|
Alba Mons
Alba Mons (formerly and still occasionally known as Alba Patera, a term that has since been restricted to the volcano's summit caldera; also initially known as the Arcadia ring) is a volcano located in the northern Tharsis region of the planet Mars. It is the biggest volcano on Mars in terms of surface area, with volcanic flow fields that extend for at least from its summit.Cattermole, 2001, p. 85. Although the volcano has a span comparable to that of the United States, it reaches an elevation of only at its highest point.Carr, 2006, p. 54. This is about one-third the height of Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano on the planet. The flanks of Alba Mons have very gentle slopes. The average slope along the volcano's northern (and steepest) flank is 0.5°, which is over five times lower than the slopes on the other large Tharsis Montes, Tharsis volcanoes. In broad profile, Alba Mons resembles a vast but barely raised welt on the planet's surface. It is a unique volcanic structure with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alba Mons Viking DIM
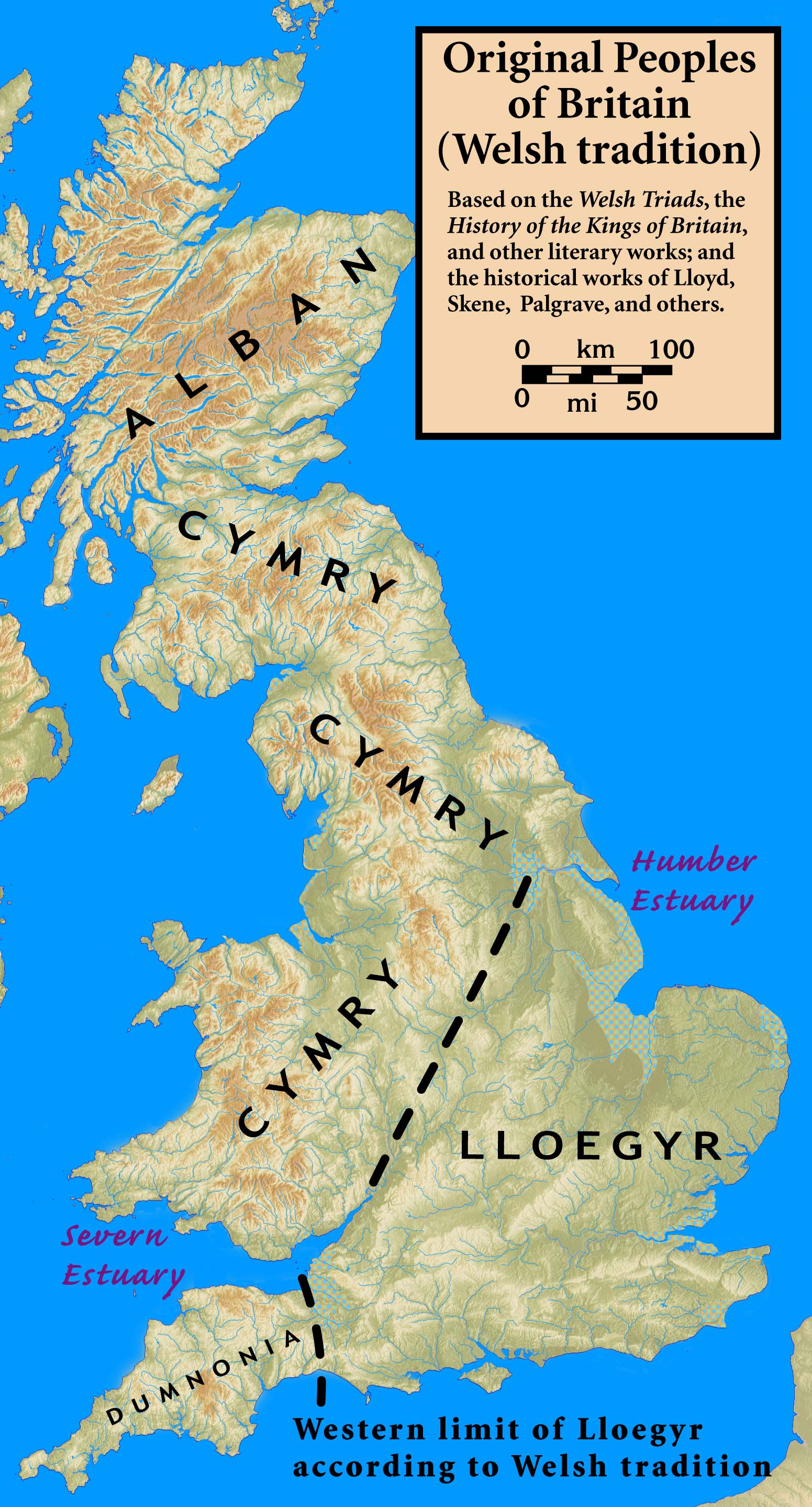
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English-language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scottish people, Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Scotland in the Late Middle Ages, Kingdom of Scotland of the late Middle Ages following the absorption of Kingdom of Strathclyde, Strathclyde and English-speaking Lothian in the 12th century. It is cognate with the Irish term ' (gen. ', dat. ') and the Manx language, Manx term ', the two other Goidelic languages, Goidelic Insular Celtic languages, as well as contemporary words used in Cornish language, Cornish (') and Welsh language, Welsh ('), both of which are Brythonic languages, Brythonic Insular Celtic languages. The third surviving Brythonic language, Breton language, Breton, instead uses ', meaning 'country of the Scots'. In the past, these terms were names for Great Britain as a whole, related to the Brythonic name Albion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fracture in the Crust (geology), crust, on land or underwater, usually at temperatures from . The volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is often also called ''lava''. A lava flow is an outpouring of lava during an effusive eruption. (An explosive eruption, by contrast, produces a mixture of volcanic ash and other fragments called tephra, not lava flows.) The viscosity of most lava is about that of ketchup, roughly 10,000 to 100,000 times that of water. Even so, lava can flow great distances before cooling causes it to solidify, because lava exposed to air quickly develops a solid crust that insulates the remaining liquid lava, helping to keep it hot and inviscid enough to continue flowing. Etymology The word ''lava'' comes from Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tharsis Quadrangle
The Tharsis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 list of quadrangles on Mars, quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Tharsis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-9 (Mars Chart-9). The name Tharsis refers to a land mentioned in the Bible. It may be at the location of the old town of Tartessus at the mouth of Guadalquivir. The quadrangle (geography), quadrangle covers the area from 90° to 135° west longitude and 0° to 30° north latitude on Mars and contains most of the Tharsis, Tharsis Rise. The plateau is about as high as Earth's Mount Everest and about as big in area as all of Europe. Tharsis contains a group of large volcanoes. Olympus Mons is the tallest. Within the quadrangle, the two largest impact craters are Poynting (Martian crater), Poynting and Paros (crater), Paros. Volcanoes Tharsis is a land of great volcanoes. Olympus Mons is the tallest known volcano in the Solar System; it is 100 times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diacria Quadrangle
The Diacria quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northwestern portion of Mars' western hemisphere and covers 180° to 240° east longitude (120° to 180° west longitude) and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Diacria quadrangle is also referred to as MC-2 (Mars Chart-2). The Diacria quadrangle covers parts of Arcadia Planitia and Amazonis Planitia. The southern and northern borders of the Diacria quadrangle are approximately and wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about (slightly less than the length of Greenland). The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars' surface area. The '' Phoenix'' lander's landing site (68.22° N, 234.25° E) lies about north of the northeastern qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcadia Quadrangle
The Arcadia quadrangle is one of a series of list of quadrangles on Mars, 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle (geography), quadrangle is located in the north-central portion of Mars’ western hemisphere and covers 240° to 300° east longitude (60° to 120° west longitude) and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Arcadia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-3 (Mars Chart-3). The name comes from a mountainous region in southern Greece. It was adopted by IAU, in 1958. The southern and northern borders of the Arcadia quadrangle are approximately 3,065 km and 1,500 km wide, respectively. The north to south distance is about 2,050 km (slightly less than the length of Greenland). The quadrangle covers an approximate area of 4.9 million square km, or a little over 3% of Mars’ surface a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alba Mons MOLA Zoom 64
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English-language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kingdom of Scotland of the late Middle Ages following the absorption of Strathclyde and English-speaking Lothian in the 12th century. It is cognate with the Irish term ' (gen. ', dat. ') and the Manx term ', the two other Goidelic Insular Celtic languages, as well as contemporary words used in Cornish (') and Welsh ('), both of which are Brythonic Insular Celtic languages. The third surviving Brythonic language, Breton, instead uses ', meaning 'country of the Scots'. In the past, these terms were names for Great Britain as a whole, related to the Brythonic name Albion. Etymology The term first appears in classical texts as ' or ' (in Ptolemy's writings in Greek), and later as ' in Latin documents. Historically, the term refers to Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the structural integrity of such a chamber, greatly diminishing its capacity to support its own roof and any substrate or rock resting above. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a Volcanic crater, crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur over the course of a century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times within a given window of 100 years. Only eight caldera-forming collapses are known to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded on 28 July 1919 in Brussels, Belgium and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. the Union had 85 national members and 12,734 individual members, spanning 90 countries and territories. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Crater
An impact crater is a depression (geology), depression in the surface of a solid astronomical body formed by the hypervelocity impact event, impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Impact craters are typically circular, though they can be elliptical in shape or even irregular due to events such as landslides. Impact craters range in size from microscopic craters seen on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program to simple bowl-shaped depressions and vast, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth. Impact craters are the dominant geographic features on many solid Solar System objects including the Moon, Mercury (planet), Mercury, Callisto (moon), Callisto, Ganymede (moon), Ganymede, and most small moons and asteroids. On other planet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patera
In the material culture of classical antiquity, a ''patera'' () or ''phiale'' ( ) is a shallow ceramic or metal libation bowl. It often has a bulbous indentation ('' omphalos'', "belly button") in the center underside to facilitate holding it, in which case it is sometimes called a ''mesomphalic phiale''. It typically has no handles, and no feet. Although the two terms may be used interchangeably, particularly in the context of Etruscan culture, ''phiale'' is more common in reference to Greek forms, and ''patera'' in Roman settings. The form should be distinguished from a drinking cup with handles, and often a stem, of which the most common type is called a '' kylix'', and a circular platter with a pair of C-handles is not a ''patera'', though a few ''paterae'' have single long straight handles (see ''trulla'' below). Use Libation was a central and vital aspect of ancient Greek religion, and one of the simplest and most common forms of religious practice. It is one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
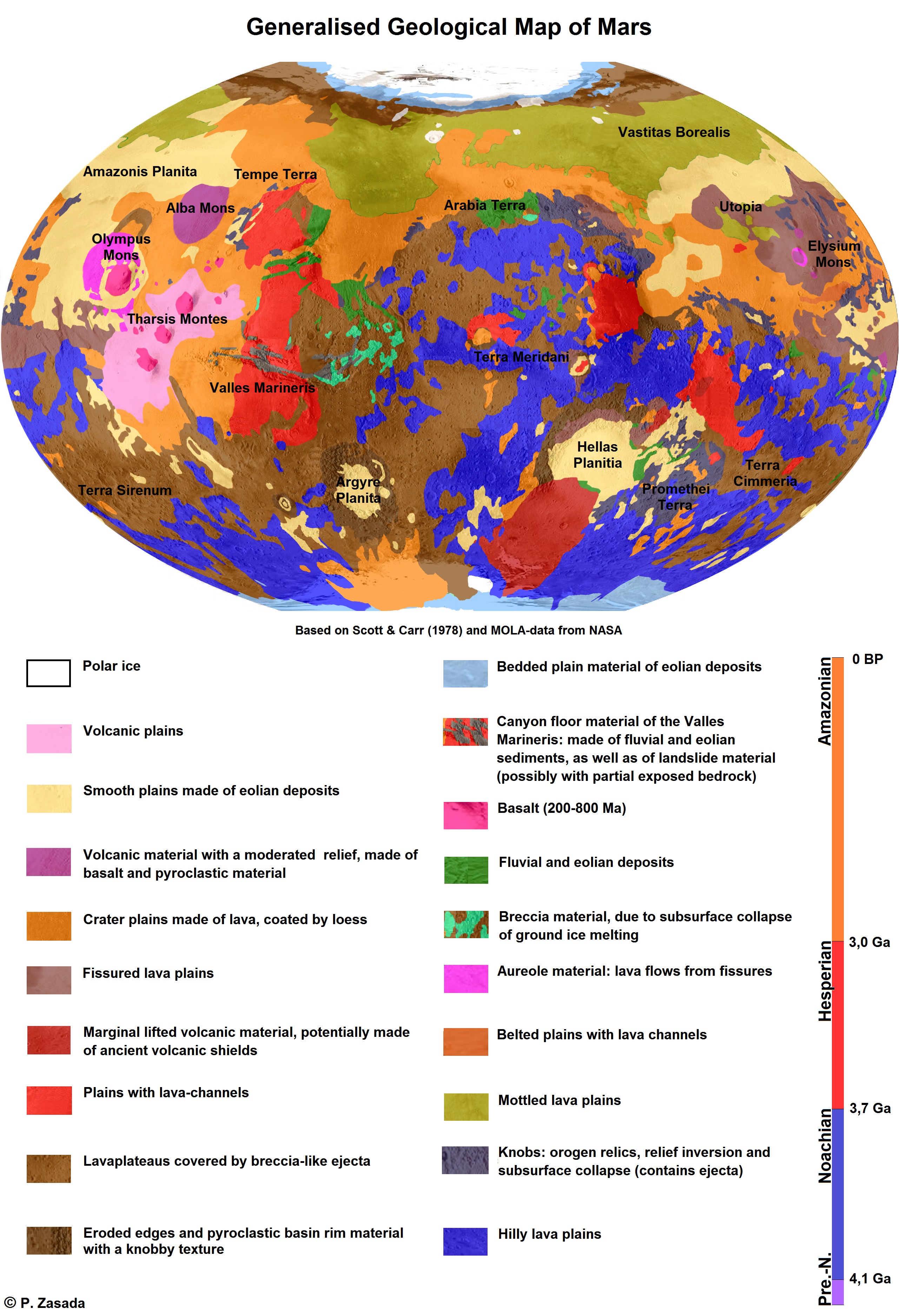
Geology Of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term ''geology'' is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. A neologism, areology, from the Greek word ''Arēs'' (Mars), sometimes appears as a synonym for Mars's geology in the popular media and works of science fiction (e.g. Kim Stanley Robinson's Mars trilogy). The term areology is also used by the Areological Society. Geological map of Mars (2014) File:Geologic Map of Mars figure2.pdf, Figure 2 for the geologic map of Mars Composition of Mars Mars is a terrestrial planet, which has undergone the process of planetary differentiation. The ''InSight'' l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |