|
Alexander Spotswood
Major-General Alexander Spotswood (12 December 1676 – 7 June 1740) was a British army officer, explorer and colonial administrator who served as the governor of Virginia from 1710 to 1722. After an unsatisfactory military career, in 1710 he was appointed as Virginia's governor, a post he held for twelve years. During that period, Spotswood engaged in the exploration of the territories beyond the western border, of which he was the first to see the economic potentials. In 1716 he organised and led an expedition west of the mountains, known as Knights of the Golden Horseshoe Expedition, with which he established the Crown's dominion over the territory between the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Shenandoah Valley, thus taking a decisive step for the future British expansion to the West. As the governor of Virginia, Spotswood's first preoccupation was to make sea routes safe and fight against the pirates. After a long effort, the famous pirate Blackbeard was hunted down and kil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Bridges (painter)
Charles Bridges (baptized 2 April 1672 – buried 18 December 1747) was an England, English painter and missionary active in Virginia from 1735 to 1744. He is the first documented painter known to have worked in Virginia. Life and career Bridges was christened in the parish of Barton Seagrave in Northamptonshire, and was the son of John Bridges and Elizabeth Trumbull Bridges. His family was of the gentry, and was well-educated; a brother, John Bridges (topographer), John Bridges, was a barrister and well-regarded historian of Northamptonshire. He married Alice Flower on 4 August 1687, at Saint Marylebone, near London; the couple had at least three children, a son and two daughters. Bridges was a member of the Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge, having worked for the organization in London from 1699 to 1713 and serving for a time as a liaison to local charity schools. Just when Bridges became a painter is unknown, though it is assumed that he had some training. Only one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Oudenarde
