Zond program on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Zond () was the name given to two distinct series of
Zond () was the name given to two distinct series of
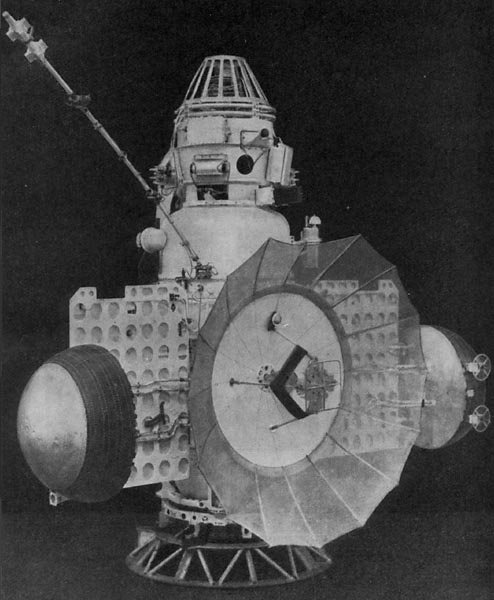 The first three missions were based on the model 3MV planetary probe, intended to explore
The first three missions were based on the model 3MV planetary probe, intended to explore
Very detailed information about the Soyuz 7K-L1 used in Zond 4-8
{{URSS space probes Missions to the Moon Soviet lunar program
 Zond () was the name given to two distinct series of
Zond () was the name given to two distinct series of Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
robotic spacecraft
Uncrewed spacecraft or robotic spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input, such as remote control, or remote guidance. They may also be autonomous, in which t ...
launched between 1964 and 1970. The first series, based on the 3MV planetary probe, was intended to gather information about nearby planets.
The second series of test spacecraft was intended as a precursor to remote-controlled robotic circumlunar loop flights, using a stripped-down variant of Soyuz spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraf ...
, consisting of the service
Service may refer to:
Activities
* Administrative service, a required part of the workload of university faculty
* Civil service, the body of employees of a government
* Community service, volunteer service for the benefit of a community or a ...
and descent modules, but lacking the orbital module.
Two tortoises and other lifeforms aboard Zond 5 were the first terrestrial organisms to travel around the Moon and return to Earth.
Missions based on the 3MV planetary probe
 The first three missions were based on the model 3MV planetary probe, intended to explore
The first three missions were based on the model 3MV planetary probe, intended to explore Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
and Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
. After two failures, Zond 3 was sent on a test mission, becoming the second spacecraft to photograph the far side of the Moon (after Luna 3
Luna 3, or E-2A No.1 (), was a Soviet spacecraft launched in 1959 as part of the Luna programme. It was the first mission to photograph the far side of the Moon and the third Soviet space probe to be sent to the neighborhood of the Moon. The hi ...
). It then continued out to the orbit of Mars in order to test telemetry and spacecraft systems.
Circumlunar missions
The missions Zond 4 through Zond 8 were test flights for the Soviet Moonshot during the Moon race. TheSoyuz 7K-L1
Soyuz 7K-L1 "Zond" spacecraft was designed to launch cosmonaut, cosmonauts from the Earth to circle the Moon without going into lunar orbit in the context of the Soviet crewed lunar programs, Soviet crewed Moon-flyby program in the Moon race. ...
(also mentioned just as L1) spacecraft was used for the Moon-aimed missions, stripped down to make it possible to launch around the Moon from the Earth. They were launched on the Proton rocket
Proton (, formal designation: UR-500) is an expendable launch system used for both commercial and Russian government space launches. The first Proton rocket was launched in 1965. Modern versions of the launch system are still in use , making it ...
which was just powerful enough to send the Zond on a free return trajectory around the Moon without going into lunar orbit (the same kind of path flown by Apollo 13
Apollo 13 (April 1117, 1970) was the seventh crewed mission in the Apollo program, Apollo space program and would have been the third Moon landing. The craft was launched from Kennedy Space Center on April 11, 1970, but the landing was abort ...
in its emergency abort). With minor modification, Zond was capable of carrying two cosmonauts.
In the beginning, there were serious reliability problems with both the new Proton rocket and the similarly new Soyuz spacecraft, but the test flights pressed ahead with some glitches. The majority of test flights from 1967 to 1970 ( Zond 4 to Zond 8) showed problems during re-entry.
The Zond spacecraft made only uncrewed automatic flights. Four of these suffered malfunctions that would have injured or killed any crew. Instrumentation flown on these missions gathered data on micrometeor flux, solar and cosmic ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the ...
s, magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
s, radio emissions, and solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the Stellar corona, corona. This Plasma (physics), plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy betwee ...
. Many photographs were taken and biological payloads were also flown.
Timetable
3MV planetary probe based missions
* Zond 1 ** Launched 2 April 1964 ** Communications lost 14 May 1964 ** Venus flyby 14 July 1964 * Zond 2 ** Launched 30 November 1964 ** Communications lost May 1965 ** Mars flyby 6 August 1965 * Zond 3 ** Launched 18 July 1965 ** Lunar Flyby 20 July 1965 ** Communications lost 3 March 1966Soyuz 7K-L1/L1S test missions
* Kosmos 146 ** Launched 10 March 1967 ** Prototype Soyuz 7K-L1P launched by Proton into planned highly elliptical Earth orbit. * Kosmos 154 ** Launched 8 April 1967 ** Prototype Soyuz 7K-L1P launched by Proton and failed to go into a planned translunar trajectory. * Zond 1967A ** Launched 28 September 1967 ** Fell off course 60 seconds after launch. Escape tower took the Zond capsule safely away. The rocket crashed downrange. ** Attempted Lunar flyby * Zond 1967B ** Launched 22 November 1967 ** Second stage failure. The Zond capsule was safely recovered. The rocket crashed downrange. ** Attempted Lunar flyby * Zond 4 ** Launched 2 March 1968 ** Study of remote regions of circumterrestrial space, development of new on-board systems and units of space stations. ** Returned to Earth 7 March 1968 – Self destruct system automatically blew up the capsule at altitude, off the African coast at Guinea. * Zond 1968A ** Launched 23 April 1968 ** Second stage failed 260 seconds after launch. ** Attempted Lunar flyby * Zond 1968B (Zond 7K-L1 s/n 8L) ** Launched 21 July 1968 ** Block D stage exploded on the pad, killing three people. * Zond 5 ** Launched 15 September 1968 ** Circumlunar 18 September 1968 ** Returned to Earth 21 September 1968 ** A biological payload of two Russian tortoises, wine flies, meal worms, plants, seeds, bacteria, and other living matter was included in the flight and were the first Earth lifeforms to travel around the Moon and return safely. ** The first spacecraft to circle the Moon and return to land on Earth. * Zond 6 ** Launched 10 November 1968 ** Circumlunar 14 November 1968 ** Returned to Earth 17 November 1968 ** The second circumlunar spaceflight to include lifeforms from Earth, Zond 6 carried a biological payload of turtles, flies, and bacteria. It also carried scientific probes includingcosmic ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the ...
, micrometeoroid
A micrometeoroid is a tiny meteoroid: a small particle of rock in space, usually weighing less than a gram. A micrometeorite is such a particle that survives passage through Earth's atmosphere and reaches Earth's surface.
The term "micrometeoro ...
detectors, and photographic equipment.
* Zond 1969A
** Launched 20 January 1969
** Stage two shut down 25 seconds early. Automatic flight abort. The capsule was safely recovered.
** Attempted Lunar flyby
* Zond L1S-1
** Launched 21 February 1969
** First stage failure. The capsule escape system fired 70 seconds after launch. The capsule was recovered.
** Attempted Lunar orbiter and N1 rocket test
* Zond L1S-2
** Launched 3 July 1969
** First stage failure. The Zond capsule was recovered.
** Attempted Lunar orbiter and N1 rocket test
* Zond 7
** Launched 7 August 1969
** Lunar flyby 11 August 1969
** Returned to Earth 14 August 1969
** Zond 7 carried four turtles.
* Zond 8
** Launched 20 October 1970
** Lunar flyby 24 October 1970
** Returned to Earth 27 October 1970
* '' Zond 9''
** Planned but cancelled. Planned for July 1969, carrying a crew of Pavel Popovich and Vitali Sevastyanov, but never flew.
* '' Zond 10''
** Planned but cancelled
See also
* Zond failed missions *List of missions to the Moon
Missions to the Moon have been numerous and include some of the earliest space missions, conducting exploration of the Moon since 1959.
The first partially successful lunar mission was Luna 1 (January 1959), the first probe to leave Earth ...
References
Very detailed information about the Soyuz 7K-L1 used in Zond 4-8
{{URSS space probes Missions to the Moon Soviet lunar program