Youth Side Lock on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The sidelock of youth (also called a Horus lock, Prince's lock, Princess' lock, lock of childhood or side braid) was an identifying characteristic of the
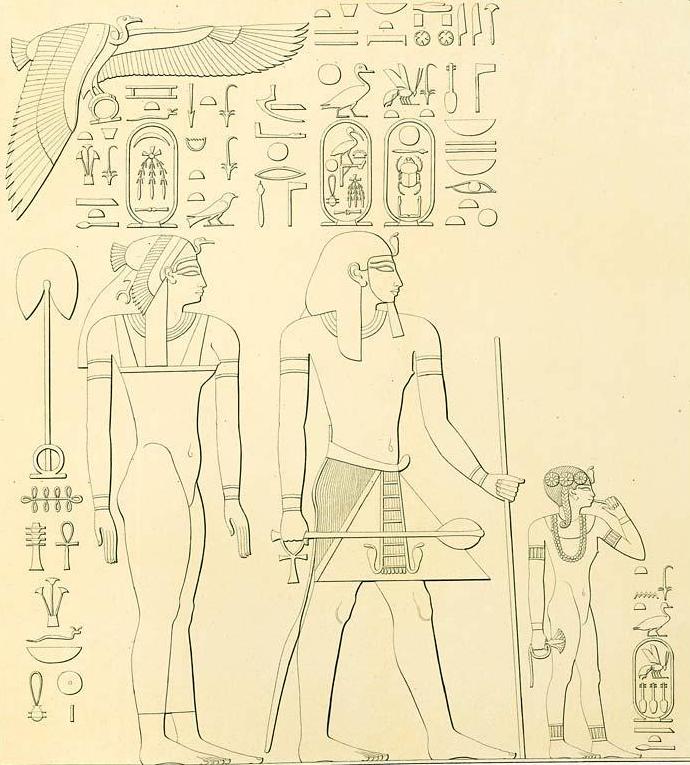 The sidelock of youth was used by the children of the pharaohs, not only to show them to be children, but also to indicate their connection to the youthful
The sidelock of youth was used by the children of the pharaohs, not only to show them to be children, but also to indicate their connection to the youthful
Horus lock on Khaemwaset (Son of Rameses II)
Ancient Egyptian culture Hairstyles
child
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking ...
in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
. It symbolically indicates that the wearer is a legitimate heir of Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wikt:wsjr, wsjr'') was the ancient Egyptian deities, god of fertility, agriculture, the Ancient Egyptian religion#Afterlife, afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was ...
. The sidelock was used as a divine attribute from at least as early as the Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning –2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth Dynast ...
.
In earlier depictions, the sidelock can be seen with short hat-like hairstyles in, for example, mortuary cult
A mortuary cult (also called a funerary cult or death cult) is a ceremonial and religious form of a cult fostered over a certain duration of time, often lasting for generations or even dynasties. It concerns deceased people kept in the memories of ...
s. Later it was usually attached to an almost shoulder-length wig, which was worn in three styles: curled, straight, or in tresses. Based on the connection between sidelocks and children, Egyptologists
This is a partial list of Egyptologists. An Egyptologist is any archaeologist, historian, linguist, or art historian who specializes in Egyptology, the scientific study of Ancient Egypt and its antiquities. Demotists are Egyptologists who speciali ...
coined the term "sidelock of youth". They were worn by both mortal and divine children.
Forms
The name "sidelock of youth" is not entirely accurate, since it is usually abraid
A braid (also referred to as a plait; ) is a complex structure or pattern formed by interlacing three or more strands of flexible material such as textile yarns, wire, or hair.
The simplest and most common version is a flat, solid, three-strand ...
rather than a lock, with its end twisted into a spiral. In Middle Kingdom depictions, the end is rolled to the front.Rolf Gundlach, Matthias Rochholz. ''Ägyptische Tempel'', pp. 304–307 and 310–311.
The sidelock was generally worn on the right. In relief
Relief is a sculpture, sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces remain attached to a solid background of the same material. The term ''wikt:relief, relief'' is from the Latin verb , to raise (). To create a sculpture in relief is to give ...
s it can be depicted on the left or the right, since otherwise the lock would not be visible on a figure in profile facing left. A strand of hair was separated off from the side of the skull, itself further separated into three individual braids. The braided portion was held in place by a clasp at its point of origin.
Thereafter there were several different possibilities, such as the triple braided sidelock, whose three strands converged in a spiral. Only in a few cases was it gathered with a clasp at its point of origin and ended with a spiral but left as a loose lock of hair in between.
Further types of divine sidelock are also known. The Horus
Horus (), also known as Heru, Har, Her, or Hor () in Egyptian language, Ancient Egyptian, is one of the most significant ancient Egyptian deities who served many functions, most notably as the god of kingship, healing, protection, the sun, and t ...
lock, like the sidelock, was braided from three strands of hair, which seem to terminate in a claw-like shape and are connected with the goddess Mafdet
Mafdet (also Mefdet, Maftet) was a goddess in the ancient Egyptian religion. She was often depicted wearing a skin of a cheetah, and protected against the bite of snakes and scorpions. She was part of the pantheon of ancient Egyptian deities tha ...
in Egyptian mythology
Egyptian mythology is the collection of myths from ancient Egypt, which describe the actions of the Egyptian pantheon, Egyptian gods as a means of understanding the world around them. The beliefs that these myths express are an important part ...
.
Mythological significance
 The sidelock of youth was used by the children of the pharaohs, not only to show them to be children, but also to indicate their connection to the youthful
The sidelock of youth was used by the children of the pharaohs, not only to show them to be children, but also to indicate their connection to the youthful Horus
Horus (), also known as Heru, Har, Her, or Hor () in Egyptian language, Ancient Egyptian, is one of the most significant ancient Egyptian deities who served many functions, most notably as the god of kingship, healing, protection, the sun, and t ...
. Like them, the young Horus had worn the sidelock as the heir apparent of his father Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wikt:wsjr, wsjr'') was the ancient Egyptian deities, god of fertility, agriculture, the Ancient Egyptian religion#Afterlife, afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was ...
.
In accordance with the mythological precedent, the children of the king, as his designated heirs, received the Horus lock as an indication of the special duties that were bound up with that status. In iconography, royal children were depicted naked and sucking on their finger, with their heads shaved entirely bald except for the sidelock.
Amenhotep I
Amenhotep I () or Amenophis I ( from Ancient Greek Ἀμένωφις), was the second Pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of Egypt. His reign is generally dated from 1526 to 1506 BC (Low Chronology).
He was a son of Ahmose I and Ahmose-Nefertari but ...
, as well as Thutmoses III, reused the special form of the Middle Kingdom, which is connected with their revival of the imagery of the Middle Kingdom more generally. Again in the Late Period, the Middle Kingdom depiction of the sidelock was revived.
With the beginning of the New Kingdom
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
** "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995
* "New" (Daya song), 2017
* "New" (No Doubt song), 1 ...
, the lock of youth achieved central significance as a special symbol of the princes and princesses of the 18th Dynasty
The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVIII, alternatively 18th Dynasty or Dynasty 18) is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty ...
. Particularly notable is the connection of the lock of youth with princesses, who as children of the reigning king were also seen as probable heirs and therefore were also depicted with the Horus lock.
See also
*Payot
Sidelocks in English, or ''pe'ot'' in Hebrew, English language, anglicized as payot (, "corners") or payes (), is the Hebrew term for sidelocks or sideburns. Payot are worn by some men and boys in the Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jewish community ...
Bibliography
* Erika Feucht. ''Das Kind im Alten Ägypten - Die Stellung des Kindes in Familie und Gesellschaft nach altägyptischen Texten und Darstellungen''. Campus, Frankfurt/Main 1995, . * Victorine von Gonzenbach. ''Untersuchungen zu den Knabenweihen im Isiskult der römischen Kaiserzeit.'' Rudolf Habelt, Bonn 1957. * Rolf Gundlach, Matthias Rochholz. ''Ägyptische Tempel''. Gerstenberg, Hildesheim 1994, .References
{{reflistExternal links
Horus lock on Khaemwaset (Son of Rameses II)
Ancient Egyptian culture Hairstyles