|
African Pluvial Periods
African pluvial periods are an obsolete system of climatic periods previously used by paleontologists working in East Africa. Background The sedimentary deposits left by ancient lakes in East Africa had enabled Louis Leakey and post-war paleontologists to define major climatic periods considered wet, interspersed with drier periods. Of progressively decreasing durations, they each bore the name of the site where the first clues had been collected: Kageran ( Kagera), Kamasian, Kanjeran (Kanjera) and Gamblian. Paleontologists believed that the quasi-arid zones then became wooded savannahs where animals and prehistoric hunter-gatherers could thrive. Chronology These ancient climatic periods were only very approximately dated: * Kageran: Calabrian (Early Pleistocene) The Kageran takes its name from the Kagera River, which flows through Rwanda and northwestern Tanzania before flowing into Lake Victoria. * Kamasian: Early Middle or Central Pleistocene; the Kamasian was more or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontology
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geologic time, and assess the interactions between prehistoric organisms and their natural environment. While paleontological observations are known from at least the 6th century BC, the foundation of paleontology as a science dates back to the work of Georges Cuvier in 1796. Cuvier demonstrated evidence for the concept of extinction and how life of the past was not necessarily the same as that of the present. The field developed rapidly over the course of the following decades, and the French word ''paléontologie'' was introduced for the study in 1822, which was derived from the Ancient Greek word for "ancient" and words describing relatedness and a field of study. Further advances in the field accompanied the work of Charles Darwin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
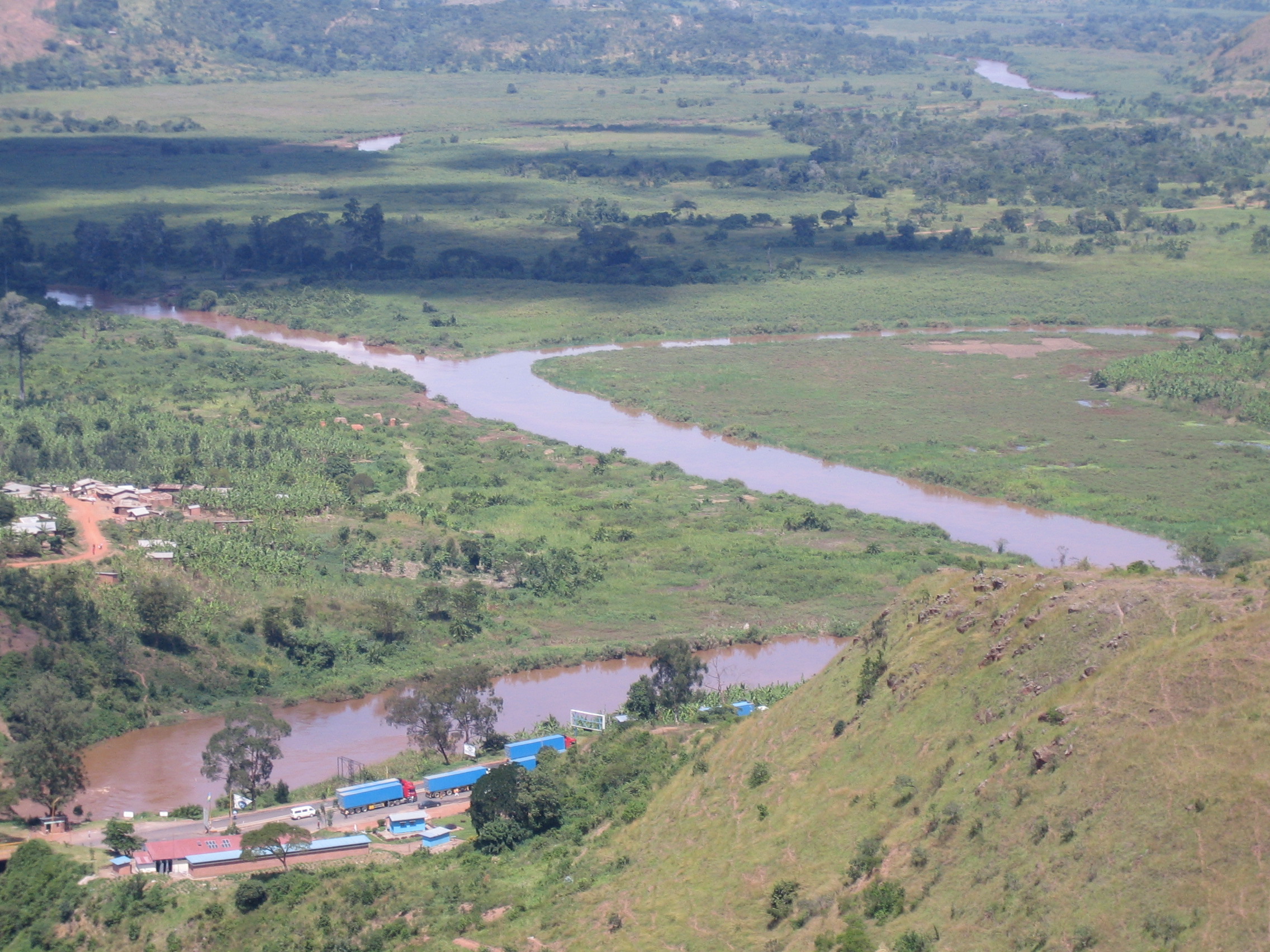
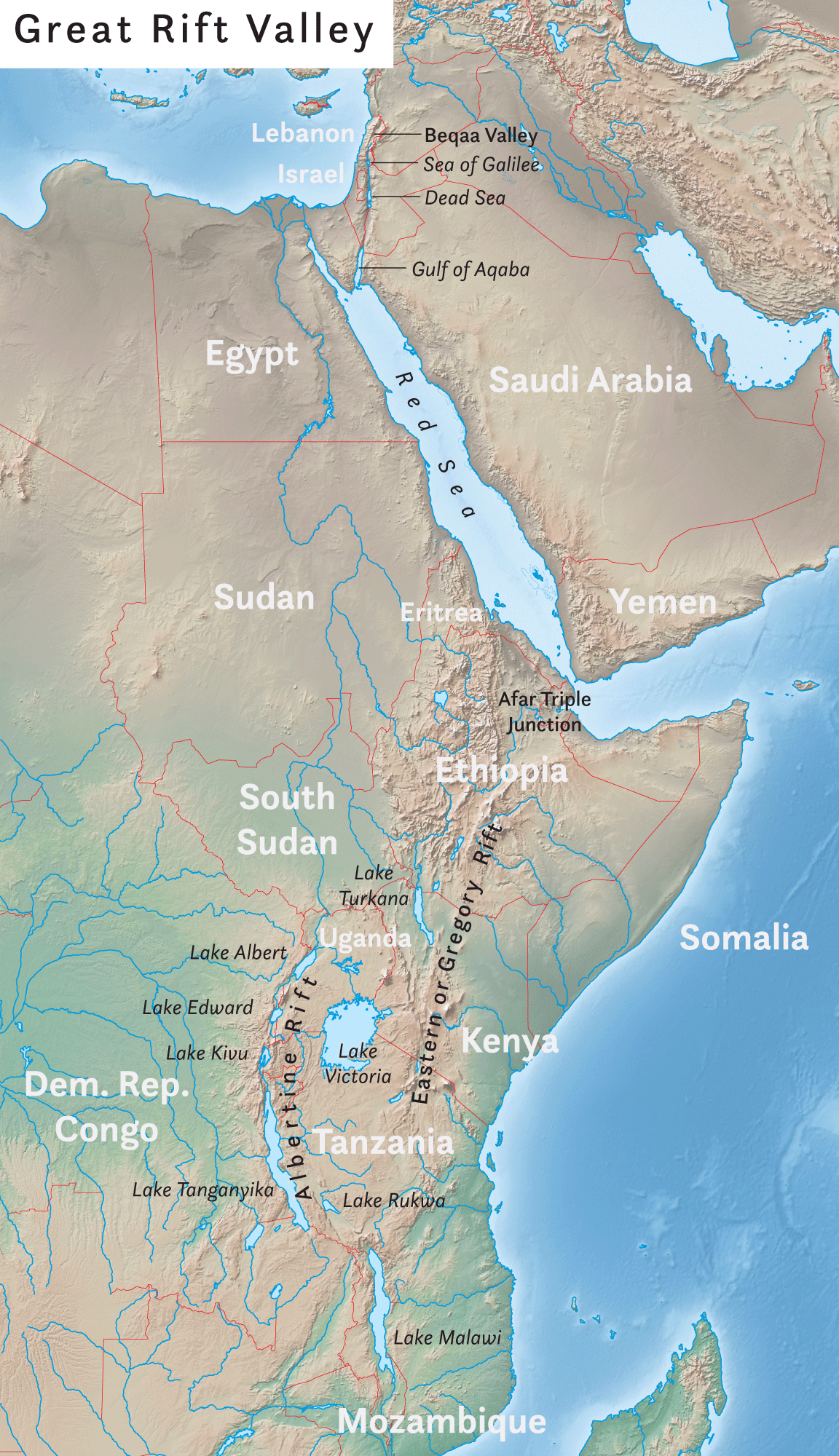
Great Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley () is a series of contiguous geographic depressions, approximately 6,000 or in total length, the definition varying between sources, that runs from the southern Turkish Hatay Province in Asia, through the Red Sea, to Mozambique in Southeast Africa. While the name remains in some usages, it is rarely used in geology where the term "Afro-Arabian Rift System" is preferred. This valley extends southward from Western Asia into the eastern part of Africa, where several deep, elongated lakes, called ribbon lakes, exist on the rift valley floor, Lake Malawi and Lake Tanganyika being two such examples. The region has a unique ecosystem and contains a number of Africa's wildlife parks. The term Great Rift Valley is most often used to refer to the valley of the East African Rift, the divergent plate boundary which extends from the Afar triple junction southward through eastern Africa, and is in the process of splitting the African plate into two new and sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Of Africa
The climate of Africa is a range of climates such as the equatorial climate, the tropical wet and dry climate, the tropical monsoon climate, the semi-arid climate (semi-desert and steppe), the desert climate (hyper-arid and arid), the humid subtropical climate, and the subtropical highland climate. Temperate climates are rare across the continent except at very high elevations and along the fringes. In fact, the climate of Africa is more variable by rainfall amount than by temperatures, which are consistently high. African deserts are the sunniest and the driest parts of the continent, owing to the prevailing presence of the subtropical ridge with subsiding, hot, dry air masses. Africa holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, the highest sunshine duration, and more. Owing to Africa's position across equatorial and subtropical latitudes in both the northern and southern hemisphere, sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mousterian Pluvial
The Mousterian Pluvial is a mostly obsolete term for a prehistoric wet and rainy (pluvial) period in North Africa. It was described as beginning around 50,000 years before the present ( BP), lasting roughly 20,000 years, and ending ca. 30,000 BP. Terminology and definition In Africa, the Mousterian industry was an archaeological term for a category of Middle Stone Age (or Middle Paleolithic) stone tool production. During the time that archaeological dates were determined by radiocarbon decay, the production of such tools was once thought to have occurred just before the limit of radiocarbon dating at 40,000 to 35,000 BP. In Europe, Mousterian tools were made by archaic Neanderthals. In Africa, such tools were made by early anatomically-modern ''Homo sapiens''. Similar people also made similar tools which are categorized as Alterian. To avoid confusion about their makers, the Mousterian and Alterian tools are now sometimes grouped as Aterian. With more recent dating methods, the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbassia Pluvial
