VGA on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Video Graphics Array (VGA) is a
 The
The


 The VGA supports all graphics modes supported by the MDA, CGA and EGA cards, as well as multiple new modes.
The VGA supports all graphics modes supported by the MDA, CGA and EGA cards, as well as multiple new modes.
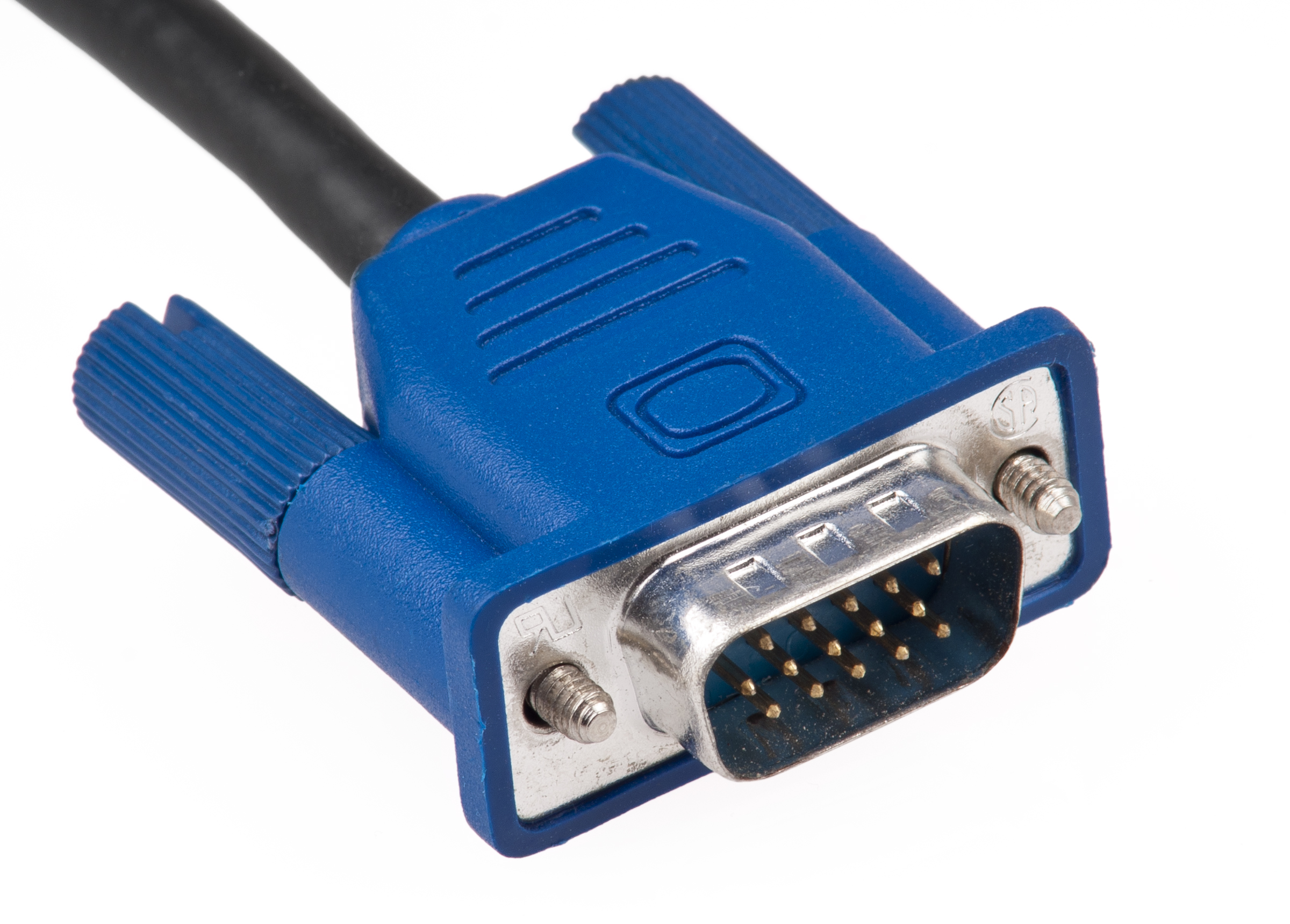

 The standard VGA monitor interface is a 15-pin D-subminiature connector in the "E" shell, variously referred to as "DE-15", "HD-15" and erroneously "DB-15(HD)".
All VGA connectors carry
The standard VGA monitor interface is a 15-pin D-subminiature connector in the "E" shell, variously referred to as "DE-15", "HD-15" and erroneously "DB-15(HD)".
All VGA connectors carry
VGA pinout and signals descriptions
{{Audio and video interfaces and connectors Products introduced in 1987 Computer display standards American inventions IBM video hardware Analog communication interfaces Analog video connectors IBM PS/2
video display controller
A video display controller (VDC), also called a display engine or display interface, is an integrated circuit which is the main component in a video-signal generator, a device responsible for the production of a TV video signal in a computing ...
and accompanying de facto graphics standard, first introduced with the IBM PS/2
The Personal System/2 or PS/2 is IBM's second generation of personal computers. Released in 1987, it officially replaced the IBM Personal Computer, IBM PC, IBM Personal Computer XT, XT, IBM Personal Computer/AT, AT, and IBM PC Convertible, PC Co ...
line of computers in 1987, which became ubiquitous in the IBM PC compatible
An IBM PC compatible is any personal computer that is hardware- and software-compatible with the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) and its subsequent models. Like the original IBM PC, an IBM PC–compatible computer uses an x86-based central p ...
industry within three years. The term can now refer to the computer display standard
Computer display standards are a combination of aspect ratio, display size, display resolution, color depth, and refresh rate. They are associated with specific expansion cards, video connectors, and monitors.
History
Various computer dis ...
, the 15-pin D-subminiature
The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.
Description ...
VGA connector
The Video Graphics Array (VGA) connector is a standard connector used for computer video output. Originating with the 1987 IBM PS/2 and its VGA graphics system, the 15-pin connector went on to become ubiquitous on PCs, as well as many monitors ...
, or the resolution characteristic of the VGA hardware.
VGA was the last IBM graphics standard to which the majority of IBM PC compatible computer manufacturers conformed, making it the lowest common denominator
In mathematics, the lowest common denominator or least common denominator (abbreviated LCD) is the lowest common multiple of the denominators of a set of fractions. It simplifies adding, subtracting, and comparing fractions.
Description
The l ...
that virtually all post-1990 PC graphics hardware can be expected to implement.
VGA was adapted into many extended forms by third parties, collectively known as Super VGA
Super VGA (SVGA) or Extended VGA is a broad term that covers a wide range of computer display standards that extended IBM's VGA specification.
When used as shorthand for a resolution, as VGA and XGA often are, SVGA refers to a resolution of 800& ...
, then gave way to custom graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal ...
s which, in addition to their proprietary interfaces and capabilities, continue to implement common VGA graphics modes and interfaces to the present day.
The VGA analog interface standard has been extended to support resolutions of up to for general usage, with specialized applications improving it further still.
Hardware design
 The
The color palette
In color theory, a color scheme is a combination of 2 or more colors used in aesthetic or practical design. Aesthetic color schemes are used to create style and appeal. Colors that create a color harmony, harmonious feeling when viewed togethe ...
random access memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of electronic computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written ...
(RAM) and its corresponding digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC, D/A, D2A, or D-to-A) is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function.
DACs are commonly used in musi ...
(DAC) were integrated into one chip (the RAMDAC
A Brooktree RAMDAC
A RAMDAC (random-access memory digital-to-analog converter) is a combination of three fast digital-to-analog converters (DACs) with a small static random-access memory (SRAM) used in computer graphics display controllers or ...
) and the cathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms on an oscilloscope, a ...
controller (CRTC
The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC; ) is a public organization in Canada tasked with the mandate as a regulatory agency tribunal for various electronic communications, covering broadcasting and telecommunic ...
) was integrated into a main VGA chip, which eliminated several other chips in previous graphics adapters, so VGA only additionally required external video RAM and timing crystals.
This small part count allowed IBM to include VGA directly on the PS/2 motherboard, in contrast to prior IBM PC models PC, PC/XT
The IBM Personal Computer XT (model 5160, often shortened to PC/XT) is the second computer in the IBM Personal Computer line, released on March 8, 1983. Except for the addition of a built-in hard drive and extra expansion slots, it is very simi ...
, and PC AT
The IBM Personal Computer AT (model 5170, abbreviated as IBM AT or PC/AT) was released in 1984 as the fourth model in the IBM Personal Computer line, following the IBM PC/XT and its IBM Portable PC variant. It was designed around the Intel 802 ...
which required a separate display adapter installed in a slot in order to connect a monitor. The term "array" rather than "adapter" in the name denoted that it was not a complete independent expansion device, but a single component that could be integrated into a system.
Unlike the graphics adapters that preceded it (MDA
MDA, mda or variants may refer to:
Businesses and organizations Political parties
* Meghalaya Democratic Alliance (2003–2008), in India
* Meghalaya Democratic Alliance (2018–present), in India
* Movement for Democracy in Africa, in Burkina F ...
, CGA, EGA and many third-party options) there was initially no discrete VGA card released by IBM. The first commercial implementation of VGA was a built-in component of the IBM PS/2, in which it was accompanied by 256 KB of video RAM, and a new DE-15 connector replacing the DE-9 used by previous graphics adapters. IBM later released the standalone ''IBM PS/2 Display Adapter'', which utilized the VGA but could be added to machines that did not have it built in.
On some machines and cables, pin 9 was missing. All pin 9 does is power an EEPROM chip in the monitor which tells the graphics card the capabilities on the monitor. Systems or cables missing this are likely using an older version of VGA.
Capabilities


Standard graphics modes
* in 4 or 16 colors (CGA/EGA compatibility) * in 256 colors (Mode 13h
Mode 13h is the standard 256-color mode on VGA graphics hardware introduced in 1987 with the IBM PS/2. It has a resolution of pixels. It was used in computer games and art/animation software of the late 1980s and early to mid-1990s. "13h" refer ...
)
* and in 16 colors or monochrome (CGA/EGA compatibility)
* in 16 colors or monochrome
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, mon ...
The 16-color and 256-color modes had fully redefinable palettes, with each entry selected from an 18-bit (262,144-color) gamut.
The other modes defaulted to standard EGA or CGA compatible palettes and instructions, but still permitted remapping of the palette with VGA-specific commands.
graphics mode
The resolution (at 256 colors rather than 16) was originally used by IBM in PGC graphics (which VGA offers no backward compatibility for) but did not see wide adoption until VGA was introduced. As the VGA began to be cloned in great quantities by manufacturers who added ever-increasing capabilities, its , 16-color mode became the de facto lowest common denominator of graphics cards. By the mid 1990s, a ×16 graphics mode using the VGA memory and register specifications was expected by operating systems such asWindows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft and the first of its Windows 9x family of operating systems, released to manufacturing on July 14, 1995, and generally to retail on August 24, 1995. Windows 95 merged ...
and OS/2 Warp 3.0, which provided no support for lower resolutions or bit depths, or support for other memory or register layouts without additional drivers. Well into the 2000s, even after the VESA
VESA (), formally known as Video Electronics Standards Association, is an American standards organization, technical standards organization for computer display standards. The organization was incorporated in California in July 1989To retrieve ...
standard for graphics cards became commonplace, the "VGA" graphics mode remained a compatibility option for PC operating systems.
Other graphics modes
Nonstandard display modes can be implemented, with horizontal resolutions of: *512 to 800 pixels wide, in 16 colors *256 to 400 pixels wide, in 256 colors And heights of: *200, or 350 to 410 lines (including 400-line) at 70 Hz refresh rate, or *224 to 256, or 448 to 512 lines (including 240 or 480-line) at 60 Hz refresh rate *512 to 600 lines at reduced vertical refresh rates (down to 50 Hz, and including e.g. 528, 544, 552, 560, 576-line), depending on individual monitor compatibility. For example, high resolution modes with square pixels are available at or in 16 colors, or medium-low resolution at with 256 colors. Alternatively, extended resolution is available with "fat" pixels and 256 colors using, e.g. (50 Hz) or (60 Hz), and "thin" pixels, 16 colors and the 70 Hz refresh rate with e.g. mode. "Narrow" modes such as tend to preserve the same pixel ratio as in e.g. mode unless the monitor is adjusted to stretch the image out to fill the screen, as they are derived simply by masking down the wider mode instead of altering pixel or line timings, but can be useful for reducing memory requirements and pixel addressing calculations for arcade game conversions or console emulators. The PC version ofPinball Fantasies
''Pinball Fantasies'' is a 1992 pinball video game originally developed by DICE (company), Digital Illusions and published by 21st Century Entertainment in Europe for the Amiga home computers. It is the sequel to ''Pinball Dreams'', which was re ...
has the option to use non-standard modes "high res" modes, such as , allowing it to display a larger portion of the pinball table on screen.
Standard text modes
VGA also implements several text modes: *, rendered with a pixel font, with an effective resolution of *, with a font, with an effective resolution of * or , with an font grid, with an effective resolution of or pixels. As with the pixel-based graphics modes, additional text modes are possible by programming the VGA correctly, with an overall maximum of about cells and an active area spanning about cells. One variant that is sometimes seen is or , using an or font and an effective pixel display, which trades use of the more flickery 60 Hz mode for an additional 5 or 10 lines of text and square character blocks (or, at , square half-blocks).Technical details
Unlike the cards that preceded it, which used binary TTL signals to interface with a monitor (and alsocomposite
Composite or compositing may refer to:
Materials
* Composite material, a material that is made from several different substances
** Metal matrix composite, composed of metal and other parts
** Cermet, a composite of ceramic and metallic material ...
, in the case of the CGA), the VGA introduced a video interface using pure analog RGB signals, with a range of 0.7 volts peak-to-peak max. In conjunction with a 18-bit
Eighteen binary digits have 262,144 (1000000 octal, 40000 hexadecimal) distinct combinations.
Eighteen bits was a common word size for smaller computers in the 1960s, when large computers often using 36 bit words and 6-bit character sets, som ...
RAMDAC
A Brooktree RAMDAC
A RAMDAC (random-access memory digital-to-analog converter) is a combination of three fast digital-to-analog converters (DACs) with a small static random-access memory (SRAM) used in computer graphics display controllers or ...
(6-bit per RGB channel), this produced a color gamut of 262,144 colors.
The original VGA specifications follow:
*Selectable 25.175 MHz or 28.322 MHz master pixel clock
*Maximum of 640 horizontal pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
sPS/2 Video Subsystem Technical Reference Manual 1992 in graphics mode, and 720 pixels in text mode
*Maximum of 480 lines
*Refresh rate
The refresh rate, also known as vertical refresh rate, vertical scan rate or vertical frequency in reference to terminology originating with the cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), is the number of times per second that a raster-based display device displa ...
s at 60 or 70 Hz
*Vertical blank interrupt
A vertical blank interrupt (or VBI) is a hardware feature found in some legacy computer systems that generate a video signal. Cathode-ray tube based video display circuits generate vertical blanking and vertical sync pulses when the display pict ...
(Not all clone cards support this.)
*Planar
Planar is an adjective meaning "relating to a plane (geometry)".
Planar may also refer to:
Science and technology
* Planar (computer graphics), computer graphics pixel information from several bitplanes
* Planar (transmission line technologies), ...
mode: up to 16 colors (4 bit plane
A bit plane of a digital discrete signal (such as image or sound) is a set of bits corresponding to a given bit position in each of the binary numbers representing the signal.
For example, for 16-bit data representation there are 16 bit planes: ...
s)
*Packed-pixel mode: 256 colors (Mode 13h
Mode 13h is the standard 256-color mode on VGA graphics hardware introduced in 1987 with the IBM PS/2. It has a resolution of pixels. It was used in computer games and art/animation software of the late 1980s and early to mid-1990s. "13h" refer ...
)
*Hardware smooth scrolling support
*No Blitter
A blitter is a circuit, sometimes as a coprocessor or a logic block on a microprocessor, dedicated to the rapid movement and modification of data within a computer's memory. A blitter can copy large quantities of data from one memory area to a ...
**Supports fast data transfers via "VGA latch" registers
*Barrel shifter
A barrel shifter is a digital circuit that can bit shift, shift a word (data type), data word by a specified number of bits without the use of any sequential logic, only pure combinational logic, i.e. it inherently provides a binary operation. I ...
*Split screen
Split screen may refer to:
* Split screen (computing), dividing graphics into adjacent parts
* Split screen (video production), the visible division of the screen
* ''Split Screen'' (TV series), 1997–2001
* Split screen, a focusing screen in a ...
support
Signal timings
The intended standard value for the horizontal frequency of VGA's mode is exactly double the value used in theNTSC-M
NTSC (from National Television System Committee) is the first American standard for analog television, published and adopted in 1941. In 1961, it was assigned the designation System M. It is also known as EIA standard 170.
In 1953, a second ...
video system, as this made it much easier to offer optional TV-out
The term TV-out is commonly used to label the connector of equipment providing an analog video signal acceptable for a television AV input. TV-out is different from AV-out in that it only provides video, no audio.
Types of signals and their r ...
solutions or external VGA-to-TV converter boxes at the time of VGA's development. It is also at least nominally twice that of CGA, which also supported composite monitor
A composite monitor or composite video monitor is any analog video display that receives input in the form of an analog composite video signal to a defined specification. A composite video signal encodes all information on a single conductor; a ...
s.
All ''derived'' VGA timings (i.e. those which use the master 25.175 and 28.322 MHz crystals and, to a lesser extent, the nominal 31.469 kHz line rate) can be varied by software that bypasses the VGA firmware interface and communicates directly with the VGA hardware, as many MS-DOS based games did. However, only the standard modes, or modes that at least use almost exactly the same H-sync and V-sync timings as one of the standard modes, can be expected to work with the original late-1980s and early-1990s VGA monitors. The use of other timings may in fact damage such monitors and thus was usually avoided by software publishers.
Third-party "multisync" CRT monitors were more flexible, and in combination with "super EGA", VGA, and later SVGA graphics cards using extended modes, could display a much wider range of resolutions and refresh rates at arbitrary sync frequencies and pixel clock rates.
For the most common VGA mode (, 60 Hz, non-interlaced), the horizontal timings can be found in the HP Super VGA Display Installation Guide and in other places.
Typical uses of selected modes
@ 70 Hz is traditionally the video mode used for booting VGA-compatiblex86
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel, based on the 8086 microprocessor and its 8-bit-external-bus variant, the 8088. Th ...
personal computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
s 090425 epanorama.net that show a graphical boot screen, while text-mode boot uses @ 70 Hz.
This convention has been eroded in recent years, however, with POST and BIOS screens moving to higher resolutions, taking advantage of EDID
Extended Display Identification Data (EDID) and Enhanced EDID (E-EDID) are metadata formats for display devices to describe their capabilities to a video source (e.g., graphics card or set-top box). The data format is defined by a standard publish ...
data to match the resolution to a connected monitor.
@ 60 Hz is the default Windows graphics mode (usually with 16 colors), up to Windows 2000. It remains an option in XP via the boot menu "low resolution video" option and per-application compatibility mode settings, despite newer versions of Windows now defaulting to and generally not allowing any resolution below to be set.
The need for such a low-quality, universally compatible fallback has diminished since the turn of the millennium,
at 70 Hz was the most common mode for early 1990s PC games, with pixel-doubling and line-doubling performed in hardware to present a at 70 Hz signal to the monitor.
The Windows 95/98/Me LOGO.SYS boot-up image was 320 × 400 resolution, displayed with pixel-doubling to present a at 70 Hz signal to the monitor. The 400-line signal was the same as the standard text mode, which meant that pressing to return to text mode didn't change the frequency of the video signal, and thus the monitor did not have to resynchronize (which could otherwise have taken several seconds).
Connector

 The standard VGA monitor interface is a 15-pin D-subminiature connector in the "E" shell, variously referred to as "DE-15", "HD-15" and erroneously "DB-15(HD)".
All VGA connectors carry
The standard VGA monitor interface is a 15-pin D-subminiature connector in the "E" shell, variously referred to as "DE-15", "HD-15" and erroneously "DB-15(HD)".
All VGA connectors carry analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analog ...
RGBHV
Component video is an analog video signal that has been split into two or more component channels. In popular use, it refers to a type of component analog video (CAV) information that is transmitted or stored as three separate signals. Compon ...
(red, green, blue, horizontal sync
Horizontal scan rate, or horizontal frequency, usually expressed in kilohertz, is the number of times per second that a raster-scan video system transmits or displays a complete horizontal line, as opposed to vertical scan rate, the number of ti ...
, vertical sync
Analog television is the original television technology that uses analog signals to transmit video and audio. In an analog television broadcast, the brightness, colors and sound are represented by amplitude, instantaneous phase and frequency, ...
) video signals. Modern connectors also include VESA
VESA (), formally known as Video Electronics Standards Association, is an American standards organization, technical standards organization for computer display standards. The organization was incorporated in California in July 1989To retrieve ...
DDC pins, for identifying attached display devices.
Because VGA uses low-voltage analog signals, signal degradation becomes a factor with low-quality or overly long cables. Solutions include shielded cables, cables that include a separate internal coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ), is a type of electrical cable consisting of an inner Electrical conductor, conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting Electromagnetic shielding, shield, with the two separated by a dielectric (Insulat ...
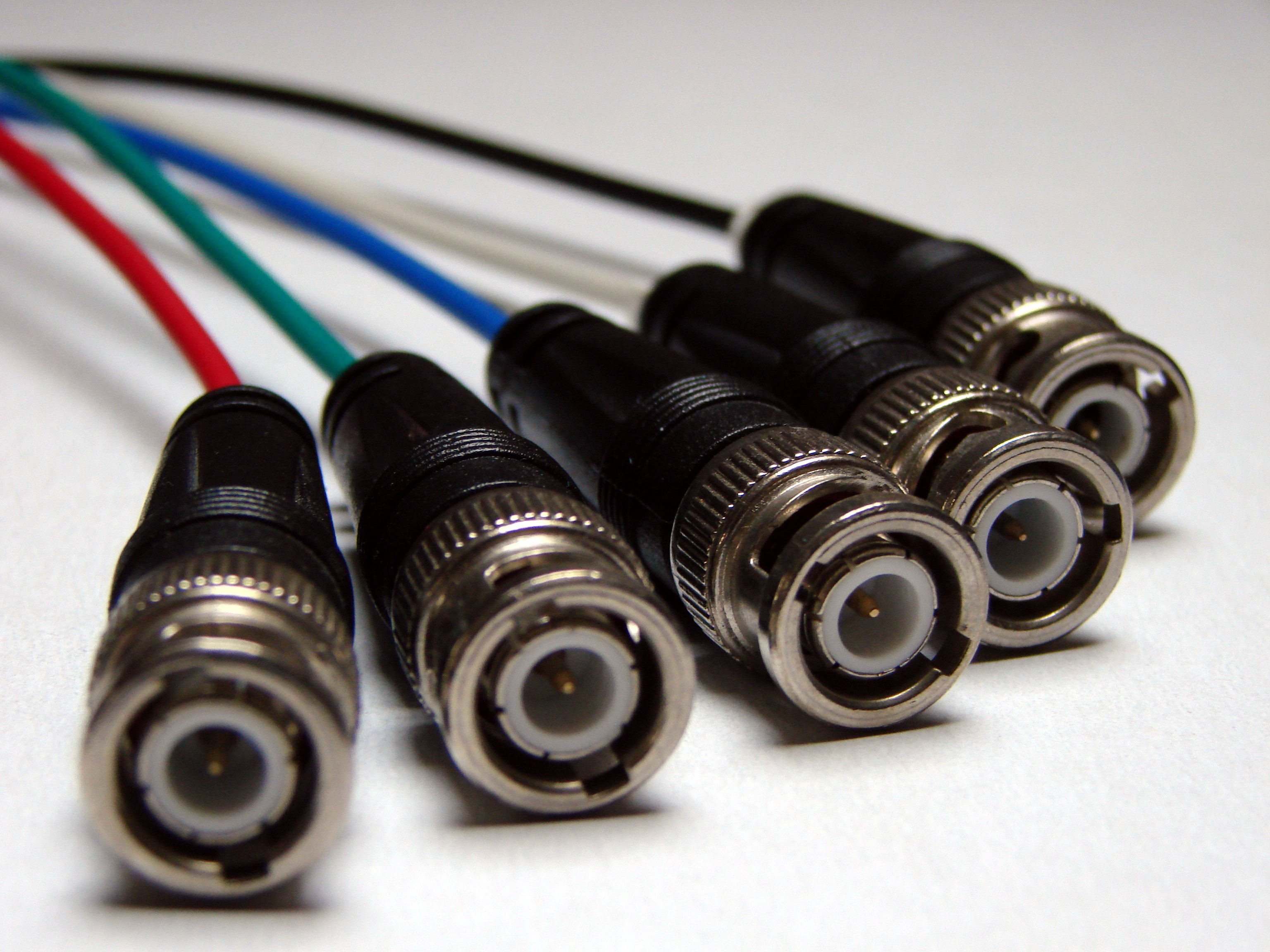
for each color signal, and "broken out" cables utilizing a separate coaxial cable with a BNC connector
The BNC connector is a miniature quick-connect/disconnect RF connector, radio-frequency connector for coaxial cable. It was introduced on military radio equipment in the 1940s, and has since become widely used in radio systems and as a common t ...
for each color signal.
BNC breakout cables typically use five connectors, one each for Red, Green, Blue, Horizontal Sync, and Vertical Sync, and do not include the other signal lines of the VGA interface. With BNC, the coaxial wires are fully shielded end-to-end and through the interconnect so that virtually no crosstalk and very little external interference can occur. The use of BNC RGB video cables predates VGA in other markets and industries.
Color palette
VGA 256 default color palette VGA palette organised into 4 groups Examples of VGA images in 640×480 with 16 colors and 320×200 with 256 colors (bottom). Dithering is used to mask color limitations. The VGA color system uses register-based palettes to map colors in various bit depths to its 18-bit output gamut. It isbackward compatible
In telecommunications and computing, backward compatibility (or backwards compatibility) is a property of an operating system, software, real-world product, or technology that allows for interoperability with an older legacy system, or with inpu ...
with the EGA and CGA adapters, but supports extra bit depth for the palette when in these modes.
For instance, when in EGA 16-color modes, VGA offers 16 palette registers, and in 256-color modes, it offers 256 registers. Each palette register contain a 3×6 bit RGB value, selecting a color from the 18-bit gamut of the DAC.
These color registers are initialized to default values IBM expected to be most useful for each mode. For instance, EGA 16-color modes initialize to the default CGA 16-color palette, and the 256-color mode initializes to a palette consisting of 16 CGA colors, 16 grey shades, and then 216 colors chosen by IBM to fit expected use cases.
After initialization they can be redefined at any time without altering the contents of video RAM, permitting palette cycling.
In the 256-color modes, the DAC is set to combine four 2-bit color values, one from each plane, into an 8-bit-value representing an index into the 256-color palette. The CPU interface combines the 4 planes in the same way, a feature called "chain-4", so that each pixel appears to the CPU as a packed 8-bit value representing the palette index.Use
The video memory of the VGA is mapped to the PC's memory via a window in the range between segments 0xA0000 and 0xBFFFF in the PC'sreal mode
Real mode, also called real address mode, is an operating mode of all x86-compatible CPUs. The mode gets its name from the fact that addresses in real mode always correspond to real locations in memory. Real mode is characterized by a 20- bit s ...
address space (A000:0000 and B000:FFFF in segment:offset notation). Typically, these starting segments are:
* 0xA0000 for EGA/VGA graphics modes (64 KB)
* 0xB0000 for monochrome text mode (32 KB)
* 0xB8000 for color text mode and CGA-compatible graphics modes (32 KB)
A typical VGA card is also provides this port-mapped I/O segment:
* 0x3B0 to 0x3DF
Due to the use of different address mappings for different modes, it is possible to have a monochrome adapter (i.e. MDA or Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the Gr ...
) and a color adapter such as the VGA, EGA, or CGA installed in the same machine.
At the beginning of the 1980s, this was typically used to display Lotus 1-2-3
Lotus 1-2-3 is a discontinued spreadsheet program from Lotus Software (later part of IBM). It was the first killer application of the IBM PC, was hugely popular in the 1980s, and significantly contributed to the success of IBM PC-compatibles ...
spreadsheets in high-resolution text on a monochrome display and associated graphics on a low-resolution CGA display simultaneously. Many programmers also used such a setup with the monochrome card displaying debugging information while a program ran in graphics mode on the other card. Several debuggers, like Borland's Turbo Debugger
Turbo Debugger (TD) is a machine-level debugger for DOS executables, intended mainly for debugging Borland Turbo Pascal, and later Turbo C programs, sold by Borland. It is a full-screen debugger displaying both Turbo Pascal or Turbo C source and ...
, D86 and Microsoft's CodeView
CodeView is a standalone debugger created by David Norris at Microsoft in 1985 as part of its development toolset. It originally shipped with Microsoft C 4.0 and later. It also shipped with Visual Basic for MS-DOS, Microsoft BASIC PDS, and a num ...
could work in a dual monitor setup. Either Turbo Debugger or CodeView could be used to debug Windows.
There were also device drivers such as ox.sys, which implemented a serial interface simulation on the monochrome display and, for example, allowed the user to receive crash messages from debugging versions of Windows without using an actual serial terminal.
It is also possible to use the "MODE MONO" command at the command prompt to redirect the output to the monochrome display. When a monochrome adapter was not present, it was possible to use the 0xB000–0xB7FF address space as additional memory for other programs.
A VGA-capable PCI
PCI may refer to:
Business and economics
* Payment card industry, businesses associated with debit, credit, and other payment cards
** Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, a set of security requirements for credit card processors
* Prov ...
/ PCIe
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripher ...
graphics card can provide legacy VGA registers in its PCI configuration space
PCI configuration space is the underlying way that the Conventional PCI, PCI-X and PCI Express perform auto configuration of the cards inserted into their bus.
Overview
PCI devices have a set of registers referred to as ''configuration space ...
, which may be remapped by BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
or operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
.
Programming
"Unchaining" the 256 KB VGA memory into four separate "planes" makes VGA's 256 KB of RAM available in 256-color modes. There is a trade-off for extra complexity and performance loss in some types of graphics operations, but this is mitigated by other operations becoming faster in certain situations: *Single-color polygon filling could be accelerated due to the ability to set four pixels with a single write to the hardware. *The video adapter could assist in copying video RAM regions, which was sometimes faster than doing this with the relatively slow CPU-to-VGA interface. *The use of multiple video pages in hardware alloweddouble buffering
In computer science, multiple buffering is the use of more than one buffer to hold a block of data, so that a " reader" will see a complete (though perhaps old) version of the data instead of a partially updated version of the data being created ...
, triple buffering
In computer science, multiple buffering is the use of more than one buffer (computer science), buffer to hold a block of data, so that a "readers-writers problem, reader" will see a complete (though perhaps old) version of the data instead of a pa ...
or split screens, which, while available in VGA's 16-color mode, was not possible using stock Mode 13h
Mode 13h is the standard 256-color mode on VGA graphics hardware introduced in 1987 with the IBM PS/2. It has a resolution of pixels. It was used in computer games and art/animation software of the late 1980s and early to mid-1990s. "13h" refer ...
.
*Most particularly, several higher, arbitrary-resolution display modes were possible, all the way up to the programmable limit of with 16 colors (or with 256 colors), as well as other custom modes using unusual combinations of horizontal and vertical pixel counts in either color mode.
Software such as Fractint, Xlib
Xlib (also known as libX11) is an X Window System protocol client library (computer science), library written in the C (programming language), C programming language. It contains subroutine, functions for interacting with an X Server (computi ...
and ColoRIX also supported tweaked 256-color modes on standard adaptors using freely-combinable widths of 256, 320, and 360 pixels and heights of 200, 240 and 256 (or 400, 480 and 512) lines, extending still further to 384 or 400 pixel columns and 576 or 600 (or 288, 300). However, was the best known and most frequently used, as it offered a standard 40-column resolution and 4:3 aspect ratio with square pixels. " × 8" resolution was commonly called Mode X
Mode X is a 256-color graphics display mode of the VGA graphics hardware for IBM PC compatibles. It was first publicized by Michael Abrash in his July 1991 column in '' Dr. Dobb's Journal'' and then in chapters 47-49 of Abrash's ''Graphics Pro ...
, the name used by Michael Abrash
Michael Abrash is an American programmer and technical writer. He has written dozens of magazine articles and multiple books on code optimization and software-rendered graphics for IBM PC compatibles. He worked at id Software in the mid-1990s on ...
when he presented the resolution in Dr. Dobb's Journal
''Dr. Dobb's Journal'' (often shortened to ''Dr. Dobb's'' or DDJ) was a monthly magazine published in the United States by UBM Technology Group, part of UBM. It covered topics aimed at computer programmers. When launched in 1976, DDJ was the fi ...
.
The highest resolution modes were only used in special, opt-in cases rather than as standard, especially where high line counts were involved. Standard VGA monitors had a fixed line scan (H-scan) rate"multisync" monitors being, at the time, expensive raritiesand so the vertical/frame (V-scan) refresh rate
The refresh rate, also known as vertical refresh rate, vertical scan rate or vertical frequency in reference to terminology originating with the cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), is the number of times per second that a raster-based display device displa ...
had to be reduced in order to accommodate them, which increased visible flicker and thus eye strain
Eye strain, also medically termed as asthenopia (), is a common eye condition characterized by nonspecific symptom, non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, pain in or around the eyes, blurred vision, headache, and occasional diplopia, double vis ...
. For example, the highest mode, being otherwise based on the matching SVGA resolution (with 628 total lines), reduced the refresh rate from 60 Hz to about 50 Hz (and , the theoretical maximum resolution achievable with 256 KB at 16 colors, would have reduced it to about 48 Hz, barely higher than the rate at which XGA monitors employed a double-frequency interlacing technique to mitigate full-frame flicker).
These modes were also outright incompatible with some monitors, producing display problems such as picture detail disappearing into overscan
Overscan is a behaviour in certain television sets in which part of the input picture is cut off by the visible bounds of the screen. It exists because cathode-ray tube (CRT) television sets from the 1930s to the early 2000s were highly variable ...
(especially in the horizontal dimension), vertical roll, poor horizontal sync
Horizontal scan rate, or horizontal frequency, usually expressed in kilohertz, is the number of times per second that a raster-scan video system transmits or displays a complete horizontal line, as opposed to vertical scan rate, the number of ti ...
or even a complete lack of picture depending on the exact mode attempted. Due to these potential issues, most VGA tweaks used in commercial products were limited to more standards-compliant, "monitor-safe" combinations, such as (square pixels, three video pages, 60 Hz), (double resolution, two video pages, 70 Hz), and (highest resolution compatible with both standard VGA monitors and cards, one video page, 60 Hz) in 256 colors, or double the horizontal resolution in 16-color mode.
Hardware manufacturers
Several companies produced VGA compatible graphic board models. * ATI: Graphics Solution Plus, Wonder series, Mach series *S3 Graphics
S3 Graphics, Ltd. was an American computer graphics company. The company sold the S3 Trio, Trio, S3 ViRGE, ViRGE, S3 Savage, Savage, and S3 Chrome, Chrome series of graphics processors. Struggling against competition from 3dfx Interactive, ATI T ...
: S3 911, 911A, 924, 801, 805, 805i, 928, 805p, 928p, S3 Vision series, S3 Trio series
*Matrox
Matrox Graphics, Inc. is a producer of graphics card, video card components and equipment for personal computers and workstations. Based in Dorval, Quebec, Canada, it was founded in 1976 by Lorne Trottier and Branko Matić. The name is derived ...
: MAGIC RGB
*Plantronics
Plantronics, Inc. is an American electronics company producing audio communications equipment for business and consumers. Its products support unified communications, mobile use, gaming and music. Plantronics is headquartered in Santa Cruz, Cal ...
: Colorplus
*Paradise Systems
Paradise Systems, Inc., was an American Graphics card, video controller and graphics adapter card manufacturer active from 1982 to 1996. The company became a subsidiary of Western Digital when they purchased Paradise in 1986; in 1995, they sold th ...
: PEGA 1, PEGA 1a, PEGA 2a
*Tseng Labs
Tseng Laboratories, Inc. (also known as Tseng Labs or TLI) was a maker of graphics chips and controllers for IBM PC compatibles, based in Newtown, Pennsylvania, and founded by Jack Hsiao Nan Tseng.
History 1983–1995
Founded in 1983, Tseng L ...
: ET3000, ET4000, ET6000
*Cirrus Logic
Cirrus Logic Inc. is an American fabless semiconductor company, fabless semiconductor supplier that specializes in analog, mixed-signal, and audio Digital signal processor, DSP integrated circuits (ICs). Since 1998, the company's headquarters have ...
: CL-GD400, CL-GD500 and CL-GD5000 series
*Trident Microsystems
Trident Microsystems Inc. was an American fabless semiconductor company that became in the 1990s a well-known supplier of integrated circuits (commonly called "chips") for video display controllers used in video cards and on motherboards for d ...
: TVGA 8000 series, TVGA 9000 series, TGUI9000 series
* IIT
*NEC
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered at the NEC Supertower in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It provides IT and network solutions, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), Inte ...
*Chips and Technologies
Chips and Technologies, Inc. (C&T), was an early fabless semiconductor company founded in Milpitas, California, in December 1984 by Gordon A. Campbell and Dado Banatao.
Its first product, announced September 1985, was a four chip Enhanced Graph ...
*SiS
Sis or SIS may refer to:
People
*Michael Sis (born 1960), American Catholic bishop
Places
* Sis (ancient city), historical town in modern-day Turkey, served as the capital of the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia.
* Kozan, Adana, the current name ...
*Tamerack
*Realtek
Realtek Semiconductor Corp. () is a Taiwanese fabless semiconductor company situated in the Hsinchu Science Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan. Realtek was founded in October 1987 and subsequently listed on the Taiwan Stock Exchange in 1998. Realtek has manu ...
*Oak Technology
Oak Technology (OAKT) was an American supplier of semiconductor chips for sound cards, graphics cards and optical storage devices such as CD-ROM, CD-RW and DVD. It achieved success with optical storage chips and its stock price increased sub ...
* LSI
*Hualon
*Cornerstone Imaging
*Winbond
Winbond Electronics Corporation () is a Taiwan-based corporation founded in 1987. It produces semiconductors and several types of integrated circuits (ICs) including dynamic random-access memory, static random-access memory, serial flash, micr ...
*AMD
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California and maintains significant operations in Austin, Texas. AMD is a hardware and fabless company that de ...
*Western Digital
Western Digital Corporation is an American data storage company headquartered in San Jose, California. Established in 1970, the company is one of the world's largest manufacturers of hard disk drives (HDDs).
History
1970s
Western Digital ...
*Intergraph
Intergraph Corporation was an American software development and services company, which now forms part of Hexagon AB. It provides enterprise engineering and geospatially powered software to businesses, governments, and organizations around the w ...
*Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog ...
*Gemini (defunct
Defunct may refer to:
* Defunct (video game), ''Defunct'' (video game), 2014
* Zombie process or defunct process, in Unix-like operating systems
See also
*
* :Former entities
* End-of-life product
* Obsolescence
{{Disambiguation ...
)
*Genoa Systems
Genoa Systems Corporation, later Genoa Electronics Corporation, was an American computer multimedia peripheral vendor based in San Jose, California, and active from 1984 to 2002. The company was once a prolific and well-known manufacturer of video ...
(defunct
Defunct may refer to:
* Defunct (video game), ''Defunct'' (video game), 2014
* Zombie process or defunct process, in Unix-like operating systems
See also
*
* :Former entities
* End-of-life product
* Obsolescence
{{Disambiguation ...
)
Successors
Super VGA (SVGA)
Super VGA (SVGA) is a display standard developed in 1988, whenNEC Home Electronics
is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered at the NEC Supertower in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It provides IT and network solutions, including cloud computing, artificia ...
announced its creation of the Video Electronics Standards Association
VESA (), formally known as Video Electronics Standards Association, is an American technical standards organization for computer display standards. The organization was incorporated in California in July 1989To retrieve the information, sear ...
(VESA). The development of SVGA was led by NEC
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered at the NEC Supertower in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It provides IT and network solutions, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), Inte ...
, along with other VESA members including ATI Technologies
ATI Technologies Inc. was a Canadian semiconductor industry, semiconductor technology corporation based in Markham, Ontario, that specialized in the development of graphics processing units and chipsets. Founded in 1985, the company listed pub ...
and Western Digital
Western Digital Corporation is an American data storage company headquartered in San Jose, California. Established in 1970, the company is one of the world's largest manufacturers of hard disk drives (HDDs).
History
1970s
Western Digital ...
. SVGA enabled graphics display resolution
A display resolution standard is a commonly used width and height dimension (display resolution) of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain com ...
s up to 800 × 600 pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
s, 56% more than VGA's maximum resolution of 640 × 480 pixels.
Extended Graphics Array (XGA)
Extended Graphics Array (XGA) is an IBM display standard introduced in 1990. Later it became the most common appellation of the 1024 × 768 pixelsdisplay resolution
The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor, or other display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resoluti ...
.
See also
*VGA text mode
VGA text mode was introduced in 1987 by IBM as part of the VGA standard for its IBM PS/2 computers. Its use on IBM PC compatibles was widespread through the 1990s and persists today for some applications on modern computers. The main features of V ...
*Graphic display resolutions
A display resolution standard is a commonly used width and height dimension (display resolution) of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain comb ...
*List of color palettes
This article is a list of the color palettes for notable computer graphics, terminals and video game console hardware.
Only a sample and the palette's name are given here. More specific articles are linked from the name of each palette, for the ...
*List of video connectors
This is a list of physical RF and video connectors and related video signal standards.
Physical connectors
D-subminiature family
DVI-related
DIN/ Mini-DIN
Others
By signal standard
See also
*Computer display standard
Computer ...
*List of monochrome and RGB color formats
This list of monochrome and RGB palettes includes generic repertoires of colors (color palettes) to produce black-and-white and RGB color pictures by a computer's display hardware. RGB is the most common method to produce colors for displays; s ...
* List of 16-bit computer hardware palettes
*List of defunct graphics chips and card companies
During the 1980s and 1990s, a relatively large number of companies appeared selling primarily 2D graphics cards and later 3D. Most of those companies have subsequently disappeared, as the increasing complexity of GPUs substantially increased rese ...
*Super VGA
Super VGA (SVGA) or Extended VGA is a broad term that covers a wide range of computer display standards that extended IBM's VGA specification.
When used as shorthand for a resolution, as VGA and XGA often are, SVGA refers to a resolution of 800& ...
* (for Japanese AX architecture computers)
*DOS/V
DOS/V is a Japanese computing initiative starting in 1990 to allow DOS on IBM PC compatibles with VGA cards to handle Double-byte character set, double-byte (DBCS) Japanese text via software alone. It was initially developed from PC DOS by IBM f ...
*DisplayPort
DisplayPort (DP) is a digital interface used to connect a video source, such as a Personal computer, computer, to a display device like a Computer monitor, monitor. Developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA), it can also car ...
and HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary digital interface used to transmit high-quality video and audio signals between devices. It is commonly used to connect devices such as televisions, computer monitors, projectors, gam ...
(which have largely replaced VGA)
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
VGA pinout and signals descriptions
{{Audio and video interfaces and connectors Products introduced in 1987 Computer display standards American inventions IBM video hardware Analog communication interfaces Analog video connectors IBM PS/2