|
Alexander Oliver Rankine
Alexander Oliver Rankine (8 December 1881 – 20 January 1956) was a British physicist who worked on the viscosity of gases, molecular dynamics, optics, acoustics and geophysics. Career Rankine carried out government research during both World Wars, working on anti-submarine technology and on fog dispersal systems. He studied and worked at University College London, and was a professor of physics at Imperial College London. Rankine is most associated with the Trouton–Rankine experiment of 1908, but he also worked on early devices for the optical transmission of sound, and improved gravimeter and magnetometer designs. The latter part of his career was spent working for the Anglo-Iranian Oil Company. He also served in a range of positions with many learned societies, including periods as president of the Physical Society and secretary to the Royal Institution. Early years Alexander Oliver Rankine was born on 8 December 1881 in Guildford, Surrey, England.Obituary: Professor A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial College London
Imperial College London, also known as Imperial, is a Public university, public research university in London, England. Its history began with Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, Prince Albert, husband of Queen Victoria, who envisioned a Albertopolis, cultural district in South Kensington that included museums, colleges, and the Royal Albert Hall. In 1907, these colleges – the Royal College of Science, the Royal School of Mines, and the City and Guilds of London Institute – merged to form the Imperial College of Science and Technology. In 1988, Imperial merged with St Mary's Hospital, London, St Mary's Hospital Medical School and then with Charing Cross and Westminster Medical School to form the Imperial College School of Medicine. The Imperial Business School was established in 2003 and officially opened by Elizabeth II, Queen Elizabeth II. Formerly a constituent college of the University of London, Imperial became an independent university in 2007. Imperial is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baptist
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches generally subscribe to the Christian theology, doctrines of soul competency (the responsibility and accountability of every person before God in Christianity, God), ''sola fide'' (salvation by faith alone), ''sola scriptura'' (the Bible is the sole infallible authority, as the rule of faith and practice) and Congregationalist polity, congregationalist church government. Baptists generally recognize two Ordinance (Christianity), ordinances: Baptism, baptism and Eucharist, communion. Diverse from their beginning, those identifying as Baptists today may differ widely from one another in what they believe, how they worship, their attitudes toward other Christians, and their understanding of what is important in Christian discipleship. Baptist mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiralty Research Laboratory
The Admiralty Research Laboratory (ARL) was a research laboratory that supported the work of the UK Admiralty. It was located in Teddington, London, England from 1921 to 1977. History During the First World War, the Anti-Submarine Division of the Admiralty had established experimental stations at Hawkcraig (Aberdour) and Parkeston Quay, Harwich, with out-stations at Dartmouth and Wemyss Bay, to work on submarine detection methods. The Admiralty also established an experimental station at Shandon, Dumbartonshire, working with the Lancashire Anti-Submarine Committee and the Clyde Anti-Submarine Committee, which subsequently moved to Teddington in 1921, becoming the Admiralty Research Laboratory. Its main fields of research expanded to include oceanography (it housed the National Institute of Oceanography from 1949 to 1953); electromagnetics and degaussing; underwater ballistics; visual aids; acoustics; infra-red radiation; photography and assessment techniques. It moved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
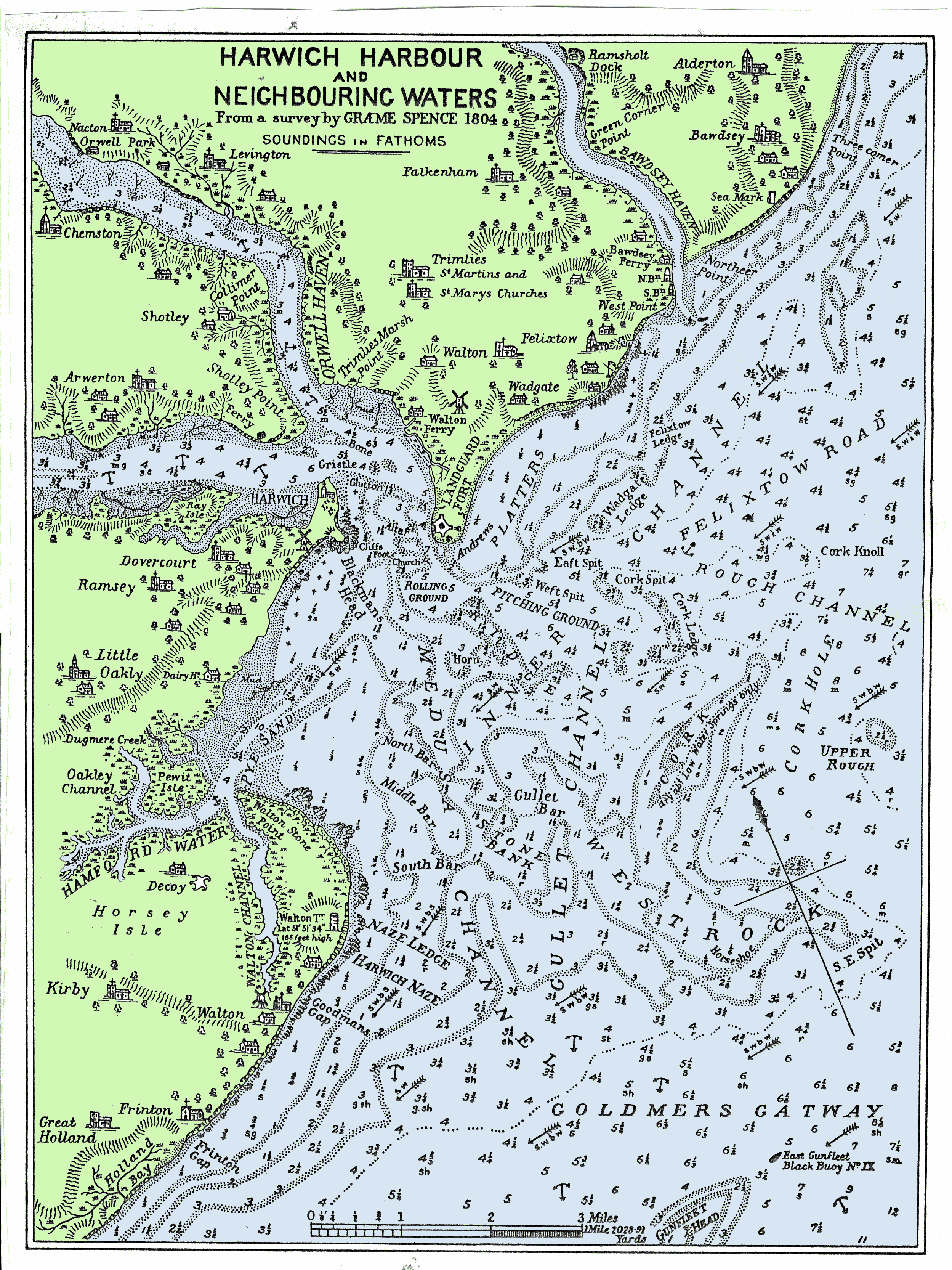
Harwich
Harwich is a town in Essex, England, and one of the Haven ports on the North Sea coast. It is in the Tendring district. Nearby places include Felixstowe to the north-east, Ipswich to the north-west, Colchester to the south-west and Clacton-on-Sea to the south. It is the northernmost coastal town in Essex. Its position on the estuaries of the Stour and Orwell rivers, with its usefulness to mariners as the only safe anchorage between the Thames and the Humber, led to a long period of civil and military maritime significance. The town became a naval base in 1657 and was heavily fortified, with Harwich Redoubt, Beacon Hill Battery, and Bath Side Battery. Harwich is the likely launch point of the ''Mayflower'', which carried English Puritans to North America, and is the presumed birthplace of ''Mayflower'' captain Christopher Jones. Harwich today is contiguous with Dovercourt and the two, along with Parkeston, are often referred to collectively as ''Harwich''. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firth Of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is a firth in Scotland, an inlet of the North Sea that separates Fife to its north and Lothian to its south. Further inland, it becomes the estuary of the River Forth and several other rivers. Name ''Firth'' is a cognate of ''fjord'', a Norse word meaning a narrow inlet. ''Forth'' stems from the name of the river; this is ('slow running') in Proto-Celtic, yielding in Old Gaelic and in Welsh. It was known as ' in Roman Empire, Roman times and was referred to as ' in Ptolemy's ''Geography_(Ptolemy), Geography''. In the Norse mythology, Norse sagas it was known as the . An early Welsh language, Welsh name is , or the 'sea of '. Geography and geology Geologically, the Firth of Forth is a fjord, formed by the Forth Glacier in the last glacial period. The drainage basin for the Firth of Forth covers a wide geographic area including places as far from the shore as Ben Lomond, Cumbernauld, Harthill, Scotland, Harthill, Penicuik and the edges of Gleneagles H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberdour
Aberdour (; Scots: , ) is a scenic and historic village on the south coast of Fife, Scotland. It is on the north shore of the Firth of Forth, looking south to the island of Inchcolm and its Abbey, and to Leith and Edinburgh beyond. According to the 2011 census, the village has a population of 1,633. The village's winding High Street lies a little inland from the coast. Narrow lanes run off it, providing access to the more hidden parts of the village and the shoreline itself. The village nestles between the bigger coastal towns of Burntisland to the east and Dalgety Bay to the west. The parish of Aberdour takes its name from this village, and had a population of 1,972 at the 2011 Census.Census of Scotland 2011, Table KS101SC – Usual Resident Population, published by National Records of Scotland. Website http://www.scotlandscensus.gov.uk/ retrieved Apr 2018. See “Standard Outputs”, Table KS101SC, Area type: Civil Parish 1930, Area: Aberdour Etymology Aberdour means 'm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Stewart Eve
Arthur Stewart Eve (22 November 1862 – 24 March 1948) was an English physicist who worked in Canada. Biography Eve was born at Silsoe, Bedfordshire, on 22 November 1862, son of John Richard Eve, surveyor and land agent, and Frederica (née Somers). He was educated at Berkhamsted School and entered Pembroke College, Cambridge in 1881. He was fifteenth wrangler and graduated in 1884. Eve was Assistant Master at Marlborough College from 1886 to 1902, and Bursar from 1897 to 1902. He then resigned and sailed on the SS ''Ivernia'' in January 1903 to New York, from where he went to McGill University, as a lecturer in mathematics. He later joined the physics department, where he worked with Ernest Rutherford. His early papers, published in 1904, showed Eve as the author, but were communicated by Rutherford. After a series of successful researches with Rutherford, Eve was appointed Associate Professor of Physics in 1909 and, in the following year, was elected a Fellow of the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Henry Bragg
Sir William Henry Bragg (2 July 1862 – 12 March 1942) was an English physicist and X-ray crystallographer who uniquelyThis is still a unique accomplishment, because no other parent-child combination has yet shared a Nobel Prize (in any field). In several cases, a parent has won a Nobel Prize, and then years later, the child has won the Nobel Prize for separate research. An example of this is with Marie Curie and her daughter Irène Joliot-Curie, who are the only mother-daughter pair. Several father-son pairs have won two separate Nobel Prizes. shared a Nobel Prize with his son Lawrence Bragg – the 1915 Nobel Prize in Physics: "for their services in the analysis of crystal structure by means of X-rays". Biography Early years Bragg was born at Westward, near Wigton, Cumberland, England, the son of Robert John Bragg, a merchant marine officer and farmer, and his wife Mary née Wood, a clergyman's daughter. When Bragg was seven years old, his mother died, and he was rais ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Sutherland (physicist)
William Sutherland (24 August 1859 – 5 October 1911) was a Scottish-born Australian theoretical physicist, physical chemist and writer for ''The Age'' (Melbourne) newspaper. R. W. Home,Sutherland, William (1859–1911), ''Australian Dictionary of Biography'', Volume 12, MUP, 1990, pp 141–142. Retrieved 7 April 2010 Early life and education Sutherland was born in Glasgow, Scotland, son of George Sutherland, a woodcarver, and his wife Jane, ''née'' Smith. William had siblings Alexander Sutherland, George Sutherland and Jane Sutherland. The family emigrated to Australia in 1864, staying in Sydney for six years and then moving to Melbourne in 1870. Sutherland later graduated from Wesley College. The headmaster was Martin Howy Irving who had been the second professor of classics at the University of Melbourne, but the influence of the second master, H. M. Andrew, afterwards professor of natural philosophy at the same university, was of more importance to Sutherland. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscosimeter
A viscometer (also called viscosimeter) is an instrument used to measure the viscosity of a fluid. For liquids with viscosities which vary with flow conditions, an instrument called a rheometer is used. Thus, a rheometer can be considered as a special type of viscometer. Viscometers can measure only constant viscosity, that is, viscosity that does not change with flow conditions. In general, either the fluid remains stationary and an object moves through it, or the object is stationary and the fluid moves past it. The drag caused by relative motion of the fluid and a surface is a measure of the viscosity. The flow conditions must have a sufficiently small value of Reynolds number for there to be laminar flow. At 20°C, the dynamic viscosity (kinematic viscosity × density) of water is 1.0038 mPa·s and its kinematic viscosity (product of flow time × factor) is 1.0022mm2/s. These values are used for calibrating certain types of viscometers. Standard laboratory viscometers for liq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory of the relationship between Spacetime, space and time. In Albert Einstein's 1905 paper, Annus Mirabilis papers#Special relativity, "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", the theory is presented as being based on just Postulates of special relativity, two postulates: # The laws of physics are Invariant (physics), invariant (identical) in all Inertial frame of reference, inertial frames of reference (that is, Frame of reference, frames of reference with no acceleration). This is known as the principle of relativity. # The speed of light in vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of light source or observer. This is known as the principle of light constancy, or the principle of light speed invariance. The first postulate was first formulated by Galileo Galilei (see ''Galilean invariance''). Background Special relativity builds upon important physics ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |