|
1803 Zwicky
1803 Zwicky, '' prov. designation'': , is a stony Phocaea asteroid and binary system from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately in diameter. It was discovered on 6 February 1967, by Swiss astronomer Paul Wild at Zimmerwald Observatory near Bern, Switzerland. It was later named after Swiss astronomer Fritz Zwicky. The discovery of a 2.5-kilometer sized companion was announced on 8 March 2021. Classification and orbit ''Zwicky'' is a member of the Phocaea family (), an asteroid family with two thousand members, named after their largest member, 25 Phocaea. It orbits the Sun in the inner main-belt at a distance of 1.8–2.9 AU once every 3 years and 7 months (1,316 days; semi-major axis of 2.35 AU). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.25 and an inclination of 22 ° with respect to the ecliptic. It was first identified as at Lowell Observatory in 1931, extending the body's observation arc by 36 years prior to its official discovery observation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Wild (Swiss Astronomer)
Paul Wild (; 5 October 1925 – 2 July 2014) was a Swiss astronomer and director of the Astronomical Institute of the University of Bern, who discovered numerous comets, asteroids and supernovae. Biography Wild was born on 5 October 1925 in the village of Wädenswil near Zürich, Switzerland. From 1944 through 1950, he studied mathematics and physics at the ETH Zurich. Thereafter, he worked at the California Institute of Technology where he researched galaxies and supernovas under the leadership of countryman Fritz Zwicky from 1951 through 1955. At the Zimmerwald Observatory, near Bern, Wild made his first cometary discovery C/1957 U1 (1957 IX) on 2 October 1957. The parabolic comet was later named "Latyshev-Wild– Burnham". Professor Wild became director of the Astronomical Institute of the University of Bern in 1980, and remained in this position until 1991. He died on 2 July 2014 at the age of 88 in Bern. Discoveries During countless nights Wild observed the ski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
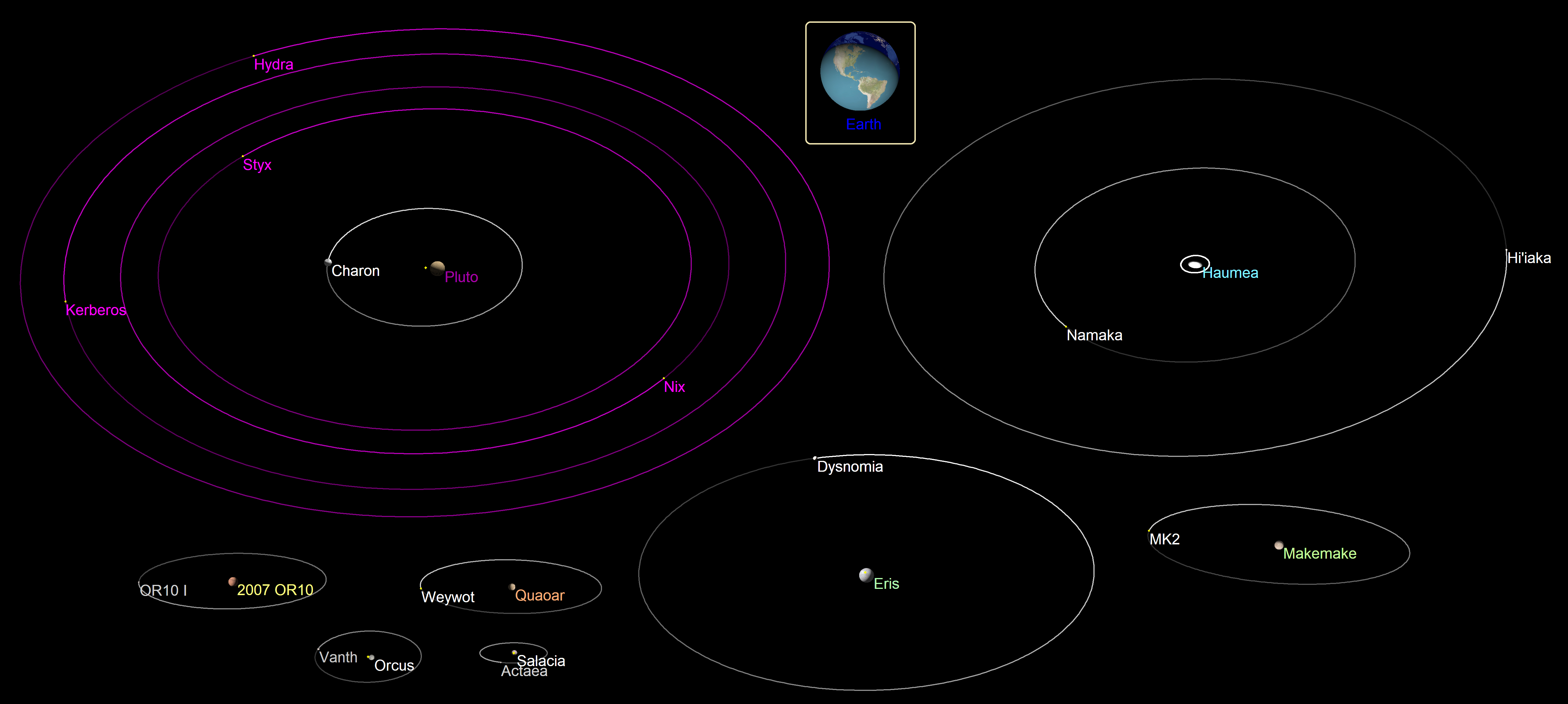
Minor-planet Moon
A minor-planet moon is an astronomical object that orbits a minor planet as its natural satellite. , there are 457 minor planets known or suspected to have moons. Discoveries of minor-planet moons (and binary objects, in general) are important because the determination of their orbits provides estimates on the mass and density of the primary, allowing insights into their physical properties that are generally not otherwise accessible. Several of the moons are quite large compared to their primaries: 90 Antiope, Mors–Somnus and Sila–Nunam (95%), Patroclus–Menoetius, Altjira and Lempo–Hiisi (90%, with Lempo–Paha at 50%). The largest known minor-planet moon in ''absolute'' size is Pluto's largest moon Charon, which itself has about half the diameter of Pluto. There are also several known ring systems around distant objects (see: '' Rings of Chariklo'' and ''Chiron''). Terminology In addition to the terms ''satellite'' and ''moon'', the term "binary" (binary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed to form a diffuse nebula. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. The last supernova directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appearing not long after Tycho's Supernova in 1572, both of which were visible to the naked eye. The supernova remnant, remnants of more recent supernovae have been found, and observations of supernovae in other galaxies suggest they occur in the Milky Way on average about three times every century. A supernova in the Milky Way would almost certainly be observable through mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Cluster
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. Clusters consist of galaxies, heated gas, and dark matter. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after superclusters. They were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. Together, galaxy groups and clusters form superclusters. Basic properties Galaxy clusters typically have the following properties: * They contain 100 to 1,000 galaxies, hot X-ray emitting gas and large amounts of dark matter. Details are described in the "Composition" section. * They have total masses of 1014 to 1015 solar masses. * They typically have diameters from 1 to 5 Mpc ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caltech
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech) is a private university, private research university in Pasadena, California, United States. The university is responsible for many modern scientific advancements and is among a small group of Institute of Technology (United States), institutes of technology in the United States that are devoted to the instruction of pure and applied sciences. The institution was founded as a preparatory and vocational school by Amos G. Throop in 1891 and began attracting influential scientists such as George Ellery Hale, Arthur Amos Noyes, and Robert Andrews Millikan in the early 20th century. The vocational and preparatory schools were disbanded and spun off in 1910, and the college assumed its present name in 1920. In 1934, Caltech was elected to the Association of American Universities, and the antecedents of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which Caltech continues to manage and operate, were established between 1936 and 1943 under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''minor planet'', but that year's meeting IAU definition of planet, reclassified minor planets and comets into dwarf planets and Small Solar System body, small Solar System bodies (SSSBs).Press release, IAU 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes International Astronomical Union, August 24, 2006. Accessed May 5, 2008. In contrast to the eight official planets of the Solar System, all minor planets fail to clearing the neighborhood, clear their orbital neighborhood. Minor planets include asteroids (near- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observation Arc
In observational astronomy, the observation arc (or arc length) of a Solar System body is the time period between its earliest and latest observations, used for tracing the body's path. It is usually given in days or years. The term is mostly used in the discovery and tracking of asteroids and comets. Arc length has the greatest influence on the accuracy of an orbital estimate. The number, spacing of intermediate observations, and timestamps have a lesser effect. Short arcs A very short arc leaves a high uncertainty parameter. The object might be in one of many different orbits, at many distances from Earth. In some cases, the initial arc was too short to determine if the object was in orbit around the Earth, or orbiting out in the asteroid belt. With a 1-day observation arc, was thought to be a trans-Neptunian dwarf planet, but is now known to be a 1 km main-belt asteroid. With an observation arc of 3 days, was thought to be a Mars-crossing asteroid that could be a thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lowell Observatory
Lowell Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona, United States. Lowell Observatory was established in 1894, placing it among the oldest observatories in the United States, and was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1965. and In 2011, the Observatory was named one of "The World's 100 Most Important Places" by Time Magazine. It was at the Lowell Observatory that the dwarf planet Pluto was discovered in 1930 by Clyde Tombaugh. The observatory was founded by astronomer Percival Lowell of Boston's Lowell family and is overseen by a sole trustee, a position historically handed down through the family. The first trustee was Lowell's third cousin Guy Lowell (1916–1927). Percival's nephew Roger Putnam served from 1927 to 1967, followed by Roger's son Michael (1967–1987), Michael's brother William Lowell Putnam III (1987–2013), and current trustee W. Lowell Putnam. Multiple astronauts attended the Lowell Observatory in 1963 while the moon was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth's orbit, Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the fixed stars, background of stars – specifically the Zodiac constellations. The planets of the Solar System can also be seen along the ecliptic, because their orbital planes are very close to Earth's. The Moon's orbital plane is also similar to Earth's; the ecliptic is so named because the ancients noted that eclipses only occur when the Moon is crossing it. The ecliptic is an important Plane of reference, reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Ancient scientists were able to calculate Earth's axial tilt by comparing the ecliptic plane to that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is a hyperbola. The term derives its name from the parameters of conic sections, as every Kepler orbit is a conic section. It is normally used for the isolated two-body problem, but extensions exist for objects following a rosette orbit through the Galaxy. Definition In a two-body problem with inverse-square-law force, every orbit is a Kepler orbit. The eccentricity of this Kepler orbit is a non-negative number that defines its shape. The eccentricity may take the following values: * Circular orbit: * Elliptic orbit: * Parabolic trajectory: * Hyperbolic trajectory: The eccentricity is given by e = \sqrt where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-major Axis
In geometry, the major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter: a line segment that runs through the center and both foci, with ends at the two most widely separated points of the perimeter. The semi-major axis (major semiaxis) is the longest semidiameter or one half of the major axis, and thus runs from the centre, through a focus, and to the perimeter. The semi-minor axis (minor semiaxis) of an ellipse or hyperbola is a line segment that is at right angles with the semi-major axis and has one end at the center of the conic section. For the special case of a circle, the lengths of the semi-axes are both equal to the radius of the circle. The length of the semi-major axis of an ellipse is related to the semi-minor axis's length through the eccentricity and the semi-latus rectum \ell, as follows: The semi-major axis of a hyperbola is, depending on the convention, plus or minus one half of the distance between the two branches. Thus it is the distance from the ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |