|
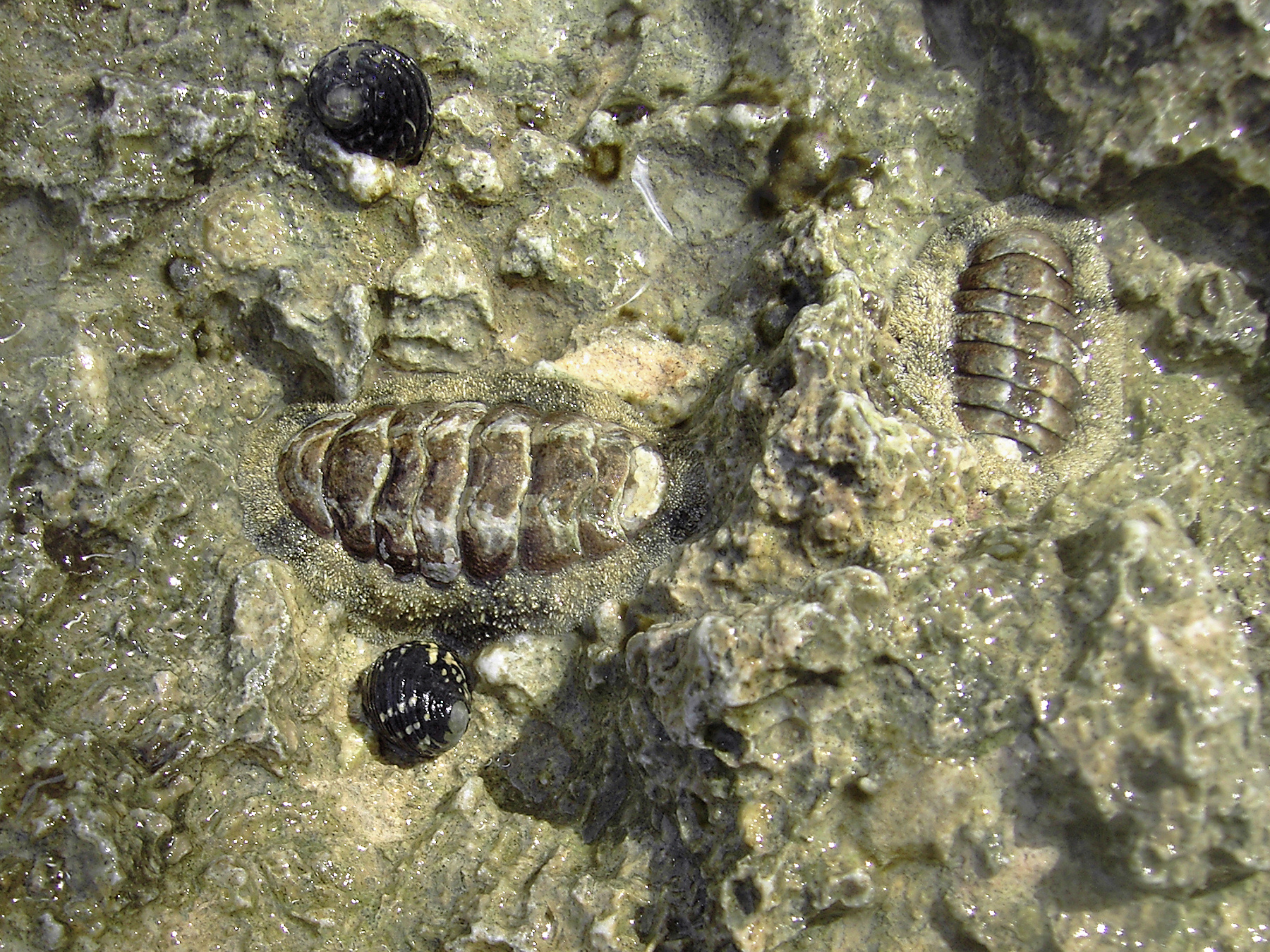
Afossochiton
''Afossochiton'' is an extinct genus of polyplacophoran molluscs. ''Afossochiton'' became extinct during the Pliocene The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58Paleogene molluscs Prehistoric chiton genera Neogene molluscs Oligocene genus first appearances [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiton
Chitons () are marine molluscs of varying size in the class Polyplacophora ( ), formerly known as Amphineura. About 940 extant and 430 fossil species are recognized. They are also sometimes known as sea cradles or coat-of-mail shells or suck-rocks, or more formally as loricates, polyplacophorans, and occasionally as polyplacophores. Chitons have a shell composed of eight separate shell plates or valves. These plates overlap slightly at the front and back edges, and yet articulate well with one another. Because of this, the shell provides protection at the same time as permitting the chiton to flex upward when needed for locomotion over uneven surfaces, and even allows the animal to curl up into a ball when dislodged from rocks. The shell plates are encircled by a skirt known as a girdle. Habitat Chitons live worldwide, from cold waters through to the tropics. They live on hard surfaces, such as on or under rocks, or in rock crevices. Some species live quite high in the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The number of additional fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000, and the proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine biology, marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat, as numerous groups are freshwater mollusc, freshwater and even terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial species. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class (biology), classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurobiology, neurologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic, Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time scale, which placed the four most recent major glaciations entirely within the Pleistocene, the Pliocene also included the Gelasian Stage, which lasted from 2.59 to 1.81 Ma, and is now included in the Pleistocene. As with other older geologic periods, the Stratum, geological strata that define the start and end are well-identified but the exact dates of the start a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleogene Molluscs
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the first period of the Cenozoic Era, the tenth period of the Phanerozoic and is divided into the Paleocene, Eocene, and Oligocene epochs. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg", although the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation "" for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps. Much of the world's modern vertebrate diversity originated in a rapid surge of diversification in the early Paleogene, as survivors of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event took advantage of empty ecologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Chiton Genera
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neogene Molluscs
The Neogene ( ,) is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period million years ago. It is the second period of the Cenozoic and the eleventh period of the Phanerozoic. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by Paleogene and Neogene and, despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. During this period, mammals and birds continued to evolve into modern forms, while other groups of life remained relatively unchanged. The first humans (''H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
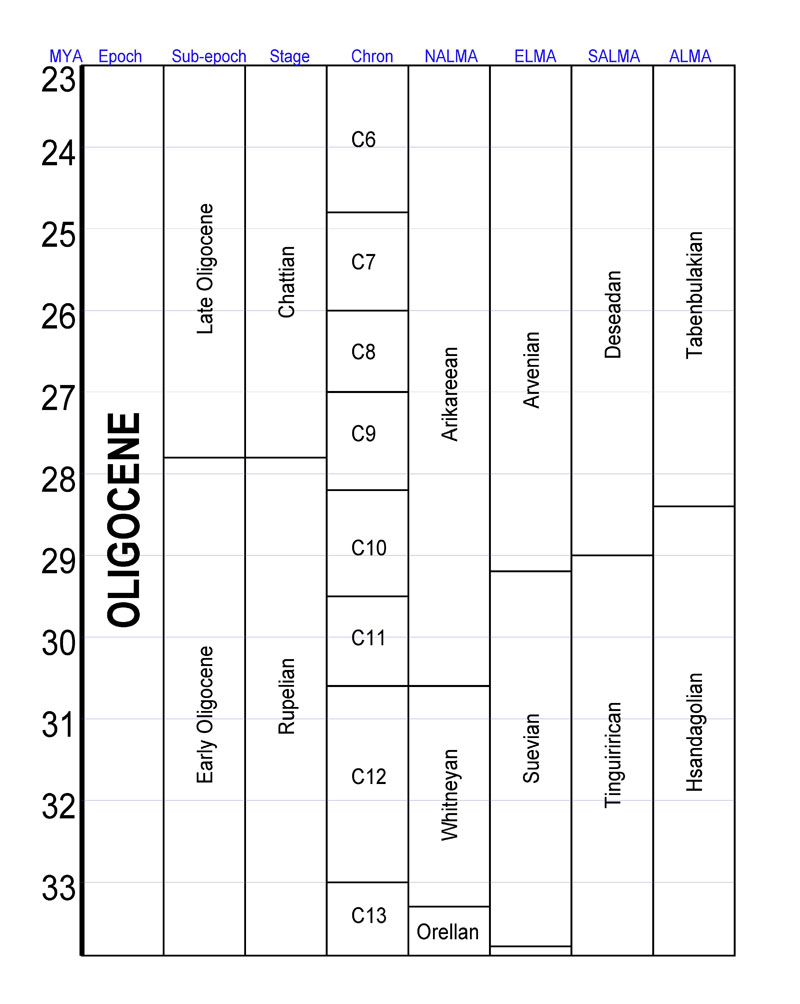
Oligocene Genus First Appearances
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major changes during the Oligocene included a global expansion of gras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |