|
768
__NOTOC__ Year 768 ( DCCLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 768 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Frankish Kingdom * September 24 – King Pepin III (the Short) dies at Saint-Denis, Neustria. The Frankish Kingdom is divided between his two sons: Charlemagne and Carloman I. According to Salic law Charlemagne receives the outer parts of the kingdom bordering on the sea, namely Neustria, western Aquitaine, and the northern parts of Austrasia; while Carloman is awarded his uncle's former share, the inner parts: southern Austrasia, Septimania, eastern Aquitaine, Burgundy, Provence, Swabia, and the lands bordering Italy. * Waiofar, duke of Aquitaine, and his family are captured and executed by the Franks in the forest of Périgord. Waiofar's kinsman Hunald II succeeds to his claims and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepin The Short
the Short (; ; ; – 24 September 768), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian dynasty, Carolingian to become king. Pepin was the son of the Frankish prince Charles Martel and his wife Rotrude of Hesbaye, Rotrude. Pepin's upbringing was distinguished by the ecclesiastical education he had received from the Christian monasticism, Christian monks of the Basilica of Saint-Denis, Abbey Church of St. Denis, near Paris. Succeeding his father as the Mayor of the Palace in 741, Pepin reigned over Francia jointly with his elder brother, Carloman (mayor of the palace), Carloman. Pepin ruled in Neustria, Burgundy, and Provence, while his older brother Carloman established himself in Austrasia, Alemannia, and Thuringia. The brothers were active in suppressing revolts led by the Bavarians, Aquitanians, Saxons, and the Alemanni in the early years of their reign. In 743, they ended the by choosing Childeric III, who was to be the last Merovingian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian Empire from 800, holding these titles until his death in 814. He united most of Western Europe, Western and Central Europe, and was the first recognised emperor to rule from the west after the fall of the Western Roman Empire approximately three centuries earlier. Charlemagne's reign was marked by political and social changes that had lasting influence on Europe throughout the Middle Ages. A member of the Frankish Carolingian dynasty, Charlemagne was the eldest son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon. With his brother, Carloman I, he became king of the Franks in 768 following Pepin's death and became the sole ruler three years later. Charlemagne continued his father's policy of protecting the papacy and became its chief defender, remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
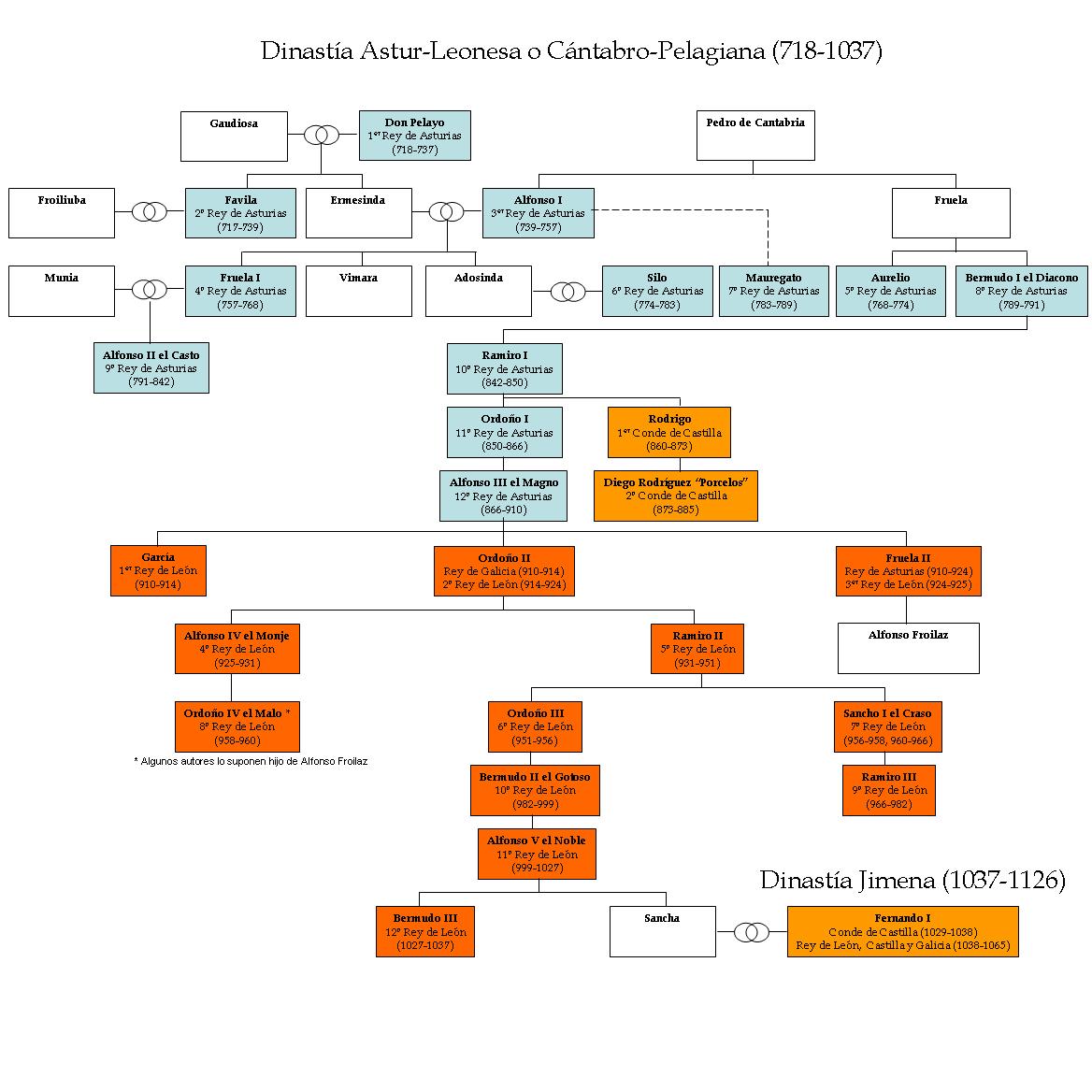
King Of Asturias
This is a list of the rulers of the Kingdom of Asturias, a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula during the Early Middle Ages. It originated as a refuge for Visigothic Kingdom, Visigothic nobles following the Umayyad conquest of Hispania, conquest of Iberia by the Umayyad Caliphate. Following the forced abdication of Alfonso III of Asturias, Alfonso III by his sons in 910, the kingdom was split into three: Kingdom of Asturias, Asturias, Kingdom of León, León, and Kingdom of Galicia, Galicia. All three were reunited in 924 under the Kingdom of León. For later kings, see the list of Leonese monarchs and the list of Galician monarchs. From 1388, the title Prince of Asturias has been used for the heirs to the Kingdom of Castile, Castillian and Spain, Spanish thrones. List Timeline ImageSize = width:600 height:550 #Tamaño de la imagen: ancho, alto PlotArea = width:50 height:530 left:50 bottom:10 #Tamaño de la gráfica en sí dentro de la imagen: ancho, alto, margen izquierdo, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waiofar
Waiofar, also spelled Waifar, Waifer or Waiffre (died 2 June 768), was the last independent Duke of Aquitaine from 745 to 768. He peacefully succeeded his father, Hunald I, after the latter entered a monastery. He also inherited the conflict with the rising Carolingian family and its leader, Pepin the Short, who was king of the Franks after 751 and thus Waiofar's nominal suzerain. War with Pepin 752–760 The beginning of open conflict between Waiofar and Pepin can be dated to 753, when the duke of Aquitaine granted asylum to Pepin's brother Grifo after the latter was forced to flee Francia because of his failed attempt at usurping the Duchy of Bavaria from its rightful lord. Pepin's immediate reaction is not recorded, but Grifo was subsequently assassinated while preparing to leave Aquitaine for Rome. In 751, according to the '' Chronicle of Moissac'', Waiofar sacked the city of Narbonne (''Narbonam depraedat''), the centre of Islamic rule north of the Pyrenees, having be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruela I Of Asturias
Fruela I ( – 14 January 768), also referred to as Froila I and nicknamed "the Cruel," was the King of Asturias from 757 until his assassination. He was the eldest son of Alfonso I and continued his father's war against the Moors. Pelayo, the founder of the Kingdom of Asturias, was his maternal grandfather. History During his reign, he suppressed uprisings from both the Basques and the Galicians; following his victory over the Basques, he took a Basque noblewoman from Alava named Munia as his wife. Basque country was relatively untouched following the revolt; on the contrary, Fruela laid waste to Galicia after suppressing the uprising. He also defeated a Cordoban army led by Omar, son of Abd al-Rahman I; Omar was killed as a result of the battle.de Caunedo, Nicolás Castor (28 May 1854).Un cronicón del siglo IX". ''Semanario Pintoresco Español'' 22: 171 – via Hemeroteca Digital. The city of Oviedo was also founded during his reign when the abbot Máximo and his uncle F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunald II
Hunald II, also spelled Hunold, Hunoald, Hunuald or Chunoald (French: ''Hunaud''), was the Duke of Aquitaine from 768 until 769. He was probably the son of Duke Waiofar, who was assassinated on the orders of King Pippin the Short in 768. He laid claim to the duchy following Pippin's death later that year, but his revolt was crushed by Pippin's eldest son, Charlemagne. Hunald fled to the Duchy of Gascony, but he was handed over to Charlemagne and put into captivity. Nothing more is heard of him. Following the naming patterns of the time, Hunald was probably named after his grandfather, Hunald I. All the members of his family, including himself, bore names of Germanic origin. Certain historians have advanced the hypothesis that Hunald I, who retired to a monastery in 745, came out of retirement to lead it again in 768. This is unlikely on chronological grounds, and there is a tradition that Hunald I died at Rome in 756. Most historians treat the two as different people. When Waiofar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carloman I
Carloman I (28 June 751 – 4 December 771), German Karlmann, Karlomann, was king of the Franks from 768 until his death in 771. He was the second surviving son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon and was a younger brother of Charlemagne. His death allowed Charlemagne to take all of Francia. Split of the Frankish kingdom At the age of 3 he was, together with his father Pepin the Short and his elder brother Charlemagne, anointed King of the Franks and titled "Patrician of the Romans" by Pope Stephen II, who had left Rome to beg the Frankish King for assistance against the Lombards. Carloman and Charlemagne each inherited half of the Kingdom of the Franks upon Pepin's death. His share was based in the centre of the Frankish Kingdom, with his capital at Soissons, and consisted of the Parisian basin, the Massif Central, the Languedoc, Provence, Burgundy, southern Austrasia, Alsace, and Alemannia; the regions were poorly integrated and surrounded by those bequeathed to Charle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically hereditary and patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, but nobility also existed in such regimes as the Dutch Republic (1581–1795), the Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurelius Of Asturias
