|
Absolute Angular Momentum
In meteorology, absolute angular momentum is the angular momentum in an 'absolute' coordinate system (absolute time and space). Introduction Angular momentum equates with the cross product of the position (vector) of a particle (or fluid parcel) and its absolute linear momentum , equal to , the product of mass and velocity. Mathematically, :\mathbf = \mathbf \times m \mathbf Definition Absolute angular momentum sums the angular momentum of a particle or fluid parcel in a relative coordinate system and the angular momentum of that relative coordinate system. Meteorologists typically express the three vector components of velocity (eastward, northward, and upward). The magnitude of the absolute angular momentum per unit mass :\left, \frac\ = M = u r \cos (\phi) + \Omega r^2 \cos^2(\phi) where * represents absolute angular momentum per unit mass of the fluid parcel (in ), * represents distance from the center of the Earth to the fluid parcel (in ), * represents earth-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agriculture, construction, weather warnings and disaster management. Along with climatology, atmospheric physics and atmospheric chemistry, meteorology forms the broader field of the atmospheric sciences. The interactions between Earth's atmosphere and its oceans (notably El Niño and La Niña) are studied in the interdisciplinary field of hydrometeorology. Other interdisciplinary areas include biometeorology, space weather and planetary meteorology. Marine weather forecasting relates meteorology to maritime and coastal safety, based on atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water. Meteorologists study meteorological phenomena driven by solar radiation, Earth's rotation, ocean currents and other factors. These include everyday ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the planetary surface of the Earth, the average height of the troposphere is in the tropics; in the middle latitudes; and in the high latitudes of the polar regions in winter; thus the average height of the troposphere is . The term ''troposphere'' derives from the Greek words ''tropos'' (rotating) and ''sphere, sphaira'' (sphere) indicating that rotational turbulence mixes the layers of air and so determines the structure and the phenomena of the troposphere. The rotational friction of the troposphere against the planetary surface affects the flow of the air, and so forms the planetary boundary layer (PBL) that varies in height from hundreds of meters up to . The measures of the PBL vary according to the latitude, the landform, and the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Angular Momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction (geometry), direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycle and motorcycle dynamics, Bicycles and motorcycles, flying discs, Rifling, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Academic Press
Academic Press (AP) is an academic book publisher founded in 1941. It launched a British division in the 1950s. Academic Press was acquired by Harcourt, Brace & World in 1969. Reed Elsevier said in 2000 it would buy Harcourt, a deal completed the next year, after a regulatory review. Thus, Academic Press is now an imprint of Elsevier. Academic Press publishes reference books, serials and online products in the subject areas of: * Communications engineering * Economics * Environmental science * Finance * Food science and nutrition * Geophysics * Life sciences * Mathematics and statistics * Neuroscience * Physical sciences * Psychology Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ... Well-known products include the '' Methods in Enzymology'' series and encyclopedias such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . Just as a linear force is a push or a pull applied to a body, a torque can be thought of as a twist applied to an object with respect to a chosen point; for example, driving a screw uses torque to force it into an object, which is applied by the screwdriver rotating around its axis to the drives on the head. Historical terminology The term ''torque'' (from Latin , 'to twist') is said to have been suggested by James Thomson and appeared in print in April, 1884. Usage is attested the same year by Silvanus P. Thompson in the first edition of ''Dynamo-Electric Machinery''. Thompson describes his usage of the term as follows: Today, torque is referred to using d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Stress (mechanics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that describes forces present during deformation. For example, an object being pulled apart, such as a stretched elastic band, is subject to ''tensile'' stress and may undergo elongation. An object being pushed together, such as a crumpled sponge, is subject to ''compressive'' stress and may undergo shortening. The greater the force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. Stress has dimension of force per area, with SI units of newtons per square meter (N/m2) or pascal (Pa). Stress expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while ''strain'' is the measure of the relative deformation of the material. For example, when a solid vertical bar is supporting an overhead weight, each particle in the bar pushes on the particles immediately below it. When a liquid is in a closed container under pressure, each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Eddy (fluid Dynamics)
In fluid dynamics, an eddy is the swirling of a fluid and the reverse current (water), current created when the fluid is in a Turbulence, turbulent flow regime. The moving fluid creates a space devoid of downstream-flowing fluid on the downstream side of the object. Fluid behind the obstacle flows into the void creating a swirl of fluid on each edge of the obstacle, followed by a short reverse flow of fluid behind the obstacle flowing upstream, toward the back of the obstacle. This phenomenon is naturally observed behind large emergent rocks in swift-flowing rivers. An eddy is a movement of fluid that deviates from the general flow of the fluid. An example for an eddy is a vortex which produces such deviation. However, there are other types of eddies that are not simple vortices. For example, a Rossby wave is an eddy which is an undulation that is a deviation from mean flow, but does not have the local closed streamlines of a vortex. Swirl and eddies in engineering The propensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Pressure Gradient
In hydrodynamics and hydrostatics, the pressure gradient (typically of air but more generally of any fluid) is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the pressure increases the most rapidly around a particular location. The pressure gradient is a dimensional quantity expressed in units of pascals per metre (Pa/m). Mathematically, it is the gradient of pressure as a function of position. The gradient of pressure in hydrostatics is equal to the ''body force density'' (generalised Stevin's Law). In petroleum geology and the petrochemical sciences pertaining to oil wells, and more specifically within hydrostatics, pressure gradients refer to the gradient of vertical pressure in a column of fluid within a wellbore and are generally expressed in pounds per square inch per foot (psi/ft). This column of fluid is subject to the compound pressure gradient of the overlying fluids. The path and geometry of the column is totally irrelevant; only the vertical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Zonal And Meridional
Zonal and meridional flow are directions and regions of fluid flow on a globe. Zonal flow follows a pattern along latitudinal lines, latitudinal circles or in the west–east direction. Meridional flow follows a pattern from north to south, or from south to north, along the Earth's longitude lines, longitudinal circles ( meridian) or in the north–south direction. These terms are often used in the atmospheric and earth sciences to describe global phenomena, such as "meridional wind", or "zonal average temperature". In the context of physics, zonal flow connotes a tendency of flux to conform to a pattern parallel to the equator of a sphere. In meteorological term regarding atmospheric circulation, zonal flow brings a temperature contrast along the Earth's longitude. Extratropical cyclones in zonal flows tend to be weaker, moving faster and producing relatively little impact on local weather. Extratropical cyclones in meridional flows tend to be stronger and move slower. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Earth Radius
Earth radius (denoted as ''R''🜨 or ''R''E) is the distance from the center of Earth to a point on or near its surface. Approximating the figure of Earth by an Earth spheroid (an oblate ellipsoid), the radius ranges from a maximum (equatorial radius, denoted ''a'') of about to a minimum (polar radius, denoted ''b'') of nearly . A globally-average value is usually considered to be with a 0.3% variability (±10 km) for the following reasons. The International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG) provides three reference values: the ''mean radius'' (''R'') of three radii measured at two equator points and a pole; the ''authalic radius'', which is the radius of a sphere with the same surface area (''R''); and the ''volumetric radius'', which is the radius of a sphere having the same volume as the ellipsoid (''R''). All three values are about . Other ways to define and measure the Earth's radius involve either the spheroid's radius of curvature or the actual topography. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Sidereal Day
Sidereal time ("sidereal" pronounced ) is a system of timekeeping used especially by astronomers. Using sidereal time and the celestial coordinate system, it is easy to locate the positions of celestial objects in the night sky. Sidereal time is a "time scale that is based on Earth's rate of rotation measured relative to the fixed stars". A sidereal day (also known as the sidereal rotation period) represents the time for one rotation about the planet axis relative to the stars. Viewed from the same location, a star seen at one position in the sky will be seen at the same position on another night at the same time of day (or night), if the day is defined as a sidereal day. This is similar to how the time kept by a sundial (Solar time) can be used to find the location of the Sun. Just as the Sun and Moon appear to rise in the east and set in the west due to the rotation of Earth, so do the stars. Both solar time and sidereal time make use of the regularity of Earth's rot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
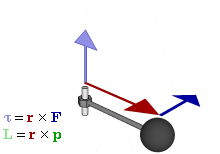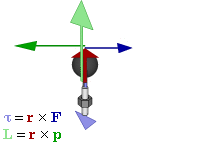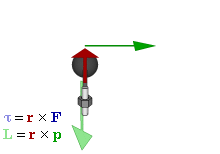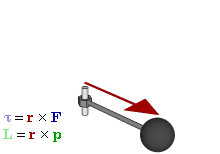 |
Angular Momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction (geometry), direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycle and motorcycle dynamics, Bicycles and motorcycles, flying discs, Rifling, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |