|
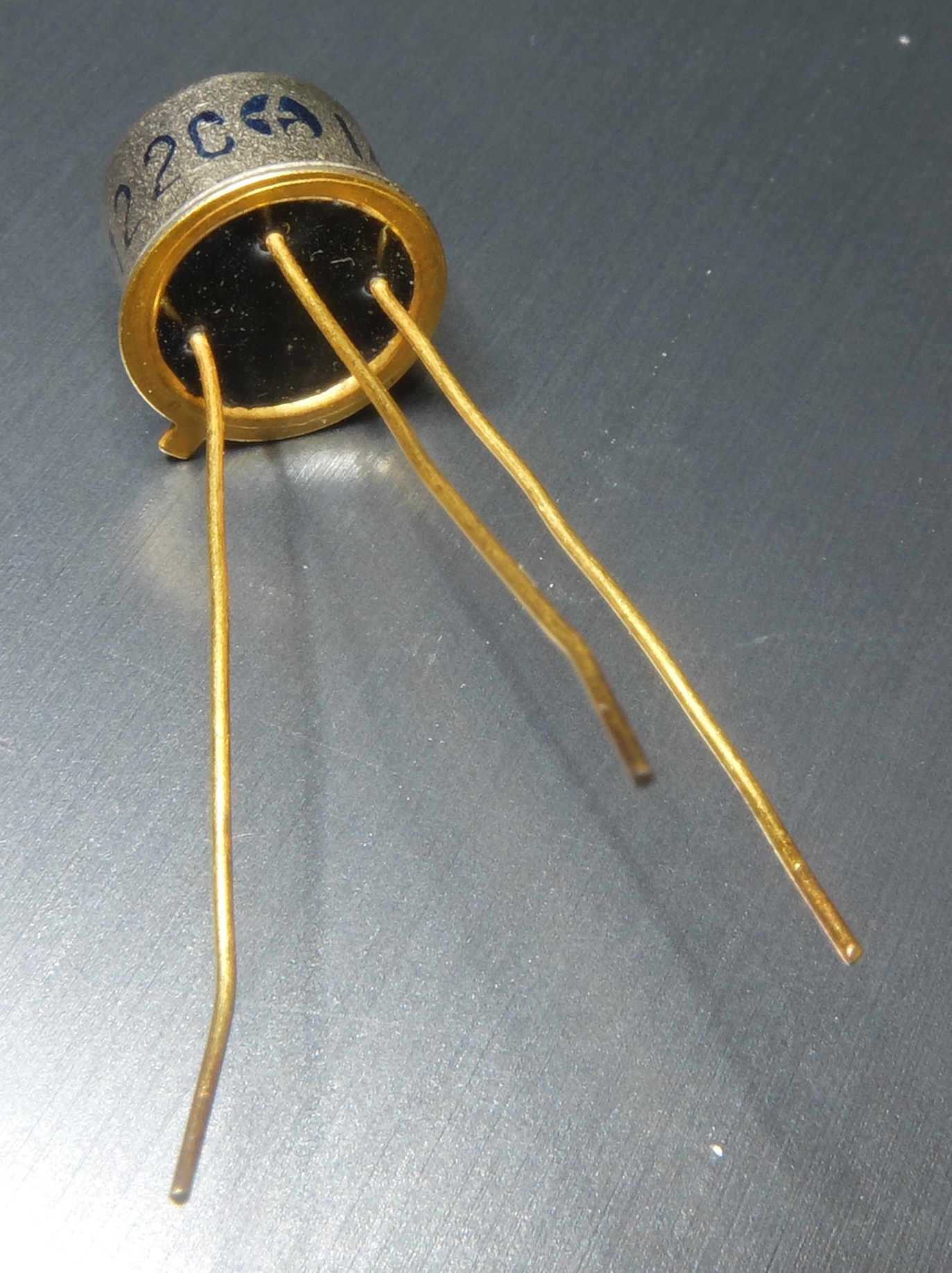
2N696
The 2N696 and 2N697 were the first silicon transistors manufactured in Silicon Valley, in 1958, by Fairchild Semiconductor. Fairchild introduced itself to the world via its advertisements for these transistors, which were identical except for a post-manufacturing binning on current gain. The 2N696/2N697 NPN mesa transistor was developed by a team led by Gordon Moore. The first batch of 100 was sold to IBM for $150 each () in order to build the computer for the B-70 bomber. More transistors were sold to Autonetics to build the guidance system for the Minuteman ballistic missile. The 2N696 and 2N697 were popular devices, quickly copied by several other semiconductor companies, including Texas Instruments, Rheem Semiconductor, and others including Hoffman Electronics Corp. and Industro Transistor Corp. In a 1960 advertisement, Fairchild bragged, "The Fairchild 2N696 and 2N697 are the world's most copied transistors. We have now copied them ourselves in scaled down versions. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TO-5
In electronics, TO-5 is a designation for a standardized metal semiconductor package used for transistors and some integrated circuits. The ''TO'' element stands for "transistor outline" and refers to a series of technical drawings produced by JEDEC. The first commercial silicon transistors, the 2N696 and 2N697 from Fairchild Semiconductor, came in a TO-5 package. Construction and orientation The tab is located 45° from pin 1, which is typically the emitter. The typical TO-5 package has a base diameter of , a cap diameter of , a cap height of . The pins are isolated from the package by individual glass-metal seals, or by a single resin potting. Sometimes one pin is connected directly to the metal case. Variants Several variants of the original TO-5 package have the same cap dimensions but differ in the number and length of the leads (wires). Somewhat incorrectly, TO-5 and TO-39 are often used in manufacturer's literature as synonyms for any package with the cap dimensions of T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. Founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument, it became a pioneer in the manufacturing of transistors and of integrated circuits. Schlumberger bought the firm in 1979 and sold it to National Semiconductor in 1987; Fairchild was spun off as an independent company again in 1997. In September 2016, Fairchild was acquired by ON Semiconductor. The company had locations in the United States at San Jose, California; San Rafael, California; South Portland, Maine; West Jordan, Utah; and Mountaintop, Pennsylvania. Outside the US it operated locations in Australia; Singapore; Bucheon, South Korea; Penang, Malaysia; Suzhou, China; and Cebu, Philippines, among others. History 1950s In 1955, William Shockley founded Shockley Semiconductor Laboratory, funded by Beckman Instruments in Mountain View, California; his plan was to develop a new type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shockley Sidewalk Circuit
Shockley is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Dolores Cooper Shockley, American pharmacist * D.J. Shockley, American football player *William Shockley, winner of the Nobel Prize for physics Fictional characters *Detective Ben Shockley, protagonist of the 1977 film '' The Gauntlet'' See also *Shockley Semiconductor Laboratory Shockley Semiconductor Laboratory was a pioneering semiconductor developer founded by William Shockley, and funded by Beckman Instruments, Inc., in 1955. It was the first high technology company in what came to be known as Silicon Valley to w ... * William Shockley (other) {{surname, Shockley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild Ad Electronics-1958-08-15
Fairchild may refer to: Organizations * Fairchild Aerial Surveys, operated in cooperation with a subsidiary of Fairey Aviation Company * Fairchild Camera and Instrument * List of Sherman Fairchild companies, "Fairchild" companies * Fairchild Fashion Media * Fairchild Group, a Chinese-language media company in Canada ** Fairchild TV, a Cantonese-language television channel in Canada owned by the Fairchild Group * Fairchild-Hiller Corporation, U.S. aviation company ** Fairchild Aircraft, an aircraft manufacturer, division of Fairchild, also variously known as Fairchild-Hiller, Fairchild-Republic and Fairchild-Dornier ** Fairchild Aircraft Ltd. (Canada), a Canadian aircraft manufacturer ** Fairchild Industries, Inc. ; U.S. aviation company, successor to Fairchild Hiller Corporation ** Fairchild Corporation, U.S. aviation company, successor to Fairchild Industries * Fairchild Publications, Inc. * Fairchild Recording Equipment Corporation * Fairchild Semiconductor, an American semico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that serves as a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical areas San Mateo County and Santa Clara County. San Jose is Silicon Valley's largest city, the third-largest in California, and the tenth-largest in the United States; other major Silicon Valley cities include Sunnyvale, Santa Clara, Redwood City, Mountain View, Palo Alto, Menlo Park, and Cupertino. The San Jose Metropolitan Area has the third-highest GDP per capita in the world (after Zurich, Switzerland and Oslo, Norway), according to the Brookings Institution, and, as of June 2021, has the highest percentage of homes valued at $1 million or more in the United States. Silicon Valley is home to many of the world's largest high-tech corporations, including the headquarters of more than 30 businesses in the Fortune 1000, and thousands of startup com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Binning
Product binning is the categorizing of finished products based on their characteristics. Any mining, harvesting, or manufacturing process will yield products spanning a range of quality and desirability in the marketplace. Binning allows differing quality products to be priced appropriately for various uses and markets. Economic and legal theory Product binning and grading allows a degree of price discrimination which may be easier to defend legally, since it can be based on real or perceived differences in product quality. In order to undergo binning, manufactured products require testing, usually performed by machines in bulk. Binning allows large variances in performance to be condensed into a smaller number of marketed designations. This ensures coherency in the marketplace, with tiers of performance clearly delineated. The immediate result of this practice is that, for legal and reputational reasons, products sold under a certain designation must meet that designation at a ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Moore
Gordon Earle Moore (born January 3, 1929) is an American businessman, engineer, and the co-founder and chairman emeritus of Intel Corporation. He is also the original proponent of Moore's law. As of March 2021, Moore's net worth is reported to be $12.6 billion. Education Moore was born in San Francisco, California, and grew up in nearby Pescadero, where his father was the county sheriff. He attended San José State University for two years before transferring to the University of California, Berkeley, where he received a B.S. degree in chemistry in 1950. In September 1950, Moore enrolled at the California Institute of Technology. While at Caltech, Moore minored in physics and received a Ph.D. in chemistry in 1954. Moore conducted postdoctoral research at the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University from 1953 to 1956. Scientific career Fairchild Semiconductor Laboratory Moore joined MIT and Caltech alumnus William Shockley at the Shockley Semi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American XB-70 Valkyrie
The North American Aviation XB-70 Valkyrie was the prototype version of the planned B-70 nuclear-armed, deep-penetration supersonic strategic bomber for the United States Air Force Strategic Air Command. Designed in the late 1950s by North American Aviation (NAA), the six-engined Valkyrie was capable of cruising for thousands of miles at Mach 3+ while flying at . At these speeds, it was expected that the B-70 would be practically immune to interceptor aircraft, the only effective weapon against bomber aircraft at the time. The bomber would spend only a brief time over a particular radar station, flying out of its range before the controllers could position their fighters in a suitable location for an interception. Its high speed made the aircraft difficult to see on radar displays and its high-altitude and high-speed capabilities could not be matched by any contemporaneous Soviet interceptor or fighter aircraft. The introduction of the first Soviet surface-to-air missiles i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonetics
Autonetics was a division of North American Aviation that produced various avionics but is best known for their inertial navigation systems used in submarines and intercontinental ballistic missiles. Its 188-acre facility in Anaheim, California, with 36,000 employees, was the city's largest employer. Through a series of mergers, Autonetics is now part of Boeing. Origin Autonetics originated in North American Aviation's Technical Research Laboratory, a small unit in the Los Angeles Division's engineering department, in 1945. In 1946, the laboratory won an Army Air Forces contract to develop a 175 to 500 mile range glide missile. The work and the lab expanded, and by June 1948, all of the Aerophysics Laboratory was consolidated at Downey, California. The evolution of the Navaho missile program then resulted in the establishment of Autonetics as a separate division of North American Aviation in 1955, first located in Downey, moving to Anaheim, California in 1963. Divisions Autonetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGM-30 Minuteman
The LGM-30 Minuteman is an American land-based intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) in service with the Air Force Global Strike Command. , the LGM-30G Minuteman III version is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States and represents the land leg of the U.S. nuclear triad, along with the Trident submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) and nuclear weapons carried by long-range strategic bombers. Development of the Minuteman began in the mid-1950s when basic research indicated that a solid-fuel rocket motor could stand ready to launch for long periods of time, in contrast to liquid-fueled rockets that required fueling before launch and so might be destroyed in a surprise attack. The missile was named for the colonial minutemen of the American Revolutionary War, who could be ready to fight on short notice. The Minuteman entered service in 1962 as a deterrence weapon that could hit Soviet cities with a second strike and countervalue counterattack if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globally. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog chips and embedded processors, which account for more than 80% of its revenue. TI also produces TI digital light processing technology and education technology products including calculators, microcontrollers, and multi-core processors. The company holds 45,000 patents worldwide as of 2016. Texas Instruments emerged in 1951 after a reorganization of Geophysical Service Incorporated, a company founded in 1930 that manufactured equipment for use in the seismic industry, as well as defense electronics. TI produced the world's first commercial silicon transistor in 1954, and the same year designed and manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheem Semiconductor
{{dab ...
Rheem may refer to: * Rheem Manufacturing Company * Rheem, California (other), places in California * Rheem Creek *Rheem Classic The Fort Smith Classic was a golf tournament on the Nationwide Tour. It is held each year at Hardscrabble Country Club in Fort Smith, Arkansas. It was the only annual PGA Tour event in the United States, U.S. state of Arkansas. The 2010 purse was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |