|
7-day Rolling Average
In statistics, a moving average (rolling average or running average or moving mean or rolling mean) is a calculation to analyze data points by creating a series of averages of different selections of the full data set. Variations include: simple, cumulative, or weighted forms. Mathematically, a moving average is a type of convolution. Thus in signal processing it is viewed as a low-pass finite impulse response filter. Because the boxcar function outlines its filter coefficients, it is called a boxcar filter. It is sometimes followed by downsampling. Given a series of numbers and a fixed subset size, the first element of the moving average is obtained by taking the average of the initial fixed subset of the number series. Then the subset is modified by "shifting forward"; that is, excluding the first number of the series and including the next value in the series. A moving average is commonly used with time series data to smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skip List
In computer science, a skip list (or skiplist) is a Randomized algorithm, probabilistic data structure that allows O(\log n) Average-case complexity, average complexity for search as well as O(\log n) average complexity for insertion within an ordered sequence of n elements. Thus it can get the best features of a sorted Array data structure, array (for searching) while maintaining a linked list-like structure that allows insertion, which is not possible with a static array. Fast search is made possible by maintaining a linked hierarchy of subsequences, with each successive subsequence skipping over fewer elements than the previous one (see the picture below on the right). Searching starts in the sparsest subsequence until two consecutive elements have been found, one smaller and one larger than or equal to the element searched for. Via the linked hierarchy, these two elements link to elements of the next sparsest subsequence, where searching is continued until finally searching in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median
The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a Sample (statistics), data sample, a statistical population, population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “middle" value. The basic feature of the median in describing data compared to the Arithmetic mean, mean (often simply described as the "average") is that it is not Skewness, skewed by a small proportion of extremely large or small values, and therefore provides a better representation of the center. Median income, for example, may be a better way to describe the center of the income distribution because increases in the largest incomes alone have no effect on the median. For this reason, the median is of central importance in robust statistics. Median is a 2-quantile; it is the value that partitions a set into two equal parts. Finite set of numbers The median of a finite list of numbers is the "middle" number, when those numbers are liste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Applied Statistics
The ''Journal of Applied Statistics'' or ''J.Appl.Stat.'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering applied statistics that is published by Taylor & Francis. Its ''Journal Citation Reports'' impact factor was 1.2 in 2023. Creation The journal was founded by Gopal Kanji in 1974 as the ''Bulletin in Applied Statistics (BIAS)''. Kanji remained as editor until the end of 2007. Quality rankings In 2020, the Australian Mathematical Society listed ''J.Appl.Stat.'' with a ranking of ''B'' on a scale including ''A*'', ''A'', ''B'' and ''C''. ''J.Appl.Stat.'' states that its ''Journal Citation Reports'' impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... was 0.699 in 2017 and 1.2 in 2023. References External links * {{Statistics journals Statistics journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Standards And Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of physical science, physical science laboratory programs that include Nanotechnology, nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted formally. A datum is an individual value in a collection of data. Data are usually organized into structures such as tables that provide additional context and meaning, and may themselves be used as data in larger structures. Data may be used as variables in a computational process. Data may represent abstract ideas or concrete measurements. Data are commonly used in scientific research, economics, and virtually every other form of human organizational activity. Examples of data sets include price indices (such as the consumer price index), unemployment rates, literacy rates, and census data. In this context, data represent the raw facts and figures from which useful information can be extracted. Data are collected using technique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Decay
A quantity is subject to exponential decay if it decreases at a rate proportional to its current value. Symbolically, this process can be expressed by the following differential equation, where is the quantity and (lambda Lambda (; uppercase , lowercase ; , ''lám(b)da'') is the eleventh letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoen ...) is a positive rate called the exponential decay constant, disintegration constant, rate constant, or transformation constant: :\frac = -\lambda N(t). The solution to this equation (see #Solution_of_the_differential_equation, derivation below) is: :N(t) = N_0 e^, where is the quantity at time , is the initial quantity, that is, the quantity at time . Measuring rates of decay Mean lifetime If the decaying quantity, ''N''(''t''), is the number of discrete elements in a certain set (mathematics), se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
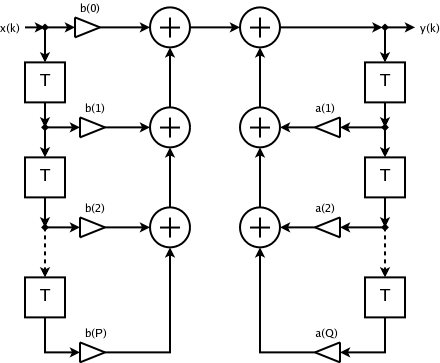
Infinite Impulse Response
Infinite impulse response (IIR) is a property applying to many linear time-invariant systems that are distinguished by having an impulse response h(t) that does not become exactly zero past a certain point but continues indefinitely. This is in contrast to a finite impulse response (FIR) system, in which the impulse response ''does'' become exactly zero at times t>T for some finite T, thus being of finite duration. Common examples of linear time-invariant systems are most electronic and digital filters. Systems with this property are known as ''IIR systems'' or ''IIR filters''. In practice, the impulse response, even of IIR systems, usually approaches zero and can be neglected past a certain point. However the physical systems which give rise to IIR or FIR responses are dissimilar, and therein lies the importance of the distinction. For instance, analog electronic filters composed of resistors, capacitors, and/or inductors (and perhaps linear amplifiers) are generally IIR filte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Number
A triangular number or triangle number counts objects arranged in an equilateral triangle. Triangular numbers are a type of figurate number, other examples being square numbers and cube numbers. The th triangular number is the number of dots in the triangular arrangement with dots on each side, and is equal to the sum of the natural numbers from 1 to . The first 100 terms sequence of triangular numbers, starting with the 0th triangular number, are Formula The triangular numbers are given by the following explicit formulas: where \textstyle is notation for a binomial coefficient. It represents the number of distinct pairs that can be selected from objects, and it is read aloud as " plus one choose two". The fact that the nth triangular number equals n(n+1)/2 can be illustrated using a visual proof. For every triangular number T_n, imagine a "half-rectangle" arrangement of objects corresponding to the triangular number, as in the figure below. Copying this arrangement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighted Moving Average Weights N=15
A weight function is a mathematical device used when performing a sum, integral, or average to give some elements more "weight" or influence on the result than other elements in the same set. The result of this application of a weight function is a weighted sum or weighted average. Weight functions occur frequently in statistics and analysis, and are closely related to the concept of a measure. Weight functions can be employed in both discrete and continuous settings. They can be used to construct systems of calculus called "weighted calculus" and "meta-calculus".Jane Grossma''Meta-Calculus: Differential and Integral'' , 1981. Discrete weights General definition In the discrete setting, a weight function w \colon A \to \R^+ is a positive function defined on a discrete set A, which is typically finite or countable. The weight function w(a) := 1 corresponds to the ''unweighted'' situation in which all elements have equal weight. One can then apply this weight to various conce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-aliasing
Anti-aliasing may refer to any of a number of techniques to combat the problems of aliasing in a sampled signal such as a digital image or digital audio recording. Specific topics in anti-aliasing include: * Anti-aliasing filter, a filter used before a signal sampler to restrict the bandwidth of a signal such as in audio applications. * Manual anti-aliasing, an artistic technique done in pixel art graphics to smooth transitions between shapes, soften lines or blur edges. * Computer-generated imagery (CGI), the application of computer graphics for creating or improving images in art, printed media, simulators, videos and video games. * Spatial anti-aliasing, the technique of minimizing aliasing when representing a high-resolution image at a lower resolution ** Fast approximate anti-aliasing (FXAA), an anti-aliasing algorithm created by Timothy Lottes under Nvidia. May also be referred to as Fast Sample Anti-aliasing (FSAA). ** Multisample anti-aliasing (MSAA), a type of spatial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |