Xenobiotic Metabolism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of
Xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of
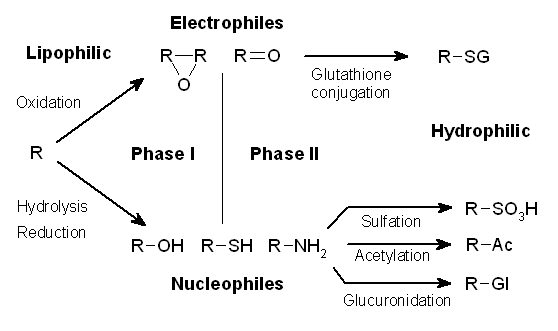 The metabolism of xenobiotics is often divided into three phases: modification, conjugation, and excretion. These reactions act in concert to detoxify xenobiotics and remove them from cells.
The metabolism of xenobiotics is often divided into three phases: modification, conjugation, and excretion. These reactions act in concert to detoxify xenobiotics and remove them from cells.
SPORCalc, an example process for exploring xenobiotic and drug metabolism databases
ref>
Directory of P450-containing SystemsUniversity of Minnesota Biocatalysis/Biodegradation Database
Drug metabolism
Drug metabolism portal
Microbial biodegradation
History
{{DEFAULTSORT:Xenobiotic Metabolism Metabolism
 Xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of
Xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell (biology), cell. The reactants, products, and Metabolic intermediate, intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are ...
s that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotic
A xenobiotic is a chemical substance found within an organism that is not naturally produced or expected to be present within the organism. It can also cover substances that are present in much higher concentrations than are usual. Natural compo ...
s, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as drugs and poisons. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms, and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds; however, in cases such as in the metabolism of alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
, the intermediates in xenobiotic metabolism can themselves be the cause of toxic effects.
Xenobiotic metabolism is divided into three phases. In phase I, enzymes such as cytochrome P450 oxidase
Cytochromes P450 (P450s or CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. However, they are not omnipresent; for example, they have not been found in ''Escherich ...
s introduce reactive or polar groups into xenobiotics. These modified compounds are then conjugated to polar compounds in phase II reactions. These reactions are catalysed by transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups (e.g. a methyl or glycosyl group) from one molecule (called the donor) to another (called the acceptor). They are involved ...
enzymes such as glutathione S-transferase
Glutathione ''S''-transferases (GSTs), previously known as ligandins, are a family of eukaryote, eukaryotic and prokaryote, prokaryotic Biotransformation#Phase II reaction, phase II metabolic isozymes best known for their ability to Catalysis, ...
s. Finally, in phase III, the conjugated xenobiotics may be further processed, before being recognised by efflux transporters and pumped out of cells.
The reactions in these pathways are of particular interest in medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
as part of drug metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set o ...
and as a factor contributing to multidrug resistance
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are ...
in infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
s and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
. The actions of some drugs as substrates or inhibitors of enzymes involved in xenobiotic metabolism are a common reason for hazardous drug interaction In pharmaceutical sciences, drug interactions occur when a drug's mechanism of action is affected by the concomitant administration of substances such as foods, beverages, or other drugs. A popular example of drug–food interaction is the effect ...
s. These pathways are also important in environmental science, with the xenobiotic metabolism of microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s determining whether a pollutant will be broken down during bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, wate ...
, or persist in the environment. The enzymes of xenobiotic metabolism, particularly the glutathione S-transferase
Glutathione ''S''-transferases (GSTs), previously known as ligandins, are a family of eukaryote, eukaryotic and prokaryote, prokaryotic Biotransformation#Phase II reaction, phase II metabolic isozymes best known for their ability to Catalysis, ...
s are also important in agriculture, since they may produce resistance to pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s and herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page f ...
s.
Permeability barriers and detoxification
That the exact compounds an organism is exposed to will be largely unpredictable, and may differ widely over time, is a major characteristic of xenobiotic toxic stress. The major challenge faced by xenobiotic detoxification systems is that they must be able to remove the almost-limitless number of xenobiotic compounds from the complex mixture of chemicals involved in normalmetabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
. The solution that has evolved to address this problem is an elegant combination of physical barriers and low-specificity enzymatic systems.
All organisms use cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
s as hydrophobic permeability barriers to control access to their internal environment. Polar compounds cannot diffuse across these cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
s, and the uptake of useful molecules is mediated through transport protein
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein that serves the function of moving other materials within ...
s that specifically select substrates from the extracellular mixture. This selective uptake means that most hydrophilic
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
In contrast, hydrophobes are n ...
molecules cannot enter cells, since they are not recognised by any specific transporters. In contrast, the diffusion of hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
compounds across these barriers cannot be controlled, and organisms, therefore, cannot exclude lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
-soluble xenobiotics using membrane barriers.
However, the existence of a permeability barrier means that organisms were able to evolve detoxification systems that exploit the hydrophobicity common to membrane-permeable xenobiotics. These systems therefore solve the specificity problem by possessing such broad substrate specificities that they metabolise almost any non-polar compound. Useful metabolites are excluded since they are polar, and in general contain one or more charged groups.
The detoxification of the reactive by-products of normal metabolism cannot be achieved by the systems outlined above, because these species are derived from normal cellular constituents and usually share their polar characteristics. However, since these compounds are few in number, specific enzymes can recognize and remove them. Examples of these specific detoxification systems are the glyoxalase system
The glyoxalase system is a set of enzymes that carry out the detoxification of methylglyoxal and the other reactive aldehydes that are produced as a normal part of metabolism. This system has been studied in both bacteria and eukaryotes. This detox ...
, which removes the reactive aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred ...
methylglyoxal, and the various antioxidant systems that eliminate reactive oxygen species.
Phases of detoxification
 The metabolism of xenobiotics is often divided into three phases: modification, conjugation, and excretion. These reactions act in concert to detoxify xenobiotics and remove them from cells.
The metabolism of xenobiotics is often divided into three phases: modification, conjugation, and excretion. These reactions act in concert to detoxify xenobiotics and remove them from cells.
Phase I - modification
In phase I, a variety of enzymes acts to introduce reactive and polar groups into their substrates. One of the most common modifications is hydroxylation catalysed by the cytochrome P-450-dependent mixed-function oxidase system. These enzyme complexes act to incorporate an atom of oxygen into nonactivated hydrocarbons, which can result in either the introduction of hydroxyl groups or N-, O- and S-dealkylation of substrates. The reaction mechanism of the P-450 oxidases proceeds through the reduction of cytochrome-bound oxygen and the generation of a highly-reactive oxyferryl species, according to the following scheme:Phase II - conjugation
In subsequent phase II reactions, these activated xenobiotic metabolites are conjugated with charged species such asglutathione
Glutathione (GSH, ) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources ...
(GSH), sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many ...
, glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
, or glucuronic acid
Glucuronic acid (GCA, from ) is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine (hence the name "uronic acid"). It is found in many natural gum, gums such as gum arabic ( 18%), xanthan, and kombucha tea and is important for the metabolism of ...
. These reactions are catalysed by a large group of broad-specificity transferases, which in combination can metabolise almost any hydrophobic compound that contains nucleophilic or electrophilic groups. One of the most important of these groups are the glutathione S-transferase
Glutathione ''S''-transferases (GSTs), previously known as ligandins, are a family of eukaryote, eukaryotic and prokaryote, prokaryotic Biotransformation#Phase II reaction, phase II metabolic isozymes best known for their ability to Catalysis, ...
s (GSTs). The addition of large anionic groups (such as GSH) detoxifies reactive electrophile
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively Electric charge, charged, have an ...
s and produces more polar metabolites that cannot diffuse across membranes, and may, therefore, be actively transported.
Phase III - further modification and excretion
After phase II reactions, the xenobiotic conjugates may be further metabolised. A common example is the processing of glutathione conjugates to acetylcysteine ( mercapturic acid) conjugates. Here, the γ-glutamate andglycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
residues in the glutathione molecule are removed by Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Gamma-glutamyltransferase (also γ-glutamyltransferase, GGT, gamma-GT, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; ) is a transferase (a type of enzyme) that catalyzes the transfer of gamma- glutamyl functional groups from molecules such as glutathion ...
and dipeptidases. In the final step, the cystine
Cystine is the oxidized derivative of the amino acid cysteine and has the formula (SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H)2. It is a white solid that is poorly soluble in water. As a residue in proteins, cystine serves two functions: a site of redox reactions and a mec ...
residue in the conjugate is acetylated.
