|
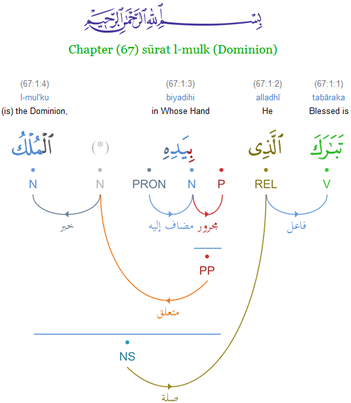
Adjective Phrase
An adjective phrase (or adjectival phrase) is a phrase whose Head (linguistics), head is an adjective. Almost any grammar or syntax textbook or dictionary of linguistics terminology defines the adjective phrase in a similar way, e.g. Kesner Bland (1996:499), Crystal (1996:9), Greenbaum (1996:288ff.), Haegeman and Guéron (1999:70f.), Brinton (2000:172f.), Jurafsky and Martin (2000:362). The adjective can initiate the phrase (e.g. ''fond of steak''), conclude the phrase (e.g. ''very happy''), or appear in a medial position (e.g. ''quite upset about it''). The dependents of the head adjective—i.e. the other words and phrases inside the adjective phrase—are typically adverb or prepositional phrases, but they can also be clauses (e.g. ''louder than you are''). Adjectives and adjective phrases function in two basic ways, attributively or Predicative expression, predicatively. An attributive adjective (phrase) precedes the noun of a noun phrase (e.g. ''a very happy'' man). A predicativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase
In grammar, a phrasecalled expression in some contextsis a group of words or singular word acting as a grammatical unit. For instance, the English language, English expression "the very happy squirrel" is a noun phrase which contains the adjective phrase "very happy". Phrases can consist of a single word or a complete sentence. In theoretical linguistics, phrases are often analyzed as units of syntactic structure such as a Constituent (linguistics), constituent. There is a difference between the common use of the term ''phrase'' and its technical use in linguistics. In common usage, a phrase is usually a group of words with some special idiomatic meaning or other significance, such as "all rights reserved", "economical with the truth", "kick the bucket", and the like. It may be a euphemism, a saying or proverb, a fixed expression, a figure of speech, etc.. In linguistics, these are known as phrasemes. In theories of syntax, a phrase is any group of words, or sometimes a single w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Ambiguity
In linguistics, an expression is semantically ambiguous when it can have multiple meanings. The higher the number of synonyms a word has, the higher the degree of ambiguity. Like other kinds of ambiguity, semantic ambiguities are often clarified by context or by prosody. One's comprehension of a sentence in which a semantically ambiguous word is used is strongly influenced by the general structure of the sentence. The language itself is sometimes a contributing factor in the overall effect of semantic ambiguity, in the sense that the level of ambiguity in the context can change depending on whether or not a language boundary is crossed. '' Lexical ambiguity'' is a subtype of semantic ambiguity where a word or morpheme is ambiguous. When a lexical ambiguity results from a single word having two senses, it is called ''polysemy''. For instance, the English "foot" is polysemous since in general it refers to the base of an object, but can refer more specifically to the foot of a perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Studia Linguistica
''Studia Linguistica: A Journal of General Linguistics'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal of general linguistics established in 1947 and currently published by Wiley-Blackwell. Its current editors-in-chief are Christer Platzack (Lund University Lund University () is a Public university, public research university in Sweden and one of Northern Europe's oldest universities. The university is located in the city of Lund in the Swedish province of Scania. The university was officially foun ...) and Arthur Holmer. Linguistics journals Wiley-Blackwell academic journals Triannual journals English-language journals {{ling-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-initial Adjective Phrases
In linguistics, head directionality is a proposed Principles and parameters, parameter that classifies languages according to whether they are head-initial (the head (linguistics), head of a phrase precedes its Complement (linguistics), complements) or head-final (the head follows its complements). The Head (linguistics), head is the element that determines the category of a phrase: for example, in a verb phrase, the head is a verb. Therefore, head initial would be Verb–object word order, "VO" languages and head final would be Object–verb word order, "OV" languages. Some languages are consistently head-initial or head-final at all phrasal levels. English grammar, English is considered to be mainly head-initial (verbs precede their objects, for example), while Japanese grammar, Japanese is an example of a language that is consistently head-final. In certain other languages, such as German language, German and Gbe languages, Gbe, examples of both types of head directionality occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-final Adjective Phrases
In linguistics, head directionality is a proposed parameter that classifies languages according to whether they are head-initial (the head of a phrase precedes its complements) or head-final (the head follows its complements). The head is the element that determines the category of a phrase: for example, in a verb phrase, the head is a verb. Therefore, head initial would be "VO" languages and head final would be "OV" languages. Some languages are consistently head-initial or head-final at all phrasal levels. English is considered to be mainly head-initial (verbs precede their objects, for example), while Japanese is an example of a language that is consistently head-final. In certain other languages, such as German and Gbe, examples of both types of head directionality occur. Various theories have been proposed to explain such variation. Head directionality is connected with the type of branching that predominates in a language: head-initial structures are ''right-branchin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern Grammar, grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of Phrase structure grammar, phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a Head (linguistics), head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb, finite verb phrase constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue ( Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining character of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. History In 1956, Chomsky wrote, "A phrase-structure grammar is defined by a finite vocabulary (alphabet) Vp, and a finite set Σ of initial strings in Vp, and a finite set F of rules of the form: X → Y, where X and Y are strings in Vp." Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin ( ; zh, s=, t=, p=Guānhuà, l=Mandarin (bureaucrat), officials' speech) is the largest branch of the Sinitic languages. Mandarin varieties are spoken by 70 percent of all Chinese speakers over a large geographical area that stretches from Yunnan in the southwest to Xinjiang in the northwest and Heilongjiang in the northeast. Its spread is generally attributed to the greater ease of travel and communication in the North China Plain compared to the more mountainous south, combined with the relatively recent spread of Mandarin to frontier areas. Many varieties of Mandarin, such as Southwestern Mandarin, those of the Southwest (including Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese) and the Lower Yangtze Mandarin, Lower Yangtze, are not mutually intelligible with the Beijing dialect (or are only partially intelligible). Nevertheless, Mandarin as a group is often placed first in lists of languages by number of native speakers (with nearly one billion). Because Mandarin originated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guglielmo Cinque
Guglielmo Cinque (born 1948 in La Spezia) is an Italian linguist and professor of linguistics at the Ca' Foscari University of Venice. He is one of the leading figures in modern minimalist syntax. Cinque studied literature and linguistics at the University of Venice, at the University of Padua, and at the University of California, Berkeley. Since 1981 he has been a professor at the Ca' Foscari University. He is an honorary member of the Linguistic Society of America. Cinque works in the fields of generative grammar Generative grammar is a research tradition in linguistics that aims to explain the cognitive basis of language by formulating and testing explicit models of humans' subconscious grammatical knowledge. Generative linguists, or generativists (), ... and language typology. Together with Luigi Rizzi he belongs to the founding figures of cartographic syntax, a research area devoted to the fine structure of languages. He is the editor (together with Richard Kayne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pragmatics
In linguistics and the philosophy of language, pragmatics is the study of how Context (linguistics), context contributes to meaning. The field of study evaluates how human language is utilized in social interactions, as well as the relationship between the interpreter and the interpreted. Linguists who specialize in pragmatics are called pragmaticians. The field has been represented since 1986 by the International Pragmatics Association (IPrA). Pragmatics encompasses phenomena including implicature, speech acts, relevance theory, relevance and Conversation analysis, conversation,Mey, Jacob L. (1993) ''Pragmatics: An Introduction''. Oxford: Blackwell (2nd ed. 2001). as well as nonverbal communication. Theories of pragmatics go hand-in-hand with theories of semantics, which studies aspects of meaning, and syntax, which examines sentence structures, principles, and relationships. The ability to understand another speaker's intended meaning is called ''pragmatic competence''. In 1938 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambiguity
Ambiguity is the type of meaning (linguistics), meaning in which a phrase, statement, or resolution is not explicitly defined, making for several interpretations; others describe it as a concept or statement that has no real reference. A common aspect of ambiguity is uncertainty. It is thus an Attribute grammar, attribute of any idea or statement whose intention, intended meaning cannot be definitively resolved, according to a rule or process with a finite number of steps. (The prefix ''wikt:ambi-#Prefix, ambi-'' reflects the idea of "2 (number), two", as in "two meanings"). The concept of ambiguity is generally contrasted with vagueness. In ambiguity, specific and distinct interpretations are permitted (although some may not be immediately obvious), whereas with vague information it is difficult to form any interpretation at the desired level of specificity. Linguistic forms Lexical ambiguity is contrasted with semantic ambiguity. The former represents a choice between a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |