|
16x9
16:9 (1.7:1) is a widescreen aspect ratio with a width of 16 units and height of 9. Once seen as exotic, since 2009, it has become the most common aspect ratio for televisions and computer monitors, and is also the international standard image format for UHD, HDTV, Full HD, and SD digital television. It has replaced the "fullscreen" 4:3 aspect ratio. 16:9 (1.7:1) (spoken as "sixteen by nine" or "sixteen to nine") is the international standard format of Ultra HD, non-HD digital widescreen television and analog widescreen television systems PALplus and Wide-aspect Clear-vision. Japan's Hi-Vision originally started with a 5:3 (1.6:1) ratio but converted when the international standards group introduced a wider ratio of 16 to 9. Many digital video cameras have the capability to record in 16:9, and 16:9 is the only widescreen aspect ratio natively supported by the DVD standard. It is also the native aspect ratio of Blu-ray discs, but Blu-ray and DVD producers can also choose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PALplus
PALplus (or ''PAL+'') is an analogue television broadcasting system aimed to improve and enhance the PAL format by allowing 16:9 (or 1.77:1) aspect ratio broadcasts, while remaining compatible with existing television receivers, defined by International Telecommunication Union, ITU recommendation BT.1197-1. Introduced in 1993, it followed experiences with the HD-MAC (high definition) and D2-MAC, hybrid analogue-digital widescreen formats that were incompatible with PAL receivers. It was developed at the University of Dortmund in Germany, in cooperation with German terrestrial broadcasters and European and Japanese manufacturers. The system had some adoption across Europe during the late 1990s and helped introduce widescreen TVs in the market, but never became mainstream. A similar system, developed in Japan at the same time and named Clear-Vision, EDTV-II/ Wide-aspect Clear-vision, allows for 16:9 NTSC broadcasts. History The Multiplexed Analogue Components, MAC family of standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letterboxing (filming)
Letterboxing is the practice of transferring film shot in a widescreen aspect ratio to standard-width video formats while preserving the film's original aspect ratio. The resulting videographic image has mattes (black bars) above and below it; these mattes are part of each frame of the video signal. LBX and LTBX are identifying abbreviations for films and images thus formatted. Etymology The term refers to the shape of a letter box, a slot in a wall or door through which mail is delivered, being rectangular and wider than it is high. Early home video use The first use of letterbox in consumer video appeared with the RCA Capacitance Electronic Disc (CED) videodisc format. Initially, letterboxing was limited to several key sequences of a film such as opening and closing credits, but was later used for entire films. The first fully letterboxed CED release was ''Amarcord'' in 1984, and several others followed including '' The Long Goodbye'', '' Monty Python and the Holy Grail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samsung
The Samsung Group (or simply Samsung) ( ko, 삼성 ) is a South Korean multinational manufacturing conglomerate headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea. It comprises numerous affiliated businesses, most of them united under the ''Samsung'' brand, and is the largest South Korean (business conglomerate). Samsung has the eighth highest global brand value. Samsung was founded by Lee Byung-chul in 1938 as a trading company. Over the next three decades, the group diversified into areas including food processing, textiles, insurance, securities, and retail. Samsung entered the electronics industry The electronics industry is the economic sector that produces electronic devices. It emerged in the 20th century and is today one of the largest global industries. Contemporary society uses a vast array of electronic devices built-in automated or ... in the late 1960s and the construction and shipbuilding industries in the mid-1970s; these areas would drive its subseque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD-MAC
HD-MAC (High Definition Multiplexed Analogue Components) was a broadcast television standard proposed by the European Commission in 1986, as part of Eureka 95 project. It belongs to the MAC - Multiplexed Analogue Components standard family. It is an early attempt by the EEC to provide High-definition television (HDTV) in Europe. It is a complex mix of analogue signal (based on the Multiplexed Analogue Components standard), multiplexed with digital sound, and assistance data for decoding (DATV). The video signal (1250 lines/50 fields per second in 16:9 aspect ratio, with 1152 visible lines) was encoded with a modified D2-MAC encoder. HD-MAC could be decoded by normal D2-MAC standard definition receivers, but no extra resolution was obtained and certain artifacts were visible. To decode the signal in full resolution a specific HD-MAC tuner was required . Naming convention The European Broadcasting Union video format description is as follows: width x height can type: i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been described as a ''sui generis'' political entity (without precedent or comparison) combining the characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.8per cent of the world population in 2020, the EU generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around trillion in 2021, constituting approximately 18per cent of global nominal GDP. Additionally, all EU states but Bulgaria have a very high Human Development Index according to the United Nations Development Programme. Its cornerstone, the Customs Union, paved the way to establishing an internal single market based on standardised legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states have agree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Matte
Open matte is a filming technique that involves Matte (filmmaking), matting out the top and bottom of the film frame in the movie projector (known as a ''soft matte'') for the widescreen theatrical release and then scanning the film without a matte (at Academy ratio) for a Full screen (cinema), full screen home video release. Open matte can be used with non-anamorphic films presented in 2.20:1 or 2.39:1, but it isn't used as often, mainly because it adds too much additional headroom, depending upon how well the framing was protected or if the director chooses to create a certain visual aesthetic. Instead, those films will employ either pan and scan or Cropping (image), reframing using either the well-protected areas or the areas of interest. Films shot Anamorphic format, anamorphically use the entire 35 mm frame (except for the soundtrack area), so they must use pan and scan as a result. History The rise of television and home media saw the use of a narrow aspect ratio of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
; rm, citad federala, links=no). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Lucerne, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zurich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2022 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: link=no, Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: link=no, Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federal assembly-independent directorial republic , leader_title1 = Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Viktor Rossi , legislature = Federal Assembly , upper_house = Counci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoot And Protect
Shoot and protect is a technique used in video and film production, in which the material is shot in such a way that the areas of interest within a frame lie within a rectangular "protected area" within the frame, with margins at top and bottom and both sides. The action safe and caption safe areas then lie within this protected area. This allows the resulting material to be cropped to any of a wide range of aspect ratios, whether wider or narrower than the shooting format, without losing the most important features of each shot or having to resort to pan and scan or letterboxing. A 14:9 safe area is often chosen as a compromise between 4:3 and 16:9 frame formats. See also *Open matte Open matte is a filming technique that involves Matte (filmmaking), matting out the top and bottom of the film frame in the movie projector (known as a ''soft matte'') for the widescreen theatrical release and then scanning the film without a mat ... References Film production { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Mean
In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a set of numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). The geometric mean is defined as the th root of the product of numbers, i.e., for a set of numbers , the geometric mean is defined as :\left(\prod_^n a_i\right)^\frac = \sqrt /math> or, equivalently, as the arithmetic mean in logscale: :\exp For instance, the geometric mean of two numbers, say 2 and 8, is just the square root of their product, that is, \sqrt = 4. As another example, the geometric mean of the three numbers 4, 1, and 1/32 is the cube root of their product (1/8), which is 1/2, that is, \sqrt = 1/2. The geometric mean applies only to positive numbers. The geometric mean is often used for a set of numbers whose values are meant to be multiplied together or are exponential in nature, such as a set of growth figures: values of the human population or int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anamorphic
Anamorphic format is the cinematography technique of shooting a widescreen picture on standard 35 mm film or other visual recording media with a non-widescreen native aspect ratio. It also refers to the projection format in which a distorted image is "stretched" by an anamorphic projection lens to recreate the original aspect ratio on the viewing screen (not to be confused with anamorphic widescreen, a different video encoding concept that uses similar principles but different means). The word '' anamorphic'' and its derivatives stem from the Greek ''anamorphoun'' ("to transform"), compound of ''morphé'' ("form, shape") with the prefix ''aná'' ("back, against"). In the late 1990s and 2000s, anamorphic lost popularity in comparison to "flat" (or "spherical") formats such as Super 35 with the advent of digital intermediates; however, in the years since digital cinema cameras and projectors have become commonplace, anamorphic has experienced a considerable resurgence of popular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
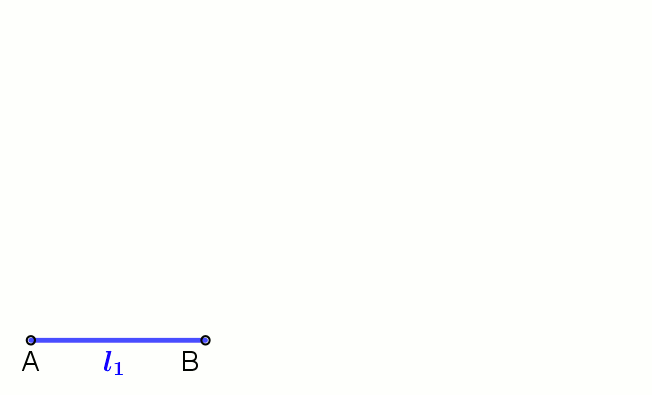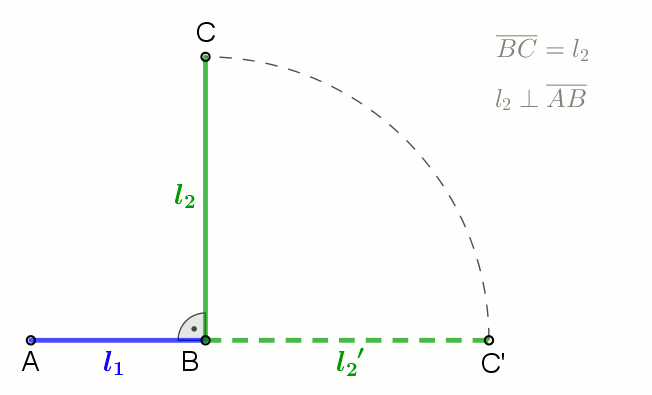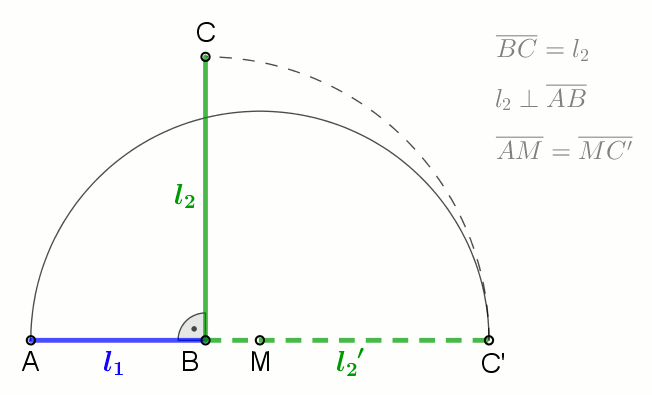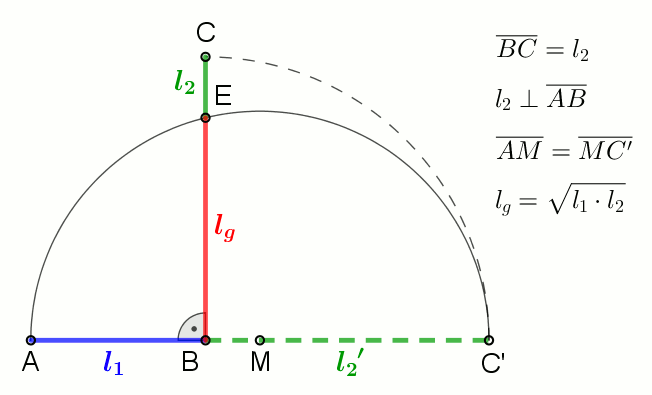
_(14929131291).jpg)