Conjugates and their metabolites can be excreted from cells in phase III of their metabolism, with the anionic groups acting as affinity tags for a variety of membrane transporters of the multidrug resistance protein (MRP) family. These proteins are members of the family of ATP-binding cassette transporter
The ABC transporters, ATP synthase (ATP)-binding cassette transporters are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene family, gene families. It is represented in all extant taxon, extant Phyl ...
s and can catalyse the ATP-dependent transport of a huge variety of hydrophobic anions, and thus act to remove phase II products to the extracellular medium, where they may be further metabolised or excreted.
Endogenous toxins
The detoxification of endogenous reactive metabolites such asperoxide
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of Chemical compound, compounds with the structure , where the R's represent a radical (a portion of a complete molecule; not necessarily a free radical) and O's are single oxygen atoms. Oxygen atoms are joined ...
s and reactive aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred ...
s often cannot be achieved by the system described above. This is the result of these species' being derived from normal cellular constituents and usually sharing their polar characteristics. However, since these compounds are few in number, it is possible for enzymatic systems to utilize specific molecular recognition to recognize and remove them. The similarity of these molecules to useful metabolites therefore means that different detoxification enzymes are usually required for the metabolism of each group of endogenous toxins. Examples of these specific detoxification systems are the glyoxalase system
The glyoxalase system is a set of enzymes that carry out the detoxification of methylglyoxal and the other reactive aldehydes that are produced as a normal part of metabolism. This system has been studied in both bacteria and eukaryotes. This detox ...
, which acts to dispose of the reactive aldehyde methylglyoxal
Methylglyoxal (MGO) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CHO. It is a reduced derivative of pyruvic acid. It is a reactive compound that is implicated in the biology of diabetes. Methylglyoxal is produced industrially by degradation ...
, and the various antioxidant
Antioxidants are Chemical compound, compounds that inhibit Redox, oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce Radical (chemistry), free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants ...
systems that remove reactive oxygen species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl ...
.
History
Studies on how people transform the substances that they ingest began in the mid-nineteenth century, with chemists discovering that organic chemicals such asbenzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is among the simplest aromatic aldehydes and one of the most industrially useful.
It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic almond-li ...
could be oxidized and conjugated to amino acids in the human body. During the remainder of the nineteenth century, several other basic detoxification reactions were discovered, such as methylation
Methylation, in the chemistry, chemical sciences, is the addition of a methyl group on a substrate (chemistry), substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replac ...
, acetylation
:
In chemistry, acetylation is an organic esterification reaction with acetic acid. It introduces an acetyl group into a chemical compound. Such compounds are termed ''acetate esters'' or simply ''acetates''. Deacetylation is the opposite react ...
, and sulfonation
In organic chemistry, aromatic sulfonation is a reaction in which a hydrogen atom on an arene is replaced by a sulfonic acid () group. Together with nitration and chlorination, aromatic sulfonation is a widely used electrophilic aromatic substi ...
.
In the early twentieth century, work moved on to the investigation of the enzymes and pathways that were responsible for the production of these metabolites. This field became defined as a separate area of study with the publication by Richard Williams of the book ''Detoxication mechanisms'' in 1947. This modern biochemical research resulted in the identification of glutathione ''S''-transferases in 1961, followed by the discovery of cytochrome P450s in 1962, and the realization of their central role in xenobiotic metabolism in 1963.
See also
*Drug design
Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the invention, inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic compound, organi ...
* Drug metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set o ...
* Microbial biodegradation
* Biodegradation
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegrada ...
* Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, wate ...
* Antioxidant
Antioxidants are Chemical compound, compounds that inhibit Redox, oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce Radical (chemistry), free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants ...
SPORCalc, an example process for exploring xenobiotic and drug metabolism databases
ref>
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
Databases *Directory of P450-containing Systems
Drug metabolism
Microbial biodegradation
History
{{DEFAULTSORT:Xenobiotic Metabolism Metabolism