|
Agni V
Agni-V (Sanskrit: अग्नि; lit. Fire) is a land based nuclear MIRV-capable Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India. The missile has a range of more than 7,000 km. It is a three-stage, road-mobile, canisterised and solid-fuelled ballistic missile. It is one of the fastest missiles in the world, reaching speeds up to 29,400 km/h. Development Agni-V is primarily for enhancing the Indian nuclear deterrence against China. Until recently, the longest range missile India had was Agni-III with a range of 3500 km. If launched from central India this range was not sufficient to reach targets on the extreme eastern and north-eastern region of China. Most of the major economic centres of China lay on its eastern seaboard. Senior defence scientist M. Natarajan disclosed in 2007 that DRDO was working on an upgraded version of the Agni-III, known as the Agni-V, and that it would be ready ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads). Conventional weapon, Conventional, Chemical weapon, chemical, and Biological agent, biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. The Nuclear weapons of the United States, United States, Russia and weapons of mass destruction, Russia, China and weapons of mass destruction, China, France and weapons of mass destruction, France, India and weapons of mass destruction, India, the United Kingdom and weapons of mass destruction, United Kingdom, Nuclear weapons and Israel, Israel, and North Korea and weapons of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
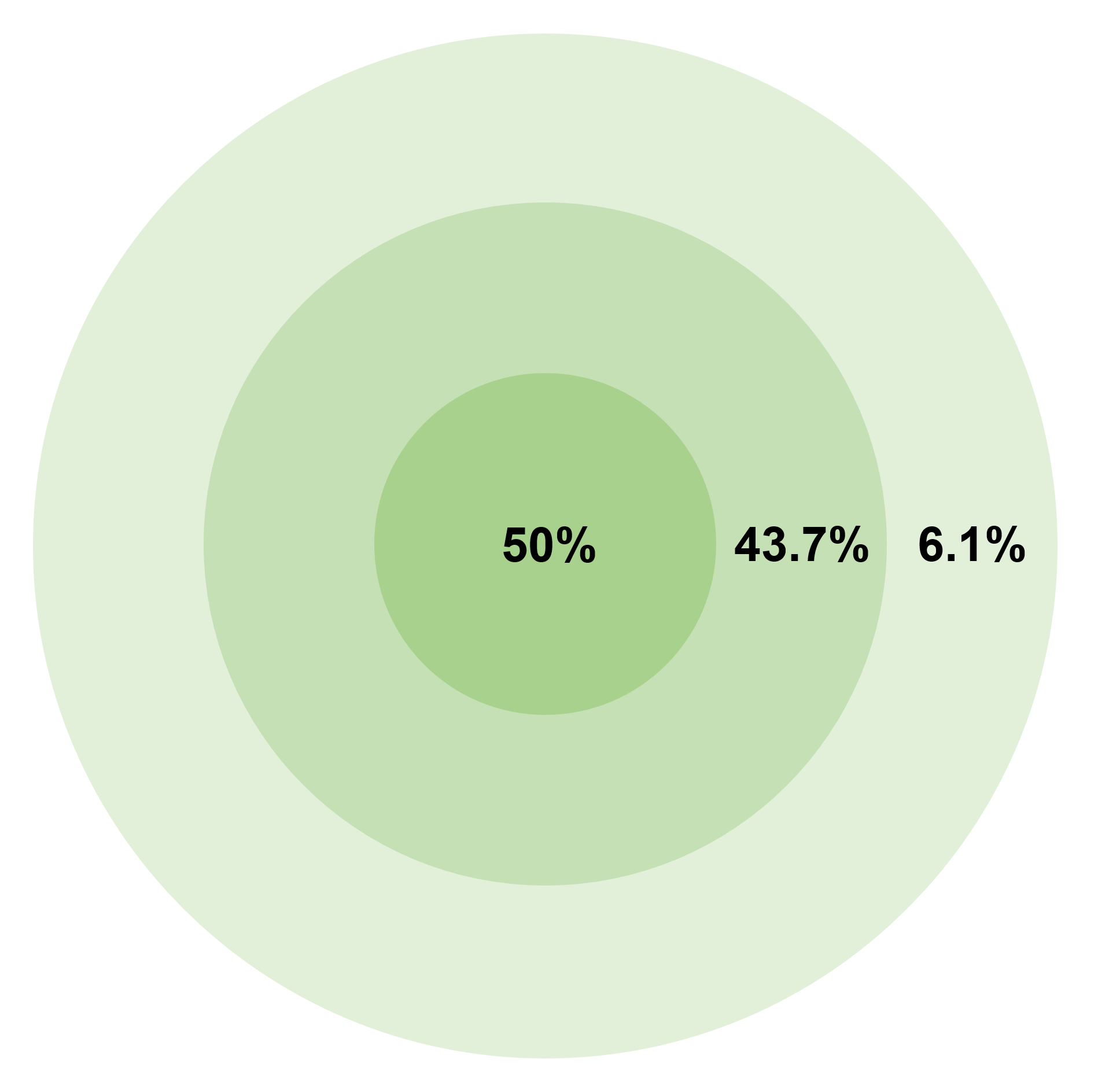
Circular Error Probable
Circular error probable (CEP),Circular Error Probable (CEP), Air Force Operational Test and Evaluation Center Technical Paper 6, Ver 2, July 1987, p. 1 also circular error probability or circle of equal probability, is a measure of a weapon system's Accuracy and precision, precision in the military science of ballistics. It is defined as the radius of a circle, centered on the aimpoint, that is expected to enclose the landing points of 50% of the Round (firearms), rounds; said otherwise, it is the median error radius, which is a 50% confidence interval. That is, if a given munitions design has a CEP of 100 m, when 100 munitions are targeted at the same point, an average of 50 will fall within a circle with a radius of 100 m about that point. There are associated concepts, such as the DRMS (distance root mean square), which is the square root of the average squared distance error, a form of the standard deviation. Another is the R95, which is the radius of the circle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Armed Forces
The Indian Armed Forces are the armed forces, military forces of the India, Republic of India. It consists of three professional uniformed services: the Indian Army, the Indian Navy, and the Indian Air Force.—— Additionally, the Indian Armed Forces are supported by the Central Armed Police Forces, the Indian Coast Guard, and the Special Frontier Force and various Jointness and integration in the Indian military, inter-service commands and institutions such as the Strategic Forces Command, the Andaman and Nicobar Command, and the Integrated Defence Staff. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Armed Forces but the executive authority and responsibility for national security is vested in the Prime Minister of India and their chosen Cabinet Committee on Security, Cabinet Ministers. The Indian Armed Forces are under the management of the Ministry of Defence (India), Ministry of Defence of the Government of India. With strength of over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NDTV
New Delhi Television Ltd is an Indian news media company focusing on broadcast and digital news publication. It was founded in 1984 by economist Prannoy Roy and journalist Radhika Roy. NDTV began as a production house for news segments, contracted by the public broadcaster Doordarshan and international satellite channels when television broadcasting was a state monopoly, and transitioned into India's first independent news network. The company launched the first 24x7 news channel in partnership with Star India in 1998. In 2003, it became an independent broadcasting network with the simultaneous launch of the Hindi and English language news channels NDTV India and NDTV 24x7. In 2022, the Adani Group, noted for its close ties with the BJP, acquired a majority stake in the company. Adani's takeover led many prominent members of the channel to resign, including Ravish Kumar. History 1984–1998: Doordarshan era In 1984, the journalist Radhika Roy and her husband, econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Press Trust Of India
The Press Trust of India Ltd., commonly known as PTI, is the largest news agency in India. It is headquartered in New Delhi and is a nonprofit cooperative among more than 450 Indian newspapers. It has over 500 full-time employees , including about 400 journalists. It also has nearly 400 part-time correspondents in most of the district headquarters of the country. PTI also has correspondents in major capitals and important business centres around the world. It was incorporated in Madras in 1947 with ''The Hindu's'' proprietor, Kasturi Srinivasan, as its Founding Chairman. It took over the operations of the Associated Press of India from Reuters in 1948–49.About PTI Press Trust of India, retrieved 14 March 2017. It provides news coverage and information of the region in both English language, English and Hindi.
|
Tessy Thomas
Tessy Thomas (born April 1963) is an Indian aerospace engineer and former Director General of Aeronautical Systems and the former Project Director for Agni-IV ballistic missile in Defence Research and Development Organisation. Early life Tessy Thomas was born during April 1963 in Kerala's Alappuzha. Career She joined the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) in 1988. Thomas began in her career working upon the Agni missile series, where she initially contributed to the guidance and control systems, focusing specifically on inertial navigation systems. She was Project Director of the Agni-V ICBM project. Personal life She is married to Saroj Kumar, a commander in the Indian Navy and they have a son,Tejas. Awards Thomas received the Lal Bahadur Shastri National Award for her contribution for making India self-reliant in the field of missile technology. She was also the recipient of the Dr Thomas Cangan Leadership Award at the Faculty of Management Studies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Laser Gyroscope
A ring laser gyroscope (RLG) consists of a ring laser having two independent counter-propagating resonant modes over the same path; the difference in phase is used to detect rotation. It operates on the principle of the Sagnac effect which shifts the nulls of the internal standing wave pattern in response to angular rotation. Interference between the counter-propagating beams, observed externally, results in motion of the standing wave pattern, and thus indicates rotation. Description The first experimental ring laser gyroscope was demonstrated in the US by Macek and Davis in 1963. Various organizations worldwide subsequently developed ring-laser technology further. Many tens of thousands of RLGs are operating in inertial navigation systems and have established high accuracy, with better than 0.01°/hour bias uncertainty, and mean time between failures in excess of 60,000 hours. Ring laser gyroscopes can be used as the stable elements (for one degree of freedom each) in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agni (missile)
The Agni missile (Sanskrit: अग्नि; lit. ''Fire'') is a family of medium to intercontinental range ballistic missiles developed by India, named after one of the five elements of nature. Agni missiles are long-range, nuclear weapons capable, surface-to-surface ballistic missiles. The first missile of the series, Agni-I was developed under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (lGMDP) and tested in 1989. After its success, the Agni missile programme was separated from the GMDP upon realizing its strategic importance. It was designated as a special programme in India's defence budget and provided adequate funds for subsequent development. , the missiles in the Agni series are being inducted into service. The family comprises the following: Agni-I The two-stage Agni technology demonstrator, with a solid-fuel first stage, was first tested at the Interim Test Range in Chandipur in 1989. It was capable of carrying a conventional payload of 1,000 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DRDO
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is an agency under the Department of Defence Research and Development in the Ministry of Defence of the Government of India, charged with the military's research and development, headquartered in New Delhi, India. It was formed in 1958 by the merger of the Technical Development Establishment and the Directorate of Technical Development and Production of the Indian Ordnance Factories with the Defence Science Organisation under the administration of Jawaharlal Nehru. Subsequently, Defence Research & Development Service (DRDS) was constituted in 1979 as a service of Group 'A' Officers / Scientists directly under the administrative control of the Ministry of Defence. With a network of 52 laboratories that are engaged in developing defence technologies covering various fields like aeronautics, armaments, electronics, land combat engineering, life sciences, materials, missiles, and naval systems, DRDO is India's largest and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centre For Air Power Studies (India)
The Centre for Air Power Studies (CAPS) is a think tank analysing issues related to national security, defence, and aerospace issues in the evolving strategic and international security environment. It was established as a research think tank on 15 September 2001, under an independent, non-profit, non-governmental trust registered in New Delhi titled "Forum for National Security Studies", officially registered under the existing regulations in New Delhi U/S 12 A of the IT Act in April 2002 and took over responsibilities for governing as the Centre for Air Power Studies (CAPS). Situated at the Western Air Command, Subroto Park in New Delhi, CAPS is India’s autonomous think tank that concentrates on subjects and disciplines relevant to the air force, especially on national defence, military affairs and strategy, air power and space and technology issues. It also focuses on national and international issues that have security implications for India. The current Director General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agni-III
The Agni-III () is an Indian intermediate-range ballistic missile inducted into service in 2011 as the successor of the Agni-II. It has a range of and can reach targets deep inside neighbouring countries including Pakistan and China. Introduction India's credible minimum deterrence envisaged a nuclear triad of counter-strike capability which required a long-range missile to provide robust second strike capability. India developed a larger missile, with a heavier payload and longer range in a compact configuration. Description The Agni-III was developed as the successor to the Agni-II. Designed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Agni-III is a two-stage ballistic missile capable of nuclear weapons delivery. DRDO formed a separate propulsion plant in September 2001 to develop large-sized solid-propellant rocket engines, including the infrastructure for propellant casting. The stubby, two-stage solid-fuel missile is compact enough for easy mobility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agni-V ICBM Night Trial Footage
Agni-V (Sanskrit: अग्नि; lit. Fire) is a land based nuclear MIRV-capable Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India. The missile has a range of more than 7,000 km. It is a three-stage, road-mobile, canisterised and solid-fuelled ballistic missile. It is one of the fastest missiles in the world, reaching speeds up to 29,400 km/h. Development Agni-V is primarily for enhancing the Indian nuclear deterrence against China. Until recently, the longest range missile India had was Agni-III with a range of 3500 km. If launched from central India this range was not sufficient to reach targets on the extreme eastern and north-eastern region of China. Most of the major economic centres of China lay on its eastern seaboard. Senior defence scientist M. Natarajan disclosed in 2007 that DRDO was working on an upgraded version of the Agni-III, known as the Agni-V, and that it would be ready ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |