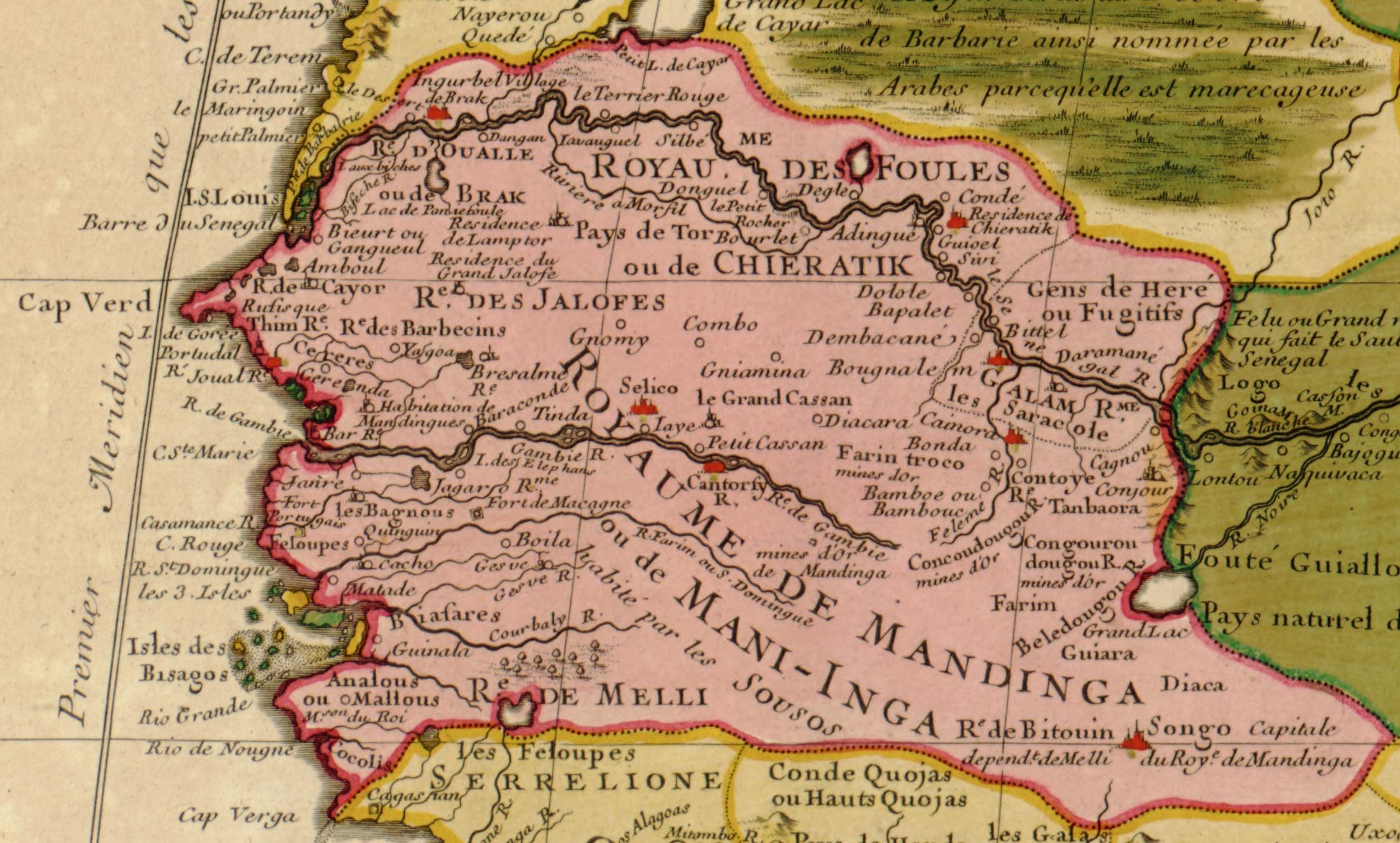
History Of Senegal
The history of Senegal is commonly divided into a number of periods, encompassing the prehistoric era, the precolonial period, colonialism, and the contemporary era. Paleolithic The earliest evidence of human life is found in the valley of the Falémé River, Falémé in the south-east. The presence of man in the Lower Paleolithic is attested by the discovery of Archaeological industry, stone tools characteristic of Acheulean such as hand axes reported by Théodore Monod at the tip of Fann-Point E-Amitié, Fann in the peninsula of Cap-Vert in 1938, or cleavers found in the south-east. There were also found stones shaped by the Levallois technique, characteristic of the Middle Paleolithic. Mousterian Industry is represented mainly by Scraper (archaeology), scrapers found in the peninsula of Cap-Vert, as well in the low and middle valleys of the Senegal River, Senegal and the Falémé. Some pieces are explicitly linked to hunting, like those found in Tiémassass, near M'Bour, a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serer Ancient History
The prehistoric and ancient history of the Serer people of modern-day Senegambia has been extensively studied and documented over the years. Much of it comes from archaeological discoveries and Serer tradition rooted in the Serer religion."Vestiges historiques, trémoins matériels du passé clans les pays Sereer". Dakar. 1993. CNRS – ORS TO M Ancient history In Charles Becker's paper titled "Vestiges historiques, trémoins matériels du passé clans les pays Sereer", two types of Serer relics were noted: "the non-material remains which are cultural in nature" and "material remains, which are many revealed through products or artefacts." The historical vestiges of Serer country in modern-day Senegambia, the diversity of Serer culture manifested across dialects, family and social organisation which reflect different historical territories were observed. Although many Serer artefacts remain unknown, unlisted and preserved despite the efforts in the 1960s and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serer History (medieval Era To Present)
The medieval history of the Serer people of Senegambia is partly characterised by resisting Islamization from perhaps the 11th century during the Almoravid movement (which would later result in the Serers of Takrur migration to the south), to the 19th century Marabout movement of Senegambia and continuation of the old Serer paternal dynasties. Resistance to Islam, 11th century According to Galvan (2004), "The oral historical record, written accounts by early Arab and European explorers, and physical anthropological evidence suggest that the various Serer peoples migrated south from the Fuuta Tooro region (Senegal River valley) beginning around the eleventh century, when Islam first came across the Sahara."Galvan, Dennis Charles, ''The State Must Be Our Master of Fire: How Peasants Craft Culturally Sustainable Development in Senegal'' Berkeley, University of California Press, 2004 p.51 Over generations these people, possibly Pulaar speaking herders originally, migrated through Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorée
(; "Gorée Island"; ) is one of the 19 (i.e. districts) of the city of Dakar, Senegal. It is an island located at sea from the main harbour of Dakar (), famous as a destination for people interested in the Atlantic slave trade. Its population as of the 2013 census was 1,680 inhabitants, giving a density of , which is only half the average density of the city of Dakar. Gorée is both the smallest and the least populated of the 19 of Dakar. Other important centres for the slave trade from Senegal were further north, at Saint-Louis, Senegal, or to the south in the Gambia, at the mouths of major rivers for trade.''Les Guides Bleus: Afrique de l'Ouest'' (1958 ed.), p. 123 It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and was one of the first 12 locations in the world to be designated as such in 1978. The name is a corruption of its original Dutch language, Dutch name Goeree, named after the Dutch island of Goeree-Overflakkee, Goeree. The island was also known as Palma, or in Portuguese. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Archives Of Senegal
The National Archives of Senegal (''Archives Nationales du Sénégal'') is headquartered in Dakar, in the Central Park building on Avenue Malick Sy. It was first called ''Archives Nationales'' in 1962, but the collection existed since 1913 as the archives of the colonial French West Africa administration. It moved from Saint-Louis to Dakar after 1958. Archivists Archivists have included: * Claude Faure (1911-1920) * Prosper Alquier (1921-1922) * Médoune Mbaye (1922-1936) * André Villard (1936-1942) * (1945-1948) * Jacques Charpy (1951-1958) * Jean-François Maurel (1958-1959) * Saliou Mbaye (1976-2005) * Babacar Ndiaye, circa 2010-2011* Fatoumata Cissé Diarra, circa 2013?-present See also * Unesco Memory of the World Register – Africa * Bibliothèque des Archives nationales du Sénégal * History of Senegal References Bibliography * (Includes information about the National Archives of Senegal) * (Includes information about the National Archives of Senegal) * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristocracy
Aristocracy (; ) is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocracy (class), aristocrats. Across Europe, the aristocracy exercised immense Economy, economic, Politics, political, and social influence. In Western Christian countries, the aristocracy was mostly equal with magnates, also known as the titled or higher nobility, however the members of the more numerous social class, the untitled lower nobility (petty nobility or gentry) were not part of the aristocracy. Classical aristocracy In ancient Greece, the Greeks conceived aristocracy as rule by the best-qualified citizens—and often contrasted it favorably with monarchy, rule by an individual. The term was first used by such ancient Greeks as Aristotle and Plato, who used it to describe a system where only the best of the citizens, chosen through a careful process of selection, would become rulers, and hereditary monarchy, hereditary rule would actually have been f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire (), also known as simply Ghana, Ghanata, or Wagadu, was an ancient western-Sahelian empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali. It is uncertain among historians when Ghana's ruling dynasty began. The first identifiable mention of the imperial dynasty in written records was made by Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī in 830. Further information about the empire was provided by the accounts of Cordoban scholar al-Bakri when he wrote about the region in the 11th century. After centuries of prosperity, the empire began its decline in the second millennium, and would finally become a vassal state of the rising Mali Empire at some point in the 13th century. Despite its collapse, the empire's influence can be felt in the establishment of numerous urban centers throughout its former territory. In 1957, the British colony of the Gold Coast, under the leadership of Kwame Nkrumah named itself Ghana upon independence. Etymology The word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamane
Lamane or laman (also laam or lam) means "master of the land" in the Serer language. The name was also sometimes the title of chiefs or kings of the Serer people of the Senegambia region which includes modern day Senegal and the Gambia. This title was also used by some kings of the Wolof kingdoms. The title is sometimes used interchangeably with the old Serer title Maad. After the Guelowars' migration to the Sine and the foundation of the Kingdom of Sine, "lamane" denotes a provincial chief answerable to the King of Sine and Saloum. Although the later lamanes were always descendants of the Serer village and town founders (the original lamanes), and their families ruled the Kingdoms of Sine, Saloum and Baol etc., the power they previously enjoyed as lamanes diminished, but they continued to make up the land-owning class. Though their power was somewhat diminished, their economic and political power was intricately linked to Serer custom, Serer history, and Serer religion. As su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Présence Africaine
''Présence Africaine'' (French for ''African Presence'') is a pan-African quarterly cultural, political, and literary magazine, published in Paris, France, and founded by Alioune Diop in 1947. In 1949, ''Présence Africaine'' expanded to include a publishing house and a bookstore on rue des Écoles in the Latin Quarter of Paris. The journal was highly influential in the Pan-Africanist movement, the decolonisation struggle of former French colonies, and the birth of the Négritude movement. Magazine The magazine published its first issue in November 1947, founded by Alioune Diop a Senegal-born professor of philosophy, along with a cast of African, European, and American intellectuals, writers, and social scientists, including Aimé Césaire, Léopold Sédar Senghor, Alioune Sarr, Richard Wright, Albert Camus, André Gide, Jean-Paul Sartre, Théodore Monod, Georges Balandier and Michel Leiris. While not all authors published in the magazine were from the African diaspora, its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |