|
(Cymene)ruthenium Dichloride Dimer
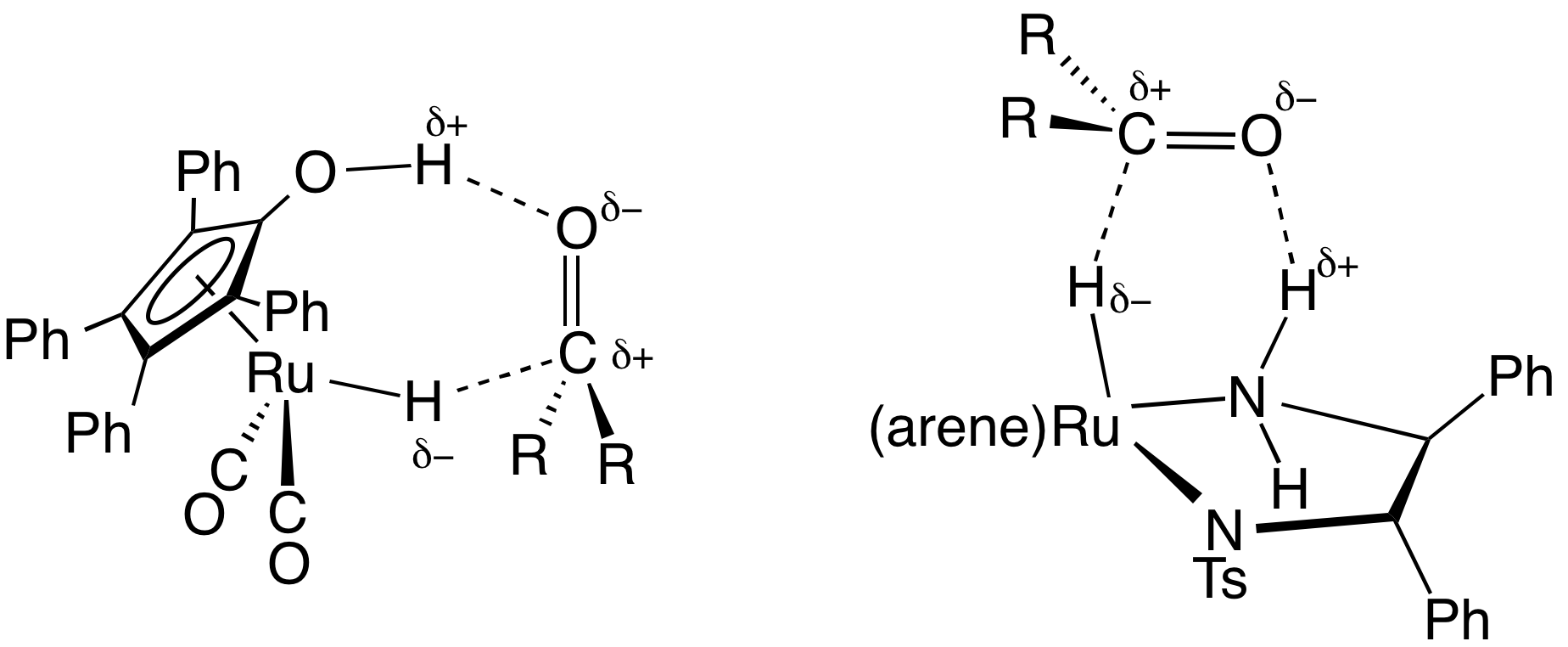
(Cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer is the organometallic compound with the formula cymene)RuCl This red-coloured, diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. The complex is structurally similar to (benzene)ruthenium dichloride dimer. Preparation and reactions The dimer is prepared by the reaction of the phellandrene with hydrated ruthenium trichloride. At high temperatures, cymene)RuClexchanges with other arenes: : cymene)RuCl+ 2 CMe → CMe)RuCl+ 2 cymene (Cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer reacts with Lewis bases to give monometallic adducts: : cymene)RuCl+ 2 PPh → 2 (cymene)RuCl(PPh) Such monomers adopt pseudo-octahedral piano-stool structures. Precursor to catalysts Treatment of cymene)RuClwith the chelating ligand Ts DPENH gives (cymene)Ru(TsDPEN-H), a catalyst for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. cymene)RuClis also used to prepare catalysts (by monomerization with dppf) used in borrowing hydrogen catalysis, a cataly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Compound
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide ( metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimers (chemistry)
Dimers is a sports betting analytics platform that provides predictive tools, data-driven insights, news, and betting content for sports fans and bettors. Operating under the umbrella of Cipher Sports Technology Group, Dimers has offices in Melbourne and New York. History Dimers.com was launched on August 1, 2020, shortly after its parent company Cipher Sports Technology Group was formed through the merger of two Australian companies: iRival Media and Hypometer Technologies. iRival Media, founded in October 2019 by Adam Fiske and Nick Slade, focused on delivering content to the sports betting market.Hypometer Technologies, established in 2015 by Katie Prowd and Darryl Woodford, specialized in predictive analytics and machine learning for sports. Dimers’ data has been cited by publications such as ''Sports Illustrated,'' ''USA Today,'' and ''The Arizona Republic ''The Arizona Republic'' is an American daily newspaper published in Phoenix. Circulated throughout Arizo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloro Complexes
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride salts like ammonium chloride ( sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride ( common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and . However, the nature of free chlorine gas as a separate substance was only recognised around 1630 by Jan Baptist van Helmont. Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organoruthenium Compounds
Organoruthenium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to ruthenium chemical bond. Several organoruthenium catalysts are of commercial interest and organoruthenium compounds have been considered for cancer therapy. The chemistry has some stoichiometric similarities with organoiron chemistry, as iron is directly above ruthenium in group 8 of the periodic table. The most important reagents for the introduction of ruthenium are ruthenium(III) chloride and triruthenium dodecacarbonyl. In its organometallic compounds, ruthenium is known to adopt oxidation states from −2 ( u(CO)4sup>2−) to +6 ( uN(Me)4sup>−). Most common are those in the +2 oxidation state, as illustrated below. File:Grubbs Catalyst 1st Generation.svg, 1st generation Grubbs catalyst File:ShvoCat.png, Shvo catalyst File:RuCymCl2.png, (cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer File:Trirutheniumdodecacarbonyl.svg, triruthenium dodecacarbonyl. File:Chloro(cyclopentadienyl)bis(triph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borrowing Hydrogen