The Abbassia Pluvial was an extended wet and rainy period in the climate history of North Africa, lasting from c. 120,000 to 90,000 years ago. As such it spans the transitional period connecting the Lower and Middle Paleolithic. As with the subsequent Mousterian Pluvial (c. 50,000 to 30,000 years ago), the Abbassia Pluvial brought wet and fertile conditions to what is now the Sahara Desert, which bloomed with lush vegetation fed by lakes, swamps, and river systems, many of which later disappeared in the drier climate that followed the pluvial. African wildlife that is now associated with the grasslands and woodlands south of the Sahara penetrated the entire North African region during the Abbassia Pluvial. Stone Age cultures (notably the Mousterian and the Aterian industries) flourished in North Africa during the Abbassia Pluvial. The shift to harsher climate conditions that came with the end of the pluvial may have promoted the emigration of modern ''Homo sapiens'' out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahara Pump Theory
The Sahara pump theory is a hypothesis that explains how flora and fauna migrated between Eurasia and Africa via a land bridge in the Levant region (the Levantine corridor). It posits that extended periods of abundant rainfall lasting many thousands of years (pluvial periods) in Africa are associated with a "wet- green Sahara" phase, during which larger lakes and more rivers existed (see North African climate cycles). This caused changes in the flora and fauna found in the area. Migration along the river corridor was halted when, during a desert phase 1.8–0.8 million years ago ( mya), the Nile ceased to flow completely and possibly flowed only temporarily in other periods due to the geologic uplift (Nubian Swell) of the Nile River region. Mechanism During periods of a wet or '' Green Sahara'', the Sahara and Arabia become a savanna grassland and African flora and fauna become common. Following inter-pluvial arid periods, the Sahara area then reverts to desert conditions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interglacial Periods
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial period, glacial and interglacial, interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma (million years ago) and is ongoing. Although geologists describe this entire period up to the present as an "ice age", in popular culture this term usually refers to the Last Glacial Period, most recent glacial period, or to the Pleistocene epoch in general. Since Earth still has polar Ice sheet, ice sheets, geologists consider the Quaternary glaciation to be ongoing, though currently in an interglacial period. During the Quaternary glaciation, ice sheets appeared, expanding during glacial periods and contracting during interglacial periods. Since the end of the last glacial period, only the Antarctic ice sheet, Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets have survived, while other sheets formed during glacial periods, such as the Laurentide Ice Sheet, hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
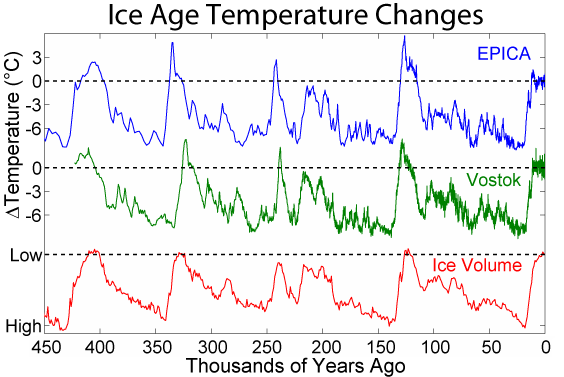
Marine Isotope Stages
Marine isotope stages (MIS), marine oxygen-isotope stages, or oxygen isotope stages (OIS), are alternating warm and cool periods in the Earth's paleoclimate, deduced from oxygen isotope data derived from deep sea core samples. Working backwards from the present, which is MIS 1 in the scale, stages with even numbers have high levels of oxygen-18 and represent cold glacial periods, while the odd-numbered stages are lows in the oxygen-18 figures, representing warm interglacial intervals. The data are derived from pollen and foraminifera (plankton) remains in drilled marine sediment cores, sapropels, and other data that reflect historic climate; these are called proxies. The MIS timescale was developed from the pioneering work of Cesare Emiliani in the 1950s, and is now widely used in archaeology and other fields to express dating in the Quaternary period (the last 2.6 million years), as well as providing the fullest and best data for that period for paleoclimatology or the stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Würm Glaciation
The Würm glaciation or Würm stage ( or ''Würm-Glazial'', colloquially often also ''Würmeiszeit'' or ''Würmzeit''; cf. ice age), usually referred to in the literature as the Würm (often spelled "Wurm"), was the last glacial period in the Alpine region. It is the youngest of the major glaciations of the region that extended beyond the Alps themselves. Like most of the other ice ages of the Pleistocene epoch, it is named after a river, in this case the Würm in Bavaria, a tributary of the Amper. The Würm ice age can be dated to about 115,000 to 11,700 years ago. Sources differ about the dates, depending on whether the long transition phases between the glacials and interglacials (warmer periods) are allocated to one or other of those periods. The average annual temperatures during the Würm ice age in the Alpine Foreland were below −3 °C (today +7 °C). That has been determined from changes in the vegetation ( pollen analysis), as well as differences in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently defined as the time between 129,000 and c. 11,700 years ago. The late Pleistocene equates to the proposed Tarantian Age of the geologic time scale, preceded by the officially ratified Chibanian (commonly known as the Middle Pleistocene). The beginning of the Late Pleistocene is the transition between the end of the Penultimate Glacial Period and the beginning of the Last Interglacial around 130,000 years ago (corresponding with the beginning of Marine Isotope Stage 5). The Late Pleistocene ends with the termination of the Younger Dryas, some 10th millennium BC, 11,700 years ago when the Holocene Epoch began. The term Upper Pleistocene is currently in use as a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |