|
Agha Kishi Beg
Agha Kishi Beg () was the Khan (title), khan of the Shaki Khanate from 1755 to 1759. Agha Kishi Beg was a son of Haji Chalabi Khan, the khan of Shaki and a grandson of the priest of the former church of Kish. In 1755, Haji Chalabi Khan died and was succeeded by his Agha Kishi Beg. In addition to fortifying the town of Shaki, Agha Kishi Beg carried on his father's policy of maintaining cordial ties with the nearby khanates of Shirvan Khanate, Shirvan and Quba Khanate, Quba. Agha Kishi Beg married the daughter of the Qazi-Qomuq chief in Daghestan, Mohammad Khan. In 1759, Agha Kishi Beg was persuaded to a meeting where he was killed by Mohammad Khan and the latters ally Soltan Ali, a well-known local figure. A grandson of Hajji Chalabi Khan, Muhammad Husayn Khan Mushtaq, was sent away to safety in Shirvan by the dignitaries of the Shaki khanate. He came back some months later, expelled the Qazi-Qomuq, and reinstated his family's rule in Shaki. References Sources * * {{EI2, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaki Khanate
The Shaki Khanate (also spelled Shakki; ) was a khanate under Iranian and later Russian suzerainty, which controlled the town of Shaki and its surroundings, now located in present-day Azerbaijan. History Since 1551, Shaki had been under the control of Safavid Iran (1501–1736), being part of its Shirvan province. It was governed by different tribal leaders, who were given the title of ''toyuldar'' (fief-holder). Following Nader's expulsion of the Ottoman Empire from the South Caucasus, Ali-Mardan and later Najaf Qoli were given the responsibility of governing Shaki. However, in 1743 a rebellion emerged under the leadership of the local leader and former tax-collector Haji Chalabi Khan as a response to the ineffective management by Nader's deputies. Najaf Qoli was murdered by the rebels, who chose Haji Chalabi Khan to be their khan. Nader Shah subsequently appointed the local leader Ja'far as the new khan, despite failing to expelling Haji Chalabi Khan from his fortress. A kh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Husayn Khan Mushtaq
Muhammad Husayn Khan Mushtaq (Persian: محمد حسین خان مشتاق, ), was the third khan of Shaki. He was described as a courageous but ruthless man by Abbasgulu agha Bakikhanov. Early years He was a grandson of Haji Chalabi. His father Hasan agha died in a battle against the Afsharid army. After the murder of his uncle Aghakishi beg, he fled to Shirvan and appealed for help from Aghasi Khan, who in turn defeated the Gazikumukh armies and retook Shaki. Reign Despite his succession, naib of Arash, Malik Ali, who was now styled " Sultan of Arash" did not acknowledge his suzerainty. Only in 1761 he was put under vassalage of the khanate thanks to the interference of Fatali khan Afshar who was at time campaigning in Karabakh. Malik Ali was killed shortly thereafter by the khan. He became allied to Fatali khan of Quba by 1760s in order to invade the Shirvan Khanate. In order to start the negotiation, Muhammad Said khan of Shirvan himself went to Fatali Khan's cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haji Chalabi Khan
Haji Chalabi Khan (1703 1755), was a statesman, warlord, ruler and founder of Shaki Khanate. Origin Born to a certain landlord Gurban beg during the reign of Sultan Husayn in 1703, he was of noble birth. Biographer Haji Seyid Abdulhamid mentions him as a 7th generation descendant of Darvish Mohammad Khan, last khan of Shaki before Safavid Invasion of Shirvan. Petrushevsky also thought of him being either Udi or Armenian origin. There are also some indications that he may have been descended from Shirvanshahs. Rebellion against Nader Shah He was supported by locals in opposition to corrupt Afsharid appointed viceroy Malik Najaf. His name was frequently mentioned in annals regarding to Nader Shah's Dagestan campaign. He was confirmed by Nader as an overseer to check corruption of Malik Najaf. However viceroy protested against it, causing locals to rebel. In course of rebellion, despite losing 500 families to Nader, Chalabi managed to murder Malik Najaf in 1743. To punis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Black Monk
The House of Black Monk was the ruling dynasty of the Shaki Khanate. It was first reported by Karim agha Shakikhanov, a scion of dynasty, in his ''Brief History of Shaki Khans'' written in Azerbaijani, included in Bernhard Dorn's "''Excerpts from Muhammedan writers''" in 1858. However he mistakenly attributed the book to some certain Haji Abdullatif Afandi, while Azerbaijani poet Salman Mumtaz concluded that in fact it was Karim Shakikhanov's work. It was republished in 1958, this time under the name of Karim agha. According to Azerbaijani historian Adalat Tahirzada, book might be commissioned by Ivan Paskevich - Russian general in Caucasus. History According to the legend, the progenitor of this house was a Christian (probably Armenian or Udi) monk living in Nukha. He married his son to a daughter of another priest serving in Kish. The monk's son, Jandar later converted to Islam, receiving the name "Alijan" (). According to another scion of the dynasty, Mustafa agha Shakikhan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khan (title)
Khan (, , ) is a historic Turkic peoples, Turkic and Proto-Mongols, Mongolic title originating among nomadic tribes in the Eurasian Steppe#Divisions, Central and Eastern Eurasian Steppe to refer to a king. It first appears among the Rouran and then the Göktürks as a variant of khagan (sovereign, emperor) and implied a subordinate ruler. In the Seljuk Empire, Seljük Empire, it was the highest noble title, ranking above malik (king) and emir (prince). In the Mongol Empire it signified the ruler of a Orda (organization), horde (''ulus''), while the ruler of all the Mongols was the khagan or great khan. It is a title commonly used to signify the head of a Pashtun Pashtun tribes, tribe or clan. The title subsequently declined in importance. During the Safavid Iran, Safavid and Qajar Iran, Qajar dynasty it was the title of an army general high noble rank who was ruling a province, and in Mughal Empire, Mughal India it was a high noble rank restricted to courtiers. After the downfal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
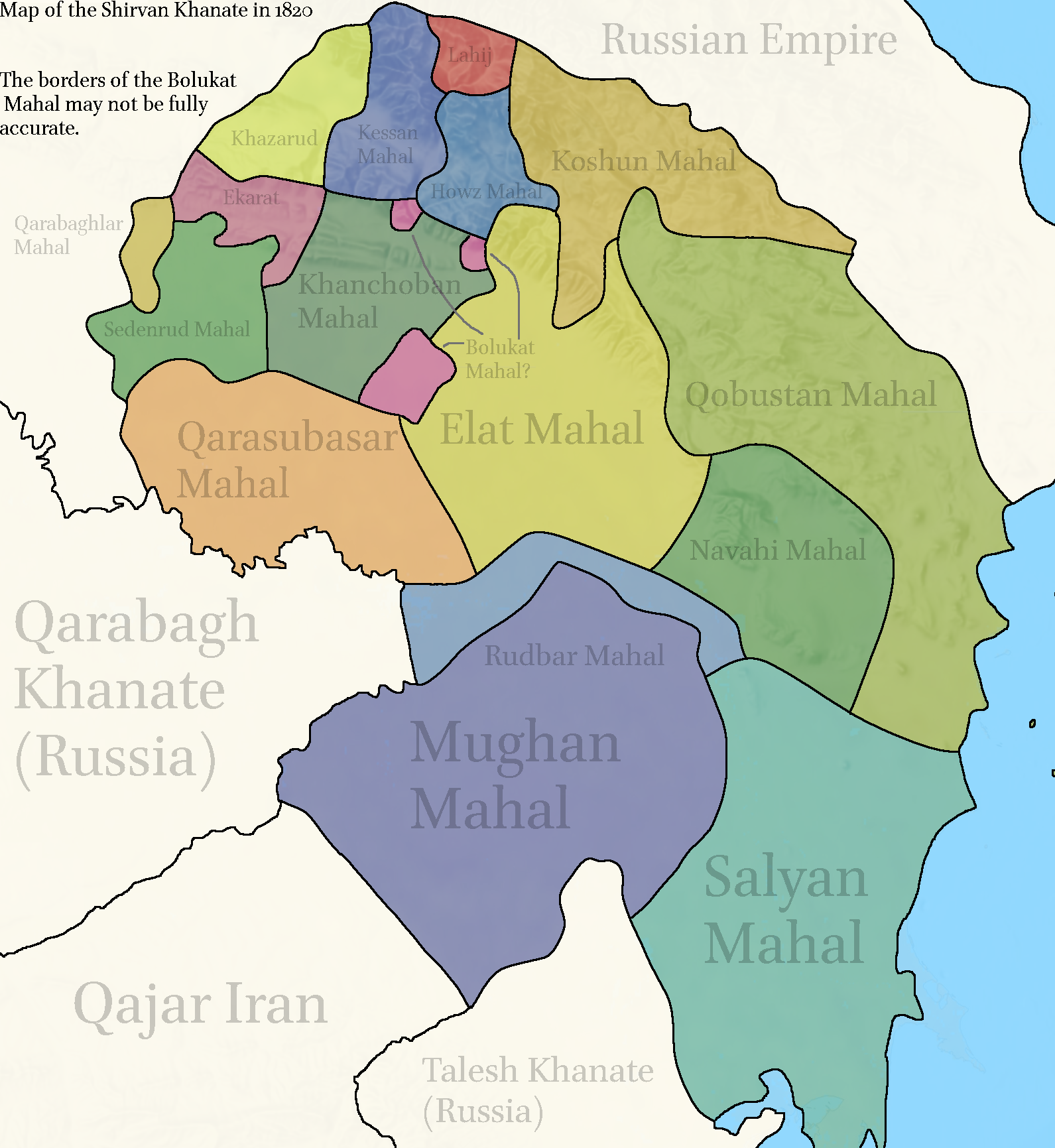
Shirvan Khanate
Shirvan Khanate () was a Caucasian khanate under Iranian suzerainty, which controlled the Shirvan region from 1761 to 1820. Background Under the Safavid dynasty of Iran, Shirvan was a leading silk manufacturer and its principal city, Shamakhi, became an important place for trade. In 1724, most of Shirvan was annexed to the Ottoman Empire by the Treaty of Constantinople. In 1734, the Iranian military leader Nader recovered Shirvan and installed Mohammad Mehdi Khan as its '' beglarbegi'' (governor-general). The following year, Mohammad Mehdi Khan was killed by rebellious dignitaries of the province. They had been incited by the governor of Darband, Morad-Ali Soltan Ostajlu. Mohammad Qasem Beg, who was a prominent dignitary of Shirvan and Nader's ''ishikaghasi-bashi'' (chamberlain), successfully appealed to Nader to pardon Shirvan. In 1735, Nader had the inhabitants of Shamakhi resettled in New Shamakhi ( Aqsu), situated 18 miles north of the Kur River. He then installed as Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quba Khanate
The Quba Khanate (also spelled Qobbeh; ) was one of the most significant semi-independent khanates that existed from 1747 to 1806, under Iranian suzerainty. It bordered the Caspian Sea to the east, Derbent Khanate to the north, Shaki Khanate to the west, and Baku and Shirvan Khanates to the south. In 1755 it captured Salyan from the Karabakh Khanate. History The khans of Quba were from the Qeytaq tribe, which was divided into two branches, the Majales and the Yengikend. The origin of the tribe is obscure. First attested in the 9th-century, only their chieftain and his family were Muslims, according to the historian al-Masudi (died 956). The chieftain bore the Turkic title of ''Salifan'', as well as the title of ''Kheydaqan-shah''. According to the 17th-century Ottoman historian, Evliya Çelebi (died 1682), the Qeytaq spoke Mongolian, but this was dismissed as a "hoax" by the Iranologist Vladimir Minorsky (died 1966), who demonstrated that Çelebi copied the alleged Mongo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daghestan
Dagestan ( ; ; ), officially the Republic of Dagestan, is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, along the Caspian Sea. It is located north of the Greater Caucasus, and is a part of the North Caucasian Federal District. The republic is the southernmost tip of Russia, sharing land borders with the countries of Azerbaijan and Georgia to the south and southwest, the Russian republics of Chechnya and Kalmykia to the west and north, and with Stavropol Krai to the northwest. Makhachkala is the republic's capital and largest city; other major cities are Derbent, Kizlyar, Izberbash, Kaspiysk, and Buynaksk. Dagestan covers an area of , with a population of over 3.1 million, consisting of over 30 ethnic groups and 81 nationalities. With 14 official languages, and 12 ethnic groups each constituting more than 1% of its total population, the republic is one of Russia's most linguistically and ethnically diverse, and one of the most heterogeneous a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Husayn Khan Mushtaq
Muhammad Husayn Khan Mushtaq (Persian: محمد حسین خان مشتاق, ), was the third khan of Shaki. He was described as a courageous but ruthless man by Abbasgulu agha Bakikhanov. Early years He was a grandson of Haji Chalabi. His father Hasan agha died in a battle against the Afsharid army. After the murder of his uncle Aghakishi beg, he fled to Shirvan and appealed for help from Aghasi Khan, who in turn defeated the Gazikumukh armies and retook Shaki. Reign Despite his succession, naib of Arash, Malik Ali, who was now styled " Sultan of Arash" did not acknowledge his suzerainty. Only in 1761 he was put under vassalage of the khanate thanks to the interference of Fatali khan Afshar who was at time campaigning in Karabakh. Malik Ali was killed shortly thereafter by the khan. He became allied to Fatali khan of Quba by 1760s in order to invade the Shirvan Khanate. In order to start the negotiation, Muhammad Said khan of Shirvan himself went to Fatali Khan's cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brill Publishers
Brill Academic Publishers () is a Dutch international academic publisher of books, academic journals, and Bibliographic database, databases founded in 1683, making it one of the oldest publishing houses in the Netherlands. Founded in the South Holland city of Leiden, it maintains its headquarters there, while also operating offices in Boston, Paderborn, Vienna, Singapore, and Beijing. Since 1896, Brill has been a public limited company (). Brill is especially known for its work in subject areas such as Oriental studies, classics, religious studies, Jewish studies, Islamic studies, Asian studies, international law, and human rights. The publisher offers traditional print books, academic journals, primary source materials online, and publications on microform. In recent decades, Brill has expanded to Electronic publishing, digital publishing with ebooks and online resources including databases and specialty collections varying by discipline. History Founding by Luchtmans, 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From The Shaki Khanate
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |