|
1935 In Rail Transport
Events January events * January 2 – Chicago & North Western Railway begins ''Twin Cities 400, 400'' passenger train service between Chicago, Illinois, and Saint Paul, Minnesota; it was so named because the 400 mile trip was intended to take 400 minutes, though that pace wasn't quite reached until a few months later. Still, it was believed to be the fastest train in the world over a distance greater than . * January 28 – To mark completion of the electric line from Washington DC to New York City, the Pennsylvania Railroad runs a special train hauled by Pennsylvania Railroad 4800, the electric locomotive making a round trip from Washington to Philadelphia setting a speed record on the return run of 1 hour 50 minutes. The line, with the GG1 locomotives, begins regular revenue service on February 10. * January 31 – Union Pacific's M-10000 enters service as the ''City of Salina'' between Salina, Kansas, and Kansas City. The 116 seat train carries an average 28 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago & North Western Railway
The Chicago and North Western was a Railroad classes#Class I, Class I railroad in the Midwestern United States. It was also known as the "North Western". The railroad operated more than of track at the turn of the 20th century, and over of track in seven states before retrenchment in the late 1970s. Until 1972, when the employees purchased the company, it was named the Chicago and North Western Railway (or Chicago and North Western Railway Company). The C&NW became one of the longest railroads in the United States as a result of mergers with other railroads, such as the Chicago Great Western Railway, Minneapolis and St. Louis Railway and others. By 1995, track sales and abandonment had reduced the total mileage to about 5,000. The majority of the abandoned and sold lines were lightly trafficked branches in Iowa, Illinois, Minnesota, South Dakota and Wisconsin. Large line sales, such as those that resulted in the Dakota, Minnesota and Eastern Railroad, further helped reduce th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with about 55% of the lines in the world using it. All high-speed rail lines use standard gauge except High-speed rail in Russia, those in Russia, High-speed rail in Finland, Finland, High-speed rail in Uzbekistan, Uzbekistan, and some line sections in High-speed rail in Spain, Spain. The distance between the inside edges of the heads of the rails is defined to be 1,435 mm except in the United States, Canada, and on some heritage British lines, where it is defined in Imperial and US customary measurement systems, U.S. customary/Imperial units, British Imperial units as exactly "four feet eight and one half inches", which is equivalent to 1,435.1mm. History As railways developed and expa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5 Ft And 1520 Mm Gauge Railways
Railways with a railway track track gauge, gauge of first appeared in the United Kingdom and the United States. This gauge became commonly known as "Russian gauge", because the government of the Russian Empire chose it in 1843. Former areas and states (such as Grand Duchy of Finland, Finland) of the Empire have inherited this standard. However in 1970, Rail transport in the Soviet Union, Soviet Railways re-defined the gauge as 1,520 mm (). With about of track, 1,520 mm is the second-most common gauge in the world, after . History Great Britain, 1748 In 1748, the Wylam waggonway was built to a gauge for the shipment of coal from Wylam to Lemington down the River Tyne. In 1839, the Eastern Counties Railway was constructed. In 1840, the Northern and Eastern Railway was built. In 1844, both lines were Track gauge conversion, converted to . In 1903, the East Hill Cliff Railway, a funicular, was opened. United States, 1827 In 1827, Horatio Allen, the chief en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
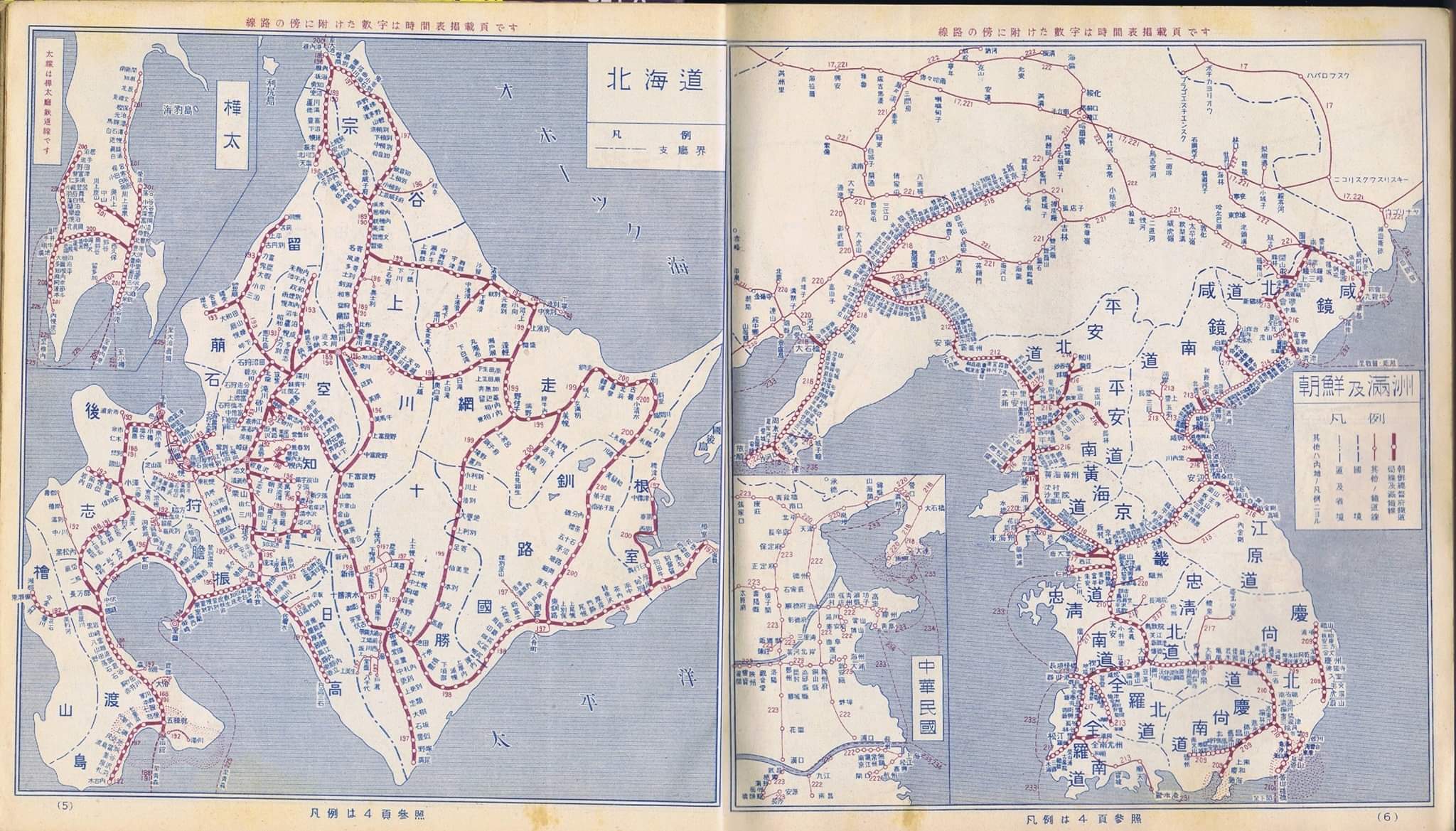
Manchukuo National Railway
The Manchukuo National Railway (Traditional Chinese and Japanese kanji: , Japanese romanization: ''Manshū Kokuyū Tetsudō'') was the state-owned national railway company of Manchukuo. Generally called the "國線" ("National Line", ''Kokusen''), it was controlled by the Manchukuo Ministry of Transportation and had its lines primarily in the central and northern parts of the country. In local newspapers it was simply referred to as "國鉄" (Japanese: ''Kokutetsu'', "National Rail"). It was built, operated and managed by the South Manchuria Railway, a state-owned national railway company of the Empire of Japan, of which the Kwantung Army frequently intervened in its affairs. History Sino-Japanese competition in railway construction In Manchuria, the division of rights in mainland China manifested itself in the form of competition in railway construction. As a result, following the end of the Russo-Japanese War, railway rights in Manchuria were split between Russia, which opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopedia, online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest-running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in Edinburgh, Scotland, in three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size; the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810), it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent contributors, and the 9th (1875–1889) and Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, 11th editions (1911) are landmark encyclopaedias for scholarship and literary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchukuo Government
Manchurian nationalism or Manchu nationalism () refers to the ethnic nationalism of the Manchu people or the territorial nationalism of the inhabitants of Manchuria, regardless of ethnic origin. Overview While ruling China proper, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty had promoted a common, "Manchufying" identity among members of the Eight Banners, its primary military forces. Manchus were thus strongly associated with the Banner system, even though there were Mongol and Han Chinese Bannermen as well. The Banner identity was not yet racial or national, but still strongly divided the mostly Manchu Banner people from the primarily Han Chinese civilians of the Qing Empire. This divide grew with the overthrow of the Qing dynasty in 1912, and the foundation of the Republic of China. Thereafter, ethnic identity grew greatly in importance, and the Banner people had to decide whether to identify as Manchu, Han Chinese, or Mongol. Many of Mongol or Han Chinese ethnic origin opted to be classified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially known as the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of Great Manchuria thereafter, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Northeast China that existed from 1932 until its dissolution in 1945. It was ostensibly founded as a republic, its territory consisting of the lands seized in the Japanese invasion of Manchuria; it was later declared to be a constitutional monarchy in 1934, though very little changed in the actual functioning of government. Manchukuo received limited diplomatic recognition, mostly from states aligned with the Axis powers, with its existence widely seen as illegitimate. The region now known as Manchuria had historically been the homeland of the Manchu people, though by the 20th century they had long since become a minority in the region, with Han Chinese constituting by far the largest ethnic group. The Manchu-led Qing dynasty, which had governed China since 17th century, was overthrown with the permanent abolition of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Eastern Railway
The Chinese Eastern Railway or CER (, , or , ''Kitaysko-Vostochnaya Zheleznaya Doroga'' or ''KVZhD''), is the historical name for a railway system in Northeast China (also known as Manchuria). The Russian Empire constructed the line from 1897 to 1902. The Railway was a concession to Russia, and later the Soviet Union, granted by the Qing dynasty government of Imperial China. The system linked Chita with Vladivostok in the Russian Far East and with Port Arthur, then an Imperial Russian leased ice-free port. The T-shaped line consisted of three branches: * the western branch, now the Harbin–Manzhouli Railway * the eastern branch, now the Harbin–Suifenhe Railway * the southern branch, now part of the Beijing–Harbin Railway which intersected in Harbin. Saint Petersburg administered the railway and the concession, known as the Chinese Eastern Railway Zone, from the city of Harbin, which grew into a major rail-hub. The southern branch of the CER, known as the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |