Zahumlje on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zachlumia or Zachumlia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Zahumlje, Захумље, ), also Hum, was a
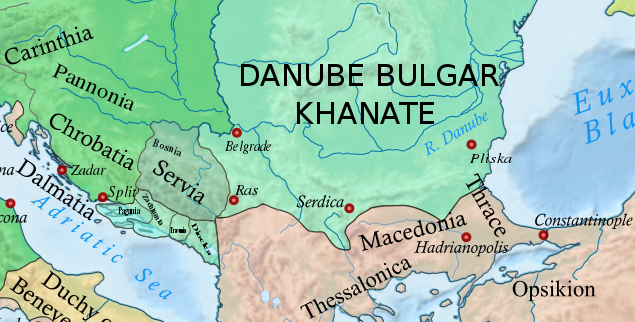

 The history of Zahumlje as a greater political entity starts with the emerging of Michael of Zahumlje, an independent South Slavic ruler who flourished in the early part of the 10th century. A neighbour of Croatian Kingdom and
The history of Zahumlje as a greater political entity starts with the emerging of Michael of Zahumlje, an independent South Slavic ruler who flourished in the early part of the 10th century. A neighbour of Croatian Kingdom and
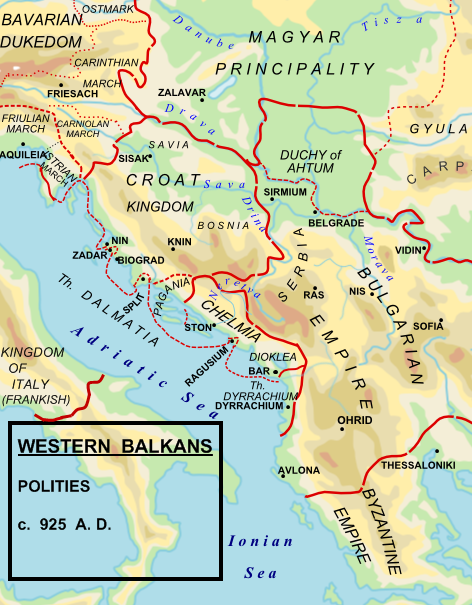
 Kočapar, the Prince of Duklja (r. 1102–1103), ruled in the name of Vukan I of Serbia. There was a split between the two, and Vukan sent forces to Duklja, making Kočapar flee to Bosnia and then Zahumlje, where he died. Zavida ruled Zahumlje before getting into a conflict with his brothers, resulting in him being exiled to Duklja, where he would have the title of ''Lord of Ribnica''. ''Grand Princes'' Desa (r. 1148–1162) and Uroš II Prvoslav ruled Serbia together 1149–1153; Desa had the title of 'Prince of Duklja, Travunija and Zahumlje', mentioned in 1150 and 1151.
About 1150, the Byzantine Emperor
Kočapar, the Prince of Duklja (r. 1102–1103), ruled in the name of Vukan I of Serbia. There was a split between the two, and Vukan sent forces to Duklja, making Kočapar flee to Bosnia and then Zahumlje, where he died. Zavida ruled Zahumlje before getting into a conflict with his brothers, resulting in him being exiled to Duklja, where he would have the title of ''Lord of Ribnica''. ''Grand Princes'' Desa (r. 1148–1162) and Uroš II Prvoslav ruled Serbia together 1149–1153; Desa had the title of 'Prince of Duklja, Travunija and Zahumlje', mentioned in 1150 and 1151.
About 1150, the Byzantine Emperor
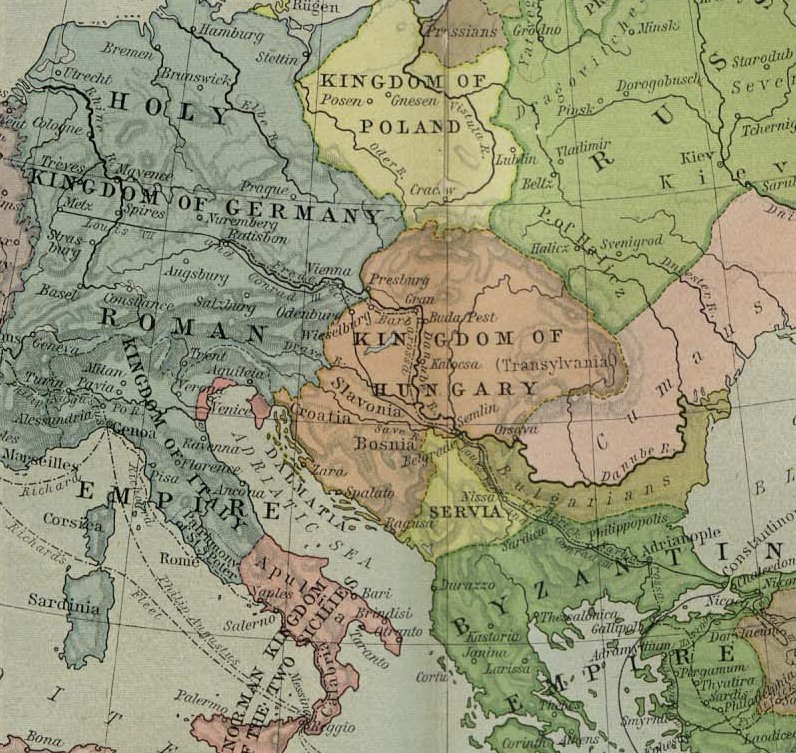
 Until beginning of the 13th century, areas of Zahumlje were under jurisdiction of the Roman Church. When
Until beginning of the 13th century, areas of Zahumlje were under jurisdiction of the Roman Church. When
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
principality located in the modern-day regions of Herzegovina
Herzegovina ( or ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Hercegovina, separator=" / ", Херцеговина, ) is the southern and smaller of two main geographical Regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Bosnia (reg ...
and southern Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
(today parts of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
and Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, respectively). In some periods it was a fully independent or semi-independent South Slavic principality. It maintained relations with various foreign and neighbouring powers (Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh of Bulgaria, Asparuh, moved south to the northe ...
, Kingdom of Croatia, Principality of Serbia
The Principality of Serbia () was an autonomous, later sovereign state in the Balkans that came into existence as a result of the Serbian Revolution, which lasted between 1804 and 1817. Its creation was negotiated first through an unwritten agre ...
) and later was subjected (temporarily or for a longer period) to Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
, Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Principality was ruled by the Obrenović dynast ...
, Kingdom of Bosnia
The Kingdom of Bosnia ( / Краљевина Босна), or Bosnian Kingdom (''Bosansko kraljevstvo'' / Босанско краљевство), was a medieval kingdom that lasted for nearly a century, from 1377 to 1463, and evolved out of the ...
, and at the end to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
.
Etymology
Zachlumia is a derivative of ''Hum'', from Proto-Slavic '' *xŭlmŭ'', borrowed from a Germanic language (cf. Proto-Germanic '' *hulma-''), meaning ''"Hill"''. South Slavic ''Zahumlje'' is named after the mountain of Hum (za + Hum "behind the Hum"), above Bona, at the mouth of the Buna. The principality is named ''Zahumlje'' or ''Hum'' inSerbo-Croatian
Serbo-Croatian ( / ), also known as Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS), is a South Slavic language and the primary language of Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro. It is a pluricentric language with four mutually i ...
(Serbian Cyrillic
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet (, ), also known as the Serbian script, (, ), is a standardized variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language. It originated in medieval Serbia and was significantly reformed in the 19th cen ...
: Захумље, Хум). It is ''Zachlumia'' in Latin, Хлъмъ in Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic ( ) is the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language and the oldest extant written Slavonic language attested in literary sources. It belongs to the South Slavic languages, South Slavic subgroup of the ...
, and Ζαχλούμων χώρα ("land of Zachlumians") in Greek. The names ''Chelmania'', ''Chulmia'' and ''terra de Chelmo'' appear in later Latin and Italian chronicles.
Geography
''De Administrando Imperio
(; ) is a Greek-language work written by the 10th-century Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII. It is a domestic and foreign policy manual for the use of Constantine's son and successor, the Emperor Romanos II. It is a prominent example of Byz ...
'' described the polity of Zachlumia as: ''"From Ragusa begins the domain of the Zachlumi (Ζαχλοῦμοι) and stretches along as far as the river Orontius: and on the side of the coast it is neighbour to the Pagani, but on the side of the mountain country it is neighbour to the Croats on the north and to Serbia at the front ... Those who live there now, Zachlumi, are Serbs, from the time of that prince who claimed the protection of the Emperor Heraclius
Heraclius (; 11 February 641) was Byzantine emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular emperor Phocas.
Heraclius's reign was ...
. In the territory of the Zachlumi are the inhabited cities of Stagnon, Mokriskik, Iosli, Galoumainik, Dobriskik"''.
The '' Chronicle of the Priest of Duklja'' (14th or 16th century) described the geography under the rule of the South Slavic ("Red Croatia
Red Croatia (; ) is a pseudohistorical term used for the southeastern parts of Roman Dalmatia and some other territories, including parts of present-day Montenegro, Albania, the Herzegovina region of Bosnia and Herzegovina and southeastern Croat ...
") rulers, Hum had two major cities: Bona and Hum. The main settlements in Zachlumia were Ston
Ston () is a settlement and a municipality in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County of Croatia, located at the south of isthmus of the Pelješac peninsula.
History
Because of its geopolitical and strategic position, Ston has had a rich history since ...
, Ošlje, Dobar, the towns of Mokriskik and Glumainik. The principality sprang from Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
(Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
) to the northwest and Pagania to the west; to the mountain of Kalinovik and the Gatačko polje
Gatačko polje (, sr-Cyrl, Гатачко поље) is a '' polje'' (karst field) within the Gacko municipality in Bosnia and Herzegovina, spanning 57–60 km2, being ca. 24 km long and ca. 3,6 km wide, in the northwest–southeast ...
, where it bordered Travunia
Travunia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Travunija, Травунија; ; ; ) was a South Slavic medieval principality that was part of Medieval Serbia (850–1371), and later the Medieval Bosnia (1373–1482). The principality became hereditar ...
. The eastern border of Zahumlje went along the line Popovo-Ljubinje
Ljubinje ( sr-cyrl, Љубиње) is a town and municipality in Republika Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is situated in southeastern part of Herzegovina. As of 2013, the town has a population of 2,744 inhabitants, while the municipality has 3 ...
- Dabar and met with the Travunian border at the city of Ragusa. Zachlumia was split on 9 zhupanates: Ston
Ston () is a settlement and a municipality in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County of Croatia, located at the south of isthmus of the Pelješac peninsula.
History
Because of its geopolitical and strategic position, Ston has had a rich history since ...
, Popovo, Dubrava, Luka, Dabar, Žapska, Gorička and Večenik around Neretva
The Neretva (, sr-Cyrl, Неретва), also known as Narenta, is one of the largest rivers of the eastern part of the Adriatic basin. Four Hydroelectricity, hydroelectric power plants with Dam, large dams (higher than 15 metres) provide flood ...
. Zahumlje had access to the Adriatic Sea with the Pelješac
Pelješac (; Chakavian: ; ) is a peninsula in southern Dalmatia in Croatia. The peninsula is part of the Dubrovnik-Neretva County and is the second largest peninsula in Croatia. From the isthmus that begins at Ston, to the top of Cape Loviš ...
peninsula and faced Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
northwards.
Slavic settlement
Slavs invaded Balkans duringJustinian I
Justinian I (, ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign was marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was ...
(r. 527–565), when eventually up to 100,000 Slavs raided Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
. The Western Balkans was settled with ''Sclaveni
The ' (in Latin language, Latin) or ' (Sclaveni#Terminology, various forms in Greek language, Greek) were Early Slavs, early Slavic tribes that raided, invaded and settled in the Balkans in the Early Middle Ages and eventually became one of the p ...
'' (Sklavenoi), the east with Antes. The Sklavenoi plundered Thrace in 545, and again the next year. In 551, the Slavs crossed Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names of European cities in different languages (M–P)#N, names in other languages), less often spelled in English as Nish, is the list of cities in Serbia, third largest city in Serbia and the administrative cente ...
initially headed for Thessalonica, but ended up in Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
. In 577 some 100,000 Slavs poured into Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
and Illyricum, pillaging cities and settling down. Hum had also a large number of Vlachs
Vlach ( ), also Wallachian and many other variants, is a term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate speakers of Eastern Romance languages living in Southeast Europe—south of the Danube (the Balkan peninsula ...
who were descendent from a pre-Slavic population. Related to Romanians and originally speaking a language related to Romanian, the Vlachs of what was Hum are today Slavic speaking.
History
7th century
In the second decade of the 7th century, the Avars and their Slavic subjects occupied most of the Byzantine province of Dalmatia, including the territory of what would become Zahumlje, sacking towns and enslaving or displacing the local population. Some of the Slavs and Avars might have permanently settled in the occupied areas. They attackedConstantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
in 626 but were defeated by the Byzantines, after which the Avars ceased to play a significant role in the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
.
Around 630, during the reign of Byzantine Emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
Heraclius
Heraclius (; 11 February 641) was Byzantine emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular emperor Phocas.
Heraclius's reign was ...
, Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian lan ...
and Croats
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ...
(Slavic tribes) led by their respective aristocracies entered the western Balkans from the north, which was approved by the emperor. They inhabited areas that had been devastated by the Avars, where Byzantium (East Roman Empire) had generally been reduced to only nominal rule. According to ''DAI'', Zahumlje was one of the regions settled by the Serbs from an area near Thessaloniki who previously arrived there from White Serbia
White Serbia ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Бела Србија, Bela Srbija; ), also called Boiki (; sr-Cyrl-Latn, link=no, Бојка, Bojka), is the name applied to the assumed homeland of the Sorbs (tribe), White Serbs ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, link=no, Бели С ...
, but a closer reading of the source suggests that the Constantine VII's consideration about the population's ethnic identity is based on Serbian political rule and influence during the time of Časlav of Serbia and does not indicate ethnic origin. According to Noel Malcolm, today's western Serbia was area where Serbs settled in 7th century and from there they expanded their rule on territory of Zachlumia. According to Tibor Živković the area of the Vistula where the Litziki ancestors of Michael of Zahumlje originate was the place where White Croats
The White Croats (; ; ; ), also known simply as Croats, were a group of Early Slavs, Early Slavic tribes that lived between East Slavs, East Slavic and West Slavs, West Slavic tribes in the historical region of Galicia (Eastern Europe), Galicia n ...
would be expected and not White Serbs
The Sorbs, also known as Serbs or White Serbs in Serbian historiography, were an Early Slavic tribe settled between the Saale-Elbe valley and the Lusatian Neisse (in present-day Saxony and Thuringia). They were part of the Polabian Slavs and ...
, and it's unclear whether the Zachlumians "in the migration period to the Balkans really were Serbs or Croats or Slavic tribes which in alliance with Serbs or Croats arrived in the Balkans". According to Francis Dvornik the Zachlumians "had a closer bond of interest with the Croats than with the Serbs, since they seem to have migrated to their new home not with the Serbs, but with the Croats". Michael's tribal origin is related to the oral tradition from '' Historia Salonitana'' by Thomas the Archdeacon about seven or eight tribes of nobles called ''Lingones'' who arrived from Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
and settled in Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
. Much of Dalmatia was sometime earlier settled by the Croats, and Zahumlje bordered their territory on the north. According to Thomas the Archdeacon, when describing the reign of Croatian king Stephen Držislav in the late 10th century, notes that Duchy of Hum (Zachlumia or Chulmie) was a part of the Kingdom of Croatia, before and after Stjepan Držislav:
9th century


Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
, King of the Franks
The Franks, Germanic peoples that invaded the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, were first led by individuals called dux, dukes and monarch, reguli. The earliest group of Franks that rose to prominence was the Salian Franks, Salian Mero ...
from 768 until his death in 814, expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ...
(800) that incorporated much of western and central Europe. He brought the Frankish state face to face with the West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic langu ...
to the northeast and the Avars and South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, ...
to the southeast of the Frankish empire. Dalmatia which was southeast of the Frankish empire, was chiefly in the hands of South Slavic tribes. North of Dubrovnik these came to be under Croatian ''župans'' (princes) and eventually came to consider themselves Croatians, while many of those to the south of Dubrovnik were coming to consider themselves Serbs. Despite Frankish overlordship, the Franks had almost no role in Dalmatia ( Dalmatian Croatia and Zahumlje) in the period from the 820s through 840s.
In 866, a major Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
raid along Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
struck Budva
Budva (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Будва, or ) is a town in the Coastal Montenegro, Coastal region of Montenegro. It had 27,445 inhabitants as of 2023, and is the centre of Budva Municipality. The coastal area around Budva, called the Budv ...
and Kotor
Kotor (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Котор, ), historically known as Cattaro (from Italian language, Italian: ), is a town in Coastal Montenegro, Coastal region of Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Bay of Kotor. The city has ...
, and then laid siege to Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik, historically known as Ragusa, is a city in southern Dalmatia, Croatia, by the Adriatic Sea. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, a Port, seaport and the centre of the Dubrovni ...
in 867. The city of Dubrovnik appealed to Byzantine Emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
Basil the Macedonian
Basil I, nicknamed "the Macedonian" (; 811 – 29 August 886), was List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine emperor from 867 to 886. Born to a peasant family in Macedonia (theme), Macedonia, he rose to prominence in the imperial court after gainin ...
, who responded by sending over one hundred ships. Finally, the 866–867 Saracens' siege of Dubrovnik, which lasted fifteen months, was raised due to the intervention of Basil I, who sent a fleet under the command of Niketas Oryphas in relief of the city. After this successful intervention, the Byzantine navy
The Byzantine navy was the Navy, naval force of the Byzantine Empire. Like the state it served, it was a direct continuation from its Roman navy, Roman predecessor, but played a far greater role in the defence and survival of the state than its ...
sailed along the coast collecting promises of loyalty to the empire from the Dalmatian cities. At this moment the local Slavic tribes (in Zahumlje, Travunija, and Konavle), who had aided the intervention, also accepted Byzantine suzerainty. Afterwards, the Slavs of Dalmatia and Zahumlje took part in the Byzantine military actions against the Arabs in Bari
Bari ( ; ; ; ) is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Bari and of the Apulia Regions of Italy, region, on the Adriatic Sea in southern Italy. It is the first most important economic centre of mainland Southern Italy. It is a port and ...
in 870–871. The Roman cities in Dalmatia had long been pillaged by the Slavic tribes in the mountaines around them. Basil I allowed the towns to pay tribute to the Slavic tribes to reduce the Slavs raiding. Presumably a large portion of this tribute went to the prince of Dalmatian Croatia. In late 870s, the theme of Dalmatia ("thema Dalmatias") was established, but with no real Byzantine authority. These small cities in the region (also Dyrrachium) did not stretch into the hinterlands, and had none military capacity, thus Basil I paid a tax of '72 gold coins' to the princes of Zahumlje and Travunia.
In 879, the Pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
asked for help from duke Zdeslav Trpimirović for an armed escort for his delegates across southern Dalmatia and Zahumlje. Later in 880, the Pope ask the same from Zdeslav's successor, prince Branimir.
10th century
 The history of Zahumlje as a greater political entity starts with the emerging of Michael of Zahumlje, an independent South Slavic ruler who flourished in the early part of the 10th century. A neighbour of Croatian Kingdom and
The history of Zahumlje as a greater political entity starts with the emerging of Michael of Zahumlje, an independent South Slavic ruler who flourished in the early part of the 10th century. A neighbour of Croatian Kingdom and Principality of Serbia
The Principality of Serbia () was an autonomous, later sovereign state in the Balkans that came into existence as a result of the Serbian Revolution, which lasted between 1804 and 1817. Its creation was negotiated first through an unwritten agre ...
as well as an ally of Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, he was nevertheless able to maintain independent rule throughout at least a good part of his reign.
Michael have come into territorial conflict with the neighbouring prince Peter Gojniković, the ruler of inner Serbia, who was extending his power westwards. To eliminate that threat and as a close ally of Bulgaria, Michael warned the Bulgarian Tsar Simeon I about the alliance between Peter and Symeon's enemy, the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
. In 912 Michael kidnapped the Venetian Doge's son Peter Badoari that was returning to Venice from Constantinople and sent him to Czar Simeon as a sign of loyalty. Symeon attacked inner Serbia and captured Peter, who later died in prison, and Michael was able to restore the majority of control.
The ''Historia Salonitana maior'', whose composition may have begun in the late 13th century, cites a letter of Pope John X to Tomislav, "king (''rex'') of the Croats", in which he refers to the first council in some detail. If the letter is authentic, it shows that the council was attended not only by the bishops of Croatian and Byzantine Dalmatia, but also by Tomislav, whose territory also included the Byzantine cities of Dalmatia, and by a number of Michael's representatives. Zahumlje may have been under Croatian influence, but remained a separate political entity. Both Zahumlje and Croatia were under the religious jurisdiction of the Archbishopric of Split. In this letter, John describes Michael as "the most excellent leader of the Zachlumi" (''excellentissimus dux Chulmorum''), and is mentioned the Ston bishopric (''ecclesia Stagnensis'') which jurisdiction remained under Split until 1022. It is uncertain whether the inscription and depiction of a Slavic ruler in the Church of St. Michael in Ston is a reference to Michael of Zahumlje, the 12th century Mihailo I of Duklja
Mihailo Vojislavljević ( sr-cyr, Михаило Војислављевић) was a medieval Serbian king and the ruler of Duklja, Dioclea (Duklja), from 1046 to 1081, initially as a Byzantine vassal holding the title of ''protospatharios'', then ...
or St. Michael himself.
After the Italian city of Siponto
Siponto (, ) was an ancient port town and bishopric of Magna Graecia in Apulia, southern Italy. The town was abandoned after earthquakes in the 13th century; today the area is administered as a ''frazione'' of the ''comune'' of Manfredonia, in t ...
() was heavily jeopardized by the raiding Arabs and Langobards, Mihailo won a magnificent military victory by taking the city upon the recommendations from Constantinople and orders from his ally, King Tomislav Trpimirovic, but didn't keep it permanently. Mihailo Višević entered into closer relations with the Byzantine Empire, after the death of Bulgaria's Tsar Simeon. He gained the grand titles of the Byzantine court as '' anthypatos'' and patrician (''patrikios
The patricians (from ) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom and the early Republic, but its relevance waned after the Conflict of the Orders (494 BC to 287 B ...
''). He remained as ruler of Zahumlje into the 940s, while maintaining good relations with the Papacy
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
.
Post-Michael of Zahumlje period
After the death of Michael (after c. 930s or 940s), the fate of Zahumlje is uncertain due to lack of historical sources about it. Some historians believe that Zahumlje came under the rule of prince Časlav of Serbia, but there's no evidence for it and ''DAI'' which was written in the mid-10th century clearly states that Zachlumia is a separate polity from Serbia. The 13th century Thomas the Archdeacon claimed that the Croatian kingdom included Zachlumia before and after Stephen Držislav (969–997), but that's also disputable. In the late 990s, Bulgarian Tsar Samuel made client states out of most of the Balkans, including Duklja and Zahumlje. In 998, Samuel launched a major campaign againstJovan Vladimir
Jovan Vladimir or John Vladimir ( sr-cyr, Јован Владимир; – 22 May 1016) was the ruler of Duklja, the most powerful Serbs, Serbian principality of the time, from around 1000 to 1016. He ruled during the protracted war betwee ...
to prevent a Byzantine-Serbian alliance, resulting in a surrender. The Bulgarian troops proceeded to pass through Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
, taking control of Kotor
Kotor (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Котор, ), historically known as Cattaro (from Italian language, Italian: ), is a town in Coastal Montenegro, Coastal region of Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Bay of Kotor. The city has ...
and journeying to Dubrovnik. Although they failed to take Dubrovnik, they devastated the surrounding villages. The Bulgarian army then attacked Croatia in support of the rebel princes Krešimir III and Gojslav and advanced northwest as far as Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, enter ...
, Trogir and Zadar
Zadar ( , ), historically known as Zara (from Venetian and Italian, ; see also other names), is the oldest continuously inhabited city in Croatia. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar ...
, then northeast through Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
and Raška and returned to Bulgaria.
11th century
By 1020, Byzantine EmperorBasil I
Basil I, nicknamed "the Macedonian" (; 811 – 29 August 886), was List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine emperor from 867 to 886. Born to a peasant family in Macedonia (theme), Macedonia, he rose to prominence in the imperial court after gainin ...
expanded control in the whole region, but the Byzantines used local elite to rule over local polities although under Byzantine vassalage and supervision of Byzantine officials. In the Pope Benedict VIII's bull from 27 September 1022 is mentioned Zahumlje kingdom (''regno Lachomis''), and would be again in the bull of Pope Gregory VII
Pope Gregory VII (; 1015 – 25 May 1085), born Hildebrand of Sovana (), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 22 April 1073 to his death in 1085. He is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church.
One of the great ...
from 1076 (as ''regno Zaculmi''), which confirmed the jurisdiction of the archdiocese of Dubrovnik.
In a charter dated July 1039, Ljutovid of Zahumlje who was an independent Slavic ruler of Zahumlje, styled himself ''"Ljutovit, protospatharios epi tou Chrysotriklinou, hypatos, strategos"'' of Serbia and Zahumlje. According to historian Paul Stephenson, it "suggests that he had been courted by the emperor, and awarded nominal rights neighbouring lands, including Duklja, which was at the time at war with the empire.
According to historical sources, the Serbian lands were under Byzantine control or vassalage until 1040s, but not under a direct control. Vojislav of Duklja (fl. 1018–1043) soon took Zahumlje from the Byzantines. During the rule of Constantine Bodin
Constantine Bodin ( Bulgarian and , ''Konstantin Bodin''; 1072–1101) was a medieval king and the ruler of Duklja, the most powerful Serbian principality of the time, from 1081 to 1101, succeeding his father, Mihailo Vojislavljević ( 10 ...
(r. 1081–1101), neither Bosnia, Serbia nor Zahumlje was ever integrated into Doclea, each retained its own nobility and institutions and simply acquired a Vojislavljević to head the local structure as Prince or Duke. Zahumlje subsequently became part of the Grand Principality of Serbia
The Grand Principality of Serbia ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Великожупанска Србија, Velikožupanska Srbija, separator=" / "), also known by the anachronistic exonym Raška (region), Rascia ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Рашка, Raška, separator=" ...
.
12th century
 Kočapar, the Prince of Duklja (r. 1102–1103), ruled in the name of Vukan I of Serbia. There was a split between the two, and Vukan sent forces to Duklja, making Kočapar flee to Bosnia and then Zahumlje, where he died. Zavida ruled Zahumlje before getting into a conflict with his brothers, resulting in him being exiled to Duklja, where he would have the title of ''Lord of Ribnica''. ''Grand Princes'' Desa (r. 1148–1162) and Uroš II Prvoslav ruled Serbia together 1149–1153; Desa had the title of 'Prince of Duklja, Travunija and Zahumlje', mentioned in 1150 and 1151.
About 1150, the Byzantine Emperor
Kočapar, the Prince of Duklja (r. 1102–1103), ruled in the name of Vukan I of Serbia. There was a split between the two, and Vukan sent forces to Duklja, making Kočapar flee to Bosnia and then Zahumlje, where he died. Zavida ruled Zahumlje before getting into a conflict with his brothers, resulting in him being exiled to Duklja, where he would have the title of ''Lord of Ribnica''. ''Grand Princes'' Desa (r. 1148–1162) and Uroš II Prvoslav ruled Serbia together 1149–1153; Desa had the title of 'Prince of Duklja, Travunija and Zahumlje', mentioned in 1150 and 1151.
About 1150, the Byzantine Emperor Manuel I Komnenos
Manuel I Komnenos (; 28 November 1118 – 24 September 1180), Latinized as Comnenus, also called Porphyrogenitus (; " born in the purple"), was a Byzantine emperor of the 12th century who reigned over a crucial turning point in the history o ...
displeased with king Radoslav of Duklja, divided up his lands between princes of the old Serbian family of Zavida, and Stefan Nemanja secured the land of Hum. After 1168 when Nemanja was raised to the Serbian throne with Manuel's favor, Hum passed to his brother Miroslav. He married a sister of Ban Kulin, who in meantime acquired the throne of Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
. The subjects of Miroslav and Kulin included both Catholic and Orthodox. Prince Miroslav himself was Orthodox. In meantime, both Bosnia and Hum had been fought between Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
and Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
. The Catholics supported the former and the Orthodox the latter. A support of the growing heresy seemed the best solution for both Kulin and Miroslav.
Following the death of Emperor Manuel in 1180 Miroslav started ecclesiastical superior of Hum. He refused to allow Rainer, Latin Archbishop of Spalato (Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, enter ...
) whom he considered to be an agent of Hungarian king, to consecrate a bishop for the town of Ston
Ston () is a settlement and a municipality in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County of Croatia, located at the south of isthmus of the Pelješac peninsula.
History
Because of its geopolitical and strategic position, Ston has had a rich history since ...
. In addition, Miroslav confiscated the Archbishop's money. Rainer complained to the Pope Alexander III
Pope Alexander III (c. 1100/1105 – 30 August 1181), born Roland (), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 September 1159 until his death in 1181.
A native of Siena, Alexander became pope after a Papal election, ...
, who sent Teobald to report on the matter. The Pope's nuncio Teobald found Miroslav as a patron of heretics. After this, the Pope wrote to king Béla III of Hungary who was overlord of Hum (which Miroslav did not recognize), telling him to see that Miroslav performed his duty, but Miroslav remained as ''Prince of Hum''. In 1190–1192, Stefan Nemanja briefly assigned the rule of Hum to his son Rastko Nemanjić, while Miroslav held the Lim region with Bijelo Polje. Rastko however took monastic vows and Miroslav continued ruling Hum after 1192.
Latin vengeance came in March 1198, when Andrew II of Hungary
Andrew II (, , , ; 117721 September 1235), also known as Andrew of Jerusalem, was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1205 and 1235. He ruled the Principality of Halych from 1188 until 1189/1190, and again between 1208/1209 and ...
become the prince of Dalmatia, Croatia and Hum, while Miroslav died a year after and his wife was living in exile. The Miroslav Gospels are the oldest surviving documents written in Serbian recension of Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic ( ) is the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language and the oldest extant written Slavonic language attested in literary sources. It belongs to the South Slavic languages, South Slavic subgroup of the ...
, very likely produced for the Church of St Peter in Lima, commissioned by prince Miroslav.
13th century
 Until beginning of the 13th century, areas of Zahumlje were under jurisdiction of the Roman Church. When
Until beginning of the 13th century, areas of Zahumlje were under jurisdiction of the Roman Church. When Sava
The Sava, is a river in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. From its source in Slovenia it flows through Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally reac ...
became the first archbishop of Serbia in 1219, he appointed Ilarion as the Orthodox bishop of Hum.
Andrija Mirosavljević is entitled the rule of Hum, but the Hum nobility chose his brother Petar. Andrija is exiled to Rascia, to the court of his cousin Grand Prince Stefan Nemanjić. In the meantime, Petar fought successfully with neighbouring Bosnia and Croatia. Stefan Nemanjić sided with Andrija and went to war and secured Hum and Popovo field for Andrija sometime after his accession. Petar was defeated and crossed the Neretva, continuing to rule the west and north of the Neretva, which had around 1205 been briefly occupied by Andrew II of Hungary
Andrew II (, , , ; 117721 September 1235), also known as Andrew of Jerusalem, was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1205 and 1235. He ruled the Principality of Halych from 1188 until 1189/1190, and again between 1208/1209 and ...
. Toljen II, the son of Toljen Mirosavljević, succeeded as prince, ruling 1227–1237. Andrija's sons Bogdan
Bogdan (Cyrillic: Богдан) is a Slavic masculine name that appears in the South Slavic languages and in Polish, Romanian and Moldovan. It is derived from the Slavic words ''Bog'' (Cyrillic: Бог), meaning 'god', and ''dan'' (Cyrillic: ...
, Radoslav and George succeed as princes of Hum in 1249, Radoslav held the supreme rule. During the war against Ragusa, he aided his kinsman Stephen Uroš I of Serbia, at the same time swearing allegiance to Béla IV of Hungary
Béla IV (1206 – 3 May 1270) was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1235 and 1270, and Duke of Styria from 1254 to 1258. As the oldest son of Andrew II of Hungary, King Andrew II, he was crowned upon the initiative of a group ...
. Following an earthquake in the Hum capital of Ston, the Serbian Orthodox bishop of Hum moved to the church of St Peter and St Paul built on the Lim River
The Lim (Serbian Cyrillic: Лим, ) or Vermosh River () is a river that flows through Albania, Montenegro, Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina and is long.Radoslav of Zahumlje was from 1254 a vassal of Hungary, but probably afterwards his land were absorbed into Serbia. However, he was at war with Serbia in 1268, while still under Hungarian suzerainty. But seeking to centralize his realm, Stephen Uroš I of Serbia tried to stamp out regional differences by dropping references to Zahumlje (Hum), Trebinje and Duklja (Zeta), and called himself "King of all Serbian land and the Coast". Miroslav's descendants dropped to the level of other local nobles.
 In the beginning of the 15th century,
In the beginning of the 15th century,
Ulla Tillander-Godenhielm (2005): The Russian Imperial Award System During the Reign of Nicolas II, p. 446.
/ref>
14th century
Paul I Šubić of Bribir as Ban of Croatia and Dalmatia controlled Croatia from Gvozd Mountain to the river Neretva mouth. Paul became Lord of all of Bosnia in 1299. Although supporting the king, Paul continued to act independently, and ruled over a large portion of modern-day Croatia and Bosnia. In the course of the war between Stephen Uroš II Milutin and Stephen Dragutin, Paul Šubić in 1301-1303 expanded not only into western Hum, but also beyond the Neretva river, and took the region ofNevesinje
Nevesinje ( sr-cyrl, Невесиње) is a town and municipality in Republika Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. As of 2013, the town has a population of 5,162 inhabitants, while the municipality has 12,961 inhabitants.
Geography
The municipality o ...
and Ston
Ston () is a settlement and a municipality in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County of Croatia, located at the south of isthmus of the Pelješac peninsula.
History
Because of its geopolitical and strategic position, Ston has had a rich history since ...
. He also fought over Kotor
Kotor (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Котор, ), historically known as Cattaro (from Italian language, Italian: ), is a town in Coastal Montenegro, Coastal region of Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Bay of Kotor. The city has ...
and its surroundings, but without further territorial gains. In 1304 Paul appointed his eldest son, Mladen II, as Lord of Hum, and administrative governorship positions were granted to his vassals Konstantin (until 1307) and Izan Nelipčić (1307-1313). Mladen succeeded his father in 1312, and as part of Hungarian-Italian initiative, and with Milutin and Dragutin concluding a peace between themselves, began a new war in eastern Zachlumia. The initial Mladen's success, was soon followed by Milutin's capture of Mladen's brother, and to get him back Mladen Šubić had to agree to restore eastern Hum to Milutin. After this agreement in 1313 the Neretva again became the border between eastern and western Hum.
By 1325, the Branivojević family had emerged as strongest in Hum. Probably at their highest point they ruled from Cetina River to the town of Kotor
Kotor (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Котор, ), historically known as Cattaro (from Italian language, Italian: ), is a town in Coastal Montenegro, Coastal region of Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Bay of Kotor. The city has ...
. Though nominal vassals of Serbia, the Branivojević family attacked Serbian interests and other local nobles of Hum, who in 1326 turned against Serbia and Branivojević family. The Hum nobles approached to Stjepan Kotromanić II, the ban of Bosnia, who then annexed most of Hum. The Draživojevići of Nevesinje as vassals of Bosnian Ban, become the leading family of Hum in the 1330s. Because of the war in 1327-1328 between Serbia and Dubrovnik, Bosnian lordship of inner Hum and the war in Macedonia, Stephen Uroš IV Dušan sold Ston
Ston () is a settlement and a municipality in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County of Croatia, located at the south of isthmus of the Pelješac peninsula.
History
Because of its geopolitical and strategic position, Ston has had a rich history since ...
and Pelješac
Pelješac (; Chakavian: ; ) is a peninsula in southern Dalmatia in Croatia. The peninsula is part of the Dubrovnik-Neretva County and is the second largest peninsula in Croatia. From the isthmus that begins at Ston, to the top of Cape Loviš ...
to Dubrovnik, and turned to the east to acquire all of Macedonia.
The region was overwhelmed by the House of Kotromanić from Bosnia in 1322–1326. By the mid-14th century, Bosnia apparently reached a peak under Ban Tvrtko I
Stephen Tvrtko I ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Stjepan/Stefan Tvrtko, Стјепан/Стефан Твртко; 1338 – 10 March 1391) was the king of Bosnia, first king of Kingdom of Bosnia, Bosnia. A member of the House of Kotromanić, h ...
who came into power in 1353.
15th century
 In the beginning of the 15th century,
In the beginning of the 15th century, Hrvoje Vukčić Hrvatinić
Hrvoje Vukčić Hrvatinić (c. 1350–1416) was a medieval Bosnian nobleman and magnate, Grand Duke of Bosnia, Knez of Donji Kraji, and Duke of Split. He was the most prominent member of the Hrvatinić noble family, and one of the major feu ...
ruled over the western Hum, and Sandalj Hranić Kosača ruled over its eastern part, while the Neretva river remain a border between their possessions.
The territory on the right bank of the Lower Neretva was at the time controlled by Kosača vassals, a local clan and magnates of Radivojević–Jurjević–Vlatković.
Bosnian regional lord Stjepan Vukčić Kosača
Stjepan Vukčić Kosača (1404–1466) was a powerful Bosnian Nobility, nobleman who was politically active from 1435 to 1466; the last three decades of Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Middle Ages, Bosnian medieval history. During this period, ...
ruled over Zahumlje, or Humska zemlja as it was called at this point. In 1448 he assumed the title ''herzog'' and styled himself ''Herzog of Hum and the Coast, Grand Duke of Bosnia, Knyaz of Drina, and the rest,'' and since 1450, ''Herzog of Saint Sava, Lord of Hum, Grand Duke of Bosnia, Knyaz of Drina, and the rest''. This "Saint Sava" part of the title had considerable public relations value, because Sava's relics were consider miracle-working by people of all Christian faiths. Stjepan's title will prompt the Ottomans
Ottoman may refer to:
* Osman I, historically known in English as "Ottoman I", founder of the Ottoman Empire
* Osman II, historically known in English as "Ottoman II"
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empir ...
to start calling ''Humska zemlja'' by using the possessive form of the noun ''Herceg'', ''Hercegs land(s) (Herzegovina
Herzegovina ( or ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Hercegovina, separator=" / ", Херцеговина, ) is the southern and smaller of two main geographical Regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Bosnia (reg ...
), which remains a long-lasting legacy in the name of Bosnia and Herzegovina to this day.: "Tako se pojam Humska zemlja postepeno gubi da ustupi mjesto novom imenu zemlje hercega Stjepana — Hercegovini."
In 1451 he attacked Dubrovnik, and laid siege to the city.Viator (1978), pp. 388–389. He had earlier been made a Ragusan nobleman and, consequently, the Ragusan government now proclaimed him a traitor. A reward of 15,000 ducat
The ducat ( ) coin was used as a trade coin in Europe from the later Middle Ages to the 19th century. Its most familiar version, the gold ducat or sequin containing around of 98.6% fine gold, originated in Venice in 1284 and gained wide inter ...
s, a palace in Dubrovnik worth 2,000 ducats, and an annual income of 300 ducats was offered to anyone who would kill him, along with the promise of hereditary Ragusan nobility which also helped hold this promise to whoever did the deed. Stjepan was so scared by the threat that he finally raised the siege.
Demographics
12th–13th centuries
Most of Hum's territory was inhabited bySlavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
, and Vlachs
Vlach ( ), also Wallachian and many other variants, is a term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate speakers of Eastern Romance languages living in Southeast Europe—south of the Danube (the Balkan peninsula ...
, and belonged to the Eastern Church
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in the Eastern Mediterranean region or locations further east, south or north. The term does not describe a ...
after the Great Schism. Hum's coastal region, including its capital Ston
Ston () is a settlement and a municipality in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County of Croatia, located at the south of isthmus of the Pelješac peninsula.
History
Because of its geopolitical and strategic position, Ston has had a rich history since ...
, had a mixed population of Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
s and Orthodox.
14th–15th centuries
In contrast to Bosnia, where Roman Catholicism andBosnian Church
The Bosnian Church ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=/, Crkva bosanska, Црква босанска) was an autonomous Christian church in medieval Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Historians traditionally connected the church with the Bogomils, although this ...
were firmly established, eastern parts of Hum was mostly Orthodox, from 13th century and the rise of Nemanjići. In the 14th- and 15th centuries, there was an influx of settlers from the ''župa
A župa, or zhupa, is a historical type of administrative division in Southeast Europe and Central Europe, that originated in medieval South Slavs, South Slavic culture, commonly translated as "county" or "parish". It was mentioned for the first t ...
'' of Trebinje
Trebinje ( sr-Cyrl, Требиње, ) is a city and municipality in Republika Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is the southernmost city in Bosnia and Herzegovina and is situated on the banks of the Trebišnjica river in the region of East Her ...
, around forts Klobuk, Ledenica and Rudina, and the ''Hum lands'' around Gacko
Gacko ( sr-cyrl, Гацко) is a town and municipality in Republika Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is situated in the region of East Herzegovina (Bosnia and Herzegovina), East Herzegovina. As of 2013, the town has a population of 5,784 inh ...
and Dabar, to Kotor
Kotor (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Котор, ), historically known as Cattaro (from Italian language, Italian: ), is a town in Coastal Montenegro, Coastal region of Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Bay of Kotor. The city has ...
. The people from Hum were mostly girls from Gacko, who took up working as servants to wealthy families.
List of rulers
* Michael of Zahumlje, independent Slavic ruler of Zahumlje, Prince of Zahumlje 910–940 *Stephen Držislav of Croatia
Stephen or Steven is an English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the firs ...
, King of Croatia
This is a complete list of dukes and kings of Croatia () under domestic ethnic and elected Dynasty, dynasties during the Duchy of Croatia (until 925), the Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), the Croatia in personal union with Hungary, Kingdom of Croa ...
969–997
* Dragimir, Prince of Travunia and Zachlumia (as a part of Duklja) 1000–1018
* Part of Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
: 1018–1039
* Ljutovid, Prince of Hum 1039–1054
* Mihailo Vojislavljević
Mihailo Vojislavljević ( sr-cyr, Михаило Војислављевић) was a medieval Serbian king and the ruler of Dioclea (Duklja), from 1046 to 1081, initially as a Byzantine vassal holding the title of '' protospatharios'', then after ...
, Prince, and King of Duklja 1054–1081
* Bodin Vojislavljević, King of Duklja 1081–1101
* Vladimir II of Duklja, King of Duklja c. 1103–1113
* George I of Duklja, King of Duklja c. 1113–1118 and 1125–1131
* Desa, Duke of Zahumlje 1149–1162
* Miroslav of Hum Prince of Zahumlje 1162–1190
* Rastko of Nemanja 1190–1192 ruling in the name of Stefan Nemanja
* Miroslav of Hum Prince of Zahumlje 1192
* Toljen of Hum Prince of Zahumlje 1192–1196 (He married a daughter of Duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of Royal family, royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobi ...
Berthold von Meran, Margrave
Margrave was originally the Middle Ages, medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or a monarchy, kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain Feudal ...
of Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
)
* To Hungary 1198–1199
* Petar, son of Miroslav, Duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of Royal family, royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobi ...
of Zahumlje 1196–1216 and a count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: ...
of the city of Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, enter ...
1222–1225.
* In 1216 Stephen the First-Crowned divided Hum:
**Mainland of Zachlumia:
*** Stefan Radoslav of Serbia, Prince of Serbia and Zahumlje 1216–1228
*** Toljen II, son of Toljen, Duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of Royal family, royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobi ...
of Upper Zahumlje 1228–1239
**Coastal Zachlumia:
*** Andrija, son of Miroslav, Prince of the Seaside and Duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of Royal family, royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobi ...
of Southern Zahumlje 1216–1239
* Union of Zachlumia:
* Andrija, 1239–1250
* Radoslav of Zahumlje, Bogdan I and George I 1249–1252 (brothers, sons of Andrew)
* Radoslav of Zahumlje and George I 1252–1268
* George I 1268–1280
* Bogdan II 1280–1299
* Mladen I Šubić of Bribir, a Croatian noble and Bosnian Ban from 1299 to 1304
* Paul I Šubić of Bribir, a Ban of Croatia
Ban of Croatia () was the title of local rulers or office holders and after 1102, viceroys of Croatia. From the earliest periods of the Croatian state, some provinces were ruled by Ban (title), bans as a ruler's representative (viceroy) and sup ...
and Lord of all of Bosnia from 1304 to 1312
* Mladen II Šubić of Bribir, ''"Ban the Croats and Bosnia and general lord of Hum country"'' 1312–1322
* Nikola
Nikola () is a given name which, like Nicholas, is a version of the Greek '' Nikolaos'' (Νικόλαος) and it means "the winner of the people". It is common as a masculine given name in the South Slavic countries (Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bul ...
, Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The ...
of Zahumlje 1322–1326. Son of Bogdan I (or Radoslav). He married Katarina Kotromanić in 1338
* Stjepan Kotromanic II, a Bosnian Ban from 1326 to 1353
* Tvrtko, the first Bosnian King 1353–1391
* Stephen Dabiša of Bosnia
Stephen or Steven is an English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the firs ...
1391–1395
* Helen I 1395–1398
* Stephen Ostoja of Bosnia
Stephen OstojaHis name in Bosnian is rendered Stjepan Ostoja (), while in Croatian it is Stjepan Ostoja. In Serbian, he is called Stefan Ostoja (). ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Stjepan Ostoja, Стјепан Остоја; died September 141 ...
1398– 1404
* Stephen Tvrtko II of Bosnia 1404–1409
* Stephen Ostoja of Bosnia
Stephen OstojaHis name in Bosnian is rendered Stjepan Ostoja (), while in Croatian it is Stjepan Ostoja. In Serbian, he is called Stefan Ostoja (). ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Stjepan Ostoja, Стјепан Остоја; died September 141 ...
(again) 1409–1418
* Sandalj Hranić Kosača, Grand Duke of Hum from 1418 to 1435
* Stjepan Vukčić Kosača
Stjepan Vukčić Kosača (1404–1466) was a powerful Bosnian Nobility, nobleman who was politically active from 1435 to 1466; the last three decades of Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Middle Ages, Bosnian medieval history. During this period, ...
(1435–1466) was Bosnian noble. In 1448. changed his title from "Vojvode of Bosnia" into "Herceg ukeof Hum and the Coast", and from 1449 into "Herceg of Saint Sava
Saint Sava (, ; Old Church Slavonic: ; Glagolitic: ; ; 1169 or 1174 – 14 January 1235/6), known as the Enlightener or the Illuminator, was a Serbs, Serbian prince and Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox monk, abbot of Studenica Monastery, Studeni ...
" .
* Vlatko Hercegović
Vlatko Hercegović ( sr-Cyrl, Влатко Херцеговић; –1489), was the second and the last ''Duchy of Saint Sava, Herzog of Saint Sava'', succeeding his father Stjepan Vukčić in 1466.
Succession
After the fall of the Bosnian king ...
from 1466 to 1481
Legacy
The historical name of the region is officially represented in the name of the Eparchy of Zahumlje and Herzegovina of theSerbian Orthodox Church
The Serbian Orthodox Church ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Српска православна црква, Srpska pravoslavna crkva) is one of the autocephalous (ecclesiastically independent) Eastern Orthodoxy, Eastern Orthodox Eastern Orthodox Church#Constit ...
. Also, the honorific title ''Grand Voivode
Voivode ( ), also spelled voivod, voievod or voevod and also known as vaivode ( ), voivoda, vojvoda, vaivada or wojewoda, is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe in use since the Early Mid ...
(Duke) of Zahumlije'' has been granted at times to junior members of the Petrović-Njegoš dynasty that ruled in Montenegro
, image_flag = Flag of Montenegro.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Montenegro.svg
, coa_size = 80
, national_motto =
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map = Europe-Mont ...
until 1918. The last grand duke of Zahumlije was Prince Peter of Montenegro, who died in 1932./ref>
See also
*History of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a country in Southeast Europe on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. It has had permanent settlement since the Neolithic, Neolithic Age. By the early historical period it was inhabited by Illyrians and Celts. Christianity arr ...
* History of Dalmatia
* History of Croatia
At the time of the Roman Empire, the area of modern Croatia comprised two Roman provinces, Pannonia and Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia. After the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, the ...
* History of Serbia
The history of Serbia covers the historical development of Serbia and of its predecessor states, from the Early Stone Age to the present state, as well as that of the Serbian people and of the areas they ruled historically. Serbian habitatio ...
References
Footnotes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * John the Deacon, ''Chronicon Venetum'', ed. A later edition is that by G. Monticolo (1890), Rome: Forzani. The relevant passage is also found in * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
{{Authority control Medieval history of the Balkans 1050s disestablishments in Europe States and territories established in the 9th century 9th-century establishments in Europe tr:Hum Prensliği