White House on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The White House is the
The White House is the
 President Washington visited
President Washington visited
 The White House is the
The White House is the official residence
An official is someone who holds an office (function or mandate, regardless of whether it carries an actual working space with it) in an organization or government and participates in the exercise of authority (either their own or that of th ...
and workplace of the president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue
Pennsylvania Avenue is a primarily diagonal street in Washington, D.C. that connects the United States Capitol with the White House and then crosses northwest Washington, D.C. to Georgetown (Washington, D.C.), Georgetown. Traveling through So ...
NW in Washington, D.C., it has served as the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before Presidency of John Adams, his presidency, he was a leader of ...
in 1800 when the national capital was moved from Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
. "The White House" is also used as a metonym
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something associated with that thing or concept. For example, the word "wikt:suit, suit" may refer to a person from groups commonly wearing business attire, such ...
to refer to the Executive Office of the President of the United States
The Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP) comprises the offices and agencies that support the work of the president at the center of the executive branch of the United States federal government. The office consists o ...
.
The residence was designed by Irish-born architect James Hoban in the Neoclassical style. Hoban modeled the building on Leinster House in Dublin, a building which today houses the Oireachtas
The Oireachtas ( ; ), sometimes referred to as Oireachtas Éireann, is the Bicameralism, bicameral parliament of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The Oireachtas consists of the president of Ireland and the two houses of the Oireachtas (): a house ...
, the Irish legislature. Constructed between 1792 and 1800, its exterior walls are Aquia Creek sandstone painted white. When Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
moved into the house in 1801, he and architect Benjamin Henry Latrobe
Benjamin Henry Boneval Latrobe (May 1, 1764 – September 3, 1820) was a British-American Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical architect who immigrated to the United States. He was one of the first formally trained, professional architects in ...
added low colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or curv ...
s on each wing to conceal what then were stables and storage. In 1814, during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
, the mansion was set ablaze by British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
forces in the burning of Washington, destroying the interior and charring much of the exterior. Reconstruction began almost immediately, and President James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American Founding Father of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. He was the last Founding Father to serve as presiden ...
moved into the partially reconstructed Executive Residence in October 1817. Exterior construction continued with the addition of the semicircular South Portico in 1824 and the North Portico in 1829.
Because of crowding within the executive mansion itself, President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
had all work offices relocated to the newly constructed West Wing in 1901. Eight years later, in 1909, President William Howard Taft
William Howard Taft (September 15, 1857March 8, 1930) served as the 27th president of the United States from 1909 to 1913 and the tenth chief justice of the United States from 1921 to 1930. He is the only person to have held both offices. ...
expanded the West Wing and created the first Oval Office
The Oval Office is the formal working space of the president of the United States. Part of the Executive Office of the President of the United States, it is in the West Wing of the White House, in Washington, D.C.
The oval room has three lar ...
, which was eventually moved and expanded. In the Executive Residence, the third floor attic was converted to living quarters in 1927 by augmenting the existing hip roof with long shed dormers. A newly constructed East Wing was used as a reception area for social events; Jefferson's colonnades connected the new wings. The East Wing alterations were completed in 1946, creating additional office space. By 1948, the residence's load-bearing walls and wood beams were found to be close to failure. Under Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. As the 34th vice president in 1945, he assumed the presidency upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt that year. Subsequen ...
, the interior rooms were completely dismantled and a new internal load-bearing steel frame
Steel frame is a building technique with a "skeleton frame" of vertical steel columns and horizontal I-beams, constructed in a rectangular grid to support the floors, roof and walls of a building which are all attached to the frame. The develop ...
was constructed inside the walls. On the exterior, the Truman Balcony was added. Once the structural work was completed, the interior rooms were rebuilt.
The present-day White House complex includes the Executive Residence, the West Wing, the East Wing, the Eisenhower Executive Office Building
The Eisenhower Executive Office Building (EEOB), formerly known as the Old Executive Office Building (OEOB), and originally known as the State, War, and Navy Building (SWAN Building), is a Federal government of the United States, United States ...
, which previously served the State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or simply the State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs o ...
and other departments (it now houses additional offices for the president's staff and the vice president), and Blair House, a guest residence. The Executive Residence is made up of six stories: the Ground Floor, State Floor, Second Floor, and Third Floor, and a two-story basement
A basement is any Storey, floor of a building that is not above the grade plane. Especially in residential buildings, it often is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the Furnace (house heating), furnace, water heating, ...
. The property is a National Heritage Site owned by the National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government, within the US Department of the Interior. The service manages all List ...
and is part of President's Park. In 2007, it was ranked second on the American Institute of Architects
The American Institute of Architects (AIA) is a professional organization for architects in the United States. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C. AIA offers education, government advocacy, community redevelopment, and public outreach progr ...
list of America's Favorite Architecture.
Early history
1789–1800
Following his inauguration on April 30, 1789, PresidentGeorge Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
occupied two private houses in New York City, which served as the nation's first executive mansion. He lived at the first, Walter Franklin House, which was owned by Treasury Commissioner Samuel Osgood, at 3Cherry Street, through late February 1790. The executive mansion moved to the larger quarters at Alexander Macomb House at 39–41 Broadway, where Washington stayed with his wife Martha and a small staff until August 1790. In May 1790, construction began on Government House, a new official residence in Manhattan
Manhattan ( ) is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City. Coextensive with New York County, Manhattan is the County statistics of the United States#Smallest, larg ...
.
Washington, however, never lived at Government House since the national capital was moved to Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
in 1790, where it remained through 1800. The July 1790 Residence Act designated the capital be permanently located in the new Federal District
A federal district is a specific administrative division in one of various federations. These districts may be under the direct jurisdiction of a federation's national government, as in the case of federal territory (e.g., India, Malaysia), or the ...
, and temporarily in Philadelphia for ten years while the permanent capital was built. Philadelphia rented the mansion of Robert Morris, a merchant, at 190 High Street, now 524–30 Market Street, as the President's House, which Washington occupied from November 1790 to March 1797. Since the house was too small to accommodate the 30 people who then made up the presidential family, staff, and servants, Washington had the house enlarged.
President John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before Presidency of John Adams, his presidency, he was a leader of ...
, who succeeded Washington and served as the nation's second president, occupied the High Street mansion in Philadelphia from March 1797 to May 1800. Philadelphia began construction of a much grander presidential mansion several blocks away in 1792. It was nearly completed by the time of Adams' 1797 inauguration. However, Adams chose not to occupy it, saying he did not have Congressional authorization to lease the building. It remained vacant until 1800 when it was sold to the University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (Penn or UPenn) is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. One of nine colonial colleges, it was chartered in 1755 through the efforts of f ...
.
On Saturday, November 1, 1800, Adams became the first president to occupy the White House. President's House in Philadelphia was converted into Union Hotel and then used for stores before being demolished in 1832.
Architectural competition
The President's House was a major feature of Pierre (Peter) Charles L'Enfant's 1791plan
A plan is typically any diagram or list of steps with details of timing and resources, used to achieve an Goal, objective to do something. It is commonly understood as a modal logic, temporal set (mathematics), set of intended actions through wh ...
for the newly established federal city of Washington, D.C. After L'Enfant's dismissal in early 1792, Washington and his Secretary of State, Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
, who both had personal interests in architecture, agreed that the design of the President's House and the Capitol would be chosen in a design competition.
Nine proposals were submitted for the new presidential residence with the award going to Irish-American architect James Hoban. Hoban supervised the construction of both the U.S. Capitol and the White House. Hoban was born in Ireland and trained at the Dublin Society of Arts. He emigrated to the U.S. after the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
, first seeking work in Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
and later finding success in South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, where he designed the state capitol in Columbia.
 President Washington visited
President Washington visited Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the List of municipalities in South Carolina, most populous city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint of South Carolina's coastline on Charleston Harbor, an inlet of the Atla ...
, in May 1791 on his Southern Tour, and saw the Charleston County Courthouse then under construction, which had been designed by Hoban. Washington is reputed to have met with Hoban during the visit. The following year, Washington summoned the architect to Philadelphia and met with him in June 1792.
On July 16, 1792, the president met with the commissioners of the federal city to make his judgment in the architectural competition. His review is recorded as being brief, and he quickly selected Hoban's submission.
Design influences
The Neoclassical design of the White House is based primarily on architectural concepts inherited from the Roman architectVitruvius
Vitruvius ( ; ; –70 BC – after ) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled . As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissan ...
and the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio. The design of the upper floors also includes elements based on Dublin's Leinster House, which later became the seat of the Irish parliament (Oireachtas
The Oireachtas ( ; ), sometimes referred to as Oireachtas Éireann, is the Bicameralism, bicameral parliament of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The Oireachtas consists of the president of Ireland and the two houses of the Oireachtas (): a house ...
). The upper windows with alternate triangular and segmented pediments are inspired by the Irish building. Additionally, several Georgian-era Irish country houses have been suggested as sources of inspiration for the overall floor plan, including the bow-fronted south front and the former niches in the present-day Blue Room.
The first official White House guide, published in 1962, suggested a link between Hoban's design for the South Portico and Château de Rastignac, a neoclassical country house in La Bachellerie in the Dordogne
Dordogne ( , or ; ; ) is a large rural departments of France, department in south west France, with its Prefectures in France, prefecture in Périgueux. Located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region roughly half-way between the Loire Valley and ...
region of France. Construction on the French house was initially started before 1789, interrupted by the French Revolution for 20 years, and then finally built between 1812 and 1817 based on Salat's pre-1789 design.
The conceptual link between the two houses has been criticized because Hoban did not visit France. Supporters of the connection contend that Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
, during his tour of Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in F ...
in 1789, viewed Salat's architectural drawings, which were on file at École Spéciale d'Architecture. On his return to the U.S., Jefferson then shared the influence with Washington, Hoban, Monroe, and Benjamin Henry Latrobe
Benjamin Henry Boneval Latrobe (May 1, 1764 – September 3, 1820) was a British-American Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical architect who immigrated to the United States. He was one of the first formally trained, professional architects in ...
.
Construction
Construction of the White House began at noon on October 13, 1792, with the laying of the cornerstone. The main residence and foundations of the house were built largely by employedEuropeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common ancestry, language, faith, historical continuity, etc. There are ...
, whilst enslaved African-Americans quarried stone used in the construction. Much of the other work on the house was done by immigrants, many of whom had not yet obtained citizenship, including the sandstone walls, which were erected by Scottish masons, the high-relief rose, and garland decorations above the north entrance and the fish scale pattern beneath the pediments of the window hoods.
There are conflicting claims as to where the sandstone used in the construction of the White House originated. Some reports suggest sandstone from the Croatian island of Brač
Brač is a Croatian island in the Adriatic Sea, with an area of ,
making it the largest island in Dalmatia, and the third largest in the Adriatic. It is separated from the mainland by the Brač Channel, which is wide.Pučišća quarry whose stone was used to build the ancient Diocletian's Palace in Split, was used in the building's original construction. However, researchers believe limestone from the island was used in the 1902 renovations and not the original construction. Others suggest the original sandstone simply came from Aquia Creek in Stafford County, Virginia, since importation of the stone at the time would have proved too costly. The initial construction took place over a period of eight years at a reported cost of $232,371.83 (). Although not yet completed, the White House was ready for occupancy circa November 1, 1800.
Pierre L'Enfant's plan for a grand palace was five times larger than the house that was eventually built. Due in part to material and labor shortages, the finished structure contained only two main floors instead of the planned three, and a less costly brick served as a lining for the stone façades. When construction was finished, the porous sandstone walls were
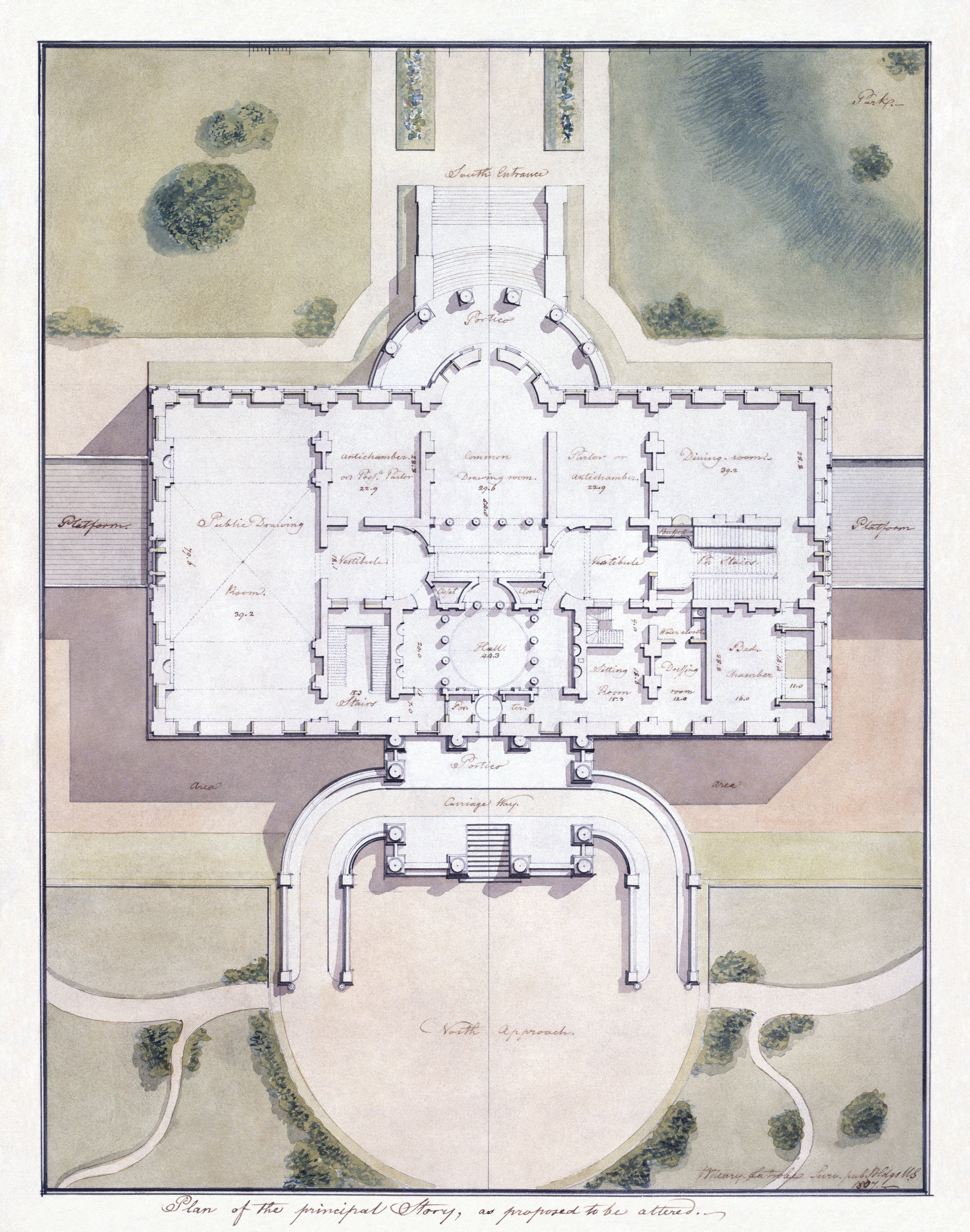 The main entrance is located on the north façade under a porte cochere with Ionic columns. The ground floor is hidden by a raised carriage ramp and
The main entrance is located on the north façade under a porte cochere with Ionic columns. The ground floor is hidden by a raised carriage ramp and
 By the time of the
By the time of the
 Decades of poor maintenance, the construction of a fourth-story attic during the Coolidge administration, and the addition of a second-floor balcony over the south portico for
Decades of poor maintenance, the construction of a fourth-story attic during the Coolidge administration, and the addition of a second-floor balcony over the south portico for

 The original residence is in the center. Two
The original residence is in the center. Two
File:WhSouthLawn.JPEG, Marine One prepares to land on the South Lawn, where State Arrival Ceremonies are held.
File:White House, Blue Sky.jpg, A view from the south, with the south fountain
File:1122-WAS-The White House.JPG, A view from the north, with the north fountain

 On May 20, 1995, primarily as a response to the
On May 20, 1995, primarily as a response to the
File:The First Presidential Mansion.jpg, The first presidential mansion, Samuel Osgood House in
The White House Historical Association
with historical photos, online tours and exhibits, timelines, and facts
part of the
The White House Museum
a detailed online tour *
of White House and grounds * Video tours: ** ** ** *
Virtual tour of the White House
provided by Google Arts & Culture {{Portal bar, Architecture, National Register of Historic Places, Politics, United States 1800 establishments in Washington, D.C. Buildings and structures in the United States destroyed by arson Buildings of the United States government in Washington, D.C. Burned houses in the United States Federal architecture in Washington, D.C. Historic house museums in Washington, D.C. Homes of United States Founding Fathers Houses completed in 1800 Houses on the National Register of Historic Places in Washington, D.C. James Hoban buildings National Historic Landmarks in Washington, D.C. Neoclassical architecture in Washington, D.C. Pennsylvania Avenue Presidential homes in the United States Presidential museums in Washington, D.C. Presidential residences in the United States President's Park Rebuilt buildings and structures in the United States Reportedly haunted houses Reportedly haunted locations in Washington, D.C. War of 1812 sites Neoclassical palaces
whitewash
Whitewash, calcimine, kalsomine, calsomine, asbestis or lime paint is a type of paint made from slaked lime ( calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2) or chalk (calcium carbonate, CaCO3), sometimes known as "whiting". Various other additives are sometimes ...
ed with a mixture of lime, rice glue, casein, and lead, giving the house its familiar color and name.
Architectural description
 The main entrance is located on the north façade under a porte cochere with Ionic columns. The ground floor is hidden by a raised carriage ramp and
The main entrance is located on the north façade under a porte cochere with Ionic columns. The ground floor is hidden by a raised carriage ramp and parapet
A parapet is a barrier that is an upward extension of a wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/brea ...
. The central three bays are situated behind a prostyle portico that was added . The windows of the four bays flanking the portico, at first-floor level, have alternating pointed and segmented pediment
Pediments are a form of gable in classical architecture, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the cornice (an elaborated lintel), or entablature if supported by columns.Summerson, 130 In an ...
s, while the second-floor pediments are flat. A lunette
A lunette (French ''lunette'', 'little moon') is a crescent- or half-moon–shaped or semi-circular architectural space or feature, variously filled with sculpture, painted, glazed, filled with recessed masonry, or void.
A lunette may also be ...
fanlight
A fanlight is a form of lunette window (transom window), often semicircular or semi-elliptical in shape, with glazing (window), glazing bars or tracery sets radiating out like an open Hand fan, fan. It is placed over another window or a doorway, ...
and a sculpted floral festoon surmount the entrance. The roofline is hidden by a balustraded parapet
A parapet is a barrier that is an upward extension of a wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/brea ...
.
The three-level southern façade combines Palladian and neoclassical architectural styles. The ground floor is rusticated in the Palladian fashion. The south portico was completed in 1824. At the center of the southern façade is a neoclassical projected bow of three bays. The bow is flanked by five bays, the windows of which, as on the north façade, have alternating segmented and pointed pediments at first-floor level. The bow has a ground-floor double staircase leading to an Ionic colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or curv ...
d loggia and the Truman Balcony, built in 1946. The more modern third floor is hidden by a balustraded parapet and plays no part in the composition of the façade.
Naming conventions
The building was originally variously referred to as the President's Palace, Presidential Mansion, or President's House. The earliest evidence of the public calling it the "White House" was recorded in 1811. A myth emerged that during the rebuilding of the structure after the Burning of Washington, white paint was applied to mask the burn damage it had suffered, giving the building its namesake hue. The name "Executive Mansion" was used in official contexts until PresidentTheodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
established "The White House" as its formal name in 1901 via Executive Order. The current letterhead wording and arrangement of "The White House" with the word "Washington" centered beneath it dates to the administration of Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
.
Although the structure was not completed until some years after the presidency of George Washington, there is speculation that the name of the traditional residence of the president of the United States may have been derived from Martha Washington's home, White House Plantation, in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, where the nation's first president courted the first lady in the mid-18th century.
Evolution of the White House
Early use, 1814 burning, and reconstruction
On Saturday, November 1, 1800,John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before Presidency of John Adams, his presidency, he was a leader of ...
, who was residing at President's House in Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, the national capital from 1790 to 1800, became the first president to take residence in the building. The next day he wrote his wife Abigail:
"I pray Heaven to bestow the best of blessings on this House, and all that shall hereafter inhabit it. May none but honest and wise men ever rule under this roof."
President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
had Adams's blessing carved into the mantel in the State Dining Room.
Adams lived in the house only briefly before Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
moved into the "pleasant country residence" in 1801. Despite his complaints that the house was too big ("big enough for two emperors, one pope, and the grand lama in the bargain"), Jefferson considered how the White House might be expanded and improved. With Benjamin Henry Latrobe
Benjamin Henry Boneval Latrobe (May 1, 1764 – September 3, 1820) was a British-American Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical architect who immigrated to the United States. He was one of the first formally trained, professional architects in ...
, he helped lay out the design for the East and West Colonnades, small wings that helped conceal the domestic operations of laundry, a stable and storage. Today, Jefferson's colonnades link the residence with the East and West Wings.
On August 24, 1814, during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
, the White House was burned by British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
forces during the Burning of Washington, in retaliation for acts of destruction by American troops in the Canadas; much of Washington was affected by these fires as well. Only the exterior walls remained, and they had to be torn down and mostly reconstructed because of weakening from the fire and subsequent exposure to the elements, except for portions of the south wall. Of the numerous objects taken from the White House when it was sacked by the British, only three have been recovered.
White House employees and slaves rescued a copy of the Lansdowne portrait, and in 1939 a Canadian man returned a jewelry box to President Franklin Roosevelt, claiming that his grandfather had taken it from Washington; in the same year, a medicine chest that had belonged to President Madison was returned by the descendants of a Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
officer. Some observers allege that most of the spoils of war taken during the sack were lost when a convoy of British ships led by HMS ''Fantome'' sank en route to Halifax off Prospect during a storm on the night of November 24, 1814, even though ''Fantome'' had no involvement in that action.
After the fire, President James Madison
James Madison (June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison was popularly acclaimed as the ...
resided in the Octagon House from 1814 to 1815, and then in the Seven Buildings from 1815 to the end of his term. Meanwhile, both Hoban and Latrobe contributed to the design and oversight of the reconstruction, which lasted from 1815 until 1817. The south portico was constructed in 1824 during the James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American Founding Father of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. He was the last Founding Father to serve as presiden ...
administration. The north portico was built in 1830. Though Latrobe proposed similar porticos before the fire in 1814, both porticos were built as designed by Hoban. An elliptical portico at Château de Rastignac in La Bachellerie, France, with nearly identical curved stairs, is speculated as the source of inspiration due to its similarity with the South Portico, although this matter is one of great debate.
Italian artisans, brought to Washington to help in constructing the U.S. Capitol, carved the decorative stonework on both porticos. Contrary to speculation, the North Portico was not modeled on a similar portico on another Dublin building, the Viceregal Lodge (now ''Áras an Uachtaráin'', residence of the president of Ireland
The president of Ireland () is the head of state of Republic of Ireland, Ireland and the supreme commander of the Defence Forces (Ireland), Irish Defence Forces. The presidency is a predominantly figurehead, ceremonial institution, serving as ...
), for its portico postdates the White House porticos' design. For the North Portico, a variation on the Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic classical order, orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric order, Doric and the Corinthian order, Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan order, Tuscan (a plainer Doric) ...
was devised, incorporating a swag of roses between the volutes. This was done to link the new portico with the earlier carved roses above the entrance.
Overcrowding and building the West Wing
 By the time of the
By the time of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, the White House had become overcrowded. The location of the White House, just north of a canal and swampy lands, which provided conditions ripe for malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
and other unhealthy conditions, was questioned. Brigadier General Nathaniel Michler was tasked with proposing solutions to address these concerns. He proposed abandoning the use of the White House as a residence, and he designed a new estate for the first family at Meridian Hill in Washington, D.C. Congress, however, rejected the plan. Another option was Metropolis View, which is now the campus of The Catholic University of America.
When Chester A. Arthur took office in 1881, he ordered renovations to the White House to take place as soon as the recently widowed Lucretia Garfield moved out. Arthur inspected the work almost nightly and made several suggestions. Louis Comfort Tiffany was asked to send selected designers to assist. Over twenty wagonloads of furniture and household items were removed from the building and sold at a public auction. All that was saved were bust portraits of John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before Presidency of John Adams, his presidency, he was a leader of ...
and Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren ( ; ; December 5, 1782 – July 24, 1862) was the eighth president of the United States, serving from 1837 to 1841. A primary founder of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, he served as Attorney General o ...
. A proposal was made to build a new residence south of the White House, but it failed to gain support.
In the fall of 1882, work was done on the main corridor, including tinting the walls pale olive and adding squares of gold leaf, and decorating the ceiling in gold and silver, with colorful traceries woven to spell "USA". The Red Room was painted a dull Pomeranian red, and its ceiling was decorated with gold, silver, and copper stars and stripes of red, white, and blue. A fifty-foot jeweled Tiffany glass screen, supported by imitation marble columns, replaced the glass doors that separated the main corridor from the north vestibule.
In 1891, Benjamin Harrison and wife Caroline proposed major extensions to the White House, including a National Wing on the east for a historical art gallery, and a wing on the west for official functions. An initially unsuccessful plan was devised by Colonel Theodore A. Bingham that reflected the Harrison proposal. The Harrisons originated the annual placement and decoration of a Christmas tree in the house.
In 1902, however, Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
hired McKim, Mead & White to carry out expansions and renovations in a neoclassical style suited to the building's architecture, removing the Tiffany screen and all Victorian additions. Charles McKim himself designed and managed the project, which gave more living space to the president's large family by removing a staircase in the West Hall and moving executive office staff from the second floor of the residence into the new West Wing.
President William Howard Taft
William Howard Taft (September 15, 1857March 8, 1930) served as the 27th president of the United States from 1909 to 1913 and the tenth chief justice of the United States from 1921 to 1930. He is the only person to have held both offices. ...
enlisted the help of architect Nathan C. Wyeth to add additional space to the West Wing, which included the addition of the Oval Office
The Oval Office is the formal working space of the president of the United States. Part of the Executive Office of the President of the United States, it is in the West Wing of the White House, in Washington, D.C.
The oval room has three lar ...
. In 1925, Congress enacted legislation allowing the White House to accept gifts of furniture and art for the first time. The West Wing was damaged by fire on Christmas Eve 1929; Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was the 31st president of the United States, serving from 1929 to 1933. A wealthy mining engineer before his presidency, Hoover led the wartime Commission for Relief in Belgium and ...
and his aides moved back into it on April 14, 1930. In the 1930s, a second story was added, as well as a larger basement for White House staff, and President Franklin Roosevelt had the Oval Office moved to its present location: adjacent to the Rose Garden.
Truman reconstruction
 Decades of poor maintenance, the construction of a fourth-story attic during the Coolidge administration, and the addition of a second-floor balcony over the south portico for
Decades of poor maintenance, the construction of a fourth-story attic during the Coolidge administration, and the addition of a second-floor balcony over the south portico for Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. As the 34th vice president in 1945, he assumed the presidency upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt that year. Subsequen ...
took a great toll on the brick and sandstone structure built around a timber frame. By 1948, the house was declared to be in imminent danger of collapse, forcing President Truman to commission a reconstruction and to live across the street at Blair House from 1949 to 1951.
The work, completed by the firm of Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
contractor John McShain, required the complete dismantling of the interior spaces, construction of a new load-bearing internal steel frame, and the reconstruction of the original rooms within the new structure. The total cost of the renovations was about $5.7million ($ million in ). Some modifications to the floor plan were made, the largest being the repositioning of the grand staircase to open into the Entrance Hall, rather than the Cross Hall. Central air conditioning was added, as well as two additional sub-basements providing space for workrooms, storage, and a bomb shelter. The Trumans moved back into the White House on March 27, 1952.
While the Truman reconstruction preserved the house's structure, much of the new interior finishes were generic and of little historic significance. Much of the original plasterwork, some dating back to the 1814–1816 rebuilding, was too damaged to reinstall, as was the original robust Beaux Arts paneling in the East Room. President Truman had the original timber frame sawed into paneling; the walls of the Vermeil Room, Library
A library is a collection of Book, books, and possibly other Document, materials and Media (communication), media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or electron ...
, China Room, and Map Room on the ground floor of the main residence were paneled in wood from the timbers.
Jacqueline Kennedy restoration

Jacqueline Kennedy
Jacqueline Lee Kennedy Onassis ( ; July 28, 1929 – May 19, 1994) was an American writer, book editor, and socialite who served as the first lady of the United States from 1961 to 1963, as the wife of President John F. Kennedy. A popular f ...
, wife of President John F. Kennedy (1961–63), directed a very extensive and historic redecoration of the house. She enlisted the help of Henry Francis du Pont of the Winterthur Museum to assist in collecting artifacts for the mansion, many of which had once been housed there. Other antiques, fine paintings, and improvements from the Kennedy period were donated to the White House by wealthy philanthropists, including the Crowninshield family, Jane Engelhard, Jayne Wrightsman, and the Oppenheimer family.
Stéphane Boudin of the House of Jansen, a Paris interior-design firm that had been recognized worldwide, was employed by Jacqueline Kennedy to assist with the decoration. Different periods of the early republic and world history were selected as a theme for each room: the Federal style for the Green Room, French Empire for the Blue Room, American Empire for the Red Room, Louis XVI for the Yellow Oval Room, and Victorian for the president's study, renamed the Treaty Room. Antique furniture was acquired, and decorative fabric and trim based on period documents was produced and installed.
The Kennedy restoration resulted in a more authentic White House of grander stature, which recalled the French taste of Madison and Monroe. In the Diplomatic Reception Room, Mrs. Kennedy installed an antique "Vue de l'Amérique Nord" wallpaper which Zuber & Cie had designed in 1834. The wallpaper had hung previously on the walls of another mansion until 1961 when that house was demolished for a grocery store. Just before the demolition, the wallpaper was salvaged and sold to the White House.
The first White House guidebook was produced under the direction of curator Lorraine Waxman Pearce with direct supervision from Mrs. Kennedy. Sales of the guidebook helped finance the restoration.
In a televised tour of the house on Valentine's Day
Valentine's Day, also called Saint Valentine's Day or the Feast of Saint Valentine, is celebrated annually on February 14. It originated as a Christian feast day honoring a Christian martyrs, martyr named Saint Valentine, Valentine, and ...
in 1962, Kennedy showed her restoration of the White House to the public.
The White House since the Kennedy restoration
Congress enacted legislation in September 1961 declaring the White House a museum. Furniture, fixtures, and decorative arts could now be declared either historic or of artistic interest by the president. This prevented them from being sold (as many objects in the executive mansion had been in the past 150 years). When not in use or display at the White House, these items were to be turned over to theSmithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase a ...
for preservation, study, storage, or exhibition. The White House retains the right to have these items returned.
Out of respect for the historic character of the White House, no substantive architectural changes have been made to the house since the Truman renovation. Since the Kennedy restoration, every presidential family has made some changes to the private quarters of the White House, but the Committee for the Preservation of the White House must approve any modifications to the State Rooms. Charged with maintaining the historical integrity of the White House, the congressionally authorized committee works with each First Family – usually represented by the first lady, the White House curator, and the chief usher — to implement the family's proposals for altering the house.
During the Nixon Administration (1969–1974), First Lady Pat Nixon
Thelma Catherine "Pat" Nixon (; March 16, 1912 – June 22, 1993) was First Lady of the United States from 1969 to 1974 as the wife of President Richard Nixon. She also served as the Second ladies and gentlemen of the United States, second lady ...
refurbished the Green Room, Blue Room, and Red Room, working with Clement Conger, the curator appointed by President Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 until Resignation of Richard Nixon, his resignation in 1974. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
. Mrs. Nixon's efforts brought more than 600 artifacts to the house, the largest acquisition by any administration. Her husband created the modern press briefing room over Franklin Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
's old swimming pool. Nixon also added a single-lane bowling alley to the White House basement.
Computers and the first laser printer
Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics (and moderate-quality photographs) by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a Electric charge, negatively charged cylinder call ...
were added during the Carter administration
Jimmy Carter's tenure as the List of presidents of the United States, 39th president of the United States began with Inauguration of Jimmy Carter, his inauguration on January 20, 1977, and ended on January 20, 1981. Carter, a Democratic Party ...
, and the use of computer technology was expanded during the Reagan administration
Ronald Reagan's tenure as the 40th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1981, and ended on January 20, 1989. Reagan, a Republican from California, took office following his landslide victory over ...
. A Carter-era innovation, a set of solar water heating
Solar water heating (SWH) is water heating, heating water by sunlight, using a solar thermal collector. A variety of configurations are available at varying cost to provide solutions in different climates and latitudes. SWHs are widely used for ...
panels that were mounted on the roof of the White House, was removed during Reagan's presidency. Redecorations were made to the private family quarters and maintenance was made to public areas during the Reagan years. The house was accredited as a museum in 1988.
In the 1990s, Bill and Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, lawyer and diplomat. She was the 67th United States secretary of state in the administration of Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, a U.S. senator represent ...
refurbished some rooms with the assistance of Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma ...
decorator Kaki Hockersmith, including the Oval Office, the East Room, Blue Room, State Dining Room, Lincoln Bedroom, and Lincoln Sitting Room. During the administration of George W. Bush, First Lady Laura Bush
Laura Lane Welch Bush (née Welch; born November 4, 1946) is an American educator who was the first lady of the United States from 2001 to 2009 as the wife of George W. Bush, the 43rd president of the United States. Bush was previously the fir ...
refurbished the Lincoln Bedroom in a style contemporary with the Lincoln era; the Green Room, Cabinet Room, and theater were also refurbished.
The White House became one of the first wheelchair-accessible government buildings in Washington, D.C., when modifications were made during the presidency of Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
, who used a wheelchair because of his paralytic illness. In the 1990s, Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, lawyer and diplomat. She was the 67th United States secretary of state in the administration of Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, a U.S. senator represent ...
, at the suggestion of the Visitors Office director, approved the addition of a ramp in the East Wing corridor, affording easier wheelchair
A wheelchair is a mobilized form of chair using two or more wheels, a footrest, and an armrest usually cushioned. It is used when walking is difficult or impossible to do due to illnesses, injury, disabilities, or age-related health conditio ...
access for the public tours and special events that enter through the secure entrance building on the east side.
In 2003, the Bush administration reinstalled solar thermal heaters. These units are used to heat water for landscape maintenance personnel and for the presidential pool and spa. One hundred sixty-seven solar photovoltaic grid-tied panels were installed at the same time on the roof of the maintenance facility. The changes were not publicized as a White House spokeswoman said the changes were an internal matter, but the story was covered by industry trade journals. In 2013, President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
had a set of solar panel
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. These electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct ...
s installed on the roof of the White House, making it the first time solar power was used for the president's living quarters.
Layout and amenities
The current group of buildings housing the presidency is known as the White House Complex. It includes the central Executive Residence flanked by the East Wing and West Wing. The chief usher coordinates day to day household operations. The White House includes six stories and 55,000 square feet (5,100 m2) of floor space, 132 rooms and 35 bathrooms, 412 doors, 147 windows, 28 fireplaces, eight staircases, three elevators, five full-time chefs, a tennis court, a (single-lane) bowling alley, a movie theater (officially called the White House Family Theater), a jogging track, a swimming pool, and a putting green. It receives up to 30,000 visitors each week.Executive Residence
 The original residence is in the center. Two
The original residence is in the center. Two colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or curv ...
sone on the east and one on the westdesigned by Jefferson, now serve to connect the East and West Wings added later. The Executive Residence houses the president's dwelling, as well as rooms for ceremonies and official entertaining. The State Floor of the residence building includes the East Room, Green Room, Blue Room, Red Room, State Dining Room, Family Dining Room, Cross Hall, Entrance Hall, and Grand Staircase. The Ground Floor is made up of the Diplomatic Reception Room, Map Room, China Room, Vermeil Room, Library
A library is a collection of Book, books, and possibly other Document, materials and Media (communication), media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or electron ...
, the main kitchen, and other offices.
The second floor family residence includes the Yellow Oval Room, East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and West Sitting Halls, the White House Master Bedroom, President's Dining Room, the Treaty Room, Lincoln Bedroom and Queens' Bedroom, as well as two additional bedrooms, a smaller kitchen, and a private dressing room. The third floor consists of the White House Solarium, Game Room, Linen Room, a Diet Kitchen, and another sitting room (previously used as President George W. Bush's workout room).
West Wing
The West Wing houses the president's office (theOval Office
The Oval Office is the formal working space of the president of the United States. Part of the Executive Office of the President of the United States, it is in the West Wing of the White House, in Washington, D.C.
The oval room has three lar ...
) and offices of his senior staff, with room for about 50 employees. It includes the Cabinet Room, where the president conducts business meetings and where the Cabinet meets, as well as the White House Situation Room, James S. Brady Press Briefing Room, and the Roosevelt Room. In 2007, work was completed on renovations of the press briefing room, adding fiber optic cables and LCD screens for the display of charts and graphs. The makeover took 11 months and cost of $8million, of which news outlets paid $2million. In September 2010, a two-year project began on the West Wing, creating a multistory underground structure.
Some members of the president's staff are located in the adjacent Eisenhower Executive Office Building
The Eisenhower Executive Office Building (EEOB), formerly known as the Old Executive Office Building (OEOB), and originally known as the State, War, and Navy Building (SWAN Building), is a Federal government of the United States, United States ...
, which was, until 1999, called the Old Executive Office Building and was historically the State, War, and Navy building.
The Oval Office, Roosevelt Room, and other portions of the West Wing were partially replicated on a sound stage
A sound stage (also written soundstage) is a large, soundproof structure, building or room with large doors and high ceilings, used for the production of theatrical film-making and television productions, usually located on a secured movie or te ...
and used as the setting for ''The West Wing
''The West Wing'' is an American political drama television series created by Aaron Sorkin that was originally broadcast on NBC from September 22, 1999, to May 14, 2006. The series is set primarily in the West Wing of the White House, where t ...
'' television show.
East Wing
The East Wing, which contains additional office space, was added to the White House in 1942. Among its uses, the East Wing has intermittently housed the offices and staff of the first lady and the White House Social Office. Rosalynn Carter, in 1977, was the first to place her personal office in the East Wing and to formally call it the "Office of the First Lady". The East Wing was built duringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
to hide the construction of an underground bunker to be used in emergencies. The bunker has come to be known as the Presidential Emergency Operations Center.
Grounds
The White House and grounds cover just over 18 acres (about 7.3 hectares). Before the construction of the North Portico, most public events were entered from the South Lawn, the grading and planting of which was ordered by Thomas Jefferson. Jefferson also drafted a planting plan for the North Lawn that included large trees that would have mostly obscured the house from Pennsylvania Avenue. During the mid-to-late 19th century a series of ever largergreenhouse
A greenhouse is a structure that is designed to regulate the temperature and humidity of the environment inside. There are different types of greenhouses, but they all have large areas covered with transparent materials that let sunlight pass an ...
s were built on the west side of the house, where the current West Wing is located. During this period, the North Lawn was planted with ornate carpet-style flowerbeds.
The general layout of the White House grounds today is based on the 1935 design by Frederick Law Olmsted Jr. of the Olmsted Brothers
The Olmsted Brothers company was a Landscape architecture, landscape architectural firm in the United States, established in 1898 by brothers John Charles Olmsted (1852–1920) and Frederick Law Olmsted Jr. (1870–1957), sons of the landscape ar ...
firm, commissioned by President Franklin D. Roosevelt. During the Kennedy administration, the White House Rose Garden was redesigned by Rachel Lambert Mellon. The Rose Garden borders the West Colonnade. Bordering the East Colonnade is the Jacqueline Kennedy Garden, which was begun by Jacqueline Kennedy
Jacqueline Lee Kennedy Onassis ( ; July 28, 1929 – May 19, 1994) was an American writer, book editor, and socialite who served as the first lady of the United States from 1961 to 1963, as the wife of President John F. Kennedy. A popular f ...
but completed after her husband's assassination.
On the weekend of June 23, 2006, a century-old American Elm (''Ulmus americana'' L.) tree on the north side of the building came down during one of the many storms amid intense flooding. Among the oldest trees on the grounds are several magnolias (''Magnolia grandiflora
''Magnolia grandiflora'', commonly known as the southern magnolia or bull bay, is a tree of the family Magnoliaceae native to the Southeastern United States, from Virginia to central Florida, and west to East Texas. Reaching in height, it is a ...
'') planted by Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before Presidency of Andrew Jackson, his presidency, he rose to fame as a general in the U.S. Army and served in both houses ...
, including the Jackson Magnolia, reportedly grown from a sprout taken from the favorite tree of Jackson's recently deceased wife, the sprout planted after Jackson moved into the White House. The tree stood for over 200 years. In 2017, having become too weak to stand on its own, it was decided it should be removed and replaced with one of its offspring.
Michelle Obama
Michelle LaVaughn Robinson Obama ( Robinson; born January 17, 1964) is an American attorney and author who served as the first lady of the United States from 2009 to 2017, being married to Barack Obama, the 44th president of the United Stat ...
planted the White House's first organic garden and installed beehives on the South Lawn of the White House, which will supply organic produce and honey to the First Family and for state dinners and other official gatherings. In 2020, First Lady Melania Trump redesigned the Rose Garden.
Public access and security
Historical accessibility
Like the English and Irish country houses it was modeled on, the White House was, from the start, open to the public until the early part of the 20th century. Inspired by Washington's open houses in New York and Philadelphia,John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before Presidency of John Adams, his presidency, he was a leader of ...
began the tradition of the White House New Year's Reception. Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Indepe ...
permitted public tours of his house, which have continued ever since, except during wartime, and began the tradition of an annual reception on the Fourth of July.
President Jefferson held an open house for his second inaugural in 1805, and many of the people at his swearing-in ceremony at the Capitol followed him home, where he greeted them in the Blue Room. Those open houses sometimes became rowdy: in 1829, President Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before Presidency of Andrew Jackson, his presidency, he rose to fame as a general in the U.S. Army and served in both houses ...
had to leave for a hotel when roughly 20,000 citizens celebrated his inauguration inside the White House. His aides ultimately had to lure the mob outside with washtubs filled with a potent cocktail of orange juice and whiskey. The practice continued until 1885, when newly elected Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States, serving from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. He was the first U.S. president to serve nonconsecutive terms and the first Hist ...
arranged for a presidential review of the troops from a grandstand in front of the White House instead of the traditional open house.
Those receptions ended in the early 1930s. President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
briefly revived the New Year's Day open house in his first term.
Aviation incidents
In February 1974, a stolen U.S. Army helicopter landed without authorization on the White House's grounds. Twenty years later, in 1994, a stolen light plane flown by Frank Eugene Corder crashed on White House grounds, instantly killing him. During theSeptember 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
, shortly after notice of the plane impacts, the White House staff and other occupants were ordered to evacuate by the U.S. Secret Service after a call was made to them from Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport
Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport is a public airport in Arlington County, Virginia, United States, from Washington, D.C. The closest airport to the nation's capital, it is one of two airports owned by the federal government and ope ...
air traffic control staff, stating, "There is an aircraft coming at you," though an aircraft never did show up.
On May 12, 2005, as a result of increased security regarding air traffic in the capital, the White House was evacuated after an unauthorized aircraft approached the grounds. After being forced to land by two F-16 fighter jets and a Black Hawk helicopter at a small airport nearby, the pilot was identified to be a student pilot who accidentally breached White House grounds without knowledge.
On January 27, 2015, at 3 a.m. an intoxicated man flew a quadcopter drone from his apartment near the White House but lost control of it, prompting it to crash on the southeast side on White House grounds. The White House was temporarily locked down by the Secret Service shortly after an officer reported witnessing " drone flying at a low altitude." Investigators suspected that the drone accidentally flew and breached into the property because of either wind or trees.
In June 2023, fighter jets moved to intercept a light aircraft that violated Washington DC airspace near the White House, before it crashed in Virginia. All occupants in the intrusion aircraft were killed.
Closure of Pennsylvania Avenue
 On May 20, 1995, primarily as a response to the
On May 20, 1995, primarily as a response to the Oklahoma City bombing
The Oklahoma City bombing was a domestic terrorist truck bombing of the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building in Oklahoma City, United States, on April 19, 1995. The bombing remains the deadliest act of domestic terrorism in U.S. history. Perpetr ...
of April 19, 1995, the United States Secret Service
The United States Secret Service (USSS or Secret Service) is a federal law enforcement agency under the Department of Homeland Security tasked with conducting criminal investigations and providing protection to American political leaders, thei ...
closed off Pennsylvania Avenue to vehicular traffic in front of the White House, from the eastern edge of Lafayette Park to 17th Street. Later, the closure was extended an additional block to the east to 15th Street, and East Executive Avenue, a small street between the White House and the Treasury Building.
After September 11, 2001, this change was made permanent, in addition to closing E Street between the South Portico of the White House and the Ellipse. In response to the Boston Marathon bombing, the road was closed to the public in its entirety for a period of two days.
The Pennsylvania Avenue closure has been opposed by organized civic groups in Washington, D.C. They argue that the closing impedes traffic flow unnecessarily and is inconsistent with the well-conceived historic plan for the city. As for security considerations, they note that the White House is set much farther back from the street than numerous other sensitive federal buildings are.
Prior to its inclusion within the fenced compound that now includes the Old Executive Office Building to the west and the Treasury Building to the east, this sidewalk served as a queuing area for the daily public tours of the White House. These tours were suspended in the wake of the September 11 attacks. In September 2003, they resumed on a limited basis for groups making prior arrangements through their Congressional representatives or embassies in Washington for foreign nationals and submitting to background checks, but the White House remained closed to the public. Due to budget constraints, White House tours were suspended for most of 2013 due to sequestration. The White House reopened to the public in November 2013.
Protection
The White House Complex is protected by theUnited States Secret Service
The United States Secret Service (USSS or Secret Service) is a federal law enforcement agency under the Department of Homeland Security tasked with conducting criminal investigations and providing protection to American political leaders, thei ...
and the United States Park Police.
During the 2005 presidential inauguration, NASAMS (Norwegian Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile System) units were used to patrol the airspace over Washington, D.C. The same units have since been used to protect the president and all airspace around the White House, which is strictly prohibited to aircraft.
Gallery
Manhattan
Manhattan ( ) is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City. Coextensive with New York County, Manhattan is the County statistics of the United States#Smallest, larg ...
, occupied by Washington from April 1789February 1790
File:New York Second Presidential Mansion.jpg, The second presidential mansion, Alexander Macomb House, in Manhattan, occupied by Washington from February–August 1790
File:Dessin de Palladio - Projet villa des comtes Francesco et Lodovico de Trissini.jpg, Andrea Palladio's illustration, ''Project for Francesco et Lodovico de Trissini'', from the book '' I quattro libri dell'architettura'', published in 1570
File:White House North Side Comparison2.jpg, The North Portico of the White House compared to Leinster House
File:White House South Side Comparison.jpg, The Château de Rastignac compared to the South Portico of the White House,
File:PhiladelphiaPresidentsHouse.jpg, The third presidential mansion, President's House in Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, occupied by Washington from November 1790March 1797. Occupied by Adams: March 1797May 1800
File:The Government House, New York 1650665.jpg, Government House in Manhattan, built in 1790–1791, was designed to be the permanent presidential mansion, but Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
moved the national capital to Philadelphia before its completion.
File:House intended for the President Birch's Views Plate 13 (cropped).jpg, President's House in Philadelphia (built in the 1790s), was not used by any president after the presidential mansion, known as the White House, was moved from Philadelphia to the new national capital of Washington, D.C.
File:White House 1846.jpg, The earliest known photograph of the White House, taken by John Plumbe during the administration of James K. Polk
File:WhiteHouseProposedAddition.jpg, Additions proposed by architect Frederick D. Owen in 1890
File:US $20 Series 2006 Reverse.jpg, The building's north front has been on the reverse of the U.S. $20 bill since 1998; an illustration of the south side was used for 70 years prior to its issuance.
See also
* Architecture of Washington, D.C. * Art in the White House *Camp David
Camp David is a country retreat for the president of the United States. It lies in the wooded hills of Catoctin Mountain Park, in Frederick County, Maryland, near the towns of Thurmont, Maryland, Thurmont and Emmitsburg, Maryland, Emmitsburg, a ...
* Pedro Casanave
* Germantown White House
* Graphics and Calligraphy Office
* List of largest houses in the United States
* List of National Historic Landmarks in Washington, D.C.
* List of the oldest buildings in Washington, D.C.
* List of residences of presidents of the United States
Listed below are the private house, residences of the various President of the United States, presidents of the United States. Except for George Washington, all of them also lived at the White House (Executive Residence). For a list of official ...
* Number One Observatory Circle, residence of the vice president
* Replicas of the White House
* Reported White House ghosts
* White House Acquisition Trust
* White House Chief Calligrapher
* White House Chief Floral Designer
* White House Christmas tree
* White House Communications Agency
* White House Endowment Trust
* White House Executive Chef
* White House Fellows
* '' White House History''
* White House Social Secretary
* :Rooms in the White House
* White House COVID-19 outbreak
Notes
References
Further reading
* Abbott, James A. ''A Frenchman in Camelot: The Decoration of the Kennedy White House by Stéphane Boudin.'' Boscobel Restoration Inc.: 1995. . * Abbott, James A. ''Jansen.'' Acanthus Press: 2006. . * Clinton, Hillary Rodham. ''An Invitation to the White House: At Home with History.'' Simon & Schuster: 2000. . * * * Garrett, Wendell. ''Our Changing White House.'' Northeastern University Press: 1995. . * Guidas, John. ''The White House: Resources for Research at the Library of Congress.'' Library of Congress, 1992. * Huchet de Quénetain, Christophe. "De quelques bronzes dorés français conservés à la Maison-Blanche à Washington D.C." in ''La Revue'', Pierre Bergé & associés, n°6, mars 2005 pp. 54–55. . * Kenny, Peter M., Frances F. Bretter and Ulrich Leben. ''Honoré Lannuier Cabinetmaker from Paris: The Life and Work of French'' Ébiniste ''in Federal New York.''The Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, colloquially referred to as the Met, is an encyclopedic art museum in New York City. By floor area, it is the third-largest museum in the world and the largest art museum in the Americas. With 5.36 million v ...
, New York and Harry Abrams: 1998. .
* Klara, Robert. ''The Hidden White House: Harry Truman and the Reconstruction of America's Most Famous Residence.'' Thomas Dunne Books: 2013. .
* Kloss, William. ''Art in the White House: A Nation's Pride.'' White House Historical Association in cooperation with the National Geographic Society, 1992. .
* Leish, Kenneth. ''The White House.'' Newsweek Book Division: 1972. .
* McKellar, Kenneth, Douglas W. Orr, Edward Martin, et al. ''Report of the on the Renovation of the Executive Mansion.'' Commission on the Renovation of the Executive Mansion, Government Printing Office: 1952.
* Monkman, Betty C. ''The White House: The Historic Furnishing & First Families.'' Abbeville Press: 2000. .
* New York Life Insurance Company. ''The presidents from 1789 to 1908 and the History of the White House.'' New York Life Insurance Company: 1908.
* Penaud, Guy ''Dictionnaire des châteaux du Périgord.'' Editions Sud-Ouest: 1996. .
* Phillips-Schrock, Patrick. ''The White House: An Illustrated Architectural History'' (Jefferson, NC: McFarland, 2013) 196 pp.
* Seale, William. ''The President's House.'' White House Historical Association and the National Geographic Society: 1986. .
*
* Seale, William, ''The White House: The History of an American Idea.'' White House Historical Association: 1992, 2001. .
* West, J.B. with Mary Lynn Kotz. ''Upstairs at the White House: My Life with the First Ladies.'' Coward, McCann & Geoghegan: 1973. .
* Wolff, Perry. ''A Tour of the White House with Mrs. John F. Kennedy.'' Doubleday & Company: 1962.
* ''Exhibition Catalogue, Sale 6834: The Estate of Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis April 23–26, 1996.'' Sothebys, Inc.: 1996.
* ''The White House: An Historic Guide.'' White House Historical Association and the National Geographic Society: 2001. .
* ''The White House. The First Two Hundred Years,'' ed. by Frank Freidel/William Pencak, Boston 1994.
External links
*The White House Historical Association
with historical photos, online tours and exhibits, timelines, and facts
part of the
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government, within the US Department of the Interior. The service manages all List ...
The White House Museum
a detailed online tour *
of White House and grounds * Video tours: ** ** ** *
Virtual tour of the White House
provided by Google Arts & Culture {{Portal bar, Architecture, National Register of Historic Places, Politics, United States 1800 establishments in Washington, D.C. Buildings and structures in the United States destroyed by arson Buildings of the United States government in Washington, D.C. Burned houses in the United States Federal architecture in Washington, D.C. Historic house museums in Washington, D.C. Homes of United States Founding Fathers Houses completed in 1800 Houses on the National Register of Historic Places in Washington, D.C. James Hoban buildings National Historic Landmarks in Washington, D.C. Neoclassical architecture in Washington, D.C. Pennsylvania Avenue Presidential homes in the United States Presidential museums in Washington, D.C. Presidential residences in the United States President's Park Rebuilt buildings and structures in the United States Reportedly haunted houses Reportedly haunted locations in Washington, D.C. War of 1812 sites Neoclassical palaces