The Battle of Oudenarde, also known as the Battle of Oudenaarde, was a major engagement of the War of the Spanish Succession, pitting an Anglo-Dutch force consisting of eighty thousand men under the command of the Duke of Marlborough, Lord Overkirk and Prince Eugene of Savoy against a French force of eighty-five thousand men under the command of the Duc de Bourgogne and the Duc de Vendôme, the battle resulting in a great victory for the Grand Alliance. The battle was fought near the city of Oudenaarde, at the time part of the Spanish Netherlands, on 11 July 1708. With this victory, the Grand Alliance ensured the fall of various French territories, giving them a significant strategic and tactical advantage during this stage of the war. The battle was fought in the later years of the war, a conflict that had come about as a result of English, Dutch and Habsburg apprehension at the possibility of a Bourbon succeeding the deceased King of Spain, Charles II, and combining thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east of Washington, D.C., Annapolis forms part of the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The 2020 United States census, 2020 census recorded its population as 40,812, an increase of 6.3% since 2010. This city served as the seat of the Confederation Congress, formerly the Second Continental Congress, and temporary national capital of the United States in 1783–1784. At that time, General George Washington came before the body convened in the new Maryland State House and George Washington's resignation as commander-in-chief, resigned his commission as commander of the Continental Army. A month later, the Congress ratified the Treaty of Paris (1783), Treaty of Paris of 1783, ending the American Revolutionary War, with Kingdom of Great Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartagena De Indias
Cartagena ( ), known since the colonial era as Cartagena de Indias (), is a city and one of the major ports on the northern coast of Colombia in the Caribbean Region of Colombia, Caribbean Coast Region, along the Caribbean Sea. Cartagena's past role as a link in the route to the West Indies provides it with important historical value for world exploration and preservation of heritage from the great commercial maritime routes. As a former Spanish colony, it was a key port for the export of Bolivian silver to Spain and for the Slavery in Cartagena, import of enslaved Africans under the asiento system. It was defensible against Piracy in the Caribbean, pirate attacks in the Caribbean. The city's strategic location between the Magdalena River, Magdalena and Sinú River, Sinú rivers also gave it easy access to the interior of New Kingdom of Granada, New Granada and made it a main port for trade between Spain and its overseas empire, establishing its importance by the early 1540s. Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
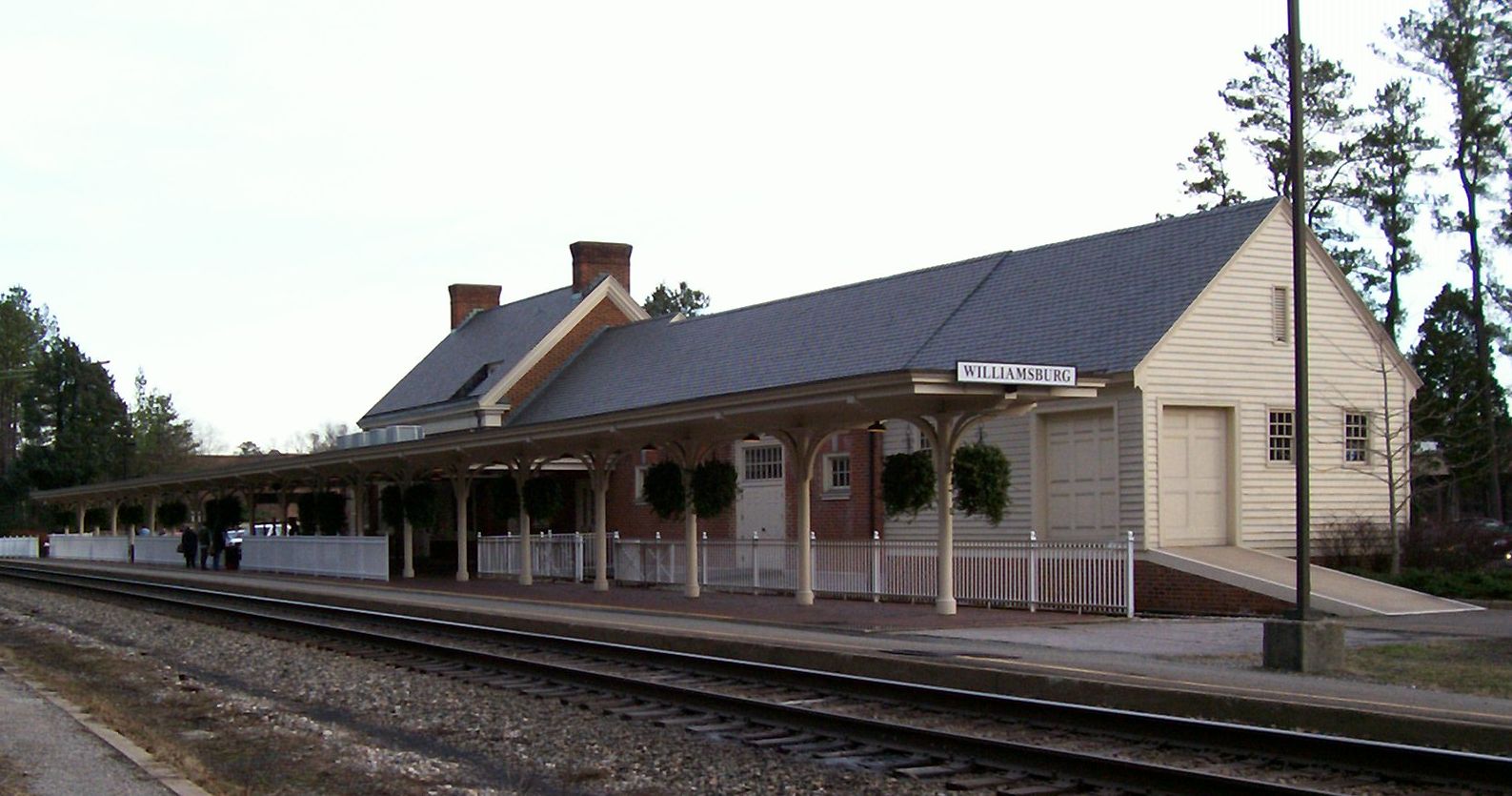
Williamsburg, Virginia
Williamsburg is an Independent city (United States), independent city in Virginia, United States. It had a population of 15,425 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Located on the Virginia Peninsula, Williamsburg is in the northern part of the Hampton Roads metropolitan area. It is bordered by James City County, Virginia, James City County on the west and south and York County, Virginia, York County on the east. English settlers founded Williamsburg in 1632 as Middle Plantation (Virginia), Middle Plantation, a fortified settlement on high ground between the James River, James and York River (Virginia), York rivers, and farther inland than their headquarters at Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown. The city functioned as the capital of the Colony of Virginia, Colony and Commonwealth of Virginia from 1699 to 1780 and became the center of political events in Virginia leading to the American Revolution. The College of William & Mary, established in 1693, is the second-oldest inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
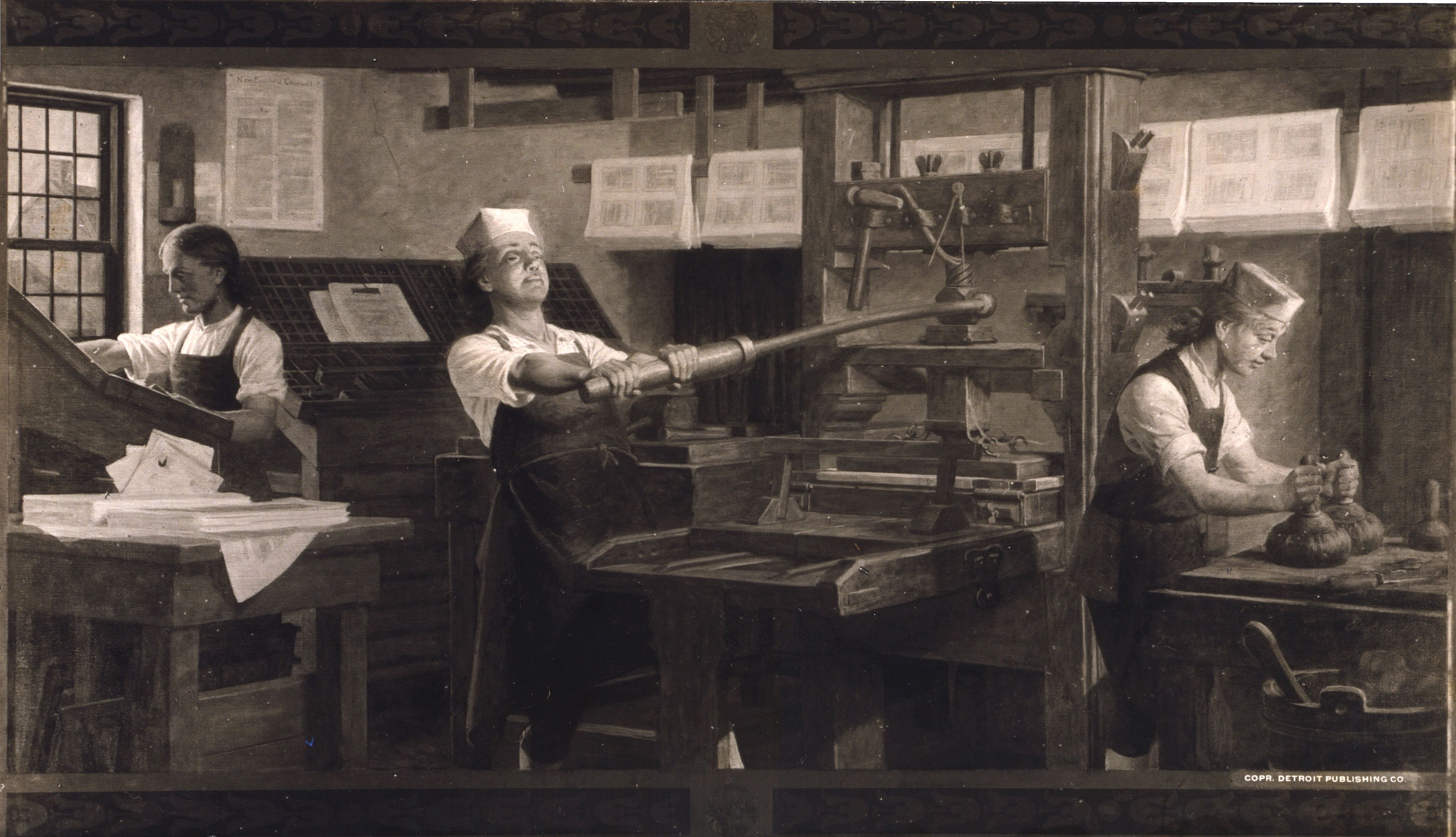
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the most influential intellectuals of his time, Franklin was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States; a Committee of Five, drafter and signer of the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence; and the first United States Postmaster General, postmaster general. Born in the Province of Massachusetts Bay, Franklin became a successful Early American publishers and printers, newspaper editor and printer in Philadelphia, the leading city in the colonies, publishing ''The Pennsylvania Gazette'' at age 23. He became wealthy publishing this and ''Poor Richard's Almanack'', which he wrote under the pseudonym "Richard Saunders". After 1767, he was associated with the ''Pennsylvania Chronicle'', a newspaper known for it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habeas Corpus
''Habeas corpus'' (; from Medieval Latin, ) is a legal procedure invoking the jurisdiction of a court to review the unlawful detention or imprisonment of an individual, and request the individual's custodian (usually a prison official) to bring the prisoner to court, to determine whether their detention is lawful. ''Habeas corpus'' is generally enforced via writ, and accordingly referred to as a writ of ''habeas corpus''. The writ of ''habeas corpus'' is one of what are called the "extraordinary", "common law", or " prerogative writs", which were historically issued by the English courts in the name of the monarch to control inferior courts and public authorities within the kingdom. The writ was a legal mechanism that allowed a court to exercise jurisdiction and guarantee the rights of all the Crown's subjects against arbitrary arrest and detention. At common law the burden was usually on the official to prove that a detention was authorized. ''Habeas corpus'' has cert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanna
Germanna was a German settlement in the Colony of Virginia, settled in two waves, first in 1714 and then in 1717. Virginia Lieutenant Governor Alexander Spotswood encouraged the immigration by advertising in Germany for miners to move to Virginia and establish a mining industry in the colony. Etymology The name "Germanna", selected by Spotswood, reflected both the German immigrants who sailed across the Atlantic to Virginia and the British Queen Anne who was in power at the time of the first settlement at Germanna. Though she died only months after the Germans arrived, her name continues to be a part of the area. History As part of a series of land grants awarded to settlers to create a buffer against the French, the Privy Council granted Spotswood in the newly created Spotsylvania County in 1720, of which the Germanna tract was the first, while he was lieutenant governor and actual executive head of the Virginia government. He served in this capacity between 1710 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
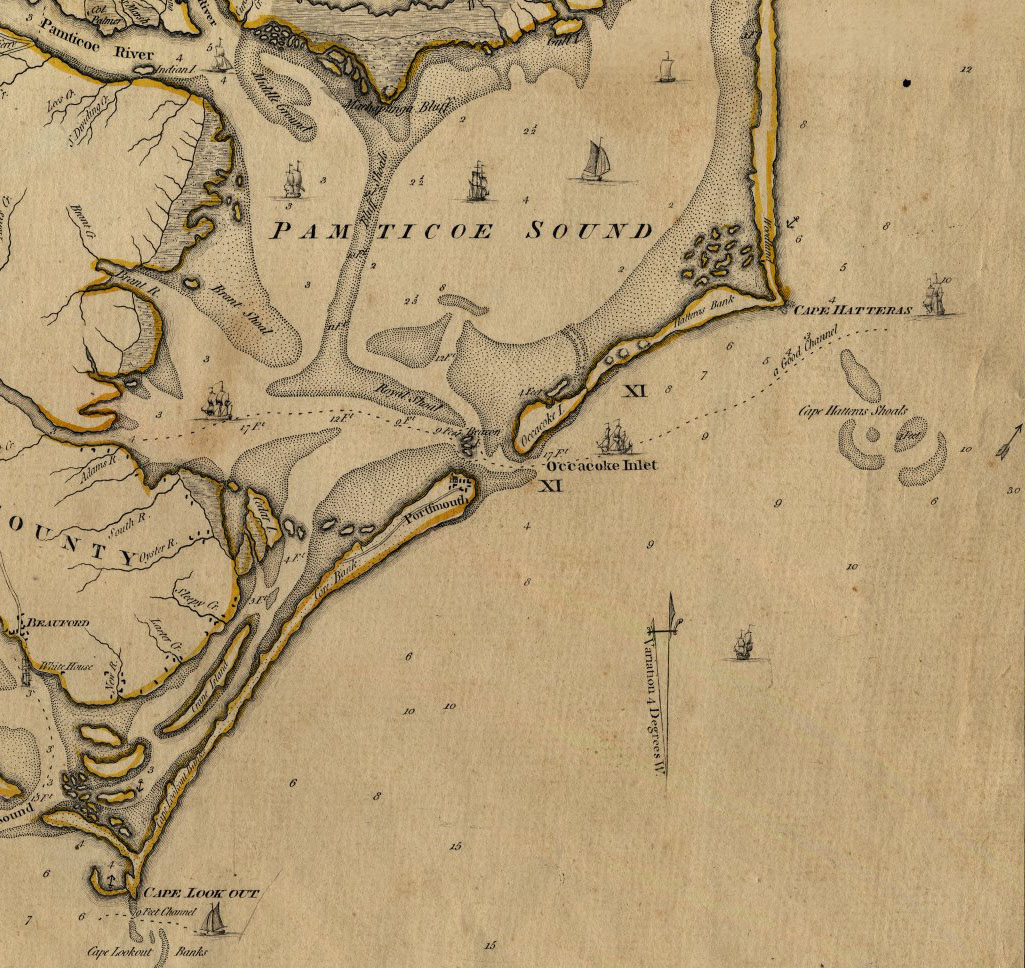
Blackbeard
Edward Teach (or Thatch; – 22 November 1718), better known as Blackbeard, was an English pirate who operated around the West Indies and the eastern coast of Britain's North American colonies. Little is known about his early life, but he may have been a sailor on privateer ships during Queen Anne's War before he settled on the Bahamian island of New Providence, a base for Captain Benjamin Hornigold, whose crew Teach joined around 1716. Hornigold placed him in command of a sloop that he had captured, and the two engaged in numerous acts of piracy. Their numbers were boosted by the addition to their fleet of two more ships, one of which was commanded by Stede Bonnet, but Hornigold retired from piracy toward the end of 1717, taking two vessels with him. Teach captured a French slave ship known as , renamed her '' Queen Anne's Revenge,'' equipped her with 40 guns, and crewed her with over 300 men. He became a renowned pirate. His nickname derived from his thick black bear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shenandoah Valley
The Shenandoah Valley () is a geographic valley and cultural region of western Virginia and the eastern panhandle of West Virginia in the United States. The Valley is bounded to the east by the Blue Ridge Mountains, to the west by the eastern front of the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians (excluding Massanutten Mountain), to the north by the Potomac River, to the south by the James River (Virginia), James River, and to the Southwest by the New River Valley. The cultural region covers a larger area that includes all of the Valley plus the Virginia Highlands to the west and the Roanoke Valley to the south. It is physical geography, physiographically located within the Ridge and Valley Province and is a portion of the Great Appalachian Valley. Geography Named for Shenandoah River, the river that stretches much of its length, the Shenandoah Valley encompasses eight counties in Virginia and two counties in West Virginia: *Augusta County, Virginia *Clarke County, Virginia *Frederick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a Physiographic regions of the United States, physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Highlands range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsylvania through Maryland, West Virginia, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. The province consists of northern and southern physiographic regions, which divide near the Roanoke River gap. To the west of the Blue Ridge, between it and the bulk of the Appalachians, lies the Great Appalachian Valley, bordered on the west by the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, Ridge and Valley province of the Appalachian range. The Blue Ridge Mountains are known for having a bluish color when seen from a distance. Trees put the "blue" in Blue Ridge, from the isoprene released into the atmosphere. This contributes to the characteristic haze on the mountains and their perceived color. Within the Blue Ridg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |