XX Trianguli on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
XX Trianguli, abbreviated XX Tri, is a 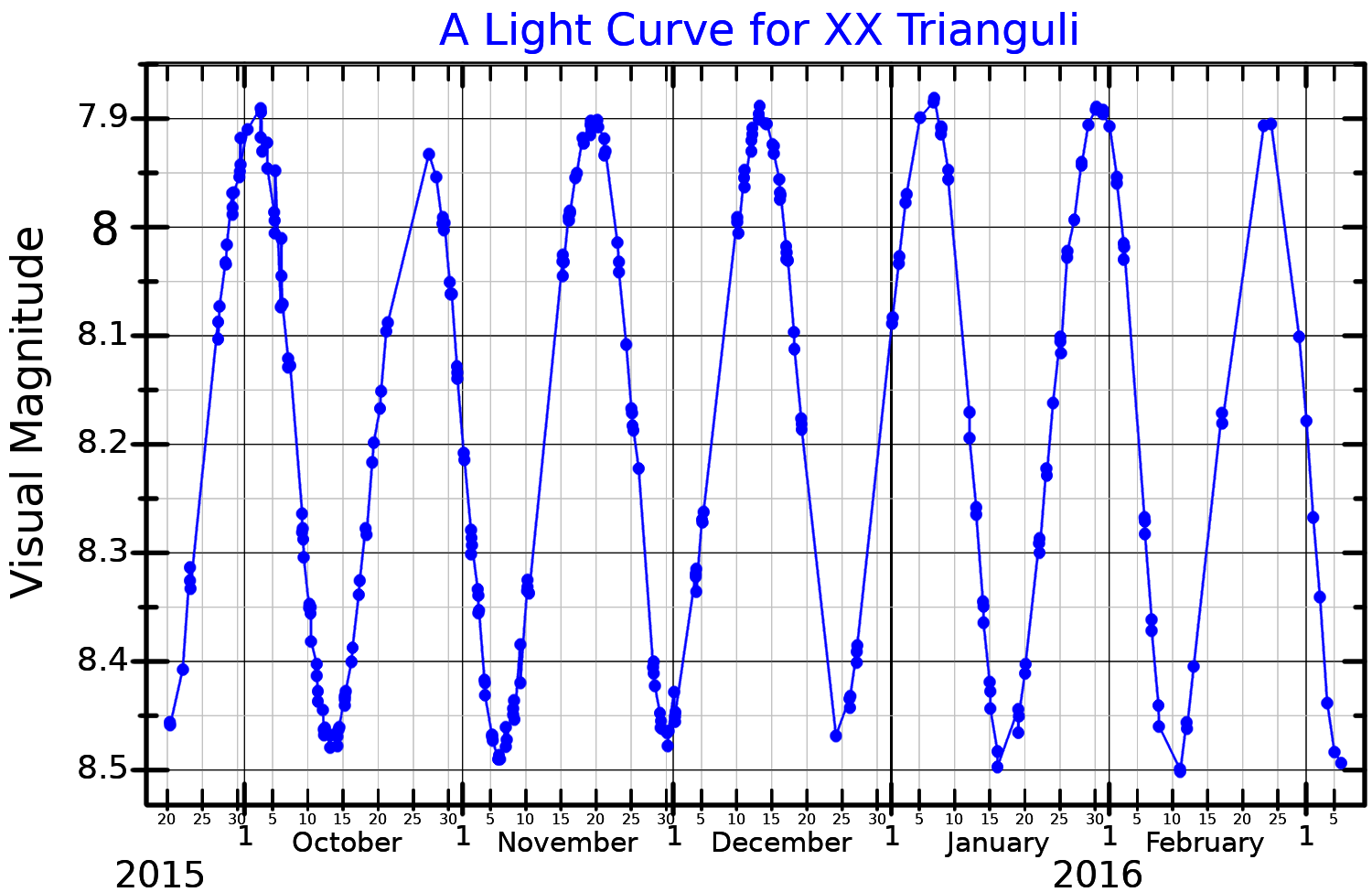 This is a single-lined
This is a single-lined
variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are ...
in the northern constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
of Triangulum
Triangulum is a small constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for "triangle", derived from its three brightest stars, which form a long and narrow triangle. Known to the ancient Babylonians and Greeks, Triangulum was one of the 48 ...
, about 1.5° to the WNW of Beta Trianguli
Beta Trianguli (Beta Tri, β Trianguli, β Tri) is the Bayer designation for a binary star system in the constellation Triangulum, located about 127 light years from Earth. Although it is only a third-magnitude star, ...
along the constellation border with Andromeda. It is classified as a RS Canum Venaticorum variable An RS Canum Venaticorum variable is a type of variable star. The variable type consists of close binary stars having active chromospheres which can cause large stellar spots. These spots are believed to cause variations in their observed luminosity. ...
and ranges in brightness from magnitude 8.1 down to 8.7, which is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. The system is located at a distance of approximately 642 light year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year (ly or lyr), is a unit of length used to express astronomical distance, astronomical distances and is equal to exactly , which is approximately 9.46 trillion km or 5.88 trillion mi. As defined by t ...
s from the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
based on parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different sightline, lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to perspective (graphica ...
, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity of a target with respect to an observer is the rate of change of the vector displacement between the two points. It is formulated as the vector projection of the target-observer relative velocity ...
of −26 km/s.
 This is a single-lined
This is a single-lined spectroscopic binary
A binary star or binary star system is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved as separate stars us ...
with an orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
of 23.96924 days. The visible component is an orange-hued K-type giant star
A giant star has a substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same surface temperature. They lie above the main sequence (luminosity class V in the Yerkes spectral classification) on the Hertzsp ...
with a stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction gratin ...
of K0 III, indicating it has exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core
Core or cores may refer to:
Science and technology
* Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages
* Core (laboratory), a highly specialized shared research resource
* Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding
* Core (optical fiber ...
then cooled and expanded off the main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color index, color versus absolute magnitude, brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or d ...
. It is around eight billion years old with 26% more mass than the Sun and has expanded to 11 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating roughly 30 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will esc ...
at an effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
of 4,620 K.
The star is "covered with large high-latitude and even polar spots
Spot or SPOT may refer to:
Places
* Spot, North Carolina, a community in the United States
* The Spot, New South Wales, a locality in Sydney, Australia
* South Pole Traverse, sometimes called the South Pole Overland Traverse
People
* Spot Col ...
and with occasional small equatorial spots". XX Tri is notable for having a huge starspot
Starspots are stellar phenomena, so-named by analogy with sunspots.
Spots as small as sunspots have not been detected on other stars, as they would cause undetectably small fluctuations in brightness. The commonly observed starspots are in gene ...
larger than the diameter of the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
, discovered using Doppler imaging
Inhomogeneous structures on stellar surfaces, i.e. temperature differences, chemical composition or magnetic fields, create characteristic distortions in the spectral lines due to the Doppler effect. These distortions will move across spectral lin ...
. For its size, the star has a rapid rotation rate of about 24 days. It has a weak, Sun-like differential rotation
Differential rotation is seen when different parts of a rotating object move with different angular velocities (or rates of rotation) at different latitudes and/or depths of the body and/or in time. This indicates that the object is not rigi ...
. The star appears to show a magnetic activity
A stellar magnetic field is a magnetic field generated by the motion of conductive Plasma (physics), plasma inside a star. This motion is created through convection, which is a form of energy transport involving the physical movement of material ...
cycle of , although only a single cycle has been observed as of 2015.
In a more recent study, the authors used more than 2,000 high-resolution spectra collected over 16 years with the STELLA robotic telescopes in Tenerife, an unprecedented amount of homogeneous spectroscopic data from a star. From the data, 99 time-series Doppler images were reconstructed, showing the spot evolution on the stellar surface between 2006 and 2022. One of the main findings of the study is that the surface changes of XX Tri do not show Sun-like magnetic cycles, based on which the authors conclude that the star's dynamo is non-periodic in nature, most likely chaotic.
This study is the first to demonstrate how the huge starspots cause a tiny displacement of XX Tri in the sky, which appears virtually as a point source when observed from Earth. The reason for this is that while the photocenter of a homogeneous (=unspotted) stellar disk is the same as the geometric center of the star, huge starspots on the stellar disk repel the photocenter in the opposite direction to the spots. In the case of XX Tri, which is 630 light-years away, the photocenter of the stellar disk can shift by up to 10% of the star's radius relative to the geometric center, causing an apparent displacement of 24 micro-arcseconds in the celestial position of the star (the diameter of a hair at a distance of 1000 km). This is similar to the expected astrometric displacement caused by a Saturn-mass planet in a one year orbit around a Sun at about 300 lightyears distance. Therefore, separating the effects of spots and exoplanets seems very challenging, if not impossible, in particular in cases of similar periodicity, the study concludes.
References
{{Sky, 02, 03, 47, , 35, 35, 28 K-type giants RS Canum Venaticorum variables Spectroscopic binaries Triangulum BD+34 0363 3130 012545 009630 Trianguli, XX