Hydrogen auto-transfer, also known as borrowing hydrogen, is the activation of a chemical reaction by temporary transfer of two hydrogen atoms from the reactant to a catalyst and return of those hydrogen atoms back to a reaction intermediate to form the final product. Two major classes of borrowing hydrogen reactions exist: (a) those that result in hydroxyl substitution, and (b) those that result in carbonyl addition. In the former case, alcohol dehydrogenation generates a transient carbonyl compound that is subject to condensation followed by the return of hydrogen. In the latter case, alcohol dehydrogenation is followed by reductive generation of a nucleophile, which triggers carbonyl addition. As borrowing hydrogen processes avoid manipulations otherwise required for discrete alcohol oxidation and the use of stoichiometric organometallic reagents, they typically display high levels of atom-economy and, hence, are viewed as examples of Green chemistry. History The Guerbet reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryōji Noyori
is a Japanese chemist. He won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2001, Noyori shared a half of the prize with William S. Knowles for the study of chirally catalyzed hydrogenations; the second half of the prize went to K. Barry Sharpless for his study in chirally catalyzed oxidation reactions ( Sharpless epoxidation). Education and career Ryōji Noyori was born in Kobe, Japan. Early in his school days Ryoji was interested in physics. His interest was kindled by the famous physicist Hideki Yukawa (1949 Nobel Prize in Physics winner), a close friend of his father. Later, he became fascinated with chemistry, after hearing a presentation on nylon at an industrial exposition. He saw the power of chemistry as being the ability to "produce high value from almost nothing". He was a student at the School of Engineering (Department of Industrial Chemistry) of the Kyoto University, where he graduated in 1961. He subsequently obtained a Master's degree in Industrial Chemistry from the Grad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer Hydrogenation
In chemistry, transfer hydrogenation is a chemical reaction involving the addition of hydrogen to a compound from a source other than molecular . It is applied in laboratory and industrial organic synthesis to saturate organic compounds and reduce ketones to alcohols, and imines to amines. It avoids the need for high-pressure molecular used in conventional hydrogenation. Transfer hydrogenation usually occurs at mild temperature and pressure conditions using organic or organometallic catalysts, many of which are chiral, allowing efficient asymmetric synthesis. It uses hydrogen donor compounds such as formic acid, isopropanol or dihydroanthracene, dehydrogenating them to , acetone, or anthracene respectively. Often, the donor molecules also function as solvents for the reaction. A large scale application of transfer hydrogenation is coal liquefaction using "donor solvents" such as tetralin. Organometallic catalysts In the area of organic synthesis, a useful family of hydrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DPEN
1,2-Diphenyl-1,2-ethylenediamine, DPEN, is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula H2NCHPhCHPhNH2, where Ph is phenyl (C6H5). DPEN exists as three stereoisomers: meso and two enantiomers S,S- and R,R-. The chiral diastereomers are used in asymmetric hydrogenation. Both diastereomers are bidentate ligands. Preparation and optical resolution 1,2-Diphenyl-1,2-ethylenediamine can be prepared from benzil by reductive amination. DPEN can be obtained as both the chiral and meso diastereomers, depending on the relative stereochemistry of the two CHPhNH2 subunits. The chiral diastereomer, which is of greater value, can be resolved into the R,R- and S,S- enantiomers using tartaric acid as the Optical resolution, resolving agent. In methanol, the R,R enantiomer has a specific rotation of [α]23 +106±1°. Asymmetric catalysis N-tosylated derivative, TsDPEN, is a ligand precursor for catalysts for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. For example, (cymene)Ru(''S'',''S''-TsDPEN) ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |