|
įž
Chinese numerals are words and characters used to denote numbers in written Chinese. Today, speakers of Chinese languages use three written numeral systems: the system of Arabic numerals used worldwide, and two indigenous systems. The more familiar indigenous system is based on Chinese characters that correspond to numerals in the spoken language. These may be shared with other languages of the Chinese cultural sphere such as Korean, Japanese, and Vietnamese. Most people and institutions in China primarily use the Arabic or mixed Arabic-Chinese systems for convenience, with traditional Chinese numerals used in finance, mainly for writing amounts on cheques, banknotes, some ceremonial occasions, some boxes, and on commercials. The other indigenous system consists of the Suzhou numerals, or ''huama'', a positional system, the only surviving form of the rod numerals. These were once used by Chinese mathematicians, and later by merchants in Chinese markets, such as those in Hong Ko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Numerals
The are numerals that are used in Japanese. In writing, they are the same as the Chinese numerals, and large numbers follow the Chinese style of grouping by 10,000. Two pronunciations are used: the Sino-Japanese () readings of the Chinese characters and the Japanese (native words, readings). Basic numbering in Japanese There are two ways of writing the numbers in Japanese: in Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3) or in Chinese numerals (, , ). The Arabic numerals are more often used in horizontal writing, and the Chinese numerals are more common in vertical writing. Most numbers have two readings, one derived from Chinese used for cardinal numbers ( reading) and a native Japanese reading ( reading) used somewhat less formally for numbers up to 10. In some cases (listed below) the Japanese reading is generally preferred for all uses. Archaic readings are marked with â . * The special reading is also found. It may be optionally used when reading individual digits of a number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numeral (linguistics)
In linguistics, a numeral in the broadest sense is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity. Some theories of grammar use the word "numeral" to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner that specify the quantity of a noun, for example the "two" in "two hats". Some theories of grammar do not include determiners as a part of speech and consider "two" in this example to be an adjective. Some theories consider "numeral" to be a synonym for "number" and assign all numbers (including ordinal numbers like "first") to a part of speech called "numerals". Numerals in the broad sense can also be analyzed as a noun ("three is a small number"), as a pronoun ("the two went to town"), or for a small number of words as an adverb ("I rode the slide twice"). Numerals can express relationships like quantity (cardinal numbers), sequence (ordinal numbers), frequency (once, twice), and part (fraction). Identifying numerals Numerals may be attributive, as in ''two dogs'', or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rod Numerals
Counting rods (į) are small bars, typically 3â14 cm (1" to 6") long, that were used by mathematicians for calculation in ancient East Asia. They are placed either horizontally or vertically to represent any integer or rational number. The written forms based on them are called rod numerals. They are a true positional numeral system with digits for 1â9 and a blank for 0, from the Warring states period (circa 475 BCE) to the 16th century. History Chinese arithmeticians used counting rods well over two thousand years ago. In 1954, forty-odd counting rods of the Warring States period (5th century BCE to 221 BCE) were found in ZuĮjiÄgÅngshÄn (åˇĻåŽļå Ŧåąą) Chu Grave No.15 in Changsha, Hunan. In 1973, archeologists unearthed a number of wood scripts from a tomb in Hubei dating from the period of the Han dynasty (206 BCE to 220 CE). On one of the wooden scripts was written: "åŊåŠäēæåŽįŽđĨ". This is one of the earliest examples of using counting-rod numeral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnamese Numerals
Historically Vietnamese has two sets of numbers: one is etymologically native Vietnamese; the other uses Sino-Vietnamese vocabulary. In the modern language the native Vietnamese vocabulary is used for both everyday counting and mathematical purposes. The Sino-Vietnamese vocabulary is used only in fixed expressions or in Sino-Vietnamese words, in a similar way that Latin and Greek numerals are used in modern English (e.g., the ''bi-'' prefix in ''bicycle''). For numbers up to one million, native Vietnamese terms are often used the most, whilst mixed Sino-Vietnamese origin words and native Vietnamese words are used for units of one million or above. Concept For non-official purposes prior to the 20th century, Vietnamese had a writing system known as HÃĄn-Nôm. Sino-Vietnamese numbers were written in cháģ¯ HÃĄn and native vocabulary was written in cháģ¯ Nôm. Hence, there are two concurrent systems in Vietnamese nowadays in the romanized script, one for native Vietnamese and one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of CJK Unified Ideographs
The Chinese, Japanese and Korean (CJK) scripts share a common background, collectively known as CJK characters. During the process called Han unification, the common (shared) characters were identified and named CJK Unified Ideographs. As of Unicode , Unicode defines a total of 97,680 characters. The term ''ideographs'' is a misnomer, as the Chinese script is not ideographic but rather logographic. Until the early 20th century, Vietnam also used Chinese characters (Cháģ¯ Nôm), so sometimes the abbreviation CJKV is used. Sources The Ideographic Research Group (IRG) is responsible for developing extensions to the encoded repertoires of CJK unified ideographs. IRG processes proposals for new CJK unified ideographs submitted by its member bodies, and after undergoing several rounds of expert review, IRG submits a consolidated set of characters to ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2 Working Group 2 (WG2) and the Unicode Technical Committee (UTC) for consideration for inclusion in the ISO/IEC 106 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Zetian
Wu Zetian (624 â 16 December 705), personal name Wu Zhao, was List of rulers of China#Tang dynasty, Empress of China from 660 to 705, ruling first through others and later in her own right. She ruled as queen consort , empress consort through her husband Emperor Gaozong of Tang, Emperor Gaozong and later as empress dowager through her sons Emperors Emperor Zhongzong of Tang, Zhongzong and Emperor Ruizong of Tang, Ruizong, from 660 to 690. She subsequently founded and ruled as Empress Regnant of the Wu Zhou dynasty of China from 16 October 690 to 21 February 705. She was the only female sovereign in the history of China who is widely Mandate of Heaven, regarded as legitimate. Under her 45-year reign, China grew larger, becoming one of the great powers of the world, its culture and economy were revitalized, and corruption in the court was reduced. She was eventually removed from power during a coup () and died a few months later. In early life, Wu was the concubine of Emper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Numerals
The Korean language has two regularly used sets of numerals: a native Korean system and Sino-Korean system. The native Korean number system is used for general counting, like counting up to 99. It is also used to count people, hours, objects, ages, and more. Sino-Korean numbers on the other hand are used for purposes such as dates, money, minutes, addresses, phone numbers, and numbers above 99. Construction For both native and Sino- Korean numerals, the teens (11 through 19) are represented by a combination of tens and the ones places. For instance, 15 would be ''sib-o'' (), but not usually ''il-sib-o'' in the Sino-Korean system, and ''yeol-daseot'' () in native Korean. Twenty through ninety are likewise represented in this place-holding manner in the Sino-Korean system, while Native Korean has its own unique set of words, as can be seen in the chart below. The grouping of large numbers in Korean follows the Chinese tradition of myriads (10000) rather than thousands (1000) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization Of Wu Chinese
Wu Chinese has four major schools of romanization. The most popular school, Common Wu Pinyin (), was developed by amateur language clubs and local learners. There are two competing schemes; both adhere to the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) and are very similar to each other. The initial scheme was "Wu Chinese Society pinyin" (, developed around 2005), and it formed the basis of "Wugniu pinyin" (, around 2016). Wu Chinese Society pinyin in general does not mark tones. The name ''Wugniu'' comes from the Shanghainese pronunciation of å´č¯. Either of them is the default romanization scheme in most learning materials. The second and historical school is the missionary school (see :zh:å´č¯æä¸åæšæĄ). This school of English-based Latin orthographies was developed by Western missionaries in the late 19th and early 20th centuries and used to write Bible translations and other educational texts. A representative romanization from this school is the Edkins romanization of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzhou Numerals
The Suzhou numerals, also known as ' (), is a numeral system used in China before the introduction of Hindu numerals. The Suzhou numerals are also known as ''Soochow numerals'', ''maâtzu'', ' (),Wikipedia entry in Chinese čåˇį å ' (), ' (), ' () and ' (). History The Suzhou numeral system is the only surviving variation of the rod numeral system. The rod numeral system is a positional numeral system used by the Chinese in mathematics. Suzhou numerals are a variation of the Southern Song rod numerals. Suzhou numerals were used as shorthand in number-intensive areas of commerce such as accounting and bookkeeping. At the same time, standard Chinese numerals were used in formal writing, akin to spelling out the numbers in English. Suzhou numerals were once popular in Chinese marketplaces, such as those in Hong Kong and Chinese restaurants in Malaysia before the 1990s, but they have gradually been supplanted by Hindu numerals. This is similar to what had happened in Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1 (number)
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
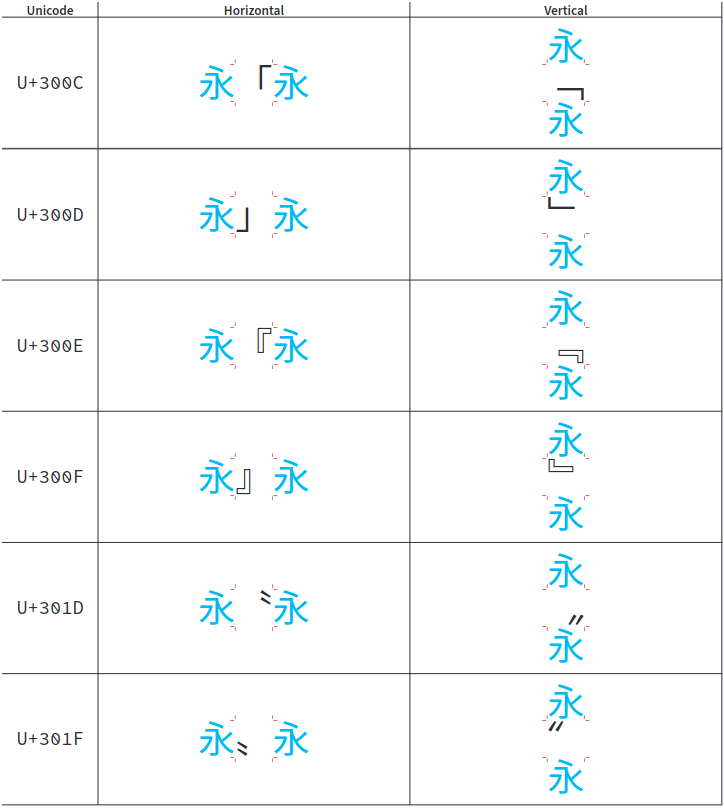
CJK Symbols And Punctuation
CJK Symbols and Punctuation is a Unicode block containing symbols and punctuation used for writing the Chinese, Japanese and Korean languages. It also contains one Chinese character. Block The block has variation sequences defined for East Asian punctuation positional variants. They use (VS01) and (VS02): Orientation Quotation marks and other punctuation have expected differences in behaviour in vertical and horizontal text. The quotation marks ã...ã, ã...ã and ã...ã rotate 90 degrees, as follows: See also General Punctuation, for variation selectors and CJK behaviour of the Latin quotation marks â...â and â...â. Chinese character The CJK Symbols and Punctuation block contains one Chinese character: . Although it is not covered under "Unified Ideographs", it is treated as a CJK character for all other intents and purposes. Emoji The CJK Symbols and Punctuation block contains two emoji: U+3030 and U+303D. The block has four standardized var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |