|
Absolutely Maximally Entangled State
The absolutely maximally entangled (AME) state is a concept in quantum information science, which has many applications in quantum error-correcting code, discrete AdS/CFT correspondence, AdS/CMT correspondenc e, and more. It is the multipartite generalization of the bipartite maximally entangled state Quantum entanglement is the phenomenon where the quantum state of each Subatomic particle, particle in a group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, even when the particles are separated by a large distance. The topic o .... Definition The bipartite maximally entangled state , \psi\rangle_ is the one for which the reduced density operators are maximally mixed, i.e., \rho_A=\rho_B=I/d. Typical examples are Bell states. A multipartite state , \psi\rangle of a system S is called absolutely maximally entangled if for any bipartition A, B of S, the reduced density operator is maximally mixed \rho_A=\rho_B=I/d, where d=\min\. Property The AME state doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Information Science
Quantum information science is a field that combines the principles of quantum mechanics with information theory to study the processing, analysis, and transmission of information. It covers both theoretical and experimental aspects of quantum physics, including the limits of what can be achieved with quantum information. The term quantum information theory is sometimes used, but it does not include experimental research and can be confused with a subfield of quantum information science that deals with the processing of quantum information. Scientific and engineering studies Quantum teleportation, Quantum entanglement, entanglement and the manufacturing of quantum computers depend on a comprehensive understanding of quantum physics and engineering. Google and IBM have invested significantly in quantum computer hardware research, leading to significant progress in manufacturing quantum computers since the 2010s. Currently, it is possible to create a quantum computer with over 100 qub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Error Correction
Quantum error correction (QEC) is a set of techniques used in quantum computing to protect quantum information from errors due to decoherence and other quantum noise. Quantum error correction is theorised as essential to achieve fault tolerant quantum computing that can reduce the effects of noise on stored quantum information, faulty quantum gates, faulty quantum state preparation, and faulty measurements. Effective quantum error correction would allow quantum computers with low qubit fidelity to execute algorithms of higher complexity or greater circuit depth. Classical error correction often employs redundancy. The simplest albeit inefficient approach is the repetition code. A repetition code stores the desired (logical) information as multiple copies, and—if these copies are later found to disagree due to errors introduced to the system—determines the most likely value for the original data by majority vote. For instance, suppose we copy a bit in the one (on) state thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AdS/CFT Correspondence
In theoretical physics, the anti-de Sitter/conformal field theory correspondence (frequently abbreviated as AdS/CFT) is a conjectured relationship between two kinds of physical theories. On one side are anti-de Sitter spaces (AdS) that are used in theories of quantum gravity, formulated in terms of string theory or M-theory. On the other side of the correspondence are conformal field theory, conformal field theories (CFT) that are quantum field theory, quantum field theories, including theories similar to the Yang–Mills theory, Yang–Mills theories that describe elementary particles. The duality represents a major advance in the understanding of string theory and quantum gravity. This is because it provides a non-perturbative formulation of string theory with certain boundary conditions and because it is the most successful realization of the holographic principle, an idea in quantum gravity originally proposed by Gerard 't Hooft and promoted by Leonard Susskind. It also prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AdS/CMT Correspondence
In theoretical physics, anti-de Sitter/condensed matter theory correspondence is the program to apply string theory to condensed matter theory using the AdS/CFT correspondence. Overview Over the decades, experimental condensed matter physicists have discovered a number of exotic states of matter, including superconductors and superfluids. These states are described using the formalism of quantum field theory, but some phenomena are difficult to explain using standard field theoretic techniques. Some condensed matter theorists including Subir Sachdev hope that the AdS/CFT correspondence will make it possible to describe these systems in the language of string theory and learn more about their behavior.Merali 2011, p. 303 So far some success has been achieved in using string theory methods to describe the transition of a superfluid to an insulator. A superfluid is a system of electrically neutral atoms that flows without any friction. Such systems are often produced in the lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximally Entangled State
Quantum entanglement is the phenomenon where the quantum state of each Subatomic particle, particle in a group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, even when the particles are separated by a large distance. The topic of quantum entanglement is at the heart of the disparity between classical physics and quantum physics: entanglement is a primary feature of quantum mechanics not present in classical mechanics. Measurement#Quantum mechanics, Measurements of physical properties such as position (vector), position, momentum, Spin (physics), spin, and polarization (waves), polarization performed on entangled particles can, in some cases, be found to be perfectly correlated. For example, if a pair of entangled particles is generated such that their total spin is known to be zero, and one particle is found to have clockwise spin on a first axis, then the spin of the other particle, measured on the same axis, is found to be anticlockwise. However, this behavior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
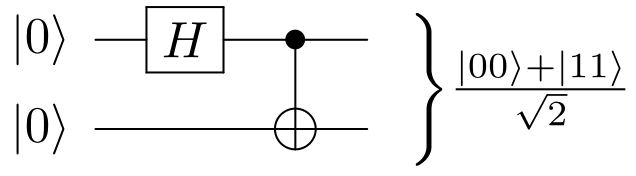
Bell State
In quantum information science, the Bell's states or EPR pairs are specific quantum states of two qubits that represent the simplest examples of quantum entanglement. The Bell's states are a form of entangled and normalized basis vectors. This normalization implies that the overall probability of the particles being in one of the mentioned states is 1: \langle \Phi, \Phi \rangle = 1. Entanglement is a basis-independent result of superposition. Due to this superposition, measurement of the qubit will " collapse" it into one of its basis states with a given probability. Because of the entanglement, measurement of one qubit will "collapse" the other qubit to a state whose measurement will yield one of two possible values, where the value depends on which Bell's state the two qubits are in initially. Bell's states can be generalized to certain quantum states of multi-qubit systems, such as the GHZ state for three or more subsystems. Understanding of Bell's states is useful in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Marginal Problem
In physics, a quantum (: quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This means that the magnitude of the physical property can take on only discrete values consisting of integer multiples of one quantum. For example, a photon is a single quantum of light of a specific frequency (or of any other form of electromagnetic radiation). Similarly, the energy of an electron bound within an atom is quantized and can exist only in certain discrete values. Atoms and matter in general are stable because electrons can exist only at discrete energy levels within an atom. Quantization is one of the foundations of the much broader physics of quantum mechanics. Quantization of energy and its influence on how energy and matter interact (quantum electrodynamics) is part of the fundamental framework for understanding and describing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holographic Error-correcting Code
Holography is a technique that allows a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is best known as a method of generating three-dimensional images, and has a wide range of other uses, including data storage, microscopy, and interferometry. In principle, it is possible to make a hologram for any type of wave. A hologram is a recording of an interference pattern that can reproduce a 3D light field using diffraction. In general usage, a hologram is a recording of any type of wavefront in the form of an interference pattern. It can be created by capturing light from a real scene, or it can be generated by a computer, in which case it is known as a computer-generated hologram, which can show virtual objects or scenes. Optical holography needs a laser light to record the light field. The reproduced light field can generate an image that has the depth and parallax of the original scene. A hologram is usually unintelligible when viewed under diffuse ambient light. When sui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Information Science
Quantum information science is a field that combines the principles of quantum mechanics with information theory to study the processing, analysis, and transmission of information. It covers both theoretical and experimental aspects of quantum physics, including the limits of what can be achieved with quantum information. The term quantum information theory is sometimes used, but it does not include experimental research and can be confused with a subfield of quantum information science that deals with the processing of quantum information. Scientific and engineering studies Quantum teleportation, Quantum entanglement, entanglement and the manufacturing of quantum computers depend on a comprehensive understanding of quantum physics and engineering. Google and IBM have invested significantly in quantum computer hardware research, leading to significant progress in manufacturing quantum computers since the 2010s. Currently, it is possible to create a quantum computer with over 100 qub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |