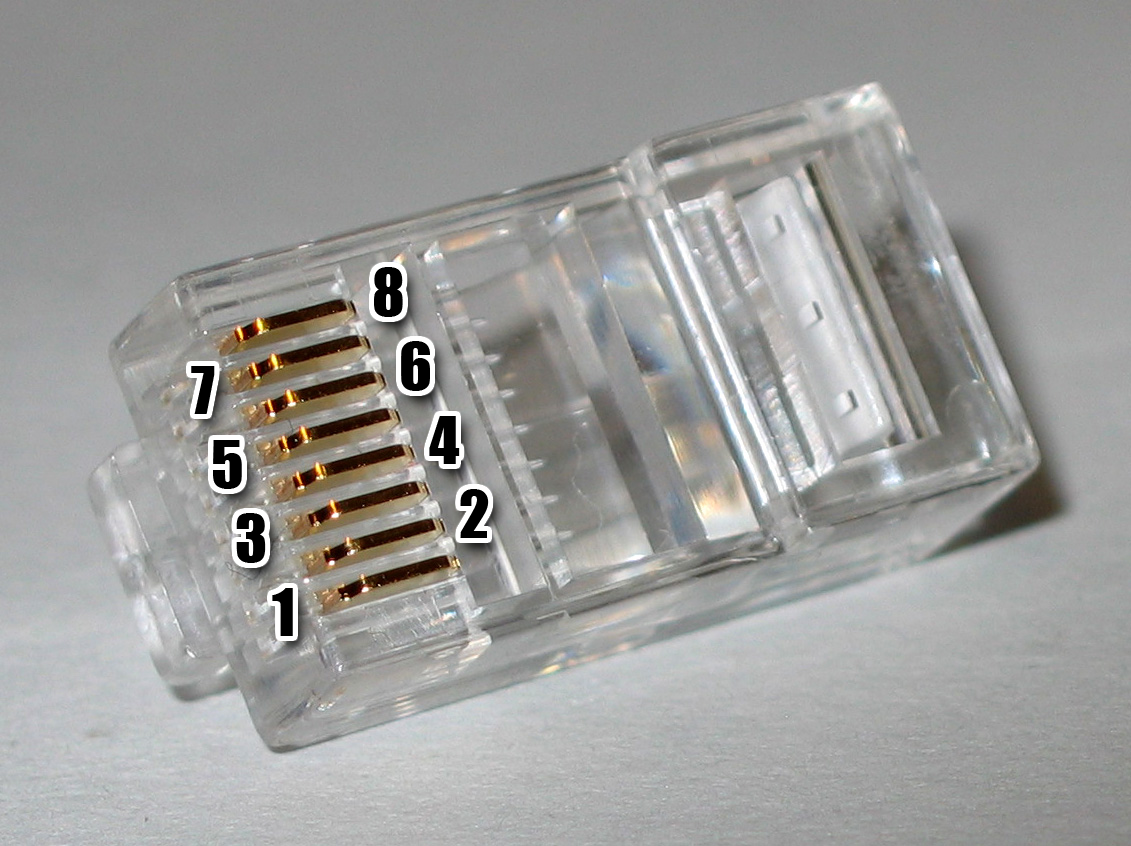
|
100BaseVG
100BaseVG is a 100 Mbit/s Ethernet standard specified to run over four pairs of category 3 cable (cable also known as voice grade, hence the "VG"). It is also called 100VG-AnyLAN because it was defined to carry both Ethernet and Token Ring frame types. 100BaseVG was originally proposed by Hewlett-Packard, ratified by the IEEE in 1995 and was practically extinct by 1998. In 2001 IEEE recorded the status of its 100BaseVG standard as being a "Withdrawn Standard" (defined as "A standard which is no longer maintained and which may contain significant obsolete or erroneous information.") Standardization 100BaseVG started in the IEEE 802.3 committee as Fast Ethernet. One faction wanted to keep carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) in order to keep it pure Ethernet, even though the collision domain problem limited the distances to one tenth that of 10BASE-T. Another faction wanted to change to a polling architecture from the hub (they called it " De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Ethernet
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common. Fast Ethernet was introduced in 1995 as the IEEE 802.3u standard and remained the fastest version of Ethernet for three years before the introduction of Gigabit Ethernet. The acronym ''GE/FE'' is sometimes used for devices supporting both standards. Nomenclature The "100" in the media type designation refers to the transmission speed of 100 Mbit/s, while the "BASE" refers to baseband signaling. The letter following the dash ("T" or "F") refers to the physical medium that carries the signal (twisted pair or fiber, respectively), while the last character ("X", "4", etc.) refers to the line code method used. Fast Ethernet is sometimes referred to as 100BASE-X, where "X" is a placeholder for the FX and TX variants. General design Fast Ethernet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Category 3 Cable
Category 3 cable, commonly known as or station wire, and less commonly known as VG or voice-grade (as, for example, in 100BaseVG), is an unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable used in telephone wiring. It is part of a family of standards defined jointly by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) and the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and published in TIA/EIA-568-B. Although designed to reliably carry data up to 10 Mbit/s, modern data networks run at much higher speeds, and or better cable is generally used for new installations. Networking was widely used in computer networking in the early 1990s for 10BASE-T Ethernet and, to a much lesser extent, for 100BaseVG Ethernet, Token Ring and 100BASE-T4. The original Power over Ethernet 802.3af specification supports the use of cable, but the later 802.3at Type 2 high-power variation does not.IEEE 802.3at-2009, clause 33.1.1c In some use cases and for short distances, Cat 3 may be capable of carrying 100BA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
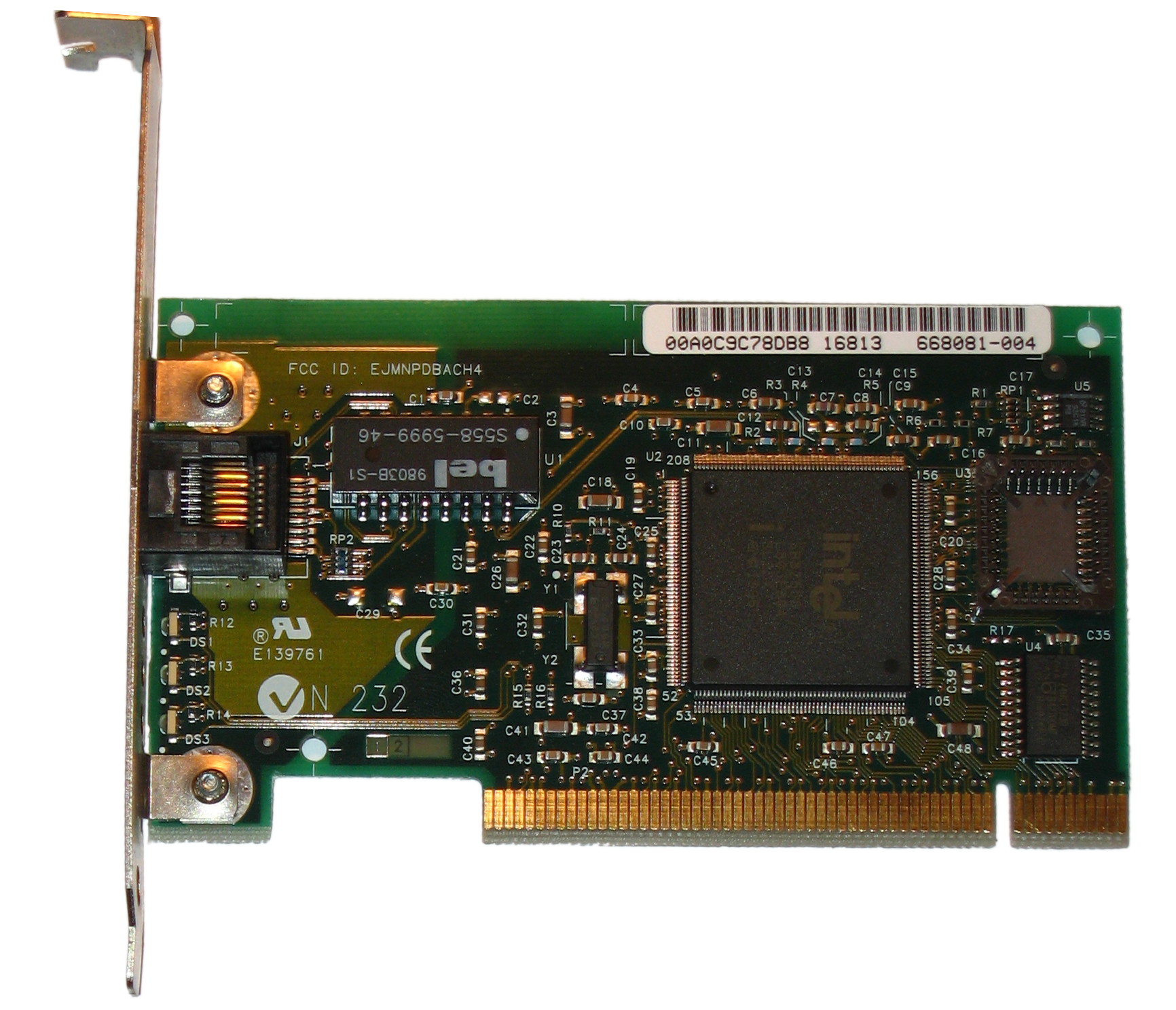
Demand Priority
Demand priority is a media-access method used in 100BaseVG, a 100 megabit per second (Mbit/s) Ethernet implementation proposed by Hewlett-Packard (HP) and AT&T Microelectronics, later standardized as IEEE 802.12. Demand priority shifts network access control from the workstation to a hub. This access method An access method is a function of a mainframe operating system that enables access to data on disk, tape or other external devices. Access methods were present in several mainframe operating systems since the late 1950s, under a variety of name ... works with a star topology. In this method, a node that wishes to transmit indicates this wish to the hub and also requests high- or regular-priority service for its transmission. After it obtains permission, the node begins transmitting to the hub. The hub is responsible for passing the transmission on to the destination node; that is, the hub is responsible for providing access to the network. A hub will pass high priority tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Category 3 Cable
Category 3 cable, commonly known as or station wire, and less commonly known as VG or voice-grade (as, for example, in 100BaseVG), is an unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable used in telephone wiring. It is part of a family of standards defined jointly by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) and the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and published in TIA/EIA-568-B. Although designed to reliably carry data up to 10 Mbit/s, modern data networks run at much higher speeds, and or better cable is generally used for new installations. Networking was widely used in computer networking in the early 1990s for 10BASE-T Ethernet and, to a much lesser extent, for 100BaseVG Ethernet, Token Ring and 100BASE-T4. The original Power over Ethernet 802.3af specification supports the use of cable, but the later 802.3at Type 2 high-power variation does not.IEEE 802.3at-2009, clause 33.1.1c In some use cases and for short distances, Cat 3 may be capable of carrying 100BA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Token Ring
Token Ring network IBM hermaphroditic connector with locking clip. Screen contacts are prominently visible, gold-plated signal contacts less so. Token Ring is a computer networking technology used to build local area networks. It was introduced by IBM in 1984, and standardized in 1989 as IEEE 802.5. It uses a special three-byte frame called a ''token'' that is passed around a logical ''ring'' of workstations or servers. This token passing is a channel access method providing fair access for all stations, and eliminating the collisions of contention-based access methods. Token Ring was a successful technology, particularly in corporate environments, but was gradually eclipsed by the later versions of Ethernet. History A wide range of different local area network technologies were developed in the early 1970s, of which one, the Cambridge Ring, had demonstrated the potential of a token passing ring topology, and many teams worldwide began working on their own implementatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE 802
IEEE 802 is a family of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standards for local area networks (LAN), personal area network (PAN), and metropolitan area networks (MAN). The IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee (LMSC) maintains these standards. The IEEE 802 family of standards has had twenty-four members, numbered 802.1 through 802.24, with a working group of the LMSC devoted to each. However, not all of these working groups are currently active. The IEEE 802 standards are restricted to computer networks carrying variable-size packets, unlike cell relay networks, for example, in which data is transmitted in short, uniformly sized units called cells. Isochronous signal networks, in which data is transmitted as a steady stream of octets, or groups of octets, at regular time intervals, are also outside the scope of the IEEE 802 standards. The number 802 has no significance: it was simply the next number in the sequence that the IEEE used for standards project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet Over Twisted Pair
Ethernet over twisted-pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. They are a subset of all Ethernet physical layers. Early Ethernet used various grades of coaxial cable, but in 1984, StarLAN showed the potential of simple unshielded twisted pair. This led to the development of 10BASE-T and its successors 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-T and 10GBASE-T, supporting speeds of 10 and 100 megabit per second, then 1 and 10 gigabit per second respectively. Two new variants of 10 megabit per second Ethernet over a ''single'' twisted pair, known as 10BASE-T1S and 10BASE-T1L, were standardized in IEEE Std 802.3cg-2019. 10BASE-T1S has its origins in the automotive industry and may be useful in other short-distance applications where substantial electrical noise is present. 10BASE-T1L is a long-distance Ethernet, supporting connections up to 1 km in length. Both of these standards are finding applications implementing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet uses coaxial cable as a shared medium, while the newer Ethernet variants use twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with switches. Over the course of its history, Ethernet data transfer rates have been increased from the original to the latest , with rates up to under development. The Ethernet standards include several wiring and signaling variants of the OSI physical layer. Systems communicating over Ethern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSMA/CD
Carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is a medium access control (MAC) method used most notably in early Ethernet technology for local area networking. It uses carrier-sensing to defer transmissions until no other stations are transmitting. This is used in combination with collision detection in which a transmitting station detects collisions by sensing transmissions from other stations while it is transmitting a frame. When this collision condition is detected, the station stops transmitting that frame, transmits a jam signal, and then waits for a random time interval before trying to resend the frame. CSMA/CD is a modification of pure carrier-sense multiple access (CSMA). CSMA/CD is used to improve CSMA performance by terminating transmission as soon as a collision is detected, thus shortening the time required before a retry can be attempted. With the growing popularity of Ethernet switches in the 1990s, IEEE 802.3 deprecated Ethernet repeaters in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbol Rate
In a digitally modulated signal or a line code, symbol rate, modulation rate or baud rate is the number of symbol changes, waveform changes, or signaling events across the transmission medium per unit of time. The symbol rate is measured in ''baud'' (Bd) or ''symbols per second''. In the case of a line code, the symbol rate is the pulse rate in pulses per second. Each symbol can represent or convey one or several bits of data. The symbol rate is related to the ''gross bit rate'', expressed in '' bits per second''. Symbols A symbol may be described as either a pulse in digital baseband transmission or a tone in passband transmission using modems. A symbol is a waveform, a state or a significant condition of the communication channel that ''persists'', for a fixed period of time. A sending device places symbols on the channel at a fixed and known symbol rate, and the receiving device has the job of detecting the sequence of symbols in order to reconstruct the transmitted data. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Code
In telecommunication, a line code is a pattern of voltage, current, or photons used to represent digital data transmitted down a communication channel or written to a storage medium. This repertoire of signals is usually called a constrained code in data storage systems. Some signals are more prone to error than others as the physics of the communication channel or storage medium constrains the repertoire of signals that can be used reliably. Common line encodings are unipolar, polar, bipolar, and Manchester code. Transmission and storage After line coding, the signal is put through a physical communication channel, either a transmission medium or data storage medium.Karl Paulsen"Coding for Magnetic Storage Mediums".2007. The most common physical channels are: * the line-coded signal can directly be put on a transmission line, in the form of variations of the voltage or current (often using differential signaling). * the line-coded signal (the ''baseband signal'') un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shielded Twisted Pair
Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring used for communications in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of improving electromagnetic compatibility. Compared to a single conductor or an untwisted balanced pair, a twisted pair reduces electromagnetic radiation from the pair and crosstalk between neighboring pairs and improves rejection of external electromagnetic interference. It was invented by Alexander Graham Bell. For additional noise immunity, twisted-pair cabling may be shielded. Cable with shielding is known as shielded twisted pair (STP) and without as unshielded twisted pair (UTP). Explanation A twisted pair can be used as a balanced line, which as part of a balanced circuit can greatly reduce the effect of noise currents induced on the line by coupling of electric or magnetic fields. The idea is that the currents induced in each of the two wires are very nearly equal. The twisting ensures that the two wires are on averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |