|
Akuaba
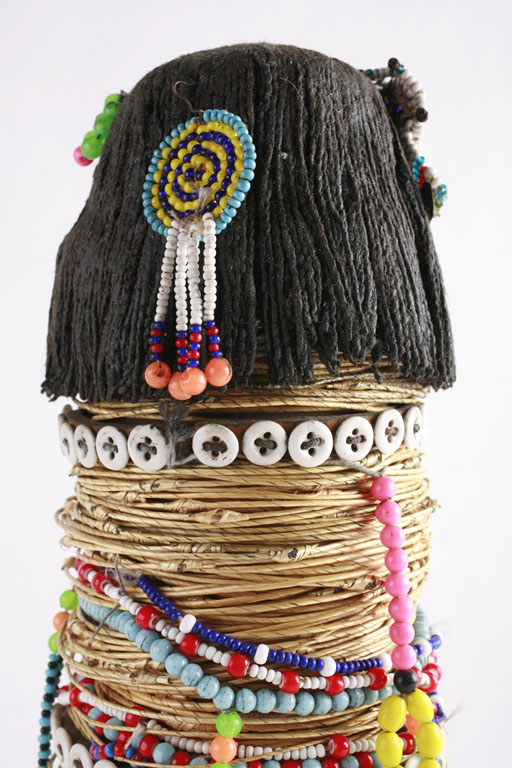
Akua'ba, also spelled akwaba or akuba, are wooden ritual fertility dolls originating from western Ghana and nearby regions. They are particularly associated with the Fanti people, who are part of the Akan group of ethnicities in Ghana and Ivory Coast. The dolls are characterized by their large, disc-like heads and are used traditionally by young women seeking to conceive a child or to ensure the attractiveness of their future children. When not in use, akua'ba are ritually washed and cared for in the traditional homestead. The treatment of the ''akua'ba'' has been described as an example of traditional beliefs that corresponds to many traditional beliefs in West African sympathetic magic. While the Fanti are best known for their akua'ba, other tribes in the West African region, such as the Kru and Igbo people, have their own distinctive styles of fertility dolls. These dolls are often used in similar ways, reflecting the importance of fertility and children in many West Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doll
A doll is a physical model, model typically of a human or humanoid character, often used as a toy for children. Dolls have also been used in traditional religious rituals throughout the world. Traditional dolls made of materials such as clay and wood are found in the Americas, Asia, Africa and Europe. The earliest documented dolls go back to the ancient civilizations of Ancient Egypt, Egypt, Ancient Greece, Greece, and Ancient Rome, Rome. They have been made as crude, rudimentary playthings as well as elaborate art. Modern doll manufacturing has its roots in Germany, from the 15th century. With Industrialisation, industrialization and new materials such as porcelain and plastic, dolls were increasingly mass-produced. During the 20th century, dolls became increasingly popular as collectibles. History, types and materials Early history and traditional dolls The earliest dolls were made from available materials such as clay, stone, wood, bone, ivory, leather, or wax. Archaeology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Art
African art encompasses modern and historical paintings, sculptures, installations, and other visual cultures originating from indigenous African diaspora, African communities across the African continent. The definition may also include the art of the African diasporas, such as art in African-American, Caribbean, and South American societies inspired by African traditions. Although diverse there are unifying artistic themes across the visual cultures from the continent of Africa. Often, art was not created for its own sake, but for social, political, or religious purposes. African art is characterized by an emphasis on conceptual or symbolic representations, rather than imitating nature, aiming to capture the subject's spiritual essence. Pottery#Africa, Pottery, Metalworking, metalwork, sculpture, Architecture of Africa, architecture, textile art, and fiber art are important Visual arts, visual art forms across Africa and may be included in the study of African Art. The term � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akuaba
Akua'ba, also spelled akwaba or akuba, are wooden ritual fertility dolls originating from western Ghana and nearby regions. They are particularly associated with the Fanti people, who are part of the Akan group of ethnicities in Ghana and Ivory Coast. The dolls are characterized by their large, disc-like heads and are used traditionally by young women seeking to conceive a child or to ensure the attractiveness of their future children. When not in use, akua'ba are ritually washed and cared for in the traditional homestead. The treatment of the ''akua'ba'' has been described as an example of traditional beliefs that corresponds to many traditional beliefs in West African sympathetic magic. While the Fanti are best known for their akua'ba, other tribes in the West African region, such as the Kru and Igbo people, have their own distinctive styles of fertility dolls. These dolls are often used in similar ways, reflecting the importance of fertility and children in many West Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Dolls
African dolls across the continent are created for young girls to play with and as a charm to ensure fertility in women. Their shape and costume vary according to region and custom. Frequently dolls are handed down from mother to daughter. Western dolls are popular in Africa and are often dressed with traditional garb. When the doll concept is considered in the context of African culture, they are usually not children's playthings, but rather objects that are laden with ritual and religious associations within the community. African dolls are used to teach, and entertain. They are supernatural intermediaries and they are manipulated for ritual purposes. Each of these dolls is unique because they are handmade and are traditionally handed down through generations. Ndebele dolls Linga Koba dolls are from the Ndebele people in Southern Africa. One of the smallest tribes of the region, the Ndebele are noted for their painted homes of brilliant colors that stand out in the drab countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Ghana
Ghana is a country of 33.48 million people and many native groups, such as: * The Akan people, Akans in the center and South of the country, * The Ga people, Ga and Adangbe in, around, and East of Accra, * The Guang people, Guan people in the rainforest, * The Dagomba people, Dagombas, Mamprusi people, Mamprusi, and related peoples in the North, * The Gurunsi languages speaking peoples in the far North, * The Gonja people, Gonjas in the Northern Region. English language, English is the official language, with the indigenous Akan language, Twi of the Ashanti people, Ashantis, the Fante language, Frafra language, Frafra, Dangme language, Dangme, Ga language, Ga, Dagbani language, Dagbani, Mampruli language, Mampruli, Gonja language, Gonja, and Ewe language, Ewe also having official status, and being taught in schools as indigenous (local) languages in the respective areas where they are predominant. People Akans The Akan people primarily live in Ghana, parts of Ivory Coast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fertility
Fertility in colloquial terms refers the ability to have offspring. In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to reproduce, which is termed fecundity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born during an individual's lifetime. In medicine, fertility refers to the ability to have children, and infertility refers to difficulty in reproducing naturally. In general, infertility or subfertility in humans is defined as not being able to conceive a child after one year (or longer) of unprotected sex. The antithesis of ''fertility'' is infertility, while the antithesis of ''fecundity'' is sterility. Demography In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to produce which is termed fecundity. While fertility can be measured, fecundity cannot be. Demographers measure the fertility rate in a variety of ways, which can be broa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghana
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to the east. Ghana covers an area of , spanning diverse ecologies, from coastal savannas to tropical rainforests. With nearly 35 million inhabitants, Ghana is the second-most populous country in West Africa. The capital and largest city is Accra; other significant cities include Tema, Kumasi, Sunyani, Ho, Cape Coast, Techiman, Tamale, and Sekondi-Takoradi. The earliest kingdoms to emerge in Ghana were Bonoman in the south and the Kingdom of Dagbon in the north, with Bonoman existing in the area during the 11th century. The Asante Empire and other Akan kingdoms in the south emerged over the centuries. Beginning in the 15th century, the Portuguese Empire, followed by other European powers, contested the area for trading r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fanti People
The modern Mfantsefo or Fante ("Fanti" is an older spelling) confederacy is a combination of Akan people and aboriginal Guan people. The Fante people are mainly located in the Central and Western regions of Ghana, occupying the forest and coastal areas. Their land stretches from the eastern part of western region in the west to Gomoa in the east. The Fante can be broadly categorized into two groups - the Borbor/Boka Fante (Akan ancestry) and the Etsii Fante (Guan ancestry). Over the last half century, Fante communities have been established as far as Gambia, Liberia,Côte d'Ivoire and even Angola due to fishing expeditions. Major Fante cities and towns in modern Ghana include Cape Coast, Saltpond,Sekondi,Elmina, Agona Swedru, Mankessim,Winneba, Shama, Apam, Komenda, Kasoa and Anomabo. According to their oral traditions, the Borbor Fante, an intrusive group, migrated from Tekyiman in the Brong Ahafo Region of Ghana and settled in Fanteland. They initially established them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akan People
The Akan () people are a kwa languages, Kwa group living primarily in present-day Ghana and in parts of Ivory Coast and Togo in West Africa. The Akan speak languages within the Central Tano languages, Central Tano branch of the Potou–Tano languages, Potou–Tano subfamily of the Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo family.''Languages of the Akan Area: Papers in Western Kwa Linguistics and on the Linguistic Geography of the Area of Ancient''. Isaac K. Chinebuah, H. Max J. Trutenau, Linguistic Circle of Accra, Basler Afrika Bibliographien, 1976, pp. 168. Subgroups of the Akan people include: the Adansi, Agona, Akuapem people, Akuapem, Akwamu, Akyem, Anyi people, Anyi, Ashanti people, Asante, Baoulé people, Baoulé, Bono people, Bono, Chakosi people, Chakosi, Fante people, Fante, Kwahu, Sefwi people, Sefwi, Wassa, Ahanta people, Ahanta, Denkyira and Nzema people, Nzema, among others. The Akan subgroups all have cultural attributes in common; most notably the tracing of royal m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs following sexual intercourse, vaginal intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a Live birth (human), live birth, a miscarriage, an Abortion#Induced, induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the Menstruation#Onset and frequency, last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the Gestational age (obstetrics), ''gestational age''; this is just over nine months. Counting by Human fertilization#Fertilization age, ''fertilization age'', the length is about 38 weeks. Implantation (embryology), Implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after Human fertilization, fertilization. An ''embryo'' is the term for the deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sympathetic Magic
Sympathetic magic, also known as imitative magic, is a type of Magic (paranormal), magic based on imitation or correspondence. Similarity and contagion James George Frazer coined the term "sympathetic magic" in ''The Golden Bough'' (1889); Richard Andree, however, anticipated Frazer, writing of sympathy-enchantment () in his 1878 . Frazer subcategorised sympathetic magic into two varieties: that relying on similarity, and that relying on contact or "contagion": Imitation Imitation involves using effigies, fetishes, or poppets to affect the environment of people, or people themselves. Voodoo dolls are an example of fetishes used in this way: the practitioner uses a lock of hair on the doll to create a link (also known as a "taglock") between the doll and the donor of this lock of hair. In this way, that which happens to the doll will also happen to the person. Correspondence Correspondence (theology), Correspondence is based on the idea that one can influence something based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Production
Mass production, also known as mass production, series production, series manufacture, or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines. Together with job production and batch production, it is one of the three main production methods. The term ''mass production'' was popularized by a 1926 article in the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' supplement that was written based on correspondence with Ford Motor Company. ''The New York Times'' used the term in the title of an article that appeared before the publication of the ''Britannica'' article. The idea of mass production is applied to many kinds of products: from fluids and particulates handled in bulk (food, fuel, chemicals and mined minerals), to clothing, textiles, parts and assemblies of parts ( household appliances and automobiles). Some mass production techniques, such as standardized sizes and production lines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |