|
Adolf Strümpell
Ernst Adolf Gustav Gottfried Strümpell, from 1893 von Strümpell (29 June 1853 – 10 January 1925), was a Baltic German neurologist. Life Strümpell was born in Neu-Autz, Courland (the present Jaunauce, Latvia), the son of the philosopher Ludwig Strümpell (1812–1899). After study in Dorpat and Leipzig, in 1875 he received his medical doctorate from the University of Leipzig, where he had as instructors Carl Wunderlich (1815–1877), Karl Thiersch (1822–1895) and Carl Ludwig (1816–1895). In 1883 he was an associate professor at Leipzig, and from 1886 to 1903 was a full professor at the University of Erlangen, succeeding Wilhelm Olivier Leube (1842–1922) as director of the medical clinic. Afterwards he was a professor at the Universities of Breslau (from 1903), Vienna (from 1909) and Leipzig (from 1910), where in 1915 he was appointed rector. Along with French neurologist Pierre Marie, he is credited with identifying and diagnosing an arthritic spinal deform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Olivier Leube
Wilhelm Olivier Leube (14 September 1842 – 16 May 1922) was a German internist born in Ulm. He studied medicine in Tübingen, Zurich, Berlin and Munich, and from 1868 worked as an assistant at the medical clinic in Erlangen. In 1872, at the University of Jena, he became a professor of pathology and special therapy, as well as director of the medical clinic. At Jena, one of his assistants was noted physician Ottomar Rosenbach (1851–1907). Afterwards he was a professor at the Universities of Erlangen (1874–1885) and Würzburg, where in 1895/96 he served as university rector. Historical Commission of the Bavarian Academy of Sciences Wilhelm Leube is remembere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Atrophy
Muscle atrophy is the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It can be caused by immobility, aging, malnutrition, medications, or a wide range of injuries or diseases that impact the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Muscle atrophy leads to muscle weakness and causes disability. Disuse causes rapid muscle atrophy and often occurs during injury or illness that requires immobilization of a limb or bed rest. Depending on the duration of disuse and the health of the individual, this may be fully reversed with activity. Malnutrition first causes fat loss but may progress to muscle atrophy in prolonged starvation and can be reversed with nutritional therapy. In contrast, cachexia is a wasting syndrome caused by an underlying disease such as cancer that causes dramatic muscle atrophy and cannot be completely reversed with nutritional therapy. Sarcopenia is age-related muscle atrophy and can be slowed by exercise. Finally, diseases of the muscles such as muscular dystrophy or myopathies can ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromegalia
Acromegaly is a disorder that results from excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There may also be an enlargement of the forehead, jaw, and nose. Other symptoms may include joint pain, thicker skin, deepening of the voice, headaches, and problems with vision. Complications of the disease may include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure. Acromegaly is usually caused by the pituitary gland producing excess growth hormone. In more than 95% of cases the excess production is due to a benign tumor, known as a pituitary adenoma. The condition is not inherited from a person's parents. Acromegaly is rarely due to a tumor in another part of the body. Diagnosis is by measuring growth hormone after a person has consumed a glucose solution, or by measuring insulin-like growth factor I in the blood. After diagnosis, medical imaging of the pituitary is carried out to deter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantile Paralysis
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe symptoms develop such as headache, neck stiffness, and paresthesia. These symptoms usually pass within one or two weeks. A less common symptom is permanent paralysis, and possible death in extreme cases.. Years after recovery, post-polio syndrome may occur, with a slow development of muscle weakness similar to that which the person had during the initial infection. Polio occurs naturally only in humans. It is highly infectious, and is spread from person to person either through fecal-oral transmission (e.g. poor hygiene, or by ingestion of food or water contaminated by human feces), or via the oral-oral route. Those who are infected may spread the disease for up to six weeks even if no symptoms are present. The disease may be diagnosed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from in the cervical and lumbar regions to in the thoracic area. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex to the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabes Dorsalis
Tabes dorsalis is a late consequence of neurosyphilis, characterized by the slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the neural tracts primarily in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord (nerve root). These patients have lancinating nerve root pain which is aggravated by coughing, and features of sensory ataxia with ocular involvement. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms may not appear for decades after the initial infection and include weakness, diminished reflexes, paresthesias (shooting and burning pains, pricking sensations, and formication), hypoesthesias (abnormally diminished sense of touch), tabetic gait (locomotor ataxia), progressive degeneration of the joints, loss of coordination, episodes of intense pain and disturbed sensation (including glossodynia), personality changes, urinary incontinence, dementia, deafness, visual impairment, positive Romberg's test, and impaired response to light ( Argyll Robertson pupil). The skeletal musculature is hypotonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Who Named It
''Whonamedit?'' is an online English-language dictionary of medical eponyms and the people associated with their identification. Though it is a dictionary, many eponyms and persons are presented in extensive articles with comprehensive bibliographies. The dictionary is hosted in Norway Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ... and maintained by medical historian Ole Daniel Enersen. References External links * Medical websites Medical dictionaries Eponyms {{online-dict-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia
Hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) is a group of inherited diseases whose main feature is a progressive gait disorder. The disease presents with progressive stiffness (spasticity) and contraction in the lower limbs. HSP is also known as hereditary spastic paraparesis, familial spastic paraplegia, French settlement disease, Strumpell disease, or Strumpell-Lorrain disease. The symptoms are a result of dysfunction of long axons in the spinal cord. The affected cells are the primary motor neurons; therefore, the disease is an upper motor neuron disease. HSP is not a form of cerebral palsy even though it physically may appear and behave much the same as spastic diplegia. The origin of HSP is different from cerebral palsy. Despite this, some of the same anti-spasticity medications used in spastic cerebral palsy are sometimes used to treat HSP symptoms. HSP is caused by defects in transport of proteins, structural proteins, cell-maintaining proteins, lipids, and other substances th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
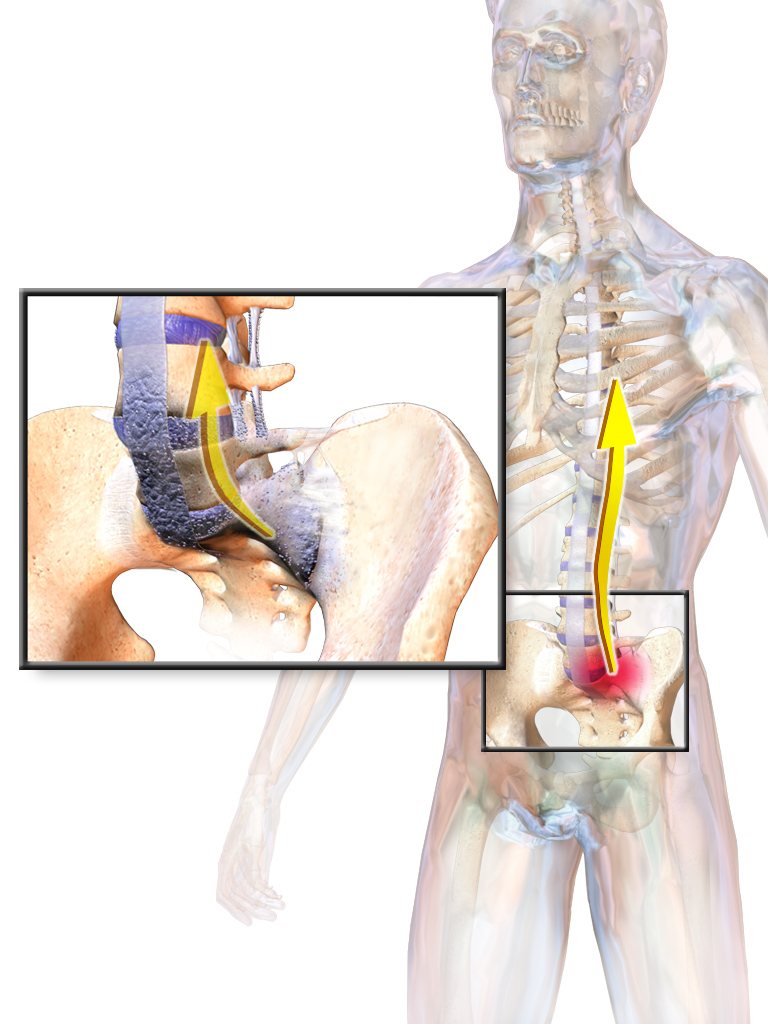
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hips, eye and bowel problems may occur as well as back pain. Joint mobility in the affected areas generally worsens over time. Although the cause of ankylosing spondylitis is unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. More than 85% of those affected in the UK have a specific human leukocyte antigen known as the HLA-B27 antigen. The underlying mechanism is believed to be autoimmune or autoinflammatory. Diagnosis is typically based on the symptoms with support from medical imaging and blood tests. AS is a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy, meaning that tests show no presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) antibodies. There is no known cure for AS. Treatments may include medication, exerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Marie
Pierre Marie (9 September 1853 – 13 April 1940) was a French neurologist and political journalist close to the SFIO. Medical Career After finishing medical school, he served as an interne (1878), working as an assistant to neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot (1825–1893) at the Salpêtrière and Bicêtre Hospitals in Paris. In 1883 he received his medical doctorate with a graduate thesis on Basedow’s disease, being promoted to ''médecin des hôpitaux'' several years later (1888). In 1907 he attained the chair of pathological anatomy at the Faculty of Medicine, and in 1917 was appointed to the chair of neurology, a position he held until 1925. In 1911 Marie became a member of the ''Académie de Médecine''. One of Marie's earlier contributions was a description of a disorder of the pituitary gland known as acromegaly. His analysis of the disease was an important contribution in the emerging field of endocrinology. Marie is also credited as the first to describe pulmonary h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |