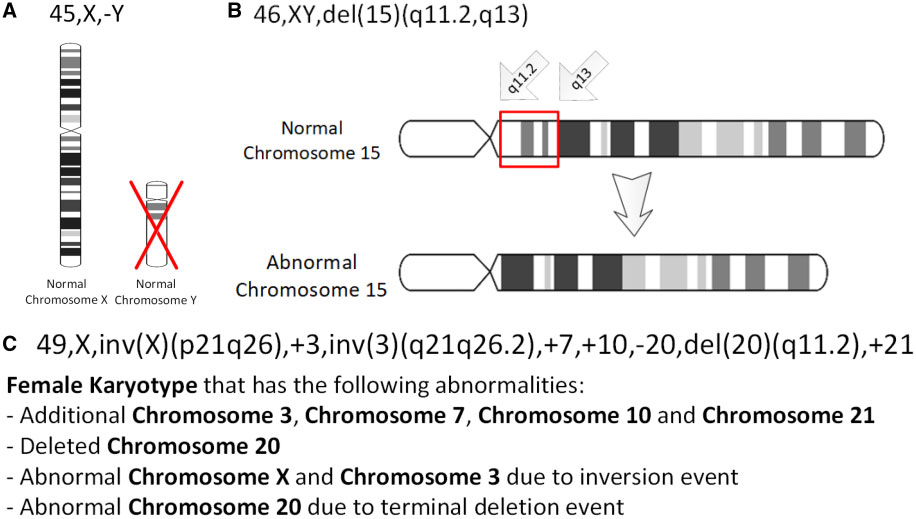
|
10q26 Deletion
10q26 deletion is an extremely rare genetic syndrome caused by terminal deletion of the long arm of chromosome 10 at 10q26. It is usually a ''de novo'' mutation. Symptoms can include "growth and mental retardation, microcephaly, triangular face, strabismus, hypertelorism, prominent nasal bridge, beaked or prominent nose, low-set dysplastic ears, various congenital heart defects, cryptorchidism, other anogenital anomalies, defect of hands/feet, limb contractures, abnormal behavior with hyperactivity, attention deficit, destructive tendency". People with the syndrome are less likely to have hearing deficits compared to those where the missing genetic material includes 10q25. The syndrome was first reported in 1979. Interstitial deletions including parts of 10q26 also have been reported, but they are more rare. Signs and symptoms Individuals who have 10q26 deletion syndrome frequently experience delays in speech and the development of motor abilities, including sitting, crawling, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Genetics
Medical genetics is the branch of medicine that involves the diagnosis and management of hereditary disorders. Medical genetics differs from human genetics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics. In contrast, the study of typically non-medical phenotypes such as the genetics of eye color would be considered part of human genetics, but not necessarily relevant to medical genetics (except in situations such as albinism). ''Genetic medicine'' is a newer term for medical genetics and incorporates areas such as gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the rapidly emerging new medical specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptorchidism
Cryptorchidism, also known as undescended testis, is the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum. The word is . It is the most common birth defect of the male genital tract. About 3% of full-term and 30% of premature infant boys are born with at least one undescended testis. However, about 80% of cryptorchid testes descend by the first year of life (the majority within three months), making the true incidence of cryptorchidism around 1% overall. Cryptorchidism may develop after infancy, sometimes as late as young adulthood, but that is exceptional. Cryptorchidism is distinct from monorchism, the condition of having only one testicle. Though the condition may occur on one or both sides, it more commonly affects the right testis. A testis absent from the normal scrotal position may be: # Anywhere along the "path of descent" from high in the posterior (retroperitoneal) abdomen, just below the kidney, to the inguinal ring # In the inguinal canal # Ectopic, havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micropenis
A micropenis or microphallus is an unusually small Human penis, penis. A common criterion is a dorsal (measured on top) Human penis size, penile length of at least 2.5 standard deviations smaller than the mean human penis size for age. A micropenis is stretched penile length equal to or less than 1.9 Centimetre, cm (0.75 Inch, in) in term Infant, infants, and 9.3 cm (3.67 in) in adults. The condition is usually recognized shortly after Childbirth, birth. The term is most often used medically when the rest of the penis, scrotum, and perineum are without Ambiguous genitalia, ambiguity, such as hypospadias. Traditionally, a microphallus describes a micropenis with hypospadias. Micropenis incidence is about 1.5 in 10,000 male newborns in North America.ScienceDaily.com (2004).Surgeons Pinch More Than An Inch From The Arm To Rebuild A Micropenis" 6 Dec. 2004, retrieved 2 April 2012. Causes Of the abnormal conditions associated with micropenis, most are conditions of reduced prenata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypospadias
Hypospadias is a common malformation in fetal development of the penis in which the urethra does not open from its usual location on the head of the penis. It is the second-most common birth defect of the male reproductive system, affecting about one of every 250 males at birth, although when including milder cases, is found in up to 4% of newborn males. Roughly 90% of cases are the less serious distal hypospadias, in which the urethral opening (the Urinary meatus, meatus) is on or near the head of the penis (Glans penis, glans). The remainder have proximal hypospadias, in which the meatus is all the way back on the shaft of the penis, near or within the scrotum. Shiny tissue or anything that typically forms the urethra instead extends from the meatus to the tip of the glans; this tissue is called the urethral plate. In most cases, the foreskin is less developed and does not wrap completely around the penis, leaving the underside of the glans uncovered. Also, a downward bending of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinodactyly
Clinodactyly is a medical term describing the curvature of a digit (a finger or toe) in the plane of the palm, most commonly the fifth finger (the "little finger") towards the adjacent fourth finger (the "ring finger"). It is a fairly common isolated anomaly which often goes unnoticed, but also occurs in combination with other abnormalities in certain genetic syndromes. The term comes . Genetics Clinodactyly is an autosomal dominant trait that has variable expressiveness and incomplete penetrance. Clinodactyly can be passed through inheritance and presents as either an isolated anomaly or a component manifestation of a genetic syndrome. Many syndromes are associated with clinodactyly, including those listed below. But the phenotype, by itself, is not a sensitive or specific diagnostic test for these syndromes (it is present in up to 18% of the normal population). * Down syndrome * Turner syndrome Turner syndrome (TS), commonly known as 45,X, or 45,X0,Also written as 45, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scoliosis
Scoliosis (: scolioses) is a condition in which a person's Vertebral column, spine has an irregular curve in the coronal plane. The curve is usually S- or C-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others, it increases over time. Mild scoliosis does not typically cause problems, but more severe cases can affect breathing and movement. Pain is usually present in adults, and can worsen with age. As the condition progresses, it may alter a person's life, and hence can also be considered a disability. It can be compared to kyphosis and lordosis, other abnormal curvatures of the spine which are in the sagittal plane (front-back) rather than the coronal (left-right). The cause of most cases is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of Genetics, genetic and environmental factors. Scoliosis most often occurs during growth spurts right before puberty. Risk factors include other affected family members. It can also occur due to anoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrognathism
Micrognathism is a condition where the jaw is undersized. It is also sometimes called mandibular hypoplasia. It is common in infants, but is usually self-corrected during growth, due to the jaws' increasing in size. It may be a cause of abnormal tooth alignment and in severe cases can hamper feeding. It can also, both in adults and children, make intubation difficult, either during anesthesia or in emergency situations. Causes According to the NCBI, the following conditions feature micrognathism: * 11q partial monosomy syndrome * 3-methylglutaconic aciduria, type VIIB * 46,XY sex reversal 4 * 4p partial monosomy syndrome * Achard syndrome * Acrofacial dysostosis Cincinnati type * Acrofacial dysostosis Rodriguez type * Acrofacial dysostosis, Catania type * Acromegaloid facial appearance syndrome * Adams-Oliver syndrome 2 * Agnathia- otocephaly complex * ALG1-congenital disorder of glycosylation * Alveolar capillary dysplasia with pulmonary venous misalignment * Ami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, or consciousness. Symptoms vary widely. Some seizures involve subtle changes, such as brief lapses in attention or awareness (as seen in absence seizures), while others cause generalized convulsions with loss of consciousness ( tonic–clonic seizures). Most seizures last less than two minutes and are followed by a postictal period of confusion, fatigue, or other symptoms. A seizure lasting longer than five minutes is a medical emergency known as status epilepticus. Seizures are classified as provoked, when triggered by a known cause such as fever, head trauma, or metabolic imbalance, or unprovoked, when no immediate trigger is identified. Recurrent unprovoked seizures define the neurological condition epilepsy. Clinical features Seizur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and developmentally inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction. Impairments resulting from deficits in self-regulation such as time management, inhibition, task initiation, and sustained attention can include poor professional performance, relationship difficulties, and numerous health risks, collectively predisposing to a diminished quality of life and a reduction in life expectancy. As a consequence, the disorder costs society hundreds of billions of US dollars each year, worldwide. It is associated with other mental disorders as well as non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment. While ADHD involves a lack of sustained attention to tasks, inhibitory deficits also can lead to diffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Heart Defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms are variable and may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure. Congenital heart defects are the most common birth defect. In 2015, they were present in 48.9 million people globally. They affect between 4 and 75 per 1,000 live births, depending upon how they are diagnosed. In about 6 to 19 per 1,000 they cause a moderate to severe degree of problems. Congenital heart defects are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deletion (genetics)
In genetics, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation) (sign: Δ) is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is left out during DNA replication. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome. Some chromosomes have fragile spots where breaks occur, which result in the deletion of a part of the chromosome. The breaks can be induced by heat, viruses, radiation, or chemical reactions. When a chromosome breaks, if a part of it is deleted or lost, the missing piece of chromosome is referred to as a deletion or a deficiency. For synapsis to occur between a chromosome with a large intercalary deficiency and a normal complete homolog, the unpaired region of the normal homolog must loop out of the linear structure into a deletion or compensation loop. The smallest single base deletion mutations occur by a single base flipping in the template DNA, followed by te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Bridge
The nasal bridge is the upper part of the nose, where the nasal bones and surrounding soft tissues provide structural support. While commonly discussed in human anatomy, nasal bridges exist in various forms across many vertebrates, particularly mammals. The shape, size, and function of the nasal bridge are influenced by evolutionary adaptations, playing a key role in Respiration (physiology), respiration, sense of smell, and thermoregulation. Anatomy Humans In humans, the nasal bridge is the elevated region of the human nose, nose between the eyes. It is primarily formed by the two small, oblong nasal bones, which meet at the midline to form the internasal suture. The nasal bridge extends from the nasal root, where the nose meets the forehead, to the lower edge of the nasal bones. Laterally, it reaches the inner canthi, the medial corners of the eyes, creating a saddle-shaped contour across the upper nose. The height and shape of the nasal bridge vary among individuals and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |