Kuril Islands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands are a volcanic
 The Kuril Islands form part of the ring of
The Kuril Islands form part of the ring of
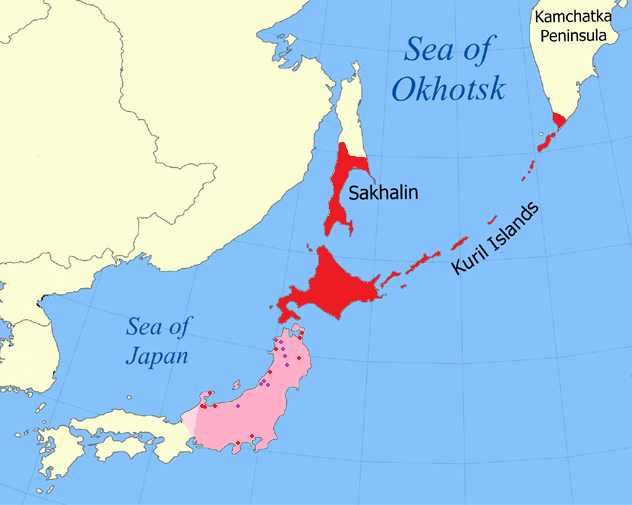 The
The
 At the very end of the 19th century, the Japanese administration started the forced assimilation of the native Ainu people. Also at this time the Ainu were granted automatic Japanese citizenship, effectively denying them the status of an indigenous group. Many Japanese moved onto former Ainu lands, including the Kuril islands. The Ainu were required to adopt Japanese names, and ordered to cease religious practices such as animal sacrifice and the custom of tattooing. Although not compulsory, education was conducted in Japanese. Prior to Japanese colonization (in 1868) about 100 Ainu reportedly lived on the Kuril islands.
At the very end of the 19th century, the Japanese administration started the forced assimilation of the native Ainu people. Also at this time the Ainu were granted automatic Japanese citizenship, effectively denying them the status of an indigenous group. Many Japanese moved onto former Ainu lands, including the Kuril islands. The Ainu were required to adopt Japanese names, and ordered to cease religious practices such as animal sacrifice and the custom of tattooing. Although not compulsory, education was conducted in Japanese. Prior to Japanese colonization (in 1868) about 100 Ainu reportedly lived on the Kuril islands.
File:Yuzhno-Kurilsk anchor.jpg, Yuzhno-Kurilsk, Kunashir
File:214 1426 Sev Kur main street wiki.jpg, Severo-Kurilsk, Paramushir
File:Atlasov.jpg, Atlasov
File:Iturup volcano Bogdan Khmelnitsky.jpg, A view of the volcano Bogdan Khmelnitsky on Iturup Island
File:Вулкан Тятя с вулкана Менделеева.jpg, Mendeleyeva in the southern part of Kunashir
File:Один из зубцов вулкана Менделеева.jpg, Yuzhno-Kurilsky District
File:Стратовулкан.jpg, Ebeko volcano, Paramushir
File:Белые скалы 5.jpg, White Rocks, Iturup
The following table lists information on the main islands from north to south:
Southern Kuriles / Northern Territories: A Stumbling-block in Russia-Japan Relationship
history and analysis by Andrew Andersen, Department of Political Science, University of Victoria, May 2001 *http://depts.washington.edu/ikip/index.shtml (Kuril Island Biocomplexity Project) * (includes space imagery)
a
Natural Heritage Protection Fund
*http://www.mofa.go.jp/region/europe/russia/territory/index.html
Chishima: Frontiers of San Francisco Treaty in Hokkaido
Short film on the disputed islands from a Japanese perspective
USGS Map showing location of Magnitude 8.3 Earthquake 46.616°N, 153.224°E Kuril Islands region, November 15, 2006 11:14:16 UTCPictures of Kuril IslandsKuril Islands
at Encyclopædia Britannica {{Authority control Kuril Islands, Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean Islands of the Sea of Okhotsk Islands of the Russian Far East Archipelagoes of Japan Geography of Northeast Asia Archipelagoes of Sakhalin Oblast Disputed islands of Asia Disputed territories in Asia Pacific Coast of Russia Landforms of the Sea of Okhotsk Volcanoes of Sakhalin Oblast Stratovolcanoes of Russia Former Japanese colonies Shipwrecks in the Sea of Okhotsk Important Bird Areas of the Kurile Islands Seabird colonies
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast
Sakhalin Oblast ( rus, Сахали́нская о́бласть, r=Sakhalinskaya oblastʹ, p=səxɐˈlʲinskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Russian ...
in the Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Easte ...
. The islands stretch approximately northeast from Hokkaido
is the list of islands of Japan by area, second-largest island of Japan and comprises the largest and northernmost prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own list of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō fr ...
in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
to Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively.
Immediately offshore along the Pacific ...
in Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk; Historically also known as , or as ; ) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, Japan's island of Hokkaido on the sou ...
from the north Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
. There are 56 islands and many minor islets. The Kuril Islands consist of the Greater Kuril Chain
Greater Kuril Chain () - a part of the Kuril Islands - is a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean. It includes North Kurils, Iturup and Kunashir.
At its south western end, the Greater Kuril Chain is separated from the Lesser Kuril Chain by the S ...
and, at the southwest end, the parallel Lesser Kuril Chain
The Lesser Kuril Chain (, or 小千島列島), is an island chain in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The islands are administered as part of Yuzhno-Kurilsky District of Sakhalin Oblast, Russia, and many sources consider the chain to be geographi ...
. The group termed the 'South Kurils' consists of those of the Lesser Kuril Chain together with Kunashir
Kunashir Island (; ; ), possibly meaning ''Black Island'' or ''Grass Island'' in Ainu language, Ainu, is the southernmost island of the Kuril Islands. The island has been under Russia, Russian administration since the end of World War II, when S ...
and Iturup
Iturup (; ), also historically known by #Names, other names, is an island in the Kuril Archipelago separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. The town of Kurilsk, administrative center of Kurilsky District, is located roughly mi ...
in the Greater Kuril Chain. The Vries Strait
Vries Strait (, ''Proliv Friza''), historically also known as the De Vries Strait, is a strait between two main islands of the Kurils. It is located between the northeastern end of the island of Iturup and the southwestern headland of Urup Islan ...
between Iturup and Urup
Urup (; , ) is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Kuril Islands chain in the south of the Sea of Okhotsk, northwest Pacific Ocean. Its name is derived from the Ainu language word ''urup'', meaning "sockeye salmon".
Geography and climate
U ...
forms the Miyabe Line dividing the North and South Kurils. The Kuril Islands cover an area of around , with a population of roughly 20,000.
The islands have been under Russian administration since their 1945 invasion by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
near the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. Japan claims the four southernmost islands, including two of the three largest (Iturup
Iturup (; ), also historically known by #Names, other names, is an island in the Kuril Archipelago separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. The town of Kurilsk, administrative center of Kurilsky District, is located roughly mi ...
and Kunashir
Kunashir Island (; ; ), possibly meaning ''Black Island'' or ''Grass Island'' in Ainu language, Ainu, is the southernmost island of the Kuril Islands. The island has been under Russia, Russian administration since the end of World War II, when S ...
), as part of its territory, as well as Shikotan
Shikotan, also known as Shpanberg or Spanberg, is an island in the Kurils administered by the Russian Federation as part of Yuzhno-Kurilsky District of Sakhalin Oblast. It is claimed by Japan as the titular , organized as part of Nemuro Subpre ...
and the unpopulated Habomai
The Habomai Islands (; ) are a group of uninhabited islets (but for the Russian guards stationed there) in the southernmost Kuril Islands.
The islands have been under Soviet/Russian administration since the 1945 invasion by the Soviet Union nea ...
islets, which has led to the ongoing Kuril Islands dispute
The Kuril Islands dispute, known as the Northern Territories dispute in Japan, is a territorial dispute between Japan and Russia over the ownership of the four southernmost Kuril Islands. The Kuril Islands are a chain of islands that stretch ...
. The disputed islands are known in Japan as the country's "Northern Territories".
Etymology
The name ''Kuril'' originates from theautonym
Autonym may refer to:
* Autonym, the name used by a person to refer to themselves or their language; see Exonym and endonym
* Autonym (botany), an automatically created infrageneric or infraspecific name
See also
* Nominotypical subspecies, in zo ...
that the Indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology)
In biogeography, a native species is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only local natural evolution (though often populari ...
Ainu had used for the islands, ''kur'', meaning 'man'. It may also be related to names for other islands that have traditionally been inhabited by the Ainu people
The Ainu are an Indigenous peoples, indigenous ethnic group who reside in northern Japan and southeastern Russia, including Hokkaido and the Tōhoku region of Honshu, as well as the land surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, such as Sakhalin, the Ku ...
, such as ''Kuyi'' or ''Kuye'' for Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An islan ...
and ''Kai'' for Hokkaido
is the list of islands of Japan by area, second-largest island of Japan and comprises the largest and northernmost prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own list of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō fr ...
. In Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
, the Kuril Islands are known as the Chishima Islands (Kanji
are logographic Chinese characters, adapted from Chinese family of scripts, Chinese script, used in the writing of Japanese language, Japanese. They were made a major part of the Japanese writing system during the time of Old Japanese and are ...
: , ), and also as the Kuriru Islands (Katakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji and in some cases the Latin script (known as rōmaji).
The word ''katakana'' means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana characters are derived fr ...
and Kanji: ). Once Russians had discovered the islands in the 18th century, they formulated a pseudo-etymology derived from the Russian 'to smoke' due to the perpetual volcanic plumes emitting from the islands' volcanoes resembling smoke.
Geography and climate
 The Kuril Islands form part of the ring of
The Kuril Islands form part of the ring of tectonic
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons.
These processes ...
instability encircling the Pacific Ocean referred to as the Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes.
It is about long and up to about wide, and surrounds most of the Pa ...
. The islands themselves are summits of stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a typically conical volcano built up by many alternating layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with ...
es that are a direct result of the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Okhotsk Plate, which forms the Kuril Trench some east of the islands. The chain has around 100 volcanoes, some 40 of which are active, and many hot springs
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a Spring (hydrology), spring produced by the emergence of Geothermal activity, geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow ...
and fumaroles
A fumarole (or fumerole) is a vent in the surface of the Earth or another rocky planet from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcani ...
. There is frequent seismic activity
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
, including a magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
8.5 earthquake in 1963 and one of magnitude 8.3 recorded on November 15, 2006, which resulted in tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
waves up to reaching the California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
coast. Raikoke Island, near the centre of the archipelago, has an active volcano which erupted again in June 2019, with emissions reaching .
The climate on the islands is generally severe, with long, cold, stormy winters and short and notoriously foggy summers. The average annual precipitation is , a large portion of which falls as snow. The Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
of most of the Kurils is subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of hemiboreal regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Fennoscandia, Northwestern Russia, Siberia, and the Cair ...
(''Dfc''), although Kunashir
Kunashir Island (; ; ), possibly meaning ''Black Island'' or ''Grass Island'' in Ainu language, Ainu, is the southernmost island of the Kuril Islands. The island has been under Russia, Russian administration since the end of World War II, when S ...
is humid continental
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depe ...
(''Dfb''). However, the Kuril Islands' climate resembles the subpolar oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring co ...
of southwest Alaska
Southwest Alaska is a region of the U.S. state of Alaska. The area is not exactly defined by any governmental administrative region(s); nor does it always have a clear geographic boundary.
Geography
Southwest Alaska includes a huge swath of terr ...
much more than the hypercontinental climate of Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
and interior Siberia, as precipitation is heavy and permafrost completely absent. It is characterized by mild summers with only 1 to 3 months above and cold, snowy, extremely windy winters below , although usually above .
The chain ranges from temperate to sub-Arctic climate types, and the vegetative cover consequently ranges from tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
in the north to dense spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' ( ), a genus of about 40 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ecosystem, boreal (taiga) regions of the Northern hemisphere. ''Picea'' ...
and larch
Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus ''Larix'', of the family Pinaceae (subfamily Laricoideae). Growing from tall, they are native to the cooler regions of the northern hemisphere, where they are found in lowland forests in the high la ...
forests on the larger southern islands. The highest elevations on the islands are Alaid volcano (highest point: ) on Atlasov Island
Atlasov Island, known in Russian as Ostrov Atlasova (Остров Атласова), or in Japanese as Araido (阿頼度島), is the northernmost island and volcano and also the highest volcano of the Kuril Islands, part of the Sakhalin Oblast ...
at the northern end of the chain and Tyatya volcano () on Kunashir Island at the southern end.
Landscape types and habitats on the islands include many kinds of beach and rocky shores, cliffs, wide rivers and fast gravelly streams, forests, grasslands, alpine tundra
Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation, with an associated harsh climate. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alpine tundra gets ...
, crater lake
Crater Lake ( Klamath: ) is a volcanic crater lake in south-central Oregon in the Western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is a tourist attraction for its deep blue color and water clarity. T ...
s and peat bogs
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and mus ...
. The soils are generally productive, owing to the periodic influxes of volcanic ash and, in certain places, owing to significant enrichment by seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adaptation, adapted to life within the marine ecosystem, marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent ...
guano
Guano (Spanish from ) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. Guano is a highly effective fertiliser due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also, to a le ...
. However, many of the steep, unconsolidated slopes are susceptible to landslides
Landslides, also known as landslips, rockslips or rockslides, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, mudflows, shallow or deep-seated slope failures and debris flows. Landslide ...
and newer volcanic activity can entirely denude a landscape. Only the southernmost island has large areas covered by trees, while more northerly islands have no trees, or spotty tree cover.
The northernmost, Atlasov Island
Atlasov Island, known in Russian as Ostrov Atlasova (Остров Атласова), or in Japanese as Araido (阿頼度島), is the northernmost island and volcano and also the highest volcano of the Kuril Islands, part of the Sakhalin Oblast ...
(Araido in Japanese), is an almost-perfect volcanic
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ...
cone rising sheer out of the sea; it has been praised by the Japanese in haiku
is a type of short form poetry that originated in Japan. Traditional Japanese haiku consist of three phrases composed of 17 Mora (linguistics), morae (called ''On (Japanese prosody), on'' in Japanese) in a 5, 7, 5 pattern; that include a ''kire ...
, wood-block print
Woodblock printing or block printing is a technique for printing text, images or patterns used widely throughout East Asia and originating in China in antiquity as a method of printing on textiles and later on paper. Each page or image is creat ...
s, and other forms, in much the same way as the better-known Mount Fuji
is an active stratovolcano located on the Japanese island of Honshu, with a summit elevation of . It is the highest mountain in Japan, the second-highest volcano on any Asian island (after Mount Kerinci on the Indonesian island of Sumatra), a ...
. Its summit is the highest point in Sakhalin Oblast
Sakhalin Oblast ( rus, Сахали́нская о́бласть, r=Sakhalinskaya oblastʹ, p=səxɐˈlʲinskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Russian ...
.
Nature
Marine
Owing to their location along the Pacific shelf edge and the confluence of Okhotsk Sea gyre and the southwardOyashio Current
The , also known as the Okhotsk Current or Kurile Current, is a cold subarctic ocean current that flows south and circulates counterclockwise in the western North Pacific Ocean. The waters of the Oyashio Current originate in the Arctic Ocean ...
, the Kuril islands are surrounded by waters that are among the most productive in the North Pacific, supporting a wide range and high abundance of marine life.
Invertebrates
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordate subphylum ...
: Extensive kelp
Kelps are large brown algae or seaweeds that make up the order (biology), order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genus, genera. Despite its appearance and use of photosynthesis in chloroplasts, kelp is technically not a plant but a str ...
beds surrounding almost every island provide crucial habitat for sea urchins
Sea urchins or urchins () are echinoderms in the class Echinoidea. About 950 species live on the seabed, inhabiting all oceans and depth zones from the intertidal zone to deep seas of . They typically have a globular body covered by a spiny p ...
, various mollusks
Mollusca is a phylum of protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The num ...
and countless other invertebrates and their associated predators. Many species of squid
A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also ...
provide a principal component of the diet of many of the smaller marine mammals and birds along the chain.
Fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
: Further offshore, walleye pollock, Pacific cod
The Pacific cod (''Gadus macrocephalus)'' is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Gadidae. It is a bottom-dwelling fish found in the northern Pacific Ocean, mainly on the continental shelf and upper slopes, to depths of about . It can grow ...
, several species of flatfish
A flatfish is a member of the Ray-finned fish, ray-finned demersal fish Order (biology), suborder Pleuronectoidei, also called the Heterosomata. In many species, both eyes lie on one side of the head, one or the other migrating through or around ...
are of the greatest commercial importance. During the 1980s, migratory Japanese sardine
Sardine and pilchard are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring suborder Clupeoidei. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century; a somewhat dubious etymology says it com ...
was one of the most abundant fish in the summer.
Pinniped
Pinnipeds (pronounced ), commonly known as seals, are a widely range (biology), distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammals. They comprise the extant taxon, extant families Odobenidae (whose onl ...
: The main pinnipeds were a significant object of harvest for the indigenous populations of the Kuril islands, both for food and materials such as skin and bone. The long-term fluctuations in the range and distribution of human settlements along the Kuril island presumably tracked the pinniped ranges. In historical times, fur seals were heavily exploited for their fur in the 19th and early 20th centuries and several of the largest reproductive rookeries, as on Raykoke island, were extirpated. In contrast, commercial harvest of the true seal
True most commonly refers to truth, the state of being in congruence with fact or reality.
True may also refer to:
Places
* True, West Virginia, an unincorporated community in the United States
* True, Wisconsin, a town in the United States
* ...
s and Steller sea lion
The Steller sea lion (''Eumetopias jubatus''), also known as Steller's sea lion or the northern sea lion, is a large, near-threatened species of sea lion, predominantly found in the coastal marine habitats of the northeast Pacific Ocean and th ...
s has been relatively insignificant on the Kuril islands proper. Since the 1960s there has been essentially no additional harvest and the pinniped populations in the Kuril islands appear to be fairly healthy and in some cases expanding. The notable exception is the now extinct Japanese sea lion
The Japanese sea lion (''Zalophus japonicus'') (, ) was an aquatic mammal that became extinct in the 1970s. It was considered to be a subspecies of the related California sea lion (''Z. californianus'') until 2003. They inhabited the western Nort ...
, which was known to occasionally haul out
Hauling out is a behaviour associated with pinnipeds ( true seals, sea lions, fur seals and walruses) temporarily leaving the water. Hauling-out typically occurs between periods of foraging activity. Rather than remain in the water, pinniped ...
on the Kuril islands.
Sea otters
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of the weasel fa ...
: Sea otters were exploited very heavily for their pelts in the 19th century, as shown by 19th- and 20th-century whaling catch and sighting records.
Seabirds
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same envi ...
: The Kuril islands are home to many millions of seabirds, including northern fulmar
The northern fulmar (''Fulmarus glacialis''), fulmar, or Arctic fulmar is an abundant seabird found primarily in subarctic regions of the North Atlantic and North Pacific oceans. There has been one confirmed sighting in the Southern Hemisphere, ...
s, tufted puffin
The tufted puffin (''Fratercula cirrhata''), also known as crested puffin, is a relatively abundant medium-sized pelagic seabird in the auk family (Alcidae) found throughout the North Pacific Ocean.
It is one of three species of puffin that make ...
s, murre
''Uria'' is a genus of seabirds in the auk family known in Europe as guillemots, in most of North America as murres, and in Newfoundland and Labrador as turr. These are medium-sized birds with mainly brown or black plumage in the breeding s ...
s, kittiwake
The kittiwakes (genus ''Rissa'') are two closely related seabird species in the gull family Laridae, the black-legged kittiwake (''Rissa tridactyla'') and the red-legged kittiwake (''Rissa brevirostris''). The epithets "black-legged" and "red- ...
s, guillemot
Guillemot is the common name for several species of seabird in the Alcidae or auk family, part of the order Charadriiformes. In Europe, the term covers two genera, '' Uria'' and '' Cepphus''. In North America the ''Uria'' species are called mu ...
s, auklets, petrel
Petrels are tube-nosed seabirds in the phylogenetic order Procellariiformes.
Description
Petrels are a monophyletic group of marine seabirds, sharing a characteristic of a nostril arrangement that results in the name "tubenoses". Petrels enco ...
s, gull
Gulls, or colloquially seagulls, are seabirds of the subfamily Larinae. They are most closely related to terns and skimmers, distantly related to auks, and even more distantly related to waders. Until the 21st century, most gulls were placed ...
s and cormorant
Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the International Ornithologists' Union (IOU) ado ...
s. On many of the smaller islands in summer, where terrestrial predators are absent, virtually every possibly hummock, cliff niche or underneath of boulder is occupied by a nesting bird. Several of the islands, including Kunashir and the Lesser Kuril Chain in the South Kurils, and the northern Kurils from Urup to Paramushir, have been recognised as Important Bird Area
An Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA) is an area identified using an internationally agreed set of criteria as being globally important for the conservation of bird populations.
IBA was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife Int ...
s (IBAs) by BirdLife International
BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding i ...
because they support populations of various threatened
A threatened species is any species (including animals, plants and fungi) which is vulnerable to extinction in the near future. Species that are threatened are sometimes characterised by the population dynamics measure of ''critical depensatio ...
bird species, including many waterbird
A water bird, alternatively waterbird or aquatic bird, is a bird that lives on or around water. In some definitions, the term ''water bird'' is especially applied to birds in freshwater ecosystems, although others make no distinction from seabi ...
s, seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adaptation, adapted to life within the marine ecosystem, marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent ...
s and wader
245px, A flock of Red_knot.html" ;"title="Dunlins and Red knot">Dunlins and Red knots
Waders or shorebirds are birds of the order Charadriiformes commonly found wikt:wade#Etymology 1, wading along shorelines and mudflats in order to foraging, ...
s.
Terrestrial
The composition of terrestrial species on the Kuril islands is dominated by Asian mainland taxa via migration from Hokkaido andSakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An islan ...
Islands and by Kamchatkan taxa from the North. While highly diverse, there is a relatively low level of endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
on a species level.
The WWF divides the Kuril Islands into two ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecological and geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and c ...
s. The southern Kurils, along with southwestern Sakhalin, comprise the South Sakhalin-Kurile mixed forests
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz' ...
ecoregion. The northern islands are part of the Kamchatka-Kurile meadows and sparse forests, a larger ecoregion that extends onto the Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively.
Immediately offshore along the Pacific ...
and Commander Islands
The Commander Islands, Komandorski Islands, or Komandorskie Islands (, ''Komandorskiye ostrova'') are a series of islands in the Russian Far East, a part of the Aleutian Islands, located about east of the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Bering Sea. ...
. The Miyabe Line dividing the differing sets of predominant plants of the Kurils corresponds to the Vries Strait between Iturup and Urup.
Because of the generally smaller size and isolation of the central islands, few major terrestrial mammals have colonized these, though red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–750 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a seconda ...
and Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
fox
Foxes are small-to-medium-sized omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull; upright, triangular ears; a pointed, slightly upturned snout; and a long, bushy tail ("brush").
Twelve species ...
es were introduced for the sake of the fur trade in the 1880s. The bulk of the terrestrial mammal biomass is taken up by rodents
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...
, many introduced in historical times. The largest southernmost and northernmost islands are inhabited by brown bear
The brown bear (''Ursus arctos'') is a large bear native to Eurasia and North America. Of the land carnivorans, it is rivaled in size only by its closest relative, the polar bear, which is much less variable in size and slightly bigger on av ...
, foxes, and martens
A marten is a weasel-like mammal in the genus ''Martes'' within the subfamily Guloninae, in the family (biology), family Mustelidae. They have bushy tails and large paws with partially retractile claws. The fur varies from yellowish to dark bro ...
. Leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a ...
s once inhabited the islands. Some species of deer
A deer (: deer) or true deer is a hoofed ruminant ungulate of the family Cervidae (informally the deer family). Cervidae is divided into subfamilies Cervinae (which includes, among others, muntjac, elk (wapiti), red deer, and fallow deer) ...
are found on the more southerly islands. It is claimed that a wild cat, the Kurilian Bobtail
The Kurilian Bobtail is a cat breed (or breed group, depending on registry) originating from the Russian Kuril Islands, as well as Sakhalin Island and the Kamchatka peninsula of Russia. Short- or long-haired, it has a semi-cobby body type and a ...
, originates from the Kuril Islands. The bobtail is due to the mutation of a dominant gene. The cat has been domesticated and exported to nearby Russia and bred there, becoming a popular domestic cat.
Among terrestrial birds, ravens
Ravens may refer to:
* Raven, a species of the genus ''Corvus'' of passerine birds
Sports
* Anderson Ravens, the intercollegiate athletic program of Anderson University in Indiana
* Baltimore Ravens, a professional American football franchise
* B ...
, peregrine falcon
The peregrine falcon (''Falco peregrinus''), also known simply as the peregrine, is a Cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan bird of prey (raptor) in the family (biology), family Falconidae renowned for its speed. A large, Corvus (genus), cro ...
s, some wren
Wrens are a family, Troglodytidae, of small brown passerine birds. The family includes 96 species and is divided into 19 genera. All species are restricted to the New World except for the Eurasian wren that is widely distributed in the Old Worl ...
s and wagtail
Wagtails are a group of passerine birds that form the genus ''Motacilla'' in the family Motacillidae. The common name and genus name are derived from their characteristic tail pumping behaviour. Together with the pipits and longclaws they form ...
s are common.
History
Early history
 The
The Ainu people
The Ainu are an Indigenous peoples, indigenous ethnic group who reside in northern Japan and southeastern Russia, including Hokkaido and the Tōhoku region of Honshu, as well as the land surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, such as Sakhalin, the Ku ...
inhabited the Kuril Islands from early times, although few records predate the 17th century. From the Kamakura period
The is a period of History of Japan, Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura, Kanagawa, Kamakura by the first ''shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the G ...
to the Muromachi period
The , also known as the , is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate ( or ), which was officially established in 1338 by the first Muromachi ...
, there were Ezo (Ainu) people called Hinomoto from the Pacific coast of Hokkaido to the Kuril region, and Mr. Ando, the Ezo Sateshiku and Ezo Kanrei, was in charge of this ("Suwa Daimyojin Ekotoba"). It is said that when turmoil broke out on Ezogashima, he dispatched troops from Tsugaru. Its activities include the Kanto Gomensen, which calls itself the Ando Suigun, and is based in Jusanminato ("Kaisen Shikimoku"), supplying Japanese products to Ezo society and purchasing large quantities of northern products and shipping them nationwide. ("Thirteen Streets").The Matsumae clan, a feudal lord of Japan, became independent from the Ando clan (the family of Goro Ando). The Japanese administration first took nominal control of the islands during the Edo period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengok ...
(1603-1868) in the form of claims by the Matsumae clan
The was a Japanese aristocratic family who were daimyo of Matsumae Domain, in present-day Matsumae, Hokkaidō, from the Azuchi–Momoyama period until the Meiji Restoration. They were given the domain as a march fief in 1590 by Toyotomi ...
. The '' Shōhō Era Map of Japan'' (), a map of Japan made by the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.
The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars ...
in 1644, shows 39 large and small islands northeast of Hokkaido's Shiretoko Peninsula
The is located on the easternmost portion of the Japanese island of Hokkaido, protruding into the Sea of Okhotsk. It is separated from the Russian Kunashir Island by the Nemuro Strait. The name Shiretoko is derived from the Ainu language, Ainu wo ...
and Cape Nosappu
is a point on the Nemuro Peninsula, Nemuro, Japan, which is the easternmost point in Hokkaidō. It is also the easternmost point in Japan which is open to the public. It is located where the waters from the Pacific Ocean meet those from the ...
. A Dutch expedition under Maarten Gerritsz Vries
Maarten Gerritszoon Vries or Fries, also referred to as de Vries, (18 February 1589 in Harlingen, Netherlands – late 1647 at sea near Manila) was a 17th-century Dutch cartographer and explorer, the first Western Europe to leave an account of ...
explored the islands in 1643. Fedot Alekseyevich Popov sailed into the area .
Russian Cossacks landed on Shumshu
Shumshu (; ; ) is the easternmost and second-northernmost island of the Kuril Islands chain, which divides the Sea of Okhotsk from the northwest Pacific Ocean. The name of the island is derived from the Ainu language, meaning "good island". It i ...
in 1711.
American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, p ...
whaleship
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales.
Terminology
The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Jap ...
s caught right whales
Right whales are three species of large baleen whales of the genus ''Eubalaena'': the North Atlantic right whale (''E. glacialis''), the North Pacific right whale (''E. japonica'') and the southern right whale (''E. australis''). They are class ...
off the islands between 1847 and 1892. Three of the ships were wrecked on the islands: two on Urup
Urup (; , ) is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Kuril Islands chain in the south of the Sea of Okhotsk, northwest Pacific Ocean. Its name is derived from the Ainu language word ''urup'', meaning "sockeye salmon".
Geography and climate
U ...
in 1855 and one on Makanrushi
Makanrushi (; Japanese 磨勘留島; Makanru-tō) is an uninhabited volcanic island located near the northern end of the Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean. Its name is derived from the Ainu language.
G ...
in 1856. In September 1892, north of Kunashir Island, a Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
n schooner
A schooner ( ) is a type of sailing ship, sailing vessel defined by its Rig (sailing), rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more Mast (sailing), masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than t ...
seized the bark ''Cape Horn Pigeon'', of New Bedford
New Bedford is a city in Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States. It is located on the Acushnet River in what is known as the South Coast (Massachusetts), South Coast region. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, New Bedford had a ...
and escorted it to Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( ; , ) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai and the capital of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia. It is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area o ...
, where it was detained for nearly two weeks.
Japanese administration
World War II
*In 1941 AdmiralIsoroku Yamamoto
was a Marshal Admiral of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) and the commander-in-chief of the Combined Fleet during World War II. He commanded the fleet from 1939 until his death in 1943, overseeing the start of the Pacific War in 1941 and J ...
ordered the assembly of the Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, Potsdam Declaration, when it was dissolved followin ...
strike-force for the Attack on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii Operation attack on Pearl Harbor in Tankan or Hitokappu Bay, Iturup
Iturup (; ), also historically known by #Names, other names, is an island in the Kuril Archipelago separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. The town of Kurilsk, administrative center of Kurilsky District, is located roughly mi ...
Island, South Kurils. The territory was chosen for its sparse population, lack of foreigners, and constant fog-coverage. The Admiral ordered the move to Hawaii on the morning of 26 November.
*On 10 July 1943 the first bombardment against the Japanese bases in Shumshu
Shumshu (; ; ) is the easternmost and second-northernmost island of the Kuril Islands chain, which divides the Sea of Okhotsk from the northwest Pacific Ocean. The name of the island is derived from the Ainu language, meaning "good island". It i ...
and Paramushir by American forces occurred. From Alexai Point Landing Field, Alexai airfield 8 B-25 Mitchells from the 77th Bombardment Squadron took off, led by Capt James L. Hudelson. This mission principally struck Paramushir.
*Another mission was flown during 11 September 1943 when the Eleventh Air Force dispatched eight B-24 Liberators and 12 B-25s. Facing reinforced Japanese defenses, 74 crew members in three B-24s and seven B-25 failed to return. 22 men were killed in action, one taken prisoner and 51 interned in Kamchatka.
*The Eleventh Air Force implemented other bombing missions against the northern Kurils, including a strike by six B-24s from the 404th Bombardment Squadron and 16 P-38s from the 54th Fighter Squadron on 5 February 1944.
*Japanese sources report that the Matsuwa military installations were subject to American air-strikes between 1943 and 1944.
*The Americans' strategic feint called "Operation Wedlock" diverted Japanese attention north and misled them about the U.S. strategy in the Pacific. The plan included air strikes by the USAAF and U.S. Navy bombers which included U.S. Navy shore bombardment and submarine operations. The Japanese increased their garrison in the north Kurils from 8,000 in 1943 to 41,000 in 1944 and maintained more than 400 aircraft in the Kurils and Hokkaido
is the list of islands of Japan by area, second-largest island of Japan and comprises the largest and northernmost prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own list of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō fr ...
area in anticipation that the Americans might invade from Alaska.
*American planners had briefly contemplated an invasion of northern Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
from the Aleutian Islands during the autumn of 1943 but rejected that idea as too risky and impractical. They considered the use of Boeing B-29 Superfortresses, on Amchitka and Shemya bases, but rejected the idea. The U.S. military maintained interest in these plans when they ordered the expansion of bases in the western Aleutians, and major construction began on Shemya. In 1945, plans for a possible invasion of Japan via the northern route were shelved.
*Between 18 August and 31 August 1945 Soviet forces Invasion of the Kuril Islands, invaded the North and South Kurils.
*The Soviets expelled the entire Japanese civilian population of roughly 17,000 by 1946.
*Between 24 August and 4 September 1945 the Eleventh Air Force of the United States Army Air Forces sent two B-24s on reconnaissance missions over the North Kuril Islands with the intention of taking photos of the Soviet Union, Soviet occupation in the area. Soviet fighters intercepted and forced them away.
In February 1945 the Yalta Agreement promised to the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
Invasion of South Sakhalin, South Sakhalin and the Invasion of the Kuril Islands, Kuril islands in return for entering the Pacific War against the Japanese during World War II. In August 1945 the Soviet Union mounted an armed invasion of South Sakhalin at the cost of over 5,000 Soviet and Japanese lives.
Russian administration
The Kuril Islands are split into three administrative districts (raions), each a part ofSakhalin Oblast
Sakhalin Oblast ( rus, Сахали́нская о́бласть, r=Sakhalinskaya oblastʹ, p=səxɐˈlʲinskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Russian ...
:
*Severo-Kurilsky District (Severo-Kurilsk)
*Kurilsky District (Kurilsk)
*Yuzhno-Kurilsky District (Yuzhno-Kurilsk)
Japan maintains a claim to the three islands of Kunashir
Kunashir Island (; ; ), possibly meaning ''Black Island'' or ''Grass Island'' in Ainu language, Ainu, is the southernmost island of the Kuril Islands. The island has been under Russia, Russian administration since the end of World War II, when S ...
, Iturup
Iturup (; ), also historically known by #Names, other names, is an island in the Kuril Archipelago separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. The town of Kurilsk, administrative center of Kurilsky District, is located roughly mi ...
, and Shikotan
Shikotan, also known as Shpanberg or Spanberg, is an island in the Kurils administered by the Russian Federation as part of Yuzhno-Kurilsky District of Sakhalin Oblast. It is claimed by Japan as the titular , organized as part of Nemuro Subpre ...
, and the Habomai
The Habomai Islands (; ) are a group of uninhabited islets (but for the Russian guards stationed there) in the southernmost Kuril Islands.
The islands have been under Soviet/Russian administration since the 1945 invasion by the Soviet Union nea ...
rocks, together called the ''Northern Territories''.
In addition, the Japanese government claims that the Kuril Islands, other than the Northern Territories and South Karafuto, are undetermined areas under international law because the San Francisco Peace Treaty does not specify where they belong and the Soviet Union did not sign it.
On 8 February 2017 the Russian government gave names to five previously unnamed Kuril islands in Sakhalin Oblast
Sakhalin Oblast ( rus, Сахали́нская о́бласть, r=Sakhalinskaya oblastʹ, p=səxɐˈlʲinskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands in the Russian ...
: Derevyanko Island (after Kuzma Derevyanko, ), Gnechko Island (after Alexey Gnechko, ), Gromyko Island (after Andrei Gromyko, ), Farkhutdinov Island (after Igor Farkhutdinov, ) and Shchetinina Island (after Anna Shchetinina, ).
Demographics
, 19,400 people inhabited the Kuril Islands, of which 16,700 lived on the four disputed southern islands and 2,600 lived on Paramushir, the northernmost large island; the islands in between are uninhabited. These include ethnic Russians, Ukrainians, Belarusians, Tatars, Nivkh people, Nivkhs, Oroch people, Oroch, Japanese people, Japanese and Ainu in Russia, Ainus. Russian Orthodox Church, Russian Orthodox Christianity is the main religion. Some of the villages are permanently occupied by Russian soldiers. Others are inhabited by civilians, who are mostly fishermen, workers in fish factories, dockers, and social sphere workers (police, medics, teachers, etc.). Construction works on the islands have attracted migrant workers from the rest of Russia and other post-Soviet states. , there were only 8 inhabited islands out of a total of 56.Economy
Fishing is the primary occupation. The islands have strategic and economic value, in terms of fisheries and also mineral deposits of pyrite, sulfur, and various polymetallic ores. There are hopes that oil exploration will provide an economic boost to the islands. In 2014, construction workers built a pier and a breakwater in Kitovy Bay, central Iturup, where barges are a major means of transport, sailing between the cove and ships anchored offshore. A new road has been carved through the woods near Kurilsk, the island's biggest village, going to the site of Yuzhno-Kurilsk Mendeleyevo Airport. Gidrostroy, the Kurils' biggest business group with interests in fishing, construction and real estate, built its second fish processing factory on Iturup island in 2006, introducing a state-of-the-art conveyor system. To deal with a rise in the demand of electricity, the local government is also upgrading a state-run geothermal power plant at Baransky, Mount Baransky, an active volcano, where steam and hot water can be found. In 2022, a special economic zone was established on the Kuril islands with special tax regimes, exemption from corporate income tax, VAT with reduced customs duties for 20 years. It is an important part of Russian government's plan to develop the Russian far east.Military
The main Russian force stationed on the islands is the 18th Machine Gun Artillery Division, 18th Machine Gun Artillery Division, which has its headquarters in Goryachiye Klyuchi, Kurilsky District, Sakhalin Oblast, Goryachiye Klyuchi on theIturup
Iturup (; ), also historically known by #Names, other names, is an island in the Kuril Archipelago separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. The town of Kurilsk, administrative center of Kurilsky District, is located roughly mi ...
Island. There are also Border Guard Service troops stationed on the islands. In February 2011, Russian President Dmitry Medvedev called for substantial reinforcements of the Kuril Islands defences. Subsequently, in 2015, additional anti-aircraft missile systems Tor missile system, Tor and Buk missile system, Buk, Coastal defence and fortification, coastal defence missile system K-300P Bastion-P, Bastion, Kamov Ka-50, Kamov Ka-52 combat helicopters and one Kilo-class submarine, ''Varshavyanka'' project submarine came on defence of Kuril Islands. During the 2022 Russian Invasion of Ukraine, it was reported that parts of the 18th Machine Gun Artillery Division were redeployed to Eastern Ukraine.
List of main islands
While in Russian sources the islands are mentioned for the first time in 1646, the earliest detailed information about them was provided by the explorer Vladimir Atlasov in 1697. In the 18th and early 19th centuries, the Kuril Islands were explored by: Danila Antsiferov, I. Kozyrevsky, Ivan Yevreinov, Fyodor Luzhin, Martin Spanberg, Adam Johann von Krusenstern, Vasily Golovnin, and Henry James Snow.See also
*2006 Kuril Islands earthquake *2007 Kuril Islands earthquake *Chishima Province *Evacuation of Karafuto and Kuriles *Invasion of the Kuril Islands *Karafuto Fortress *Karafuto Prefecture *Northern District Army (Japan), Organization of Hokkai (North) Army *Organization of Kita and Minami Fortresses *Political divisions of Karafuto Prefecture *ZemlyakNotes
References
Further reading
*Gorshkov, G. S. ''Volcanism and the Upper Mantle Investigations in the Kurile Island Arc''. Monographs in geoscience. New York: Plenum Press, 1970. *Krasheninnikov, Stepan Petrovich, and James Greive. ''The History of Kamtschatka and the Kurilski Islands, with the Countries Adjacent''. Chicago: Quadrangle Books, 1963. *Rees, David. ''The Soviet Seizure of the Kuriles''. New York: Praeger, 1985. *Takahashi, Hideki, and Masahiro Ōhara. ''Biodiversity and Biogeography of the Kuril Islands and Sakhalin''. Bulletin of the Hokkaido University Museum, no. 2-. Sapporo, Japan: Hokkaido University Museum, 2004. *Hasegawa, Tsuyoshi. ''Racing the Enemy: Stalin, Truman, and the Surrender of Japan''. 2006. . *Alan Catharine and Denis Cleary. ''Unwelcome Company. ''A fiction thriller novel set in 1984 Tokyo and the Kuriles featuring a light aircraft crash and escape from Russian-held territory.External links
Southern Kuriles / Northern Territories: A Stumbling-block in Russia-Japan Relationship
history and analysis by Andrew Andersen, Department of Political Science, University of Victoria, May 2001 *http://depts.washington.edu/ikip/index.shtml (Kuril Island Biocomplexity Project) * (includes space imagery)
a
Natural Heritage Protection Fund
*http://www.mofa.go.jp/region/europe/russia/territory/index.html
Chishima: Frontiers of San Francisco Treaty in Hokkaido
Short film on the disputed islands from a Japanese perspective
USGS Map showing location of Magnitude 8.3 Earthquake 46.616°N, 153.224°E Kuril Islands region, November 15, 2006 11:14:16 UTC
at Encyclopædia Britannica {{Authority control Kuril Islands, Archipelagoes of the Pacific Ocean Islands of the Sea of Okhotsk Islands of the Russian Far East Archipelagoes of Japan Geography of Northeast Asia Archipelagoes of Sakhalin Oblast Disputed islands of Asia Disputed territories in Asia Pacific Coast of Russia Landforms of the Sea of Okhotsk Volcanoes of Sakhalin Oblast Stratovolcanoes of Russia Former Japanese colonies Shipwrecks in the Sea of Okhotsk Important Bird Areas of the Kurile Islands Seabird colonies