Aurelius () ( 740 – 774) was the King of Asturias from 768 to his death. Born in León, he was the son of Fruela of Cantabria (son of Peter of Cantabria); nephew of Alfonso I of Asturias; and a cousin of his predecessor, Fruela I. His brother, Bermudo I, later reigned as king from 789 to 791. Aurelius was chosen as king by the Asturian nobility after Fruela I's assassination. He is believed to have been crowned in Sama. His reign appears to have been relatively quiet and peaceful, attested to by the near-absence of mention of his reign in medieval chronicles. The only event of his reign narrated in the chronicles was a rebellion of serfs, which Aurelius put down.de Caunedo, Nicolás Castor (28 May 1854).Un cronicón del siglo IX". Semanario Pintoresco Español 22: 171 – via Hemeroteca Digital. The location of the uprising is unknown, but it is the first recorded instance of anti- seignorial revolt in the history of the Iberian Peninsula. It is believed that, accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimania
Septimania is a historical region in modern-day southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of '' Gallia Narbonensis'' that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theodoric II. During the Early Middle Ages, the region was variously known as Gallia Narbonensis, Gallia, or Narbonensis. The territory of Septimania roughly corresponds with the modern French former administrative region of Languedoc-Roussillon that merged into the new administrative region of Occitanie. In the Visigothic Kingdom, which became centred on Toledo by the end of the reign of Leovigild, Septimania was both an administrative province of the central royal government and an ecclesiastical province whose metropolitan was the Archbishop of Narbonne. Originally, the Goths may have maintained their hold on the Albigeois, but if so it was conquered by the time of Chilperic I. There is archaeological evidence that some enclaves of Visi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berber People
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connections are identified by their usage of Berber languages, most of them mutually unintelligible, which are part of the Afroasiatic language family. They are indigenous to the Maghreb region of North Africa, where they live in scattered communities across parts of Morocco, Algeria, Libya, and to a lesser extent Tunisia, Mauritania, northern Mali and northern Niger. Smaller Berber communities are also found in Burkina Faso and Egypt's Siwa Oasis. Descended from Stone Age tribes of North Africa, accounts of the Imazighen were first mentioned in Ancient Egyptian writings. From about 2000 BC, Berber languages spread westward from the Nile Valley across the northern Sahara into the Maghreb. A series of Berber peoples such as the Mauri, Masaesyli, Massyli, Musulamii, Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francia
The Kingdom of the Franks (), also known as the Frankish Kingdom, or just Francia, was the largest History of the Roman Empire, post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks, Frankish Merovingian dynasty, Merovingian and Carolingian dynasty, Carolingian dynasties during the Early Middle Ages. Francia was among the last surviving Germanic kingdoms from the Migration Period era. Originally, the core Frankish territories inside the former Western Roman Empire were located close to the Rhine and Meuse rivers in the north, but Frankish chiefs such as Chlodio would eventually expand their influence within Roman territory as far as the Somme (river), Somme river in the 5th century. Childeric I, a Salian Franks, Salian Frankish king, was one of several military leaders commanding Roman forces of various ethnic affiliations in the northern part of what is now France. His son, Clovis I, succeeded in unifying most of Gaul under his rule in the 6th century by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |