|
├ętendue
Etendue or ├ętendue (; ) is a property of light in an optical system, which characterizes how "spread out" the light is in area and angle. It corresponds to the beam parameter product (BPP) in Gaussian beam optics. Other names for etendue include acceptance, throughput, light grasp, light-gathering power, optical extent, and the AΩ product. ''Throughput'' and ''AΩ product'' are especially used in radiometry and radiative transfer where it is related to the view factor (or shape factor). It is a central concept in nonimaging optics. From the source point of view, etendue is the product of the area of the source and the solid angle that the system's entrance pupil subtends as seen from the source. Equivalently, from the system point of view, the etendue equals the area of the entrance pupil times the solid angle the source subtends as seen from the pupil. These definitions must be applied for infinitesimally small "elements" of area and solid angle, which must then be su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiance
In radiometry, radiance is the radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted or received by a given surface, per unit solid angle per unit projected area. Radiance is used to characterize diffuse emission and reflection of electromagnetic radiation, and to quantify emission of neutrinos and other particles. The SI unit of radiance is the watt per steradian per square metre (). It is a ''directional'' quantity: the radiance of a surface depends on the direction from which it is being observed. The related quantity spectral radiance is the radiance of a surface per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. Historically, radiance was called "intensity" and spectral radiance was called "specific intensity". Many fields still use this nomenclature. It is especially dominant in heat transfer, astrophysics and astronomy. "Intensity" has many other meanings in physics, with the most common being power per unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etendue
Etendue or ├ętendue (; ) is a property of light in an optical system, which characterizes how "spread out" the light is in area and angle. It corresponds to the beam parameter product (BPP) in Gaussian beam optics. Other names for etendue include acceptance, throughput, light grasp, light-gathering power, optical extent, and the AΩ product. ''Throughput'' and ''AΩ product'' are especially used in radiometry and radiative transfer where it is related to the view factor (or shape factor). It is a central concept in nonimaging optics. From the source point of view, etendue is the product of the area of the source and the solid angle that the system's entrance pupil subtends as seen from the source. Equivalently, from the system point of view, the etendue equals the area of the entrance pupil times the solid angle the source subtends as seen from the pupil. These definitions must be applied for infinitesimally small "elements" of area and solid angle, which must then b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etendue In Refraction
Etendue or ├ętendue (; ) is a property of light in an optical system, which characterizes how "spread out" the light is in area and angle. It corresponds to the beam parameter product (BPP) in Gaussian beam optics. Other names for etendue include acceptance, throughput, light grasp, light-gathering power, optical extent, and the AΩ product. ''Throughput'' and ''AΩ product'' are especially used in radiometry and radiative transfer where it is related to the view factor (or shape factor). It is a central concept in nonimaging optics. From the source point of view, etendue is the product of the area of the source and the solid angle that the system's entrance pupil subtends as seen from the source. Equivalently, from the system point of view, the etendue equals the area of the entrance pupil times the solid angle the source subtends as seen from the pupil. These definitions must be applied for infinitesimally small "elements" of area and solid angle, which must then be su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
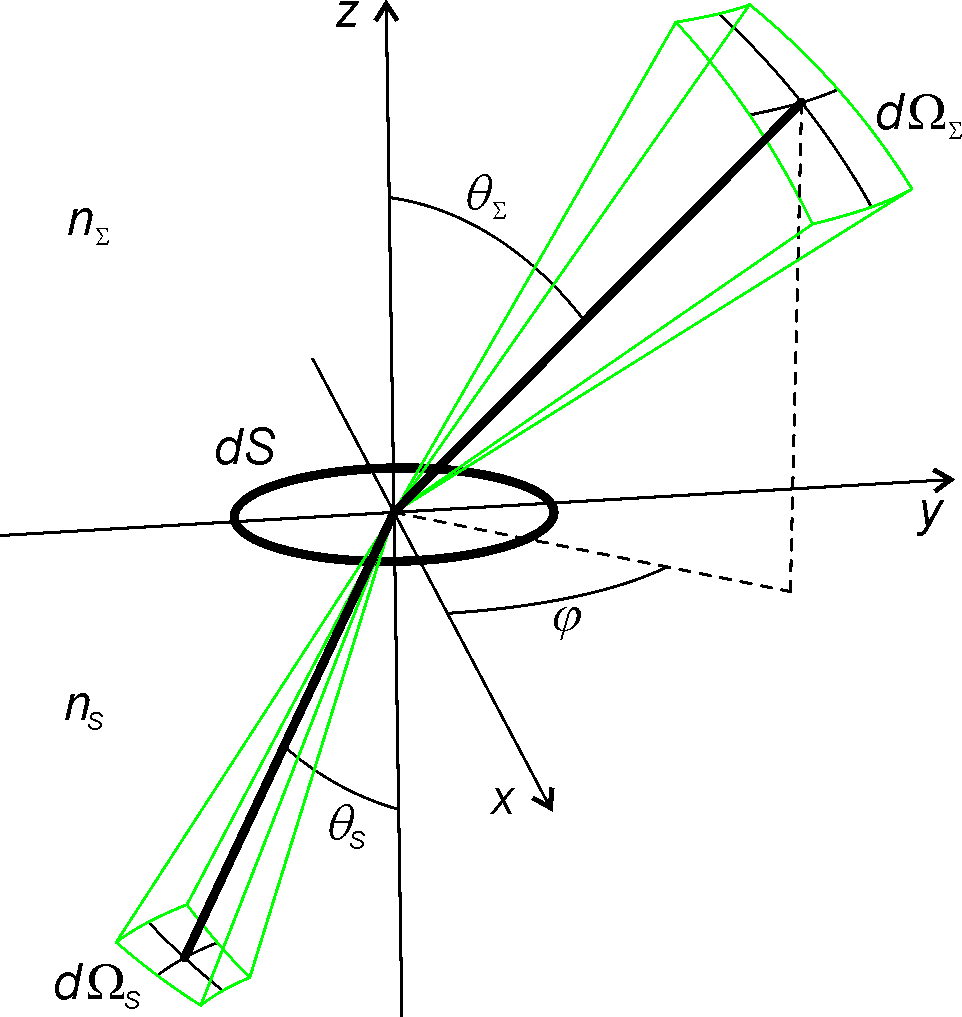
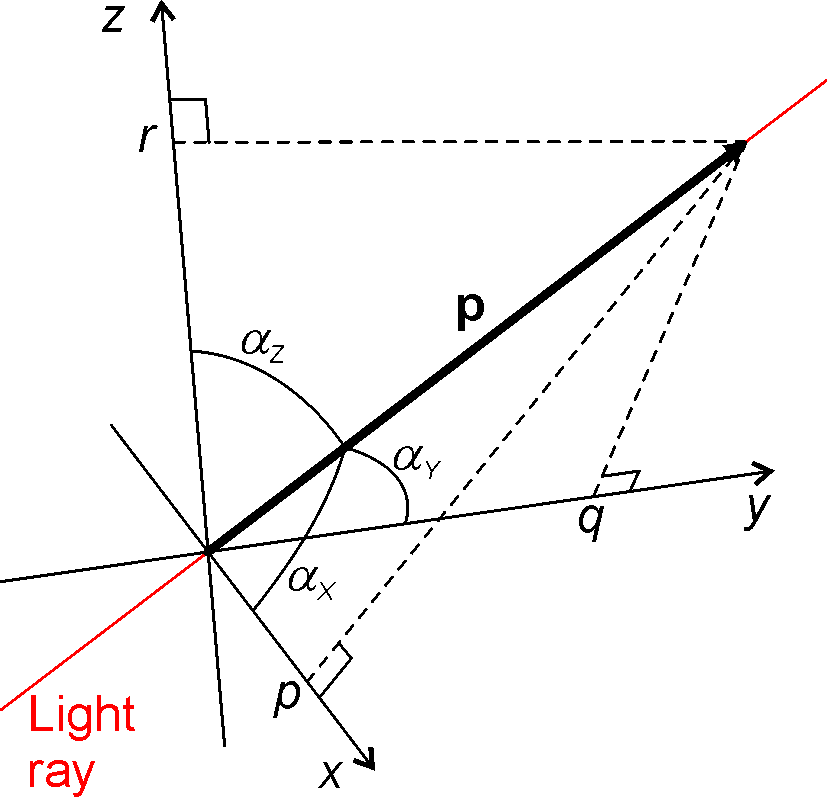
Etendue For Differential Surface Element In 2D And 3D
Etendue or ├ętendue (; ) is a property of light in an optics, optical system, which characterizes how "spread out" the light is in area and angle. It corresponds to the beam parameter product (BPP) in Gaussian beam optics. Other names for etendue include acceptance, throughput, light grasp, light-gathering power, optical extent, and the AΩ product. ''Throughput'' and ''AΩ product'' are especially used in radiometry and radiative transfer where it is related to the view factor (or shape factor). It is a central concept in nonimaging optics. From the source point of view, etendue is the product of the area of the source and the solid angle that the system's entrance pupil subtends as seen from the source. Equivalently, from the system point of view, the etendue equals the area of the entrance pupil times the solid angle the source subtends as seen from the pupil. These definitions must be applied for infinitesimally small "elements" of area and solid angle, which must th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Invariant
In optics the Lagrange invariant is a measure of the light propagating through an optical system. It is defined by :H = n\overliney - nu\overline, where and are the marginal ray height and angle respectively, and and are the chief ray height and angle. is the ambient refractive index. In order to reduce confusion with other quantities, the symbol may be used in place of . is proportional to the throughput of the optical system (related to ├ętendue). For a given optical system, the Lagrange invariant is a constant throughout all space, that is, it is invariant upon refraction and transfer. The optical invariant is a generalization of the Lagrange invariant which is formed using the ray heights and angles of any two rays. For these rays, the optical invariant is a constant throughout all space. , Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamiltonian Optics
Hamiltonian opticsH. A. Buchdahl, ''An Introduction to Hamiltonian Optics'', Dover Publications, 1993, . and Lagrangian opticsVasudevan Lakshminarayanan et al., ''Lagrangian Optics'', Springer Netherlands, 2011, . are two formulations of geometrical optics which share much of the mathematical formalism with Hamiltonian mechanics and Lagrangian mechanics. Hamilton's principle In physics, Hamilton's principle states that the evolution of a system \left(q_1,\dots,q_N\right) described by N generalized coordinates between two specified states at two specified parameters ''¤â''''A'' and ''¤â''''B'' is a stationary point (a point where the variation is zero) of the action functional, or \delta S= \delta\int_^ L\left(q_1,\cdots,q_N,\dot_1,\cdots,\dot_N,\sigma\right)\, d\sigma=0 where \dot_k=dq_k/d\sigma and L is the Lagrangian. Condition \delta S=0 is valid if and only if the Euler-Lagrange equations are satisfied, i.e., \frac - \frac\frac = 0 with k = 1, \dots, N. The momentum is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Bureau Of Weights And Measures
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (, BIPM) is an List of intergovernmental organizations, intergovernmental organisation, through which its 64 member-states act on measurement standards in areas including chemistry, ionising radiation, physical metrology, as well as the International System of Units (SI) and Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). It is headquartered in the Pavillon de Breteuil in Saint-Cloud, near Paris, France. The organisation has been referred to as IBWM (from its name in English) in older literature. Function The BIPM has the mandate to provide the basis for a single, coherent system of measurements throughout the world, traceable to the International System of Units, International System of Units (SI). This task takes many forms, from direct dissemination of units to coordination through international comparisons of national measurement standards (as in electricity and ionising radiation). Following consultation, a draft version of the BIPM Work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimensionless Quantity
Dimensionless quantities, or quantities of dimension one, are quantities implicitly defined in a manner that prevents their aggregation into unit of measurement, units of measurement. ISBN 978-92-822-2272-0. Typically expressed as ratios that align with another system, these quantities do not necessitate explicitly defined Unit of measurement, units. For instance, alcohol by volume (ABV) represents a volumetric ratio; its value remains independent of the specific Unit of volume, units of volume used, such as in milliliters per milliliter (mL/mL). The 1, number one is recognized as a dimensionless Base unit of measurement, base quantity. Radians serve as dimensionless units for Angle, angular measurements, derived from the universal ratio of 2¤Ç times the radius of a circle being equal to its circumference. Dimensionless quantities play a crucial role serving as parameters in differential equations in various technical disciplines. In calculus, concepts like the unitless ratios ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transparency (optics)
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable light scattering by particles, scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimensions are much larger than the wavelengths of the photons in question), the photons can be said to follow Snell's law. Translucency (also called translucence or translucidity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material (with or without scattering of light). It allows light to pass through but the light does not necessarily follow Snell's law on the macroscopic scale; the photons may be scattered at either of the two interfaces, or internally, where there is a change in the index of refraction. In other words, a translucent material is made up of components with different indices of refraction. A transparent material is made up of components with a uniform index of refraction. Transparent m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium (optics)
In optics, an optical medium is material through which light and other electromagnetic waves propagate. It is a form of transmission medium. The permittivity and permeability of the medium define how electromagnetic waves propagate in it. Properties The optical medium has an '' intrinsic impedance'', given by ::\eta = where E_x and H_y are the electric field and magnetic field, respectively. In a region with no electrical conductivity, the expression simplifies to: ::\eta = \sqrt\ . For example, in free space the intrinsic impedance is called the characteristic impedance of vacuum, denoted ''Z''0, and ::Z_0 = \sqrt\ . Waves propagate through a medium with velocity c_w = \nu \lambda , where \nu is the frequency and \lambda is the wavelength of the electromagnetic waves. This equation also may be put in the form : c_w = \ , where \omega is the angular frequency of the wave and k is the wavenumber of the wave. In electrical engineering, the symbol \beta, called the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wikibooks
Wikibooks (previously called ''Wikimedia Free Textbook Project'' and ''Wikimedia-Textbooks'') is a wiki-based Wikimedia project hosted by the Wikimedia Foundation for the creation of free content digital textbooks and annotated texts that anyone can edit. Initially, the project was created solely in English in July 2003; a later expansion to include additional languages was started in July 2004. As of , there are Wikibooks sites active for languages Wikimedia's MediaWiki API:Sitematrix. Retrieved from Data:Wikipedia statistics/meta.tab comprising a total of articles and recently active editors. Wikimedia's MediaWiki API:Siteinfo. Retrieved from Data:Wikipedia statistics/data.tab History The wikibooks.org domain was registered on July 19, 2003. It was launched to host and build free textbooks on subjects such as organic chemistry and physics, in response to a request by Wikipedia contributor Karl Wick. Two major sub-projects, Wikijunior and Wikiversity, were creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |