|
Air Board (Australia)
The Air Board, also known as the Administrative Air Board, or the Air Board of Administration, was the controlling body of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) from 1921 to 1976. It was composed of senior RAAF officers as well as some civilian members, and chaired by the Chief of Air Force (Australia), Chief of the Air Staff (CAS). The CAS was the operational head of the Air Force, and the other board members were responsible for specific areas of the service such as personnel, supply, engineering, and finance. Originally based in Melbourne, the board relocated to Canberra in 1961. Formed in November 1920, the Air Board's first task was to establish the air force that it was to administer; this took place in March 1921. The board was initially responsible to the Australian Air Council, which included the chiefs of the Australian Army, Army and Royal Australian Navy, Navy; after the council's dissolution in 1929 the Air Board had equal status with the other service boards, repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Australian Air Force
The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) is the principal Air force, aerial warfare force of Australia, a part of the Australian Defence Force (ADF) along with the Royal Australian Navy and the Australian Army. Constitutionally the Governor-General of Australia, governor-general of Australia is the de jure commander-in-chief of the Australian Defence Force. The Royal Australian Air Force is commanded by the Chief of Air Force (Australia), Chief of Air Force (CAF), who is subordinate to the Chief of the Defence Force (Australia), Chief of the Defence Force (CDF). The CAF is also directly responsible to the Minister for Defence (Australia), Minister for Defence, with the Department of Defence (Australia), Department of Defence administering the ADF and the Air Force. Formed in March 1921, as the Australian Air Force, through the separation of the Australian Air Corps from the Army in January 1920, which in turn amalgamated the separate aerial services of both the Army and Navy. It d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deputy Chief Of Air Force (Australia)
Deputy Chief of Air Force (DCAF) is the second most senior appointment in the Royal Australian Air Force, responsible to the Chief of Air Force (CAF). Before 1997 the position was entitled Deputy Chief of the Air Staff (DCAS). The rank associated with the position is air vice marshal Air vice-marshal (Air Vce Mshl or AVM) is an air officer rank used by some air forces, with origins from the Royal Air Force. The rank is also used by the air forces of many Commonwealth of Nations, countries which have historical British infl ... ( two-star). DCAF acts as the manager of the Air Force Headquarters (AFHQ), which provides oversight of activities in the raising, training and sustaining of assigned RAAF capabilities. The position provides strategic leadership to the RAAF as a whole, as well as policy guidance in regard to Air Force activities to the rest of the Defence organisation and Government. The current Deputy Chief of Air Force is Air Vice Marshal Harvey Reynolds. Appointees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
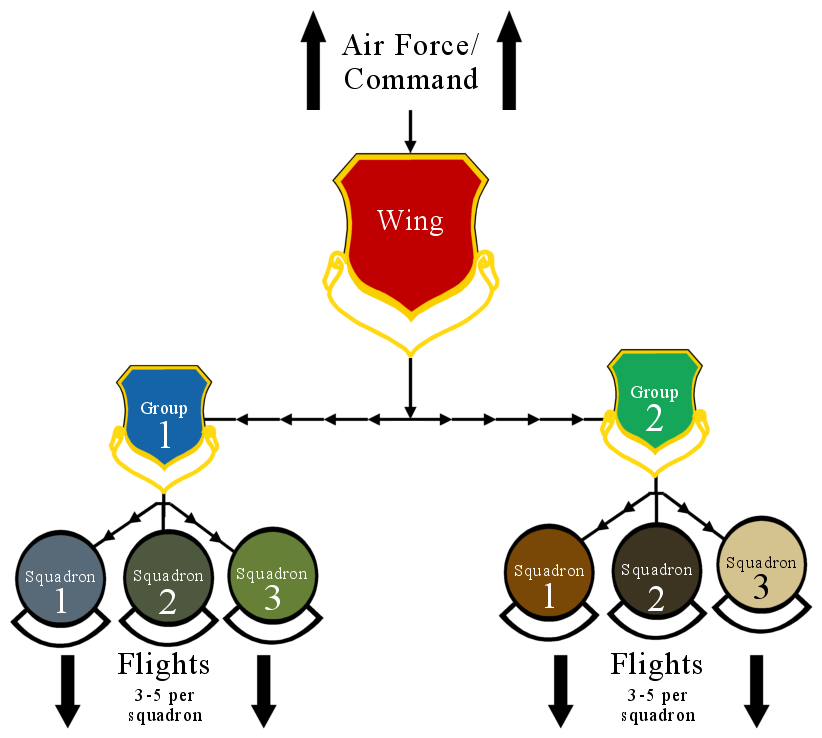
Wing (military Unit)
In military aviation, a wing is a unit of command. In most military aviation services, a wing is a relatively large formation of planes. In Commonwealth countries a wing usually comprises three squadrons, with several wings forming a group (around 10 squadrons). Each squadron will contain around 20 planes. Commonwealth usage Origins On its establishment in 1912, the British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was intended to be an inter-service, combined force of the British Army and Royal Navy. Given the rivalry that existed between the army and navy, new terminology was used, in order to avoid marking the corps out as having an army or navy ethos. While the term "wing" had been used in the cavalry, its more general use predominated. Accordingly, the word "wing", with its allusion of flight, was chosen as the term of subdivision and the corps was split into a "Military Wing" (i.e. an army wing) and a "Naval Wing". Each wing consisted of a number of squadrons (the term "squadron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percy Grant (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Sir Edmund Percy Fenwick George Grant, (23 September 1867 – 8 September 1952) was a Royal Navy officer who served as First Naval Member and Chief of the Australian Naval Staff from 1919 to 1921. Naval career Grant saw service in the Egyptian War of 1882 as well as the Brazilian Naval Mutiny in 1893. He was promoted to lieutenant on 1 October 1890, posted as a lieutenant for navigation on the battleship , and promoted to commander (Navigation) on 26 June 1902. In September 1902 he was posted to for study at the Royal Naval College, and in January the following year he was posted to the battleship HMS ''Ramillies'', serving in the Mediterranean Fleet. He went on to serve during the First World War initially as flag captain to Vice Admiral Sir Lewis Bayly in and then as flag captain and chief of staff to Admiral Sir Cecil Burney who was then second-in-command of the Grand Fleet. In that capacity he saw his ship torpedoed and crippled at the Battle of Jutland in 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Of Navy (Australia)
The Chief of Navy is the most senior appointment in the Royal Australian Navy, responsible to the Chief of the Defence Force (CDF) and the Secretary of Defence. The rank associated with the position is vice admiral ( 3-star). Vice Admiral Mark Hammond is the current Chief of Navy; he assumed the position on 6 July 2022. Appointees The following list chronologically records those who have held the post of Chief of Navy or its preceding positions. Rank and honours are as at the completion of the individual's tours. Notes {{Portal bar, Australia, Royal Australian Navy Royal Australian Navy Royal Australian Navy admirals Leadership of the Australian Defence Force Military appointments of Australia Australia Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ... Nava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Commonwealth Naval Board
The Australian Commonwealth Naval Board was the governing authority over the Royal Australian Navy from its inception and through World Wars I and II. The board was established on 1 March 1911 and consisted of civilian members of the Australian government The Australian Government, also known as the Commonwealth Government or simply as the federal government, is the national executive government of Australia, a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy. The executive consists of the pr ... as well as naval officers. References * * * History of the Royal Australian Navy {{Australia-mil-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Board (Australia)
The Military Board, also known as the Military Board of Administration, was the controlling body of the Australian Military Forces (AMF) from 1905 to 1976. It was composed of senior military and civilian members, and chaired by the Chief of the General Staff (CGS). Initially based in Melbourne, the board relocated to Canberra in 1959. On its formation in January 1905, the regular members of the Military Board were the Minister for Defence (the president of the board), the Deputy Adjutant-General, the Chief of Intelligence, the Chief of Ordnance, and a civilian Finance Member; members of the Citizens Military Force could also attend board meetings as required. The CGS position was initiated in 1909. The board as a whole was responsible for administering the AMF, subject to the control of the Minister. In November 1939 the board came under the newly formed Department of the Army in place of the Department of Defence. In July 1942 the board was dissolved and its functions assumed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Air Corps
The Australian Air Corps (AAC) was a temporary formation of the Australian military that existed in the period between the disbandment of the Australian Flying Corps (AFC) of World War I and the establishment of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) in March 1921. Raised in January 1920, the AAC was commanded by Major William Anderson, a former AFC pilot. Many of the AAC's members were also from the AFC and would go on to join the RAAF. Although part of the Australian Army, for most of its existence the AAC was overseen by a board of senior officers that included members of the Royal Australian Navy. Following the disbandment of the AFC, the AAC was a stop-gap measure intended to remain in place until the formation of a permanent and independent Australian air force. The corps' primary purpose was to maintain assets of the Central Flying School at Point Cook, Victoria, but several pioneering activities also took place under its auspices: AAC personnel set an Australian a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Flying Corps
The Australian Flying Corps (AFC) was the branch of the Australian Army responsible for operating aircraft during World War I, and the forerunner of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). The AFC was established in 1912, though it was not until 1914 that it began flight training. In 1911, at the Imperial Conference held in London, it was decided that aviation should be developed by the national armed forces of the British Empire. Australia became the first member of the Empire to follow this policy. By the end of 1911, the Army was advertising for pilots and mechanics. During 1912, pilots and mechanics were appointed, aircraft were ordered, the site of a flying school was chosen and the first squadron was officially raised. On 7 March 1913, the government officially announced formation of the Central Flying School (CFS) and an "Australian Aviation Corps", although that name was never widely used. AFC units were formed for service overseas with the Australian Imperial Force (AIF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAAF Staff College
The Australian Defence College (ADC) comprises three joint education and training organisations operated by the Australian Defence Force in Canberra, Australian Capital Territory: * the War College, * the Australian Defence Force Training Centre (ADFTC), and * the Australian Defence Force Academy (ADFA). The ADC is commanded by a Military rank, two-star Officer (armed forces), officer. Each of the educational organisations is commanded by a one-star officer or Colonel (equivalent), titled Commandant of their organisation. The last known commander was Major General Mick Ryan (general), Mick Ryan, from January 2018 to February 2022. The Australian Defence Force Warfare Training Centre and Peace Operations Training Centre are sited at a campus at Weston, Australian Capital Territory, Weston, ACT. History of Australian Defence College The current Australian Defence College has its origins in the report of the Defence Efficiency Review from May 1997. The report recommended swee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAAF College
The Royal Australian Air Force College (commonly known as the RAAF College and abbreviated as RAAFCOL) is the Royal Australian Air Force training and education academy which is responsible for all the Air Force's initial, career development, promotion and leadership training. The RAAF College is headquartered at RAAF Base Wagga, 10 km (6 mi) east of the city of Wagga Wagga, New South Wales. History The RAAF College was founded after World War II on 1 August 1947 when it was established at Point Cook as an academy training elite aircrew (and some engineering) officer cadets; the majority of the RAAF's most senior commanders received their initial training there. It was renamed as the RAAF Academy in 1961. Its role changed substantially in 2008 when the unit re-formed at RAAF Base Wagga to become a centre for training mainly airmen and airwomenThose in ranks below those of commissioned officers An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Vice-marshal (Australia)
Air vice-marshal (abbreviated as AVM) is the third highest active rank of the Royal Australian Air Force and was created as a direct equivalent of the British Royal Air Force rank of air vice-marshal. It is also considered a two-star rank. The Australian Air Corps adopted the RAF rank system on 9 November 1920 and this usage was continued by its successor, the Royal Australian Air Force. Air vice-marshal is a higher rank than air commodore and is a lower rank than air marshal. Air vice-marshal is a direct equivalent of rear admiral in the Royal Australian Navy and major general in the Australian Army. The insignia is one light blue band (on a slightly wider black band) over a light blue band on a black broad band. The equivalent rank in the Women's Auxiliary Australian Air Force, was 'air chief commandant'. See also *Air force officer rank insignia *Australian Defence Force ranks and insignia The Australian Defence Force's (ADF) ranks of officers and enlisted personn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |