Physics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Physics is the
Physics is the
 During the classical period in Greece (6th, 5th and 4th centuries BCE) and in Hellenistic times,
During the classical period in Greece (6th, 5th and 4th centuries BCE) and in Hellenistic times,
 The
The 
Justus Sustermans - Portrait of Galileo Galilei, 1636.jpg,

 Modern physics began in the early 20th century with the work of
Modern physics began in the early 20th century with the work of
 In the first decades of the 20th century physics was revolutionized by the discoveries of quantum mechanics and relativity. The changes were so fundamental that these new concepts became the foundation of "modern physics", with other topics becoming "classical physics". The majority of applications of physics are essentially classical.
The laws of classical physics accurately describe systems whose important length scales are greater than the atomic scale and whose motions are much slower than the speed of light. Outside of this domain, observations do not match predictions provided by classical mechanics.
In the first decades of the 20th century physics was revolutionized by the discoveries of quantum mechanics and relativity. The changes were so fundamental that these new concepts became the foundation of "modern physics", with other topics becoming "classical physics". The majority of applications of physics are essentially classical.
The laws of classical physics accurately describe systems whose important length scales are greater than the atomic scale and whose motions are much slower than the speed of light. Outside of this domain, observations do not match predictions provided by classical mechanics.

 Theorists seek to develop
Theorists seek to develop
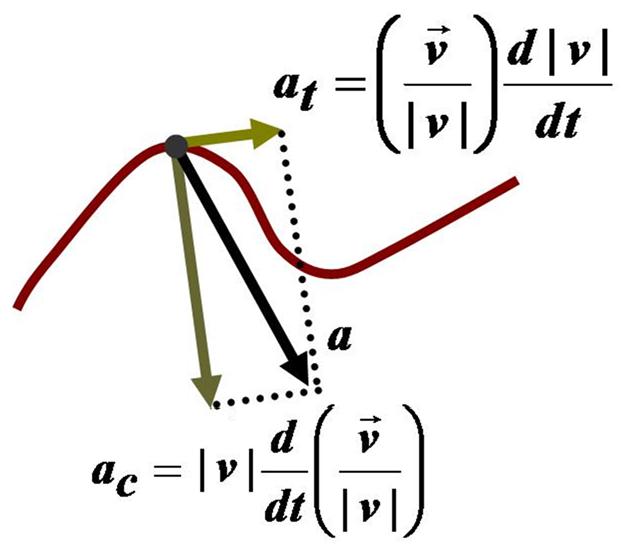 Physics covers a wide range of
Physics covers a wide range of
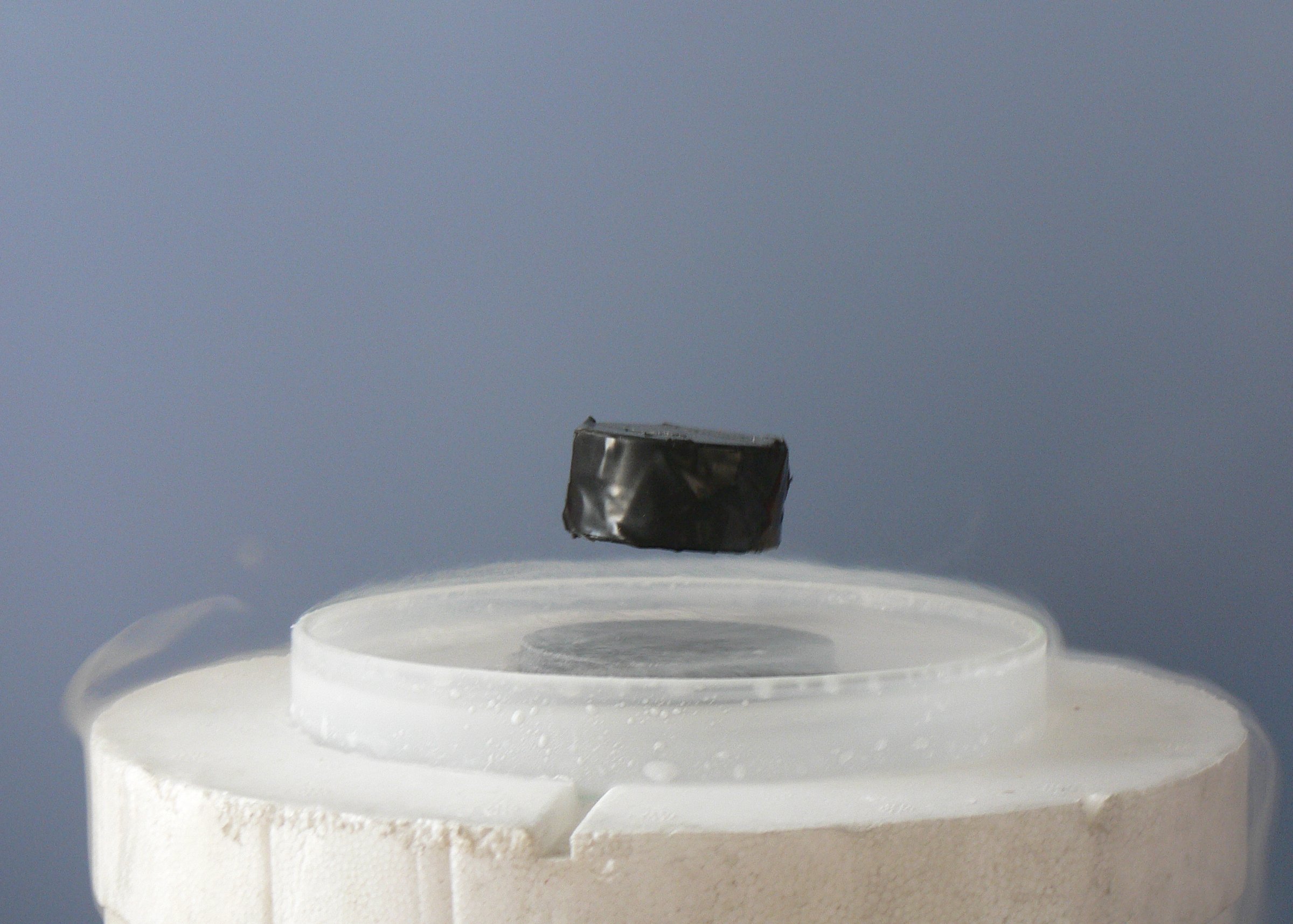
 Research in physics is continually progressing on a large number of fronts.
In condensed matter physics, an important unsolved theoretical problem is that of
Research in physics is continually progressing on a large number of fronts.
In condensed matter physics, an important unsolved theoretical problem is that of
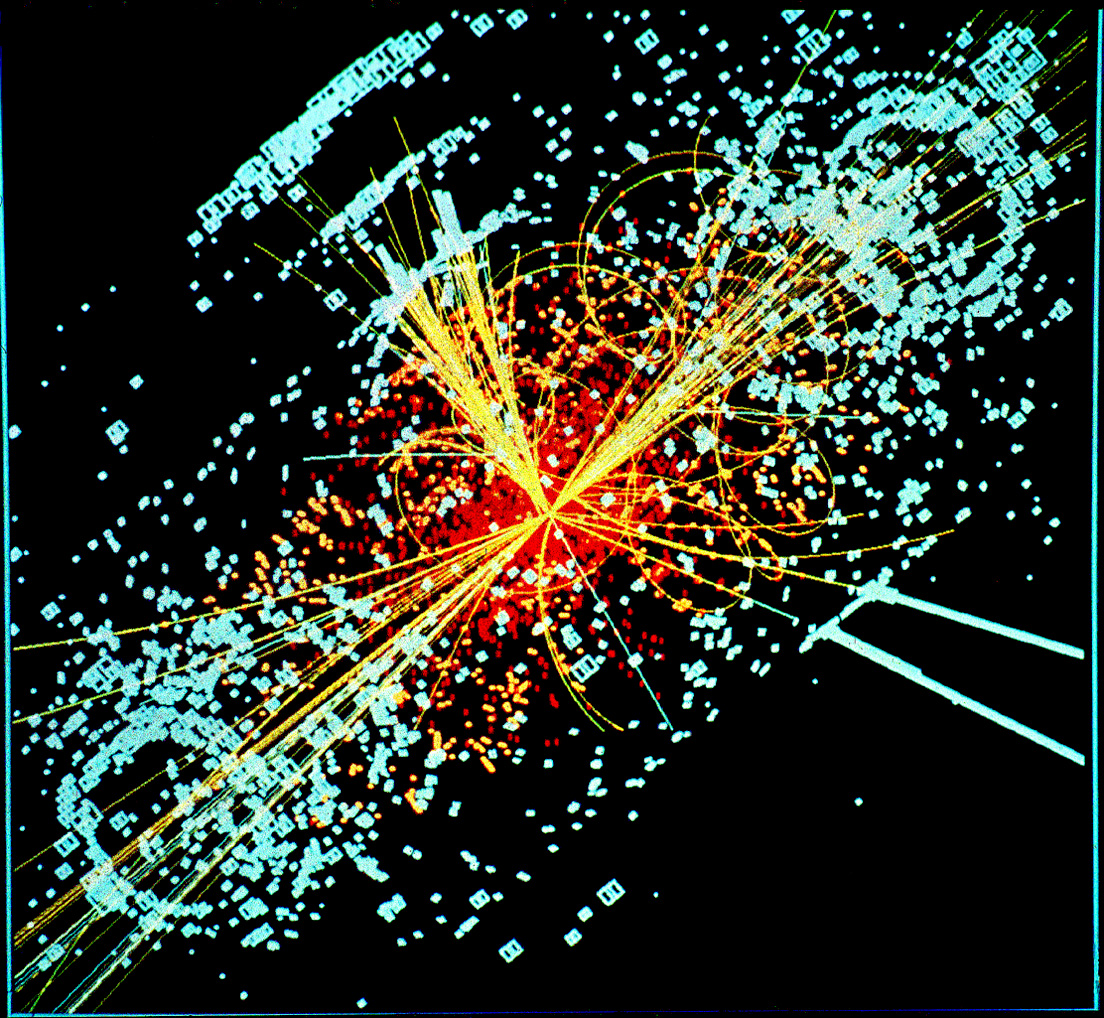 Particle physics is the study of the elementary constituents of
Particle physics is the study of the elementary constituents of
 Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic physical properties of matter. In particular, it is concerned with the "condensed" phases that appear whenever the number of particles in a system is extremely large and the interactions between them are strong.
The most familiar examples of condensed phases are
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic physical properties of matter. In particular, it is concerned with the "condensed" phases that appear whenever the number of particles in a system is extremely large and the interactions between them are strong.
The most familiar examples of condensed phases are
 Astrophysics and astronomy are the application of the theories and methods of physics to the study of
Astrophysics and astronomy are the application of the theories and methods of physics to the study of

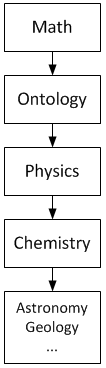 Mathematics provides a compact and exact language used to describe the order in nature. This was noted and advocated by Pythagoras,
Mathematics provides a compact and exact language used to describe the order in nature. This was noted and advocated by Pythagoras,  Ontology is a prerequisite for physics, but not for mathematics. It means physics is ultimately concerned with descriptions of the real world, while mathematics is concerned with abstract patterns, even beyond the real world. Thus physics statements are synthetic, while mathematical statements are analytic. Mathematics contains hypotheses, while physics contains theories. Mathematics statements have to be only logically true, while predictions of physics statements must match observed and experimental data.
The distinction is clear-cut, but not always obvious. For example, mathematical physics is the application of mathematics in physics. Its methods are mathematical, but its subject is physical. The problems in this field start with a "Boundary condition, mathematical model of a physical situation" (system) and a "mathematical description of a physical law" that will be applied to that system. Every mathematical statement used for solving has a hard-to-find physical meaning. The final mathematical solution has an easier-to-find meaning, because it is what the solver is looking for.
Ontology is a prerequisite for physics, but not for mathematics. It means physics is ultimately concerned with descriptions of the real world, while mathematics is concerned with abstract patterns, even beyond the real world. Thus physics statements are synthetic, while mathematical statements are analytic. Mathematics contains hypotheses, while physics contains theories. Mathematics statements have to be only logically true, while predictions of physics statements must match observed and experimental data.
The distinction is clear-cut, but not always obvious. For example, mathematical physics is the application of mathematics in physics. Its methods are mathematical, but its subject is physical. The problems in this field start with a "Boundary condition, mathematical model of a physical situation" (system) and a "mathematical description of a physical law" that will be applied to that system. Every mathematical statement used for solving has a hard-to-find physical meaning. The final mathematical solution has an easier-to-find meaning, because it is what the solver is looking for.
see also reductionism and special sciences Similarly, chemistry is often called the central science because of its role in linking the physical sciences. For example, chemistry studies properties, structures, and chemical reaction, reactions of matter (chemistry's focus on the molecular and atomic scale Difference between chemistry and physics, distinguishes it from physics). Structures are formed because particles exert electrical forces on each other, properties include physical characteristics of given substances, and reactions are bound by laws of physics, like conservation of energy, Conservation of mass, mass, and charge conservation, charge. Fundamental physics seeks to better explain and understand phenomena in all spheres, without a specific practical application as a goal, other than the deeper insight into the phenomema themselves.
 Applied physics is a general term for physics research and development that is intended for a particular use. An applied physics curriculum usually contains a few classes in an applied discipline, like geology or electrical engineering. It usually differs from engineering in that an applied physicist may not be designing something in particular, but rather is using physics or conducting physics research with the aim of developing new technologies or solving a problem.
The approach is similar to that of applied mathematics. Applied physicists use physics in scientific research. For instance, people working on accelerator physics might seek to build better particle detectors for research in theoretical physics.
Physics is used heavily in engineering. For example, statics, a subfield of
Applied physics is a general term for physics research and development that is intended for a particular use. An applied physics curriculum usually contains a few classes in an applied discipline, like geology or electrical engineering. It usually differs from engineering in that an applied physicist may not be designing something in particular, but rather is using physics or conducting physics research with the aim of developing new technologies or solving a problem.
The approach is similar to that of applied mathematics. Applied physicists use physics in scientific research. For instance, people working on accelerator physics might seek to build better particle detectors for research in theoretical physics.
Physics is used heavily in engineering. For example, statics, a subfield of  With the Uniformitarianism (science), standard consensus that the Scientific law, laws of physics are universal and do not change with time, physics can be used to study things that would ordinarily be mired in uncertainty. For example, in the study of the origin of the Earth, a physicist can reasonably model Earth's mass, temperature, and rate of rotation, as a function of time allowing the extrapolation forward or backward in time and so predict future or prior events. It also allows for simulations in engineering that speed up the development of a new technology.
There is also considerable interdisciplinarity, so many other important fields are influenced by physics (e.g., the fields of econophysics and sociophysics).
With the Uniformitarianism (science), standard consensus that the Scientific law, laws of physics are universal and do not change with time, physics can be used to study things that would ordinarily be mired in uncertainty. For example, in the study of the origin of the Earth, a physicist can reasonably model Earth's mass, temperature, and rate of rotation, as a function of time allowing the extrapolation forward or backward in time and so predict future or prior events. It also allows for simulations in engineering that speed up the development of a new technology.
There is also considerable interdisciplinarity, so many other important fields are influenced by physics (e.g., the fields of econophysics and sociophysics).
Physics at Quanta Magazine
Usenet Physics FAQ
– FAQ compiled by sci.physics and other physics newsgroups
Website of the Nobel Prize in physics
– Award for outstanding contributions to the subject
World of Physics
– Online encyclopedic dictionary of physics
''Nature Physics''
– Academic journal
Physics
– Online magazine by the American Physical Society – Directory of physics related media
The Vega Science Trust
– Science videos, including physics
– Physics and astronomy mind-map from Georgia State University
Physics at MIT OpenCourseWare
– Online course material from Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Feynman Lectures on Physics
{{Authority control Physics,
 Physics is the
Physics is the scientific
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
study of matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic par ...
, its fundamental constituents, its motion
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position with respect to time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed and frame of reference to an observer and mea ...
and behavior through space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually con ...
and time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, t ...
, and the related entities of energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
and force
A force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. The concept of force makes the everyday notion of pushing or pulling mathematically precise. Because the Magnitude ...
. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of the human intellect in its quest to understand our world and ourselves." "Physics is an experimental science. Physicists observe the phenomena of nature and try to find patterns that relate these phenomena." "Physics is the study of your world and the world and universe around you." A scientist who specializes in the field of physics is called a physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe.
Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate ca ...
.
Physics is one of the oldest academic discipline
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary education, secondary or tertiary education, tertiary higher education, higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membershi ...
s. Over much of the past two millennia, physics, chemistry, biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditar ...
, and certain branches of mathematics were a part of natural philosophy
Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature (from Latin ''philosophia naturalis'') is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe. It was dominant before the development of modern science.
From the ancient wor ...
, but during the Scientific Revolution
The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology (including human anatomy) and chemistry transformed ...
in the 17th century, these natural sciences branched into separate research endeavors. Physics intersects with many interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several other fields like sociology, anthropology, psychology, ec ...
areas of research, such as biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. ...
and quantum chemistry
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contribution ...
, and the boundaries of physics are not rigidly defined. New ideas in physics often explain the fundamental mechanisms studied by other sciences and suggest new avenues of research in these and other academic disciplines such as mathematics and philosophy.
Advances in physics often enable new technologies
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, ...
. For example, advances in the understanding of electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
, solid-state physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how the l ...
, and nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the ...
led directly to the development of technologies that have transformed modern society, such as television, computers, domestic appliance
A major appliance, also known as a large domestic appliance or large electric appliance or simply a large appliance, large domestic, or large electric, is a non-portable or semi-portable machine used for routine housekeeping tasks such as cookin ...
s, and nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s; advances in thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws o ...
led to the development of industrialization; and advances in mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to objects ...
inspired the development of calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizati ...
.
History
The word ''physics'' comes from theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
('study of nature'), which itself is a borrowing of the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
( 'natural science'), a term derived from ( 'origin, nature, property')., ,
Ancient astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest ...
is one of the oldest natural sciences. Early civilizations dating before 3000 BCE, such as the Sumerians, ancient Egyptians, and the Indus Valley Civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 B ...
, had a predictive knowledge and a basic awareness of the motions of the Sun, Moon, and stars. The stars and planets, believed to represent gods, were often worshipped. While the explanations for the observed positions of the stars were often unscientific and lacking in evidence, these early observations laid the foundation for later astronomy, as the stars were found to traverse great circle
In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point.
Any arc of a great circle is a geodesic of the sphere, so that great circles in spherical geometry ...
s across the sky, which could not explain the positions of the planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a ...
s.
According to Asger Aaboe
Asger Hartvig Aaboe (26 April 1922 – 19 January 2007) was a historian of the exact sciences and of mathematics who is known for his contributions to the history of ancient Babylonian astronomy. In his studies of Babylonian astronomy, he went b ...
, the origins of Western astronomy can be found in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
, and all Western efforts in the exact science
The exact sciences, sometimes called the exact mathematical sciences, are those sciences "which admit of absolute precision in their results"; especially the mathematical sciences. Examples of the exact sciences are mathematics, optics, astron ...
s are descended from late Babylonian astronomy
Babylonian astronomy was the study or recording of celestial objects during the early history of Mesopotamia.
Babylonian astronomy seemed to have focused on a select group of stars and constellations known as Ziqpu stars. These constellations ...
. Egyptian astronomers
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years o ...
left monuments showing knowledge of the constellations and the motions of the celestial bodies, while Greek poet Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the '' Iliad'' and the '' Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of ...
wrote of various celestial objects in his ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the '' Odys ...
'' and ''Odyssey
The ''Odyssey'' (; grc, Ὀδύσσεια, Odýsseia, ) is one of two major Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek Epic poetry, epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by moder ...
''; later Greek astronomers
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
provided names, which are still used today, for most constellations visible from the Northern Hemisphere.
Natural philosophy
Natural philosophy
Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature (from Latin ''philosophia naturalis'') is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe. It was dominant before the development of modern science.
From the ancient wor ...
has its origins in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wit ...
during the Archaic period (650 BCE – 480 BCE), when pre-Socratic philosophers
Pre-Socratic philosophy, also known as early Greek philosophy, is ancient Greek philosophy before Socrates. Pre-Socratic philosophers were mostly interested in cosmology, the beginning and the substance of the universe, but the inquiries of thes ...
like Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; grc-gre, Θαλῆς; ) was a Greek mathematician, astronomer, statesman, and pre-Socratic philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. He was one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most notably Aristotle, regard ...
rejected non-naturalistic explanations for natural phenomena and proclaimed that every event had a natural cause. They proposed ideas verified by reason and observation, and many of their hypotheses proved successful in experiment; for example, atomism
Atomism (from Greek , ''atomon'', i.e. "uncuttable, indivisible") is a natural philosophy proposing that the physical universe is composed of fundamental indivisible components known as atoms.
References to the concept of atomism and its atoms ...
was found to be correct approximately 2000 years after it was proposed by Leucippus
Leucippus (; el, Λεύκιππος, ''Leúkippos''; fl. 5th century BCE) is a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who has been credited as the first philosopher to develop a theory of atomism.
Leucippus' reputation, even in antiquity, was obscured ...
and his pupil Democritus
Democritus (; el, Δημόκριτος, ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe. ...
.
Aristotle and Hellenistic physics
 During the classical period in Greece (6th, 5th and 4th centuries BCE) and in Hellenistic times,
During the classical period in Greece (6th, 5th and 4th centuries BCE) and in Hellenistic times, natural philosophy
Natural philosophy or philosophy of nature (from Latin ''philosophia naturalis'') is the philosophical study of physics, that is, nature and the physical universe. It was dominant before the development of modern science.
From the ancient wor ...
developed along many lines of inquiry. Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical Greece, Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatet ...
(, ''Aristotélēs'') (384–322 BCE), a student of Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institutio ...
,
wrote on many subjects, including a substantial treatise on "Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which rel ...
" – in the 4th century BC. Aristotelian physics
Aristotelian physics is the form of natural science described in the works of the Greek philosopher Aristotle (384–322 BC). In his work ''Physics'', Aristotle intended to establish general principles of change that govern all natural bodies, ...
was influential for about two millennia. His approach mixed some limited observation with logical deductive arguments, but did not rely on experimental verification of deduced statements. Aristotle's foundational work in Physics, though very imperfect, formed a framework against which later thinkers further developed the field. His approach is entirely superseded today.
He explained ideas such as motion
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position with respect to time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed and frame of reference to an observer and mea ...
(and gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the str ...
) with the theory of four elements
Classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Tibet, and India had simil ...
.
Aristotle believed that each of the four classical elements (air, fire, water, earth) had its own natural place. Because of their differing densities, each element will revert to its own specific place in the atmosphere. So, because of their weights, fire would be at the top, air underneath fire, then water, then lastly earth. He also stated that when a small amount of one element enters the natural place of another, the less abundant element will automatically go towards its own natural place. For example, if there is a fire on the ground, the flames go up into the air in an attempt to go back into its natural place where it belongs. His laws of motion included: that heavier objects will fall faster, the speed being proportional to the weight and the speed of the object that is falling depends inversely on the density object it is falling through (e.g. density of air). He also stated that, when it comes to violent motion (motion of an object when a force is applied to it by a second object) that the speed that object moves, will only be as fast or strong as the measure of force applied to it. The problem of motion and its causes was studied carefully, leading to the philosophical notion of a "prime mover
Prime mover may refer to:
Philosophy
*Unmoved mover, a concept in Aristotle's writings
Engineering
* Prime mover (engine), motor, a machine that converts various other forms of energy (chemical, electrical, fluid pressure/flow, etc) into energy ...
" as the ultimate source of all motion in the world (Book 8 of his treatise ''Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which rel ...
'').
Medieval European and Islamic
 The
The Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
fell to invaders and internal decay in the fifth century, resulting in a decline in intellectual pursuits in western Europe. By contrast, the Eastern Roman Empire (usually known as the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
) resisted the attacks from invaders and continued to advance various fields of learning, including physics. In the sixth century, John Philoponus
John Philoponus (Greek: ; ; c. 490 – c. 570), also known as John the Grammarian or John of Alexandria, was a Byzantine Greek philologist, Aristotelian commentator, Christian theologian and an author of a considerable number of philosophical tr ...
challenged the dominant Aristotelian approach to science although much of his work was focused on Christian theology.
In the sixth century, Isidore of Miletus
Isidore of Miletus ( el, Ἰσίδωρος ὁ Μιλήσιος; Medieval Greek pronunciation: ; la, Isidorus Miletus) was one of the two main Byzantine Greek architects ( Anthemius of Tralles was the other) that Emperor Justinian I commissioned ...
created an important compilation of Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scienti ...
' works that are copied in the Archimedes Palimpsest
The Archimedes Palimpsest is a parchment codex palimpsest, originally a Byzantine Greek copy of a compilation of Archimedes and other authors. It contains two works of Archimedes that were thought to have been lost (the '' Ostomachion'' and the ...
.
Islamic scholarship inherited Aristotelian physics
Aristotelian physics is the form of natural science described in the works of the Greek philosopher Aristotle (384–322 BC). In his work ''Physics'', Aristotle intended to establish general principles of change that govern all natural bodies, ...
from the Greeks and during the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign ...
developed it further, especially placing emphasis on observation and ''a priori
("from the earlier") and ("from the later") are Latin phrases used in philosophy to distinguish types of knowledge, justification, or argument by their reliance on empirical evidence or experience. knowledge is independent from current ex ...
'' reasoning, developing early forms of the scientific method
The scientific method is an Empirical evidence, empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article hist ...
.
The most notable innovations under Islamic scholarship were in the field of optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultra ...
and vision, which came from the works of many scientists like Ibn Sahl, Al-Kindi
Abū Yūsuf Yaʻqūb ibn ʼIsḥāq aṣ-Ṣabbāḥ al-Kindī (; ar, أبو يوسف يعقوب بن إسحاق الصبّاح الكندي; la, Alkindus; c. 801–873 AD) was an Arab Muslim philosopher, polymath, mathematician, physician ...
, Ibn al-Haytham
Ḥasan Ibn al-Haytham, Latinized as Alhazen (; full name ; ), was a medieval mathematician, astronomer, and physicist of the Islamic Golden Age from present-day Iraq.For the description of his main fields, see e.g. ("He is one of the prin ...
, Al-Farisi Al-Farisi (lit. "the Persian") is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Salman al-Farisi (died 653 AD), a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and the first Persian who converted to Islam.
* Kamāl al-Dīn al-Fārisī (died ...
and Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islam ...
. The most notable work was '' The Book of Optics'' (also known as Kitāb al-Manāẓir), written by Ibn al-Haytham, in which he presented the alternative to the ancient Greek idea about vision. His discussed his experiments with camera obscura
A camera obscura (; ) is a darkened room with a small hole or lens at one side through which an image is projected onto a wall or table opposite the hole.
''Camera obscura'' can also refer to analogous constructions such as a box or tent in ...
, showing that light moved in a straight line; he encouraged readers to reproduce his experiments making him one of the originators of the scientific method
The scientific method is an Empirical evidence, empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article hist ...
Scientific Revolution
Physics became a separate science when early modern Europeans used experimental and quantitative methods to discover what are now considered to be thelaws of physics
Scientific laws or laws of science are statements, based on repeated experiments or observations, that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena. The term ''law'' has diverse usage in many cases (approximate, accurate, broad, or narrow) a ...
.
Major developments in this period include the replacement of the geocentric model of the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
with the heliocentric Copernican model
Copernican heliocentrism is the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. This model positioned the Sun at the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets orbiting around it in circular ...
, the laws governing the motion of planetary bodies (determined by Johannes Kepler between 1609 and 1619), Galileo's pioneering work on telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to obse ...
s and observational astronomy
Observational astronomy is a division of astronomy that is concerned with recording data about the observable universe, in contrast with theoretical astronomy, which is mainly concerned with calculating the measurable implications of physical ...
in the 16th and 17th centuries, and Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a " natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the g ...
's discovery and unification of the laws of motion and universal gravitation
Newton's law of universal gravitation is usually stated as that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distanc ...
(that would come to bear his name). Newton, and separately Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm (von) Leibniz . ( – 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat. He is one of the most prominent figures in both the history of philosophy and the history of mat ...
, developed calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizati ...
, See also Leibniz–Newton calculus controversy
In the history of calculus, the calculus controversy (german: Prioritätsstreit, lit=priority dispute) was an argument between the mathematicians Isaac Newton and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz over who had first invented calculus. The question was ...
. the mathematical study of continuous change, and Newton applied it to solve physical problems.
Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He w ...
(1564–1642) related mathematics, theoretical physics, and experimental physics.
JKepler.jpg, Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) explained planetary motions, formulating the first "natural laws" in the modern sense
GodfreyKneller-IsaacNewton-1689.jpg, Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a " natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the g ...
discovered the laws of motion and universal gravitation
Newton's law of universal gravitation is usually stated as that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distanc ...
19th century
The discovery of laws inthermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws o ...
, chemistry, and electromagnetics
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions ...
resulted from research efforts during the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
as energy needs increased. By the end of the 19th century, theories of thermodynamics, mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to objects ...
, and electromagnetics matched a wide variety of observations. Taken together these theories became the basis for what would later be called classical physics.
A few experimental results remained inexplicable. Classical electromagnetism presumed a medium, an luminiferous aether
Luminiferous aether or ether ("luminiferous", meaning "light-bearing") was the postulated medium for the propagation of light. It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently wave-based light to propagate through empty space (a vacuum), s ...
to support the propagation of waves, but this medium could not be detected. The intensity of light from hot glowing blackbody
A black body or blackbody is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence. The name "black body" is given because it absorbs all colors of light. A black body a ...
objects did not match the predictions of thermodynamics and electromagnetism. The character of electron emission
In physics, electron emission is the ejection of an electron from the surface of matter, or, in beta decay (β− decay), where a beta particle (a fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus transforming the original nucl ...
of illuminated metals differed from predictions. These failures, seemingly insignificant in the big picture would upset the physics world in first two decades of the 20th century.
20th century

 Modern physics began in the early 20th century with the work of
Modern physics began in the early 20th century with the work of Max Planck
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck (, ; 23 April 1858 – 4 October 1947) was a German theoretical physicist whose discovery of energy quanta won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918.
Planck made many substantial contributions to theoretical ...
in quantum theory and Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theor ...
's theory of relativity. Both of these theories came about due to inaccuracies in classical mechanics in certain situations. Classical mechanics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classical ...
predicted that the speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant that is important in many areas of physics. The speed of light is exactly equal to ). According to the special theory of relativity, is the upper limit fo ...
depends on the motion of the observer, which could not be resolved with the constant speed predicted by Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits.
Th ...
of electromagnetism. This discrepancy was corrected by Einstein's theory of special relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates:
# The law ...
, which replaced classical mechanics for fast-moving bodies and allowed for a constant speed of light. Black-body radiation
Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within, or surrounding, a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body (an idealized opaque, non-reflective body). It has a specific, continuous sp ...
provided another problem for classical physics, which was corrected when Planck proposed that the excitation of material oscillators is possible only in discrete steps proportional to their frequency. This, along with the photoelectric effect
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, and solid stat ...
and a complete theory predicting discrete energy levels
A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The t ...
of electron orbitals An electron orbital may refer to:
* An atomic orbital, describing the behaviour of an electron in an atom
* A molecular orbital, describing the behaviour of an electron in a molecule
See also
* Electron configuration, the arrangement of electr ...
, led to the theory of quantum mechanics improving on classical physics at very small scales.
Quantum mechanics would come to be pioneered by Werner Heisenberg
Werner Karl Heisenberg () (5 December 1901 – 1 February 1976) was a German theoretical physicist and one of the main pioneers of the theory of quantum mechanics. He published his work in 1925 in a breakthrough paper. In the subsequent series ...
, Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Rudolf Josef Alexander Schrödinger (, ; ; 12 August 1887 – 4 January 1961), sometimes written as or , was a Nobel Prize-winning Austrian physicist with Irish citizenship who developed a number of fundamental results in quantum theo ...
and Paul Dirac
Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac (; 8 August 1902 – 20 October 1984) was an English theoretical physicist who is regarded as one of the most significant physicists of the 20th century. He was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the Unive ...
. From this early work, and work in related fields, the Standard Model of particle physics
The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces (electromagnetic, weak and strong interactions - excluding gravity) in the universe and classifying all known elementary particles. It wa ...
was derived. Following the discovery of a particle with properties consistent with the Higgs boson
The Higgs boson, sometimes called the Higgs particle, is an elementary particle in the Standard Model of particle physics produced by the quantum excitation of the Higgs field,
one of the fields in particle physics theory. In the St ...
at CERN in 2012, all fundamental particles
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a subatomic particle that is not composed of other particles. Particles currently thought to be elementary include electrons, the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, anti ...
predicted by the standard model, and no others, appear to exist; however, physics beyond the Standard Model, with theories such as supersymmetry
In a supersymmetric theory the equations for force and the equations for matter are identical. In theoretical and mathematical physics, any theory with this property has the principle of supersymmetry (SUSY). Dozens of supersymmetric theories e ...
, is an active area of research. Areas of mathematics in general are important to this field, such as the study of probabilities
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an event is to occur, or how likely it is that a proposition is true. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1, where, roughly speakin ...
and groups
A group is a number of persons or things that are located, gathered, or classed together.
Groups of people
* Cultural group, a group whose members share the same cultural identity
* Ethnic group, a group whose members share the same ethnic ide ...
.
Core theories
Physics deals with a wide variety of systems, although certain theories are used by all physicists. Each of these theories was experimentally tested numerous times and found to be an adequate approximation of nature. These central theories are important tools for research into more specialized topics, and any physicist, regardless of their specialization, is expected to be literate in them. These include classical mechanics, quantum mechanics, thermodynamics and statistical mechanics,electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
, and special relativity.
Distinction between classical and modern physics
Classical theory
Classical physics includes the traditional branches and topics that were recognized and well-developed before the beginning of the 20th century—classical mechanics, thermodynamics, and electromagnetism. Classical mechanics is concerned with bodies acted on byforce
A force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. The concept of force makes the everyday notion of pushing or pulling mathematically precise. Because the Magnitude ...
s and bodies in motion
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position with respect to time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed and frame of reference to an observer and mea ...
and may be divided into statics
Statics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the analysis of force and torque (also called moment) acting on physical systems that do not experience an acceleration (''a''=0), but rather, are in static equilibrium with t ...
(study of the forces on a body or bodies not subject to an acceleration), kinematics (study of motion without regard to its causes), and dynamics (study of motion and the forces that affect it); mechanics may also be divided into solid mechanics
Solid mechanics, also known as mechanics of solids, is the branch of continuum mechanics that studies the behavior of solid materials, especially their motion and deformation under the action of forces, temperature changes, phase changes, and ...
and fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids (liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them.
It has applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, aerospace, civil, chemical and ...
(known together as continuum mechanics
Continuum mechanics is a branch of mechanics that deals with the mechanical behavior of materials modeled as a continuous mass rather than as discrete particles. The French mathematician Augustin-Louis Cauchy was the first to formulate such ...
), the latter include such branches as hydrostatics
Fluid statics or hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies the condition of the equilibrium of a floating body and submerged body "fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and the pressure in a fluid, or exerted by a fluid, on an imme ...
, hydrodynamics and pneumatics
Pneumatics (from Greek ‘wind, breath’) is a branch of engineering that makes use of gas or pressurized air.
Pneumatic systems used in industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A centrally located and ...
. Acoustics is the study of how sound is produced, controlled, transmitted and received. Important modern branches of acoustics include ultrasonics
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies f ...
, the study of sound waves of very high frequency beyond the range of human hearing; bioacoustics
Bioacoustics is a cross-disciplinary science that combines biology and acoustics. Usually it refers to the investigation of sound production, dispersion and reception in animals (including humans). This involves neurophysiological and anatomic ...
, the physics of animal calls and hearing, and electroacoustics
Acoustical engineering (also known as acoustic engineering) is the branch of engineering dealing with sound and vibration. It includes the application of acoustics, the science of sound and vibration, in technology. Acoustical engineers are typica ...
, the manipulation of audible sound waves using electronics.
Optics, the study of light, is concerned not only with visible light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 tera ...
but also with infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from aroun ...
and ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ...
, which exhibit all of the phenomena of visible light except visibility, e.g., reflection, refraction, interference, diffraction, dispersion, and polarization of light. Heat is a form of energy, the internal energy possessed by the particles of which a substance is composed; thermodynamics deals with the relationships between heat and other forms of energy. Electricity and magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particle ...
have been studied as a single branch of physics since the intimate connection between them was discovered in the early 19th century; an electric current
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume. The movin ...
gives rise to a magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and t ...
, and a changing magnetic field induces an electric current. Electrostatics
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies electric charges at rest (static electricity).
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word for am ...
deals with electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons respecti ...
s at rest, electrodynamics
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
with moving charges, and magnetostatics
Magnetostatics is the study of magnetic fields in systems where the currents are steady (not changing with time). It is the magnetic analogue of electrostatics, where the charges are stationary. The magnetization need not be static; the equatio ...
with magnetic poles at rest.
Modern theory
The discovery of relativity and of quantum mechanics in the first decades of the 20th century transformed the conceptual basis of physics without reducing the practical value of most of the physical theories developed up to that time. Consequently the topics of physics have come to be divided into "classical physics" and "modern physics", with the latter category including effects related to quantum mechanics and relativity. Classical physics is generally concerned with matter and energy on the normal scale of observation, while much of modern physics is concerned with the behavior of matter and energy under extreme conditions or on a very large or very small scale. For example, atomic andnuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the ...
study matter on the smallest scale at which chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
s can be identified. The physics of elementary particles is on an even smaller scale since it is concerned with the most basic units of matter; this branch of physics is also known as high-energy physics because of the extremely high energies necessary to produce many types of particles in particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams.
Large accelerators are used for fun ...
s. On this scale, ordinary, commonsensical notions of space, time, matter, and energy are no longer valid.
The two chief theories of modern physics present a different picture of the concepts of space, time, and matter from that presented by classical physics. Classical mechanics approximates nature as continuous, while quantum theory is concerned with the discrete nature of many phenomena at the atomic and subatomic level and with the complementary aspects of particles and waves in the description of such phenomena. The theory of relativity is concerned with the description of phenomena that take place in a frame of reference
In physics and astronomy, a frame of reference (or reference frame) is an abstract coordinate system whose origin, orientation, and scale are specified by a set of reference points― geometric points whose position is identified both mathem ...
that is in motion with respect to an observer; the special theory of relativity is concerned with motion in the absence of gravitational fields and the general theory of relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. ...
with motion and its connection with gravitation. Both quantum theory and the theory of relativity find applications in many areas of modern physics.
Fundamental concepts in modern physics include:
* Action
Action may refer to:
* Action (narrative), a literary mode
* Action fiction, a type of genre fiction
* Action game, a genre of video game
Film
* Action film, a genre of film
* ''Action'' (1921 film), a film by John Ford
* ''Action'' (1980 fil ...
* Causality
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the ca ...
* Covariance
In probability theory and statistics, covariance is a measure of the joint variability of two random variables. If the greater values of one variable mainly correspond with the greater values of the other variable, and the same holds for the le ...
* Particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, fro ...
* Physical field
In physics, a field is a physical quantity, represented by a scalar, vector, or tensor, that has a value for each point in space and time. For example, on a weather map, the surface temperature is described by assigning a number to each po ...
* Physical interaction
In physics, the fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are the interactions that do not appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four fundamental interactions known to exist: the gravitational and electro ...
* Quantum
* Statistical ensemble
In physics, specifically statistical mechanics, an ensemble (also statistical ensemble) is an idealization consisting of a large number of virtual copies (sometimes infinitely many) of a system, considered all at once, each of which represents ...
* Symmetry
* Wave
In physics, mathematics, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities. Waves can be periodic, in which case those quantities oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (r ...
Research
Scientific method
Physicists use the scientific method to test the validity of aphysical theory
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experime ...
. By using a methodical approach to compare the implications of a theory with the conclusions drawn from its related experiments and observations, physicists are better able to test the validity of a theory in a logical, unbiased, and repeatable way. To that end, experiments are performed and observations are made in order to determine the validity or invalidity of a theory.
A scientific law is a concise verbal or mathematical statement of a relation that expresses a fundamental principle of some theory, such as Newton's law of universal gravitation.
Theory and experiment

 Theorists seek to develop
Theorists seek to develop mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used in the natural sciences (such as physics, ...
s that both agree with existing experiments and successfully predict future experimental results, while experimentalists devise and perform experiments to test theoretical predictions and explore new phenomena. Although theory
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may ...
and experiment are developed separately, they strongly affect and depend upon each other. Progress in physics frequently comes about when experimental results defy explanation by existing theories, prompting intense focus on applicable modelling, and when new theories generate experimentally testable prediction
A prediction (Latin ''præ-'', "before," and ''dicere'', "to say"), or forecast, is a statement about a future event or data. They are often, but not always, based upon experience or knowledge. There is no universal agreement about the exac ...
s, which inspire the development of new experiments (and often related equipment).
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe.
Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate ca ...
s who work at the interplay of theory and experiment are called phenomenologists
Phenomenology may refer to:
Art
* Phenomenology (architecture), based on the experience of building materials and their sensory properties
Philosophy
* Phenomenology (philosophy), a branch of philosophy which studies subjective experiences and a ...
, who study complex phenomena observed in experiment and work to relate them to a fundamental theory
Fundamental may refer to:
* Foundation of reality
* Fundamental frequency, as in music or phonetics, often referred to as simply a "fundamental"
* Fundamentalism, the belief in, and usually the strict adherence to, the simple or "fundamental" i ...
.
Theoretical physics has historically taken inspiration from philosophy; electromagnetism was unified this way. Beyond the known universe, the field of theoretical physics also deals with hypothetical issues, such as parallel universes, a multiverse
The multiverse is a hypothetical group of multiple universes. Together, these universes comprise everything that exists: the entirety of space, time, matter, energy, information, and the physical laws and constants that describe them. The di ...
, and higher dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coordi ...
s. Theorists invoke these ideas in hopes of solving particular problems with existing theories; they then explore the consequences of these ideas and work toward making testable predictions.
Experimental physics expands, and is expanded by, engineering and technology. Experimental physicists who are involved in basic research
Basic research, also called pure research or fundamental research, is a type of scientific research with the aim of improving scientific theory, theories for better understanding and prediction of natural or other phenomena. In contrast, applied ...
design and perform experiments with equipment such as particle accelerators and laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The firs ...
s, whereas those involved in applied research
Applied science is the use of the scientific method and knowledge obtained via conclusions from the method to attain practical goals. It includes a broad range of disciplines such as engineering and medicine. Applied science is often contrasted ...
often work in industry, developing technologies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
s. Feynman
Richard Phillips Feynman (; May 11, 1918 – February 15, 1988) was an American theoretical physicist, known for his work in the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, the theory of quantum electrodynamics, the physics of the superflu ...
has noted that experimentalists may seek areas that have not been explored well by theorists. "In fact experimenters have a certain individual character. They ... very often do their experiments in a region in which people know the theorist has not made any guesses."
Scope and aims
phenomena
A phenomenon ( : phenomena) is an observable event. The term came into its modern philosophical usage through Immanuel Kant, who contrasted it with the noumenon, which ''cannot'' be directly observed. Kant was heavily influenced by Gottfried ...
, from elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a subatomic particle that is not composed of other particles. Particles currently thought to be elementary include electrons, the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiq ...
s (such as quark
A quark () is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All common ...
s, neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass ...
s, and electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary partic ...
s) to the largest supercluster
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn ...
s of galaxies. Included in these phenomena are the most basic objects composing all other things. Therefore, physics is sometimes called the "fundamental science". Physics aims to describe the various phenomena that occur in nature in terms of simpler phenomena. Thus, physics aims to both connect the things observable to humans to root causes, and then connect these causes together.
For example, the ancient Chinese observed that certain rocks (lodestone
Lodestones are naturally magnetized pieces of the mineral magnetite. They are naturally occurring magnets, which can attract iron. The property of magnetism was first discovered in antiquity through lodestones. Pieces of lodestone, suspen ...
and magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With ...
) were attracted to one another by an invisible force. This effect was later called magnetism, which was first rigorously studied in the 17th century. But even before the Chinese discovered magnetism, the ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
knew of other objects such as amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In M ...
, that when rubbed with fur would cause a similar invisible attraction between the two. This was also first studied rigorously in the 17th century and came to be called electricity. Thus, physics had come to understand two observations of nature in terms of some root cause (electricity and magnetism). However, further work in the 19th century revealed that these two forces were just two different aspects of one force—electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
. This process of "unifying" forces continues today, and electromagnetism and the weak nuclear force
In nuclear physics and particle physics, the weak interaction, which is also often called the weak force or weak nuclear force, is one of the four known fundamental interactions, with the others being electromagnetism, the strong interaction ...
are now considered to be two aspects of the electroweak interaction
In particle physics, the electroweak interaction or electroweak force is the unified description of two of the four known fundamental interactions of nature: electromagnetism and the weak interaction. Although these two forces appear very diff ...
. Physics hopes to find an ultimate reason (theory of everything) for why nature is as it is (see section ''Current research
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (s ...
'' below for more information).
Current research
 Research in physics is continually progressing on a large number of fronts.
In condensed matter physics, an important unsolved theoretical problem is that of
Research in physics is continually progressing on a large number of fronts.
In condensed matter physics, an important unsolved theoretical problem is that of high-temperature superconductivity
High-temperature superconductors (abbreviated high-c or HTS) are defined as materials that behave as superconductors at temperatures above , the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. The adjective "high temperature" is only in respect to previo ...
. Many condensed matter experiments are aiming to fabricate workable spintronics
Spintronics (a portmanteau meaning spin transport electronics), also known as spin electronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-sta ...
and quantum computer
Quantum computing is a type of computation whose operations can harness the phenomena of quantum mechanics, such as superposition, interference, and entanglement. Devices that perform quantum computations are known as quantum computers. Thoug ...
s.
In particle physics, the first pieces of experimental evidence for physics beyond the Standard Model have begun to appear. Foremost among these are indications that neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass ...
s have non-zero mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different element ...
. These experimental results appear to have solved the long-standing solar neutrino problem
The solar neutrino problem concerned a large discrepancy between the flux of solar neutrinos as predicted from the Sun's luminosity and as measured directly. The discrepancy was first observed in the mid-1960s and was resolved around 2002.
The flu ...
, and the physics of massive neutrinos remains an area of active theoretical and experimental research. The Large Hadron Collider has already found the Higgs boson, but future research aims to prove or disprove the supersymmetry
In a supersymmetric theory the equations for force and the equations for matter are identical. In theoretical and mathematical physics, any theory with this property has the principle of supersymmetry (SUSY). Dozens of supersymmetric theories e ...
, which extends the Standard Model of particle physics. Research on the nature of the major mysteries of dark matter and dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the unive ...
is also currently ongoing.
Although much progress has been made in high-energy, quantum, and astronomical physics, many everyday phenomena involving complexity
Complexity characterises the behaviour of a system or model whose components interact in multiple ways and follow local rules, leading to nonlinearity, randomness, collective dynamics, hierarchy, and emergence.
The term is generally used to c ...
, chaos, or turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between ...
are still poorly understood. Complex problems that seem like they could be solved by a clever application of dynamics and mechanics remain unsolved; examples include the formation of sandpiles, nodes in trickling water, the shape of water droplets, mechanisms of surface tension catastrophes, and self-sorting in shaken heterogeneous collections.
These complex phenomena have received growing attention since the 1970s for several reasons, including the availability of modern mathematical methods and computers, which enabled complex systems to be modeled in new ways. Complex physics has become part of increasingly interdisciplinary research, as exemplified by the study of turbulence in aerodynamics and the observation of pattern formation
The science of pattern formation deals with the visible, (statistically) orderly outcomes of self-organization and the common principles behind similar patterns in nature.
In developmental biology, pattern formation refers to the generation of ...
in biological systems. In the 1932 ''Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics'', Horace Lamb
Sir Horace Lamb (27 November 1849 – 4 December 1934)R. B. Potts,, '' Australian Dictionary of Biography'', Volume 5, MUP, 1974, pp 54–55. Retrieved 5 Sep 2009 was a British applied mathematician and author of several influential texts o ...
said:
Branches and fields
Fields
The major fields of physics, along with their subfields and the theories and concepts they employ, are shown in the following table. Since the 20th century, the individual fields of physics have become increasingly specialised, and today most physicists work in a single field for their entire careers. "Universalists" such as Einstein (1879–1955) andLev Landau
Lev Davidovich Landau (russian: Лев Дави́дович Ланда́у; 22 January 1908 – 1 April 1968) was a Soviet-Azerbaijani physicist of Jewish descent who made fundamental contributions to many areas of theoretical physics.
His a ...
(1908–1968), who worked in multiple fields of physics, are now very rare.
Contemporary research in physics can be broadly divided into nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
* Nuclear ...
and particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and ...
; condensed matter physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms. More generally, the s ...
; atomic, molecular, and optical physics
Atomic, molecular, and optical physics (AMO) is the study of matter-matter and light-matter interactions; at the scale of one or a few atoms and energy scales around several electron volts. The three areas are closely interrelated. AMO theory in ...
; astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline said, Astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the he ...
; and applied physics. Some physics departments also support physics education research
Physics education research (PER) is a form of discipline-based education research specifically related to the study of the teaching and learning of physics, often with the aim of improving the effectiveness of student learning. Approximatel ...
and physics outreach.
Nuclear and particle
 Particle physics is the study of the elementary constituents of
Particle physics is the study of the elementary constituents of matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic par ...
and energy and the interactions
Interaction is action that occurs between two or more objects, with broad use in philosophy and the sciences. It may refer to:
Science
* Interaction hypothesis, a theory of second language acquisition
* Interaction (statistics)
* Interactions o ...
between them. In addition, particle physicists design and develop the high-energy accelerators, detectors, and computer programs
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer progra ...
necessary for this research. The field is also called "high-energy physics" because many elementary particles do not occur naturally but are created only during high-energy collision
In physics, a collision is any event in which two or more bodies exert forces on each other in a relatively short time. Although the most common use of the word ''collision'' refers to incidents in which two or more objects collide with great fo ...
s of other particles.
Currently, the interactions of elementary particles and fields
Fields may refer to:
Music
*Fields (band), an indie rock band formed in 2006
*Fields (progressive rock band), a progressive rock band formed in 1971
* ''Fields'' (album), an LP by Swedish-based indie rock band Junip (2010)
* "Fields", a song by ...
are described by the Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is the theory describing three of the four known fundamental forces ( electromagnetic, weak and strong interactions - excluding gravity) in the universe and classifying all known elementary particles. I ...
. The model accounts for the 12 known particles of matter (quark
A quark () is a type of elementary particle and a fundamental constituent of matter. Quarks combine to form composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are protons and neutrons, the components of atomic nuclei. All common ...
s and lepton
In particle physics, a lepton is an elementary particle of half-integer spin (spin (physics), spin ) that does not undergo strong interactions. Two main classes of leptons exist: electric charge, charged leptons (also known as the electron-li ...
s) that interact via the strong
Strong may refer to:
Education
* The Strong, an educational institution in Rochester, New York, United States
* Strong Hall (Lawrence, Kansas), an administrative hall of the University of Kansas
* Strong School, New Haven, Connecticut, United St ...
, weak, and electromagnetic fundamental force
In physics, the fundamental interactions, also known as fundamental forces, are the interactions that do not appear to be reducible to more basic interactions. There are four fundamental interactions known to exist: the gravitational and electro ...
s. Dynamics are described in terms of matter particles exchanging gauge boson
In particle physics, a gauge boson is a bosonic elementary particle that acts as the force carrier for elementary fermions. Elementary particles, whose interactions are described by a gauge theory, interact with each other by the exchange of gau ...
s (gluon
A gluon ( ) is an elementary particle that acts as the exchange particle (or gauge boson) for the strong force between quarks. It is analogous to the exchange of photons in the electromagnetic force between two charged particles. Gluons bi ...
s, W and Z bosons
In particle physics, the W and Z bosons are vector bosons that are together known as the weak bosons or more generally as the intermediate vector bosons. These elementary particles mediate the weak interaction; the respective symbols are , , and ...
, and photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are Massless particle, massless ...
s, respectively). The Standard Model also predicts a particle known as the Higgs boson. In July 2012 CERN, the European laboratory for particle physics, announced the detection of a particle consistent with the Higgs boson, an integral part of the Higgs mechanism
In the Standard Model of particle physics, the Higgs mechanism is essential to explain the generation mechanism of the property "mass" for gauge bosons. Without the Higgs mechanism, all bosons (one of the two classes of particles, the other bei ...
.
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies the constituents and interactions of atomic nuclei
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in ...
. The most commonly known applications of nuclear physics are nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
generation and nuclear weapons
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
technology, but the research has provided application in many fields, including those in nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is "radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emit ...
and magnetic resonance imaging, ion implantation
Ion implantation is a low-temperature process by which ions of one element are accelerated into a solid target, thereby changing the physical, chemical, or electrical properties of the target. Ion implantation is used in semiconductor device fa ...
in materials engineering, and radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was de ...
in geology and archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts ...
.
Atomic, molecular, and optical
Atomic,molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioch ...
, and optical physics (AMO) is the study of matter—matter and light—matter interactions on the scale of single atoms and molecules. The three areas are grouped together because of their interrelationships, the similarity of methods used, and the commonality of their relevant energy scales. All three areas include both classical, semi-classical and quantum treatments; they can treat their subject from a microscopic view (in contrast to a macroscopic view).
Atomic physics studies the electron shell
In chemistry and atomic physics, an electron shell may be thought of as an orbit followed by electrons around an atom's Atomic nucleus, nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" (also called the "K shell"), followed by t ...
s of atoms. Current research focuses on activities in quantum control, cooling and trapping of atoms and ions, low-temperature collision dynamics and the effects of electron correlation on structure and dynamics. Atomic physics is influenced by the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
(see hyperfine splitting
In atomic physics, hyperfine structure is defined by small shifts in otherwise degenerate energy levels and the resulting splittings in those energy levels of atoms, molecules, and ions, due to electromagnetic multipole interaction between the nu ...
), but intra-nuclear phenomena such as fission
Fission, a splitting of something into two or more parts, may refer to:
* Fission (biology), the division of a single entity into two or more parts and the regeneration of those parts into separate entities resembling the original
* Nuclear fissio ...
and fusion
Fusion, or synthesis, is the process of combining two or more distinct entities into a new whole.
Fusion may also refer to:
Science and technology Physics
*Nuclear fusion, multiple atomic nuclei combining to form one or more different atomic nucl ...
are considered part of nuclear physics.
Molecular physics
Molecular physics is the study of the physical properties of molecules and molecular dynamics. The field overlaps significantly with physical chemistry, chemical physics, and quantum chemistry. It is often considered as a sub-field of atomic, mo ...
focuses on multi-atomic structures and their internal and external interactions with matter and light. Optical physics
Atomic, molecular, and optical physics (AMO) is the study of matter-matter and light-matter interactions; at the scale of one or a few atoms and energy scales around several electron volts. The three areas are closely interrelated. AMO theor ...
is distinct from optics in that it tends to focus not on the control of classical light fields by macroscopic objects but on the fundamental properties of optical field
An electromagnetic field (also EM field or EMF) is a classical (i.e. non-quantum) field produced by (stationary or moving) electric charges. It is the field described by classical electrodynamics (a classical field theory) and is the classical ...
s and their interactions with matter in the microscopic realm.
Condensed matter
 Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic physical properties of matter. In particular, it is concerned with the "condensed" phases that appear whenever the number of particles in a system is extremely large and the interactions between them are strong.
The most familiar examples of condensed phases are
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic physical properties of matter. In particular, it is concerned with the "condensed" phases that appear whenever the number of particles in a system is extremely large and the interactions between them are strong.
The most familiar examples of condensed phases are solids
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structura ...
and liquids, which arise from the bonding by way of the electromagnetic force
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
between atoms. More exotic condensed phases include the superfluid
Superfluidity is the characteristic property of a fluid with zero viscosity which therefore flows without any loss of kinetic energy. When stirred, a superfluid forms vortices that continue to rotate indefinitely. Superfluidity occurs in two ...
and the Bose–Einstein condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero (−273.15 °C or −459.67&n ...
found in certain atomic systems at very low temperature, the superconducting
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike ...
phase exhibited by conduction electron
In solid-state physics, the valence band and conduction band are the bands closest to the Fermi level, and thus determine the electrical conductivity of the solid. In nonmetals, the valence band is the highest range of electron energies ...
s in certain materials, and the ferromagnet
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) which results in a large observed magnetic permeability, and in many cases a large magnetic coercivity allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagnetic material ...
ic and antiferromagnet
In materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules, usually related to the spins of electrons, align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins (on different sublattices) pointing in opposite directions. ...
ic phases of spins
The spins (as in having "the spins")Diane Marie Leiva. ''The Florida State University College of Education''Women's Voices on College Drinking: The First-Year College Experience"/ref> is an adverse reaction of intoxication that causes a state of ...
on atomic lattices.
Condensed matter physics is the largest field of contemporary physics. Historically, condensed matter physics grew out of solid-state physics, which is now considered one of its main subfields. The term ''condensed matter physics'' was apparently coined by Philip Anderson when he renamed his research group—previously ''solid-state theory''—in 1967. In 1978, the Division of Solid State Physics of the American Physical Society was renamed as the Division of Condensed Matter Physics. Condensed matter physics has a large overlap with chemistry, materials science, nanotechnology
Nanotechnology, also shortened to nanotech, is the use of matter on an atomic, molecular, and supramolecular scale for industrial purposes. The earliest, widespread description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal o ...
and engineering.
Astrophysics
 Astrophysics and astronomy are the application of the theories and methods of physics to the study of
Astrophysics and astronomy are the application of the theories and methods of physics to the study of stellar structure
Stellar structure models describe the internal structure of a star in detail and make predictions about the luminosity, the color and the future evolution of the star. Different classes and ages of stars have different internal structures, reflec ...
, stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is con ...
, the origin of the Solar System, and related problems of cosmology. Because astrophysics is a broad subject, astrophysicists typically apply many disciplines of physics, including mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, relativity, nuclear and particle physics, and atomic and molecular physics.
The discovery by Karl Jansky
Karl Guthe Jansky (October 22, 1905 – February 14, 1950) was an American physicist and radio engineer who in April 1933 first announced his discovery of radio waves emanating from the Milky Way in the constellation Sagittarius. He is considere ...
in 1931 that radio signals were emitted by celestial bodies initiated the science of radio astronomy
Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation comi ...
. Most recently, the frontiers of astronomy have been expanded by space exploration. Perturbations and interference from the Earth's atmosphere make space-based observations necessary for infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from aroun ...
, ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiati ...
, gamma-ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically sh ...
, and X-ray astronomy.
Physical cosmology is the study of the formation and evolution of the universe on its largest scales. Albert Einstein's theory of relativity plays a central role in all modern cosmological theories. In the early 20th century, Hubble
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versa ...
's discovery that the universe is expanding, as shown by the Hubble diagram
Hubble's law, also known as the Hubble–Lemaître law, is the observation in physical cosmology that galaxies are moving away from Earth at speeds proportional to their distance. In other words, the farther they are, the faster they are moving a ...
, prompted rival explanations known as the steady state
In systems theory, a system or a process is in a steady state if the variables (called state variables) which define the behavior of the system or the process are unchanging in time. In continuous time, this means that for those properties ' ...
universe and the Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from t ...
.
The Big Bang was confirmed by the success of Big Bang nucleosynthesis
In physical cosmology, Big Bang nucleosynthesis (abbreviated BBN, also known as primordial nucleosynthesis) is the production of nuclei other than those of the lightest isotope of hydrogen ( hydrogen-1, 1H, having a single proton as a nucleus) ...
and the discovery of the cosmic microwave background
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all spac ...
in 1964. The Big Bang model rests on two theoretical pillars: Albert Einstein's general relativity and the cosmological principle
In modern physical cosmology, the cosmological principle is the notion that the spatial distribution of matter in the universe is homogeneous and isotropic when viewed on a large enough scale, since the forces are expected to act uniformly thro ...
. Cosmologists have recently established the ΛCDM model
The ΛCDM (Lambda cold dark matter) or Lambda-CDM model is a parameterization of the Big Bang cosmological model in which the universe contains three major components: first, a cosmological constant denoted by Lambda (Greek Λ) associated with ...
of the evolution of the universe, which includes cosmic inflation
In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation, or just inflation, is a theory of exponential expansion of space in the early universe. The inflationary epoch lasted from seconds after the conjectured Big Bang singulari ...
, dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the unive ...
, and dark matter
Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter thought to account for approximately 85% of the matter in the universe. Dark matter is called "dark" because it does not appear to interact with the electromagnetic field, which means it does not ab ...
.
Other aspects
Education
Careers
Philosophy
Physics, as with the rest of science, relies on the philosophy of science and its "scientific method
The scientific method is an Empirical evidence, empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article hist ...
" to advance knowledge of the physical world. The scientific method employs ''a priori and a posteriori'' reasoning as well as the use of Bayesian inference to measure the validity of a given theory.
Study of the philosophical issues surrounding physics, the philosophy of physics, involves issues such as the nature of Spacetime, space and time, determinism, and Metaphysics, metaphysical outlooks such as empiricism, naturalism (philosophy), naturalism, and Philosophical realism, realism.
Many physicists have written about the philosophical implications of their work, for instance Pierre-Simon Laplace, Laplace, who championed causal determinism, and Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Rudolf Josef Alexander Schrödinger (, ; ; 12 August 1887 – 4 January 1961), sometimes written as or , was a Nobel Prize-winning Austrian physicist with Irish citizenship who developed a number of fundamental results in quantum theo ...
, who wrote on quantum mechanics. The mathematical physicist Roger Penrose has been called a Platonism, Platonist by Stephen Hawking,. "I think that Roger is a Platonist at heart but he must answer for himself." a view Penrose discusses in his book, ''The Road to Reality''. Hawking referred to himself as an "unashamed reductionist" and took issue with Penrose's views.

 Mathematics provides a compact and exact language used to describe the order in nature. This was noted and advocated by Pythagoras,
Mathematics provides a compact and exact language used to describe the order in nature. This was noted and advocated by Pythagoras, Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institutio ...
, "Although usually remembered today as a philosopher, Plato was also one of ancient Greece's most important patrons of mathematics. Inspired by Pythagoras, he founded his Academy in Athens in 387 BC, where he stressed mathematics as a way of understanding more about reality. In particular, he was convinced that geometry was the key to unlocking the secrets of the universe. The sign above the Academy entrance read: 'Let no-one ignorant of geometry enter here. Galileo, 'Philosophy is written in that great book which ever lies before our eyes. I mean the universe, but we cannot understand it if we do not first learn the language and grasp the symbols in which it is written. This book is written in the mathematical language, and the symbols are triangles, circles, and other geometrical figures, without whose help it is humanly impossible to comprehend a single word of it, and without which one wanders in vain through a dark labyrinth.' – Galileo (1623), ''The Assayer''" and Newton. Some theorists, like Hilary Putnam and Penelope Maddy, hold that logical truths, and therefore mathematical reasoning, depend on the empirical world. This is usually combined with the claim that the laws of logic express universal regularities found in the structural features of the world, which may explain the peculiar relation between these fields.
Physics uses mathematics to organise and formulate experimental results. From those results, analytic solution, precise or simulation#Computer simulation, estimated solutions are obtained, or quantitative results, from which new predictions can be made and experimentally confirmed or negated. The results from physics experiments are numerical data, with their units of measure and estimates of the errors in the measurements. Technologies based on mathematics, like scientific computing, computation have made computational physics an active area of research.
 Ontology is a prerequisite for physics, but not for mathematics. It means physics is ultimately concerned with descriptions of the real world, while mathematics is concerned with abstract patterns, even beyond the real world. Thus physics statements are synthetic, while mathematical statements are analytic. Mathematics contains hypotheses, while physics contains theories. Mathematics statements have to be only logically true, while predictions of physics statements must match observed and experimental data.
The distinction is clear-cut, but not always obvious. For example, mathematical physics is the application of mathematics in physics. Its methods are mathematical, but its subject is physical. The problems in this field start with a "Boundary condition, mathematical model of a physical situation" (system) and a "mathematical description of a physical law" that will be applied to that system. Every mathematical statement used for solving has a hard-to-find physical meaning. The final mathematical solution has an easier-to-find meaning, because it is what the solver is looking for.
Ontology is a prerequisite for physics, but not for mathematics. It means physics is ultimately concerned with descriptions of the real world, while mathematics is concerned with abstract patterns, even beyond the real world. Thus physics statements are synthetic, while mathematical statements are analytic. Mathematics contains hypotheses, while physics contains theories. Mathematics statements have to be only logically true, while predictions of physics statements must match observed and experimental data.
The distinction is clear-cut, but not always obvious. For example, mathematical physics is the application of mathematics in physics. Its methods are mathematical, but its subject is physical. The problems in this field start with a "Boundary condition, mathematical model of a physical situation" (system) and a "mathematical description of a physical law" that will be applied to that system. Every mathematical statement used for solving has a hard-to-find physical meaning. The final mathematical solution has an easier-to-find meaning, because it is what the solver is looking for.
Fundamental vs. applied physics
Physics is a branch of fundamental science (also called basic science). Physics is also called "''the'' fundamental science" because all branches of natural science including chemistry, astronomy, geology, and biology are constrained by laws of physics.The Feynman Lectures on Physics Vol. I Ch. 3: The Relation of Physics to Other Sciencessee also reductionism and special sciences Similarly, chemistry is often called the central science because of its role in linking the physical sciences. For example, chemistry studies properties, structures, and chemical reaction, reactions of matter (chemistry's focus on the molecular and atomic scale Difference between chemistry and physics, distinguishes it from physics). Structures are formed because particles exert electrical forces on each other, properties include physical characteristics of given substances, and reactions are bound by laws of physics, like conservation of energy, Conservation of mass, mass, and charge conservation, charge. Fundamental physics seeks to better explain and understand phenomena in all spheres, without a specific practical application as a goal, other than the deeper insight into the phenomema themselves.

 Applied physics is a general term for physics research and development that is intended for a particular use. An applied physics curriculum usually contains a few classes in an applied discipline, like geology or electrical engineering. It usually differs from engineering in that an applied physicist may not be designing something in particular, but rather is using physics or conducting physics research with the aim of developing new technologies or solving a problem.
The approach is similar to that of applied mathematics. Applied physicists use physics in scientific research. For instance, people working on accelerator physics might seek to build better particle detectors for research in theoretical physics.
Physics is used heavily in engineering. For example, statics, a subfield of
Applied physics is a general term for physics research and development that is intended for a particular use. An applied physics curriculum usually contains a few classes in an applied discipline, like geology or electrical engineering. It usually differs from engineering in that an applied physicist may not be designing something in particular, but rather is using physics or conducting physics research with the aim of developing new technologies or solving a problem.
The approach is similar to that of applied mathematics. Applied physicists use physics in scientific research. For instance, people working on accelerator physics might seek to build better particle detectors for research in theoretical physics.
Physics is used heavily in engineering. For example, statics, a subfield of mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to objects ...
, is used in the building of bridges and other static structures. The understanding and use of acoustics results in sound control and better concert halls; similarly, the use of optics creates better optical devices. An understanding of physics makes for more realistic flight simulators, video games, and movies, and is often critical in forensic investigations.
 With the Uniformitarianism (science), standard consensus that the Scientific law, laws of physics are universal and do not change with time, physics can be used to study things that would ordinarily be mired in uncertainty. For example, in the study of the origin of the Earth, a physicist can reasonably model Earth's mass, temperature, and rate of rotation, as a function of time allowing the extrapolation forward or backward in time and so predict future or prior events. It also allows for simulations in engineering that speed up the development of a new technology.
There is also considerable interdisciplinarity, so many other important fields are influenced by physics (e.g., the fields of econophysics and sociophysics).
With the Uniformitarianism (science), standard consensus that the Scientific law, laws of physics are universal and do not change with time, physics can be used to study things that would ordinarily be mired in uncertainty. For example, in the study of the origin of the Earth, a physicist can reasonably model Earth's mass, temperature, and rate of rotation, as a function of time allowing the extrapolation forward or backward in time and so predict future or prior events. It also allows for simulations in engineering that speed up the development of a new technology.
There is also considerable interdisciplinarity, so many other important fields are influenced by physics (e.g., the fields of econophysics and sociophysics).
See also
* * * * *Lists
* * *Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ** ** * * * * * * *External links
Physics at Quanta Magazine
Usenet Physics FAQ
– FAQ compiled by sci.physics and other physics newsgroups
Website of the Nobel Prize in physics
– Award for outstanding contributions to the subject
World of Physics
– Online encyclopedic dictionary of physics
''Nature Physics''
– Academic journal
Physics
– Online magazine by the American Physical Society – Directory of physics related media
The Vega Science Trust
– Science videos, including physics
– Physics and astronomy mind-map from Georgia State University
Physics at MIT OpenCourseWare
– Online course material from Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Feynman Lectures on Physics
{{Authority control Physics,