|
216th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
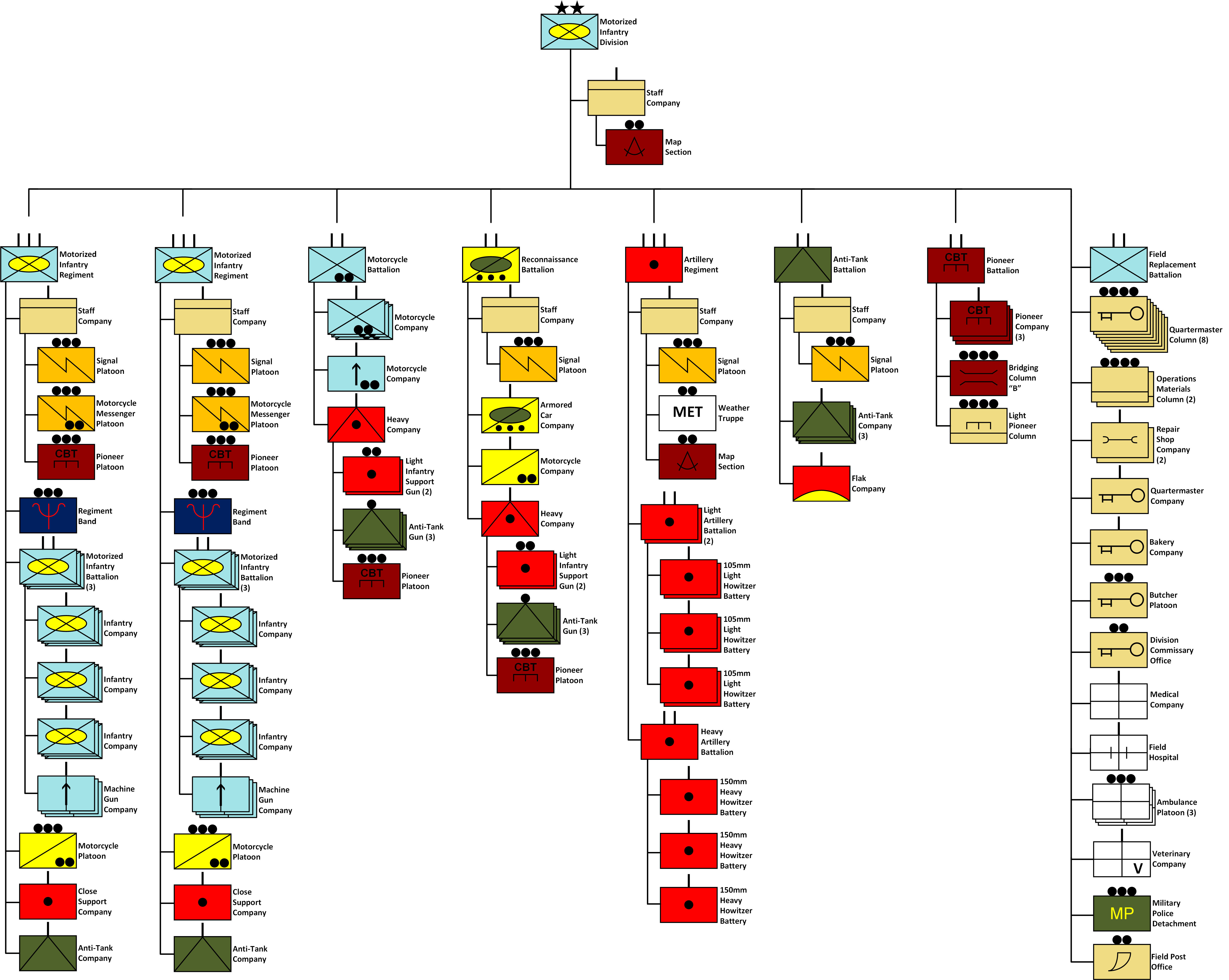
The 216th Infantry Division (german: 216. Infanterie-Division) was a German Army division that was created during the Second World War; it was active from 1939–1943. It served on the Western Front in 1940 and later took part in the Eastern Front campaign, being involved in the disastrous Battle of Kursk. Operational history The division was created on 26 August 1939 by reorganizing several Border Defense and Army Reserve units from Lower Saxony, primarily in the area surrounding the city of Hannover. It was organized under the pre-war infantry division "alter Art," structure; consisting of three 3-battalion infantry regiments (brigades), an artillery regiment of four battalions, a combat engineer battalion, a signal battalion, and an antitank battalion, as well as divisional services. Its total strength was approximately 17,200 men. The division was based at Hameln and was part of Wehrkreis XI. The 216th Infantry Division did not participate in the Invasion of Poland, since i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (German Air Force). , the German Army had a strength of 62,766 soldiers. History Overview A German army equipped, organized, and trained following a single doctrine and permanently unified under one command in 1871 during the unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia. From 1871 to 1919, the title '' Deutsches Heer'' (German Army) was the official name of the German land forces. Following the German defeat in World War I and the end of the German Empire, the main army was dissolved. From 1921 to 1935 the name of the German land forces was the '' Reichsheer'' (Army of the Empire) and from 1935 to 1945 the name '' Heer'' was used. The ''Heer'' was one of two ground forces of the Third Reich during World War II but, unlike t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich August Schack
Friedrich August Schack (27 March 1892 – 24 July 1968) was a German general during World War II. He is best known for his pyrrhic defense of Caen after the allied invasion, September 1944, and for his brief leadership of the LXXXI Army Corps defending Aachen and the Siegfried Line. Career Schack enlisted in the army, 6 August 1914 and fought in World War I. After the war he was retained in the Reichsheer where he served in junior officer roles. In 1934, Schack was appointed tactics teacher in the war college in Dresden. In 1937, he reached the rank of lieutenant colonel. Schack took part in the invasion of Poland and Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union. On 1 October 1942 he became commander of the war College in Potsdam. On 7 May 1943 he became commander of the 216th Infantry-Division. On 1 July 1943 Schack was promoted to major general and commander of the 216th Infantry division. Schack led his division in bloody combat in Orel, July 1943, during the Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Established In 1939
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry Divisions Of Germany During World War II
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''infant''. The individual-soldier term ''inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
272nd Volksgrenadier Division (Germany)
The 272nd Volksgrenadier Division (more accurately ''Volks-Grenadier Division''), was a German Army V''olksgrenadier'' division formed following the defeats of the Normandy Campaign in 1944. Composed of men taken from existing ''Heer'' (army) units and airmen and sailors retasked to infantry duties, the division fought on the retreating Western Front until it was largely encircled in the Ruhr Pocket in April 1945. Unit history The 272nd Volksgrenadier Division was formed on 17 September 1944 at the Döberitz Training Area in Germany by combining the then-forming 575th Volksgrenadier Division with the remnants of the veteran 272nd Infantry Division, which had barely managed to escape from the Allied offensives following the Normandy landings. Organized using the new ''Volksgrenadier'' division structure designed in August 1944, the division consisted of three two-battalion infantry regiments, a four-battalion artillery regiment, a combat engineer battalion, an antitank battal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles permitted. After the Nazi rise to power in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler's most overt and audacious moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi régime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and defense spending on the arms industry. The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military power. In the early part of the Second World War, the ''Wehrmacht'' employed combined arms tactics (close- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of German Divisions In World War II
This article lists divisions of the Wehrmacht (German Armed Forces) and Waffen-SS active during World War II, including divisions of the Heer (army), Luftwaffe (air force), and the Kriegsmarine (navy). Upgrades and reorganizations are shown only to identify the variant names for what is notionally a single unit; other upgrades and reorganizations are deferred to the individual articles. Due to the scope of this list, pre-war changes are not shown. Most of these divisions trained in Berlin, which is also where new military technology was kept and tested. German unit designations These designations are normally not translated and used in the German form in the unit name or description. ;''Bodenständige'': A static unit. Normally assigned to units who were deficient in transport and unable to move their own artillery. Many of these were divisions that had been mauled on the Eastern Front and were sent west to serve as coastal defence garrisons until sufficient resources were ava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Unit
Military organization or military organisation is the structuring of the armed forces of a state so as to offer such military capability as a national defense policy may require. In some countries paramilitary forces are included in a nation's armed forces, though not considered military. Armed forces that are not a part of military or paramilitary organizations, such as insurgent forces, often mimic military organizations, or use ''ad hoc'' structures, while formal military organization tends to use hierarchical forms. History The use of formalized ranks in a hierarchical structure came into widespread use with the Roman Army. In modern times, executive control, management and administration of military organization is typically undertaken by governments through a government department within the structure of public administration, often known as a ministry of defence or department of defense. These in turn manage military branches that themselves command formatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division (military)
A division is a large military unit or formation, usually consisting of between 6,000 and 25,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades; in turn, several divisions typically make up a corps. Historically, the division has been the default combined arms unit capable of independent operations. Smaller combined arms units, such as the American regimental combat team (RCT) during World War II, were used when conditions favored them. In recent times, modern Western militaries have begun adopting the smaller brigade combat team (similar to the RCT) as the default combined arms unit, with the division they belong to being less important. While the focus of this article is on army divisions, in naval usage " division" has a completely different meaning, referring to either an administrative/functional sub-unit of a department (e.g., fire control division of the weapons department) aboard naval and coast guard ships, shore commands, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav Gihr
Gustav Gihr (18 August 1894 – 31 October 1959) was a German general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing .... He commanded several infantry divisions during the war before surrendering to the Red Army in 1944. Biography On 15 May 1944 Gihr became commander of the 707th Infantry Division and fought during the Bobruisk Offensive on the Eastern Front. On 27 June 1944, at Bobruisk, Gihr was taken prisoner by the Red Army. He was released from captivity on 11 October 1955. Notes References * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Gihr, Gustov 1894 births 1959 deaths People from Tuttlingen (district) People from the Grand Duchy of Baden Major generals of the German Army (Wehrmacht) German Army personnel of World War I G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egon Von Neindorff
Egon von Neindorff (12 September 1892 – 15 April 1944) was a German general during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves of Nazi Germany. World War II On 1 July 1942 Neindorff took command of Fortress Brigade 1 in Crete. From September 1942 he commanded the 189th Reserve Division, and on 1 December 1942 was promoted to major-general. On 1 May 1943 Neindorff became commander of the 356th Infantry Division in Toulon, on 5 October 1943 he took over command of the 216th Infantry Division in Orel, on 20 October 1943 he commanded the 137th Infantry Division in Gomel, and from 16 December 1943 the 6th Infantry Division south of Gomel. From 17 January 1944 Neindorff led the 36th Infantry Division in Bobruisk. On 22 January 1944 he became commander of the German garrison at Tarnopol. In March–April 1944, it was encircled by Soviet forces. Hitler had declared Tarnopol a fortified strong point, to be held to the last man. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werner Von Gilsa
__NOTOC__ Werner Freiherr von und zu Gilsa (4 March 1889 – 8 May 1945) was a German general in the Wehrmacht during World War II, whose last assignment was as military commandant of Dresden. In 1936 he was the commander of the olympic village for the 1936 Summer Olympics. From 1 April 1941 to 4 April 1943, Gilsa was commander of the 216th Infantry Division. In the winter of 1941/42 the division was sent to the Eastern Front. Gilsa was promoted to General of Infantry on 1 July 1943. From 11 June 1943 to 23 November 1944 he was Commanding General of the LXXXIX Army Corps, which took part in the Battle of the Scheldt, from 2 October to 8 November 1944. Gilsa was Military Commander of Dresden from 15 March to May 1945. At the end of the war, Gilsa committed suicide. Awards and decorations * Iron Cross (1914) 1st Class (18 October 1914) & 1st Class (14 May 1915)Thomas 1997, p. 198. * Clasp to the Iron Cross (1939) 2nd Class (14 September 1939) & 1st Class (21 October 1939) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |