|
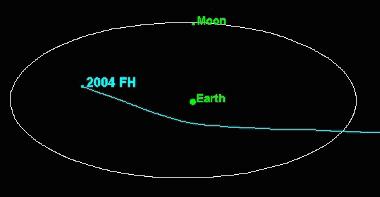
2004 FH
2004 FH is a micro-asteroid and near-Earth object of the Aten group, approximately 30 meters in diameter, that passed just above the Earth's surface on 18 March 2004, at 22:08 UTC. It was the 11th closest approach to Earth recorded . The asteroid was first observed on 16 March 2004, by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico. Orbit and classification is an Aten asteroid. It passed 43,000 km from the Earth on 18 March 2004. For comparison, geostationary satellites orbit Earth at 35,790 kilometers. Despite its small size, it is still the fourth largest asteroid detected coming closer to the Earth than the Moon. Had this object hit Earth, it would probably have detonated high in the atmosphere. It might have produced a blast measured in hundreds of kilotons of TNT, but may not have produced any effect on the ground. It could also have been an Earth-grazing fireball if it had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research
The Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) project is a collaboration of the United States Air Force, NASA, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Lincoln Laboratory for the systematic detection and tracking of near-Earth objects. LINEAR was responsible for the majority of asteroid discoveries from 1998 until it was overtaken by the Catalina Sky Survey in 2005. , LINEAR had detected 231,082 new small Solar System bodies, of which at least 2,423 were near-Earth asteroids and 279 were comets. The instruments used by the LINEAR program are located at Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site (ETS) on the White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) near Socorro, New Mexico. History In the late 1970s, the ''Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site'' facility (observatory code 704) was built at White Sands Missile Range. The project's prototype used low-light video cameras. In 1994 a new proposal was made for automated detection of asteroids, this time using newer digi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather features such as clouds and hazes), all retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere serves as a protective buffer between the Earth's surface and outer space, shields the surface from most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar radiation, keeps it warm and reduces diurnal temperature variation (temperature extremes between day and night) through heat retention (greenhouse effect), redistributes heat and moisture among different regions via air currents, and provides the chemical and climate conditions allowing life to exist and evolve on Earth. By mole fraction (i.e., by quantity of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other trace gases (see Composition below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Albedo
Albedo ( ; ) is the fraction of sunlight that is diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 (corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation) to 1 (corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation). ''Surface albedo'' is defined as the ratio of radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While directional-hemispherical reflectance factor is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds (as obtained from flux measurements) to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tumblers (small Solar System Bodies)
This is a list of tumblers, that is, small Solar System bodiess or moons that do not rotate in a fairly constant manner with a constant period. Instead of rotating around a constant axis or around an axis that itself moves evenly, they appear to tumble (see Poinsot's ellipsoid for an explanation). For true tumbling, the three moments of inertia must be different. If two are equal, then the axis of rotation will simply precess in a circle. As of 2018, there are 3 natural satellites and 198 confirmed or likely tumblers out of a total of nearly 800,000 discovered small Solar System bodies. The data is sourced from the "Lightcurve Data Base" (LCDB). The tumbling of a body can be caused by the torque from asymmetrically emitted radiation known as the YORP effect. Note that the rotation periods given below are apparent periods and are not constant for a tumbler. There is another definition of rotation, sometimes called intrinsic rotation, that relates to how the point on the object wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fast Rotators (minor Planets)
This is a list of fast rotators—"minor planets" (which includes asteroids) that have an exceptionally short rotation period, i.e. high rotation rate or spin rate. In some cases the rotation period is not constant because the object tumbles (see List of tumblers). In this list the periods are sourced from the ''Light Curve Data Base'' (LCDB), and are given in both seconds and hours. Most minor planets have rotation periods between 2 and 20 hours. , a group of 887 bodies – most of them are stony near-Earth asteroids with small diameters of barely 1 kilometre – have an estimated period of less than 2.2 hours. According to the Minor Planet Center, most small bodies are thought to be rubble pile In astronomy, a rubble pile is a celestial body that consists of numerous pieces of debris that have coalesced under the influence of gravity. Rubble piles have low density because there are large cavities between the various chunks that make the ...s – conglomerations of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCDB Quality Code
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph of the light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude of light received on the ''y''-axis and with time on the ''x''-axis. The light is usually in a particular frequency interval or band. Light curves can be periodic, as in the case of eclipsing binaries, Cepheid variables, other periodic variables, and transiting extrasolar planets; or aperiodic, like the light curve of a nova, cataclysmic variable star, supernova, microlensing event, or binary as observed during occultation events. The study of a light curve and other observations can yield considerable information about the physical process that produces such a light curve, or constrain the physical theories about it. Variable stars Graphs of the apparent magnitude of a variable star over time are commonly used to visualise and analyse their behaviour. Although the categorisation of variable star types is increasingly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnitude (astronomy)
In astronomy, magnitude is a measure of the brightness of an astronomical object, object, usually in a defined passband. An imprecise but systematic determination of the magnitude of objects was introduced in ancient times by Hipparchus. Magnitude values do not have a unit. The scale is Logarithmic scale, logarithmic and defined such that a magnitude 1 star is exactly 100 times brighter than a magnitude 6 star. Thus each step of one magnitude is \sqrt[5] \approx 2.512 times brighter than the magnitude 1 higher. The brighter an object appears, the lower the value of its magnitude, with the brightest objects reaching negative values. Astronomers use two different definitions of magnitude: apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. The ''apparent'' magnitude () is the brightness of an object and depends on an object's intrinsic luminosity, its Cosmic distance ladder, distance, and the Extinction (astronomy), extinction reducing its brightness. The ''absolute'' magnitude () describes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation Period
In astronomy, the rotation period or spin period of a celestial object (e.g., star, planet, moon, asteroid) has two definitions. The first one corresponds to the '' sidereal rotation period'' (or ''sidereal day''), i.e., the time that the object takes to complete a full rotation around its axis relative to the background stars ( inertial space). The other type of commonly used "rotation period" is the object's '' synodic rotation period'' (or ''solar day''), which may differ, by a fraction of a rotation or more than one rotation, to accommodate the portion of the object's orbital period around a star or another body during one day. Measuring rotation For solid objects, such as rocky planets and asteroids, the rotation period is a single value. For gaseous or fluid bodies, such as stars and giant planets, the period of rotation varies from the object's equator to its pole due to a phenomenon called differential rotation. Typically, the stated rotation period for a giant pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raoul Behrend
This is a list of minor-planet discoverers credited by the Minor Planet Center with the discovery of one or several minor planets (such as near-Earth and main-belt asteroids, Jupiter trojans and distant objects). , the discovery of 612,011 numbered minor planets are credited to 1,141 astronomers and 253 observatories, telescopes or surveys ''(see )''. On how a discovery is made, ''see observations of small Solar System bodies. For a description of the tables below, see ''. Discovering astronomers Discovering dedicated institutions Discovering sites Notes The discovery table consist of the following fields: * Astronomers and Institutions: links to the corresponding article about the discovering astronomer or institution on Wikipedia. If not linked, the displayed name should be a redirect to this list. For example, the page forwards to the anchored table row using the astronomer's MPC-name as ID. * Discoveries: displays the total number of discovered an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefano Sposetti
Stefano Sposetti (born 22 December 1958) is a Swiss amateur astronomer and a prolific discoverer of minor planets. He lives in Gnosca, in the Italian-speaking part of Switzerland in the Ticino Alps, where the Gnosca Observatory is located. Sposetti took images of 2004 FH, an Aten asteroid that made a sub-lunar flyby of Earth. In addition, he detects the optical counterparts of gamma-ray bursts and conducts transit photometry on exoplanets at his observatory. As of 2019, Sposetti's discoveries include 164 minor planets (numbered only). The Minor Planet Center The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. Funct ... ranks him 70th in the list of all-time, worldwide discoverers. Asteroid 22354 Sposetti has been named after him. List of discovered minor planets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petr Pravec
Petr Pravec (born September 17, 1967) is a Czech astronomer and a discoverer of minor planets, born in Třinec, Czech Republic. Pravec is a prolific discoverer of binary asteroids, expert in photometric observations and rotational lightcurves at Ondřejov Observatory. He is credited by the Minor Planet Center with the discovery and co-discovery of 350 numbered minor planets, and is leading the effort of a large consortium of stations called "BinAst" to look for multiplicity in the near-Earth objects and inner main-belt populations. He is a member of the ''Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic''. The main-belt asteroid 4790 Petrpravec, discovered by Eleanor Helin Eleanor Francis "Glo" Helin (née Francis, 19 November 1932 – 25 January 2009) was an American astronomer. She was principal investigator of the Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking (NEAT) program of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. (Some sources gi ... in 1988, is named after him. The official naming citation wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightcurve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph (discrete mathematics), graph of the Radiance, light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude (astronomy), magnitude of light received on the ''y''-axis and with time on the ''x''-axis. The light is usually in a particular frequency interval or frequency band, band. Light curves can be periodic, as in the case of eclipsing binary, eclipsing binaries, Cepheid variables, other periodic variables, and Methods of detecting extrasolar planets#Transit photometry, transiting extrasolar planets; or aperiodic, like the light curve of a nova, cataclysmic variable star, supernova, gravitational microlensing, microlensing event, or binary as observed during occultation events. The study of a light curve and other observations can yield considerable information about the physical process that produces such a light curve, or constrain the physical theories about it. Variable stars Graphs of the ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |