|
102nd Infantry Regiment (France)
The 102nd Infantry Regiment (french: 102e Régiment d'Infanterie, 102e RI) was an infantry regiment of the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. Reconstituted several times in the 19th century, it took part in the Second Opium War in China, then in the First and Second World Wars, being disbanded in 1940. French Royal Army Its ancestor regiments were the Infantry Regiment of the Line Le Dauphin (Nr. 29) and Royal-Deux Ponts (Nr 99). The Regiment was raised in 1667 by Michel De Fisicat, as ''Le Dauphin'' (nr. 29) and on 26 April 1775 split into two regiments. The 1st and 3rd battalions retained the old title and number and the 2nd and rth battalions became the new Infantry Regiment ''Perche'' (Nr 30). The Revolutionary Wars as Infantry Regiment of the Line ''Perche'' (Nr 30) Campaigns Initially, the Regiment served in the Army of the Center, at Metz. Following the Battle of Valmy on 20 September 1792, the Regiment was assigned to the Army of the Ardennes. In 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levée En Masse
''Levée en masse'' ( or, in English, "mass levy") is a French term used for a policy of mass national conscription, often in the face of invasion. The concept originated during the French Revolutionary Wars, particularly for the period following 16 August 1793, when able-bodied men aged 18 to 25 were conscripted. It formed an integral part of the creation of national identity, making it distinct from forms of conscription which had existed before this date. The term is also applied to other historical examples of mass conscription. Terminology The term ''levée en masse'' denotes a short-term requisition of all able-bodied men to defend the nation and its rise as a military tactic may be viewed in connection with the political events and developing ideology in revolutionary France—particularly the new concept of the democratic citizen as opposed to a royal subject. Central to the understanding that developed (and was promoted by the authorities) of the ''levée'' is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Lübeck
The Battle of Lübeck took place on 6 November 1806 in Lübeck, Germany between soldiers of the Kingdom of Prussia led by Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, who were retreating from defeat at the Battle of Jena–Auerstedt, and troops of the First French Empire under Marshals Murat, Bernadotte, and Soult, who were pursuing them. In this War of the Fourth Coalition action, the French inflicted a severe defeat on the Prussians, driving them from the neutral city. Lübeck is an old Baltic Sea port approximately northeast of Hamburg. After their shattering defeat in October by Napoleon at the Battle of Jena–Auerstedt, the Prussian armies withdrew to the east bank of the Elbe River and marched northeast in an attempt to reach the Oder River. Aiming to annihilate his opponents' forces, Napoleon launched his Grande Armée in a headlong pursuit. A large portion of the fleeing Prussians took refuge in the fortress of Magdeburg where they were surrounded. Another large segment was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Halle
In the Battle of Halle on 17 October 1806 a French corps led by Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte fought the Prussian Reserve under Eugene Frederick Henry, Duke of Württemberg. The French defeated their opponents, forcing the Prussians to retreat northeast toward Dessau after suffering heavy losses. The clash occurred in the War of the Fourth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars. The city of Halle is located about 30 kilometers northwest of Leipzig on the Saale River. Emperor Napoleon I of France invaded the Electorate of Saxony and inflicted two disastrous defeats on the Prussian-Saxon armies on 14 October 1806. As the beaten armies fled, Marshal Bernadotte's corps marched north and found Duke Eugene's unblooded Reserve located at Halle. At the beginning of the encounter, two French divisions rushed the bridges over the Saale on the west side of the city. They overran a weak defending force and quickly occupied the city. Later in the day, Bernadotte's troops stormed out of Hall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Austerlitz
The Battle of Austerlitz (2 December 1805/11 Frimaire An XIV FRC), also known as the Battle of the Three Emperors, was one of the most important and decisive engagements of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle occurred near the town of Austerlitz in the Austrian Empire (modern-day Slavkov u Brna in the Czech Republic). The decisive victory of Napoleon's Grande Armée at Austerlitz brought the War of the Third Coalition to a rapid end, with the Treaty of Pressburg signed by the Austrians later in the month. The battle is often cited as a tactical masterpiece, in the same league as other historic engagements like Cannae or Gaugamela.Farwell p. 64. "Austerlitz is generally regarded as one of Napoleon's tactical masterpieces and has been ranked as the equal of Arbela, Cannae, and Leuthen."Dupuy p. 102 After eliminating an Austrian army during the Ulm Campaign, French forces seized Vienna in November 1805. The Austrians avoided further conflict until the arrival of the Russians bols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Caldiero (1796)
In the Battle of Caldiero on 12 November 1796, the Habsburg army led by József Alvinczi fought a First French Republic army commanded by Napoleon Bonaparte. The French assaulted the Austrian positions, which were initially held by the army advance guard under Prince Friedrich Franz Xaver of Hohenzollern-Hechingen. The defenders held firm until reinforcements arrived in the afternoon to push back the French. This marked a rare tactical setback for Bonaparte, whose forces withdrew into Verona that evening after having suffered greater losses than their adversaries. The action occurred during the War of the First Coalition, which was part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Caldiero is a town located about east of Verona. The battle was part of the third Austrian effort to relieve the Siege of Mantua. Two Austrian forces converged toward Mantua, the main army from the east and an independent corps from the north. Both forces enjoyed early successes, driving back the outnumber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Zürich
The Second Battle of Zurich (25–26 September 1799) was a key victory by the Republican French army in Switzerland led by André Masséna over an Austrian and Russian force commanded by Alexander Korsakov near Zürich. It broke the stalemate that had resulted from the First Battle of Zurich three months earlier and led to the withdrawal of Russia from the Second Coalition. Most of the fighting took place on both banks of the river Limmat up to the gates of Zürich, and within the city itself. Background After the First Battle of Zurich Masséna had consolidated to a defensive line behind the lower reaches of the Aare River. At this time his entire army in Switzerland consisted of around 77,000 combatants, positioned as: * 1st Division ( Tharreau) in the Upper Valais and the Simplon Pass. * 2nd Division ( Lecourbe) in the St Gotthard and the valley of the Reuss. * 3rd Division (Soult) Right wing near Glarus, centre on the left bank of the Linth, the left near Adliswil on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
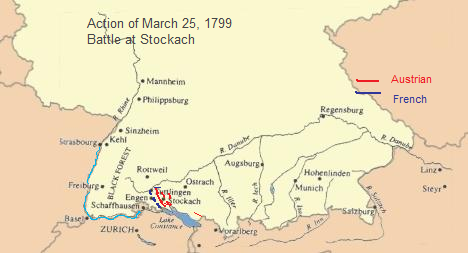
Battle Of Stockach (1799)
The Battle of Stockach occurred on 25 March 1799, when French and Austrian armies fought for control of the geographically strategic Hegau region in present-day Baden-Württemberg.There was a second battle the following year—see Second Battle of Stockach. Some older English sources refer to this as the Battle of Stochach and some French chronicles as Battle of Liptingen (or Leibtengen). In the broader military context, this battle constitutes a keystone in the first campaign in southwestern Germany during the Wars of the Second Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. It was the second battle between the French Army of the Danube, commanded by Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, and the Habsburg Army under Archduke Charles; the armies had met a few days earlier, 20–22 March, on the marshy fields southeast of Ostrach and the Pfullendorf heights. The Austrian Army's superior strength, almost three-to-one, forced the French to withdraw. At Stockach, the French concentrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ostrach
The Battle of Ostrach, also called the Battle by Ostrach, occurred on 20–21 March 1799. It was the first non-Italy-based battle of the War of the Second Coalition. The battle resulted in the victory of the Austrian forces, under the command of Archduke Charles, over the French forces, commanded by Jean-Baptiste Jourdan. The battle occurred during Holy Week, 1799, amid rain and dense fog. Initially, the French were able to take, and hold, Ostrach and the nearby hamlet of Hoßkirch plus several strategic points on the Ostrach marsh. As the engagement began, Habsburg numerical superiority overwhelmed French defenses. By evening, the French left wing was flanked and Jourdan's men retreated from Ostrach to the Pfullendorf heights. On the next morning, as Jourdan considered a counter-attack, the weather broke, and he could look down on the Austrian battle array. The numbers and dispositions of the Austrians convinced him that any attack would be useless, and that he could not hope t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Marie Barthélemy Ferino
Pierre Marie Barthélemy Ferino, (23 August 1747, Craveggia – 28 June 1816, Paris), was a general and politician of France. Born in the Savoy, he was the son of a low-ranking officer in the Habsburg military. In 1789, during the French Revolution, he went to France, where he received a commission in the French Army. In 1793, his troops deposed him, for his strict discipline, but he was immediately reinstated and rose rapidly through the ranks of the general staff. He helped to push the Austrians back to Bavaria in the 1796 summer campaign, and then covered Moreau's retreat to France later that year, defending the Rhine bridge at Hüningen until the last units had crossed to safety. Ferino commanded the southernmost wing of Army of the Danube in 1799, and participated in the battles of Ostrach and Stockach. Napoleon awarded him the Grand Cross of the Legion of Honor in 1804; in 1805, Ferino became a Senator, and in 1808, raised him to ''Count of the Empire''. His name is engrav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Jourdan
Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, 1st Count Jourdan (29 April 1762 – 23 November 1833), was a French military commander who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He was made a Marshal of the Empire by Emperor Napoleon I in 1804. He was also a Jacobin politician during the Directory phase of the French Revolution, serving as member of the Council of Five Hundred between 1797 and 1799. One of the most successful commanders of the French Revolutionary Army, Jourdan is best remembered in the Revolution for leading the French to a decisive victory over the First Coalition at the Battle of Fleurus, during the Flanders campaign. Under the Empire he was rewarded by Napoleon with the title of Marshal and continued to hold military assignments, but suffered a major defeat at the Battle of Vitoria, which resulted in the Empire's permanent loss of Spain. In 1815 he became reconciled with the Bourbon Restoration, and later supported the July Revolution and serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Danube
The Army of the Danube (french: Armée du Danube, links=no) was a field army of the French Directory in the 1799 southwestern campaign in the Upper Danube valley. It was formed on 2 March 1799 by the simple expedient of renaming the Army of Observation, which had been observing Austrian movements on the border between French First Republic and the Holy Roman Empire. It was commanded by General Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, 1st Comte Jourdan (1762–1833). The formation of the army was part of the French Directory's long term strategy to undermine Habsburg influence in the Holy Roman Empire, and, conversely, to strengthen French hegemony in central Europe after the wars of the First Coalition and the Treaty of Campo Formio in 1797. Despite the Treaty, Austria and France remained suspicious of each other's motives, and the purpose of the Army of the Observation was to watch for Austrian border transgressions. Understanding that the negotiations at the Congress of Rastatt were